Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Exercise Physiology and Metabolism - An Introduction
Exercise Physiology and Metabolism - An Introduction
Uploaded by
NicolasDarmanthé0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
6 views12 pagesThe document discusses the main energy systems in the body during exercise. It describes the phosphagen, glycolysis, Krebs cycle, and oxidative phosphorylation systems from fastest to slowest. The phosphagen system uses phosphocreatine to rapidly generate ATP. Phosphocreatine stores are regenerated through oxidative phosphorylation, which uses oxygen to resynthesize ATP and replenish phosphocreatine levels after exercise.
Original Description:
Original Title
Exercise physiology and metabolism - an introduction
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document discusses the main energy systems in the body during exercise. It describes the phosphagen, glycolysis, Krebs cycle, and oxidative phosphorylation systems from fastest to slowest. The phosphagen system uses phosphocreatine to rapidly generate ATP. Phosphocreatine stores are regenerated through oxidative phosphorylation, which uses oxygen to resynthesize ATP and replenish phosphocreatine levels after exercise.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
6 views12 pagesExercise Physiology and Metabolism - An Introduction
Exercise Physiology and Metabolism - An Introduction
Uploaded by
NicolasDarmanthéThe document discusses the main energy systems in the body during exercise. It describes the phosphagen, glycolysis, Krebs cycle, and oxidative phosphorylation systems from fastest to slowest. The phosphagen system uses phosphocreatine to rapidly generate ATP. Phosphocreatine stores are regenerated through oxidative phosphorylation, which uses oxygen to resynthesize ATP and replenish phosphocreatine levels after exercise.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 12
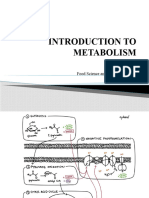
Exercise physiology
Main sources of energy
• From quickest to slowest
• Phosphocreatine (phosphagen) system
• Glycolysis (lactate system)
• Krebs and oxidative phosphorylation system (aerobic system)
• (Beta oxidation system)
Oxidative
Phosphorylation
Regenerating PCr
Recycling lactate
CO: HR vs SV tradeoff
• in healthy, lung never reaches above >60% of ventilatory (diffusion)
potential
• we are perfusion/flow limited
Explain the purpose of the phosphagen system
and how phosphocreatine stores are regenerated
• The phosphagen system is the fastest source of ATP for muscles. It provides
ATP 4 times faster than the aerobic system and 2 times faster than the
glycolysis/lactate system. Phosphocreatine (P-Cr) is stored in the
sarcoplasm of myocytes. When ATP is required, the phosphate is hydrolyzed
off the P-Cr and “added” to ADP to form ATP (phosphorylation of ADP).
• PCr requires energy/ATP to be regenerated. A phosphate is hydrolyzed off
ATP and “added” to creatine (phosphorylation of creatine). The ATP used in
this reaction originates from the highly efficient aerobic system involving
the Krebs cycle and oxidative phosphorylation. The reaction occurs post-
exercise and thus contributes to “oxygen debt”.
You might also like
- Exercise Physiology Course NotesDocument131 pagesExercise Physiology Course NotesAdam Linoby100% (16)
- Energy Systems in Sport PDFDocument29 pagesEnergy Systems in Sport PDFThe Health Therapist AcademyNo ratings yet
- Exercise Physiology 2Document38 pagesExercise Physiology 2naazminshaikh1727No ratings yet
- Three Components of Energy ExpenditureDocument26 pagesThree Components of Energy ExpenditureDustin HarrisonNo ratings yet
- 3 - Energy System and The Overall Metabolic RegulationDocument41 pages3 - Energy System and The Overall Metabolic RegulationmeralNo ratings yet
- HMS 4601 NUTRITION TO FUEL SPORTS PERFORMANCE - Case 1Document23 pagesHMS 4601 NUTRITION TO FUEL SPORTS PERFORMANCE - Case 1stijn.berkmortel1No ratings yet
- Human Energy Transfer During Physical ActivityDocument3 pagesHuman Energy Transfer During Physical Activitywarrentom3002No ratings yet
- 3.1.1.6 - Energy Systems: Learning ObjectivesDocument79 pages3.1.1.6 - Energy Systems: Learning Objectiveszedy gullesNo ratings yet
- Energy Systems in Sport & Exercise: ATP The Bodys Energy CurrencyDocument10 pagesEnergy Systems in Sport & Exercise: ATP The Bodys Energy CurrencyManoj PantaNo ratings yet
- The ATP CycleDocument10 pagesThe ATP CyclePia FerrarisNo ratings yet
- Role of ATPDocument2 pagesRole of ATPWilliamNo ratings yet
- Energy System NotesDocument3 pagesEnergy System Notesapi-267326015100% (1)
- 4.4.1 Body's Response To Exercise Concl Q'sDocument2 pages4.4.1 Body's Response To Exercise Concl Q'sLeilanie RodriguezNo ratings yet
- Energy For MovementDocument24 pagesEnergy For MovementNorieta G. LangpawenNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry, Muscle Proteins - NotesDocument6 pagesBiochemistry, Muscle Proteins - Notesamrwheed9No ratings yet
- Energy Transformation (N)Document56 pagesEnergy Transformation (N)Princess Lorreine GonzalesNo ratings yet
- 3 Types of Energy Systems in The Human BodyDocument5 pages3 Types of Energy Systems in The Human Bodyglennell castillanoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2: Fuel Utilization and Muscle Metabolism During ExerciseDocument14 pagesChapter 2: Fuel Utilization and Muscle Metabolism During ExerciseArizal AbdullahNo ratings yet
- Lecture 5 - BiochemistryDocument34 pagesLecture 5 - Biochemistryizza ghafoorNo ratings yet
- G12 Las Pe 1Document4 pagesG12 Las Pe 1Mharian BalbasNo ratings yet
- Aerobic & Anaerobic Metabolism in MusclesDocument35 pagesAerobic & Anaerobic Metabolism in MusclesDrAmit VermaNo ratings yet
- Nur Hannah BT HamzahDocument9 pagesNur Hannah BT HamzahNur Hannah Bt HamzahNo ratings yet
- L.O.5. Energy SystemsDocument9 pagesL.O.5. Energy SystemsOliviaMcCarthy6No ratings yet
- Energy ConceptsDocument7 pagesEnergy Conceptsanon_965753265No ratings yet
- Basic Energy SystemDocument10 pagesBasic Energy SystemMozil Fadzil KamarudinNo ratings yet
- Energy Systems PowerpointDocument27 pagesEnergy Systems PowerpointKellie Guest100% (1)
- 3 3 Nutrition and Energy SystemsDocument25 pages3 3 Nutrition and Energy Systemsapi-343368893No ratings yet
- Energy Systems ATP CYCLEDocument47 pagesEnergy Systems ATP CYCLECarl Von Alexi MiralpisNo ratings yet
- 4 Energy Metabolism and Metabolic RateDocument56 pages4 Energy Metabolism and Metabolic RateShafici CqadirNo ratings yet
- Bioenergetics I (20p)Document20 pagesBioenergetics I (20p)Kaveh KhabiriNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 Energy Systems Food FuelsDocument79 pagesChapter 5 Energy Systems Food Fuelsapi-115744109No ratings yet
- ATP and Its Role in Living OrganismsDocument2 pagesATP and Its Role in Living OrganismsHayze Jones50% (2)
- Group 2-2Document8 pagesGroup 2-2dalitsoNo ratings yet
- High Energy Phosphate and Immediate Compounds Produced During Muscle Conversion To MeatDocument8 pagesHigh Energy Phosphate and Immediate Compounds Produced During Muscle Conversion To MeatdalitsoNo ratings yet
- Know The Different Types of Energy Systems 5.1Document7 pagesKnow The Different Types of Energy Systems 5.1aleena khanNo ratings yet
- Is Lactic Acid A Four Letter Word?: by Patti and Warren Finke, Team OregonDocument4 pagesIs Lactic Acid A Four Letter Word?: by Patti and Warren Finke, Team OregonАлександър Антоан НиколовNo ratings yet
- Professor K.O. SOETAN Department of Veterinary Physiology and Biochemistry, University of Ibadan, IbadanDocument25 pagesProfessor K.O. SOETAN Department of Veterinary Physiology and Biochemistry, University of Ibadan, Ibadanolawandeilo123No ratings yet
- Penggunaan Energi Istirahat, Latihan PertandinganDocument65 pagesPenggunaan Energi Istirahat, Latihan PertandinganBella Nur AdhaNo ratings yet
- Basic Functions of Energy SystemsDocument11 pagesBasic Functions of Energy SystemsRiza Indelible SibullasNo ratings yet
- TriChapter37 09 Energy SystemDocument7 pagesTriChapter37 09 Energy Systembao.nguyenthienadamsNo ratings yet
- Energy Systems For Exercise: BioenergeticsDocument58 pagesEnergy Systems For Exercise: Bioenergeticsmehr6544No ratings yet
- Explain The Energy SystemsDocument7 pagesExplain The Energy Systemswillbatcup100% (1)
- Handouts in Pehealth Weeks 3 4Document10 pagesHandouts in Pehealth Weeks 3 4Glaiii CatapangNo ratings yet
- Hope 3 OutlineDocument7 pagesHope 3 OutlinelynnNo ratings yet
- Energy Systems: So We All Thought Energy Just Came From FoodDocument43 pagesEnergy Systems: So We All Thought Energy Just Came From FoodApril Joy TicaoNo ratings yet
- What Is ATPDocument15 pagesWhat Is ATPEira LeyNo ratings yet
- BTEC Sport Energy Systems MR EvansDocument7 pagesBTEC Sport Energy Systems MR EvansAlexNichols22No ratings yet
- Exercise Physiology Course Notes PDFDocument131 pagesExercise Physiology Course Notes PDFPRAJINIKUMARNo ratings yet
- Energy System: Quarter 1 Week 1Document27 pagesEnergy System: Quarter 1 Week 1Josie JavierNo ratings yet
- Week 1 2Document8 pagesWeek 1 2Aliyah M.No ratings yet
- Lactic Acid SystemDocument24 pagesLactic Acid SystemRalph Jasil Esparagoza EscanillasNo ratings yet
- HOPE-3 Q1 W1 Mod1Document10 pagesHOPE-3 Q1 W1 Mod1Dary Jea ChingNo ratings yet
- Hope - 3 Grade 12 Energy System: Quarter 1 Week 1 Module 1Document5 pagesHope - 3 Grade 12 Energy System: Quarter 1 Week 1 Module 1Angelo Dela LlarteNo ratings yet
- 8 - Physical and Phsyiological Factors in SportDocument28 pages8 - Physical and Phsyiological Factors in Sportganesh raoNo ratings yet
- Strength EnduranceDocument27 pagesStrength EnduranceAdi HidayatNo ratings yet
- Adenosine Triphosphate: Concept 2 NotesDocument6 pagesAdenosine Triphosphate: Concept 2 NotesjustinNo ratings yet
- Hope - 3 Grade 12: Energy SystemDocument9 pagesHope - 3 Grade 12: Energy SystemArmina ValdezNo ratings yet
- The Physiology of Cell Energy Production: CPTIPS.COM MonographsFrom EverandThe Physiology of Cell Energy Production: CPTIPS.COM MonographsNo ratings yet
- Sports Nutrition Handbook: Eat Smart. Be Healthy. Get On Top of Your Game.From EverandSports Nutrition Handbook: Eat Smart. Be Healthy. Get On Top of Your Game.No ratings yet
- The Science of Nutrition for Athletes: Understanding the Specific Nutritional Needs of Athletes for Optimal Performance and RecoveryFrom EverandThe Science of Nutrition for Athletes: Understanding the Specific Nutritional Needs of Athletes for Optimal Performance and RecoveryNo ratings yet