Professional Documents
Culture Documents
GPRS Basic Knowledge
Uploaded by
anthonyCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
GPRS Basic Knowledge
Uploaded by
anthonyCopyright:
Available Formats
Internal
GPRS Fundamental
ISSUE 3.0 www.huawei.com
HUAWEI TECHNOLOGIES CO., LTD. All rights reserved
GPRS principle is the basic part of the
whole system and the later products
learning. This slide will help us to
understand the GPRS system
networking and some important
procedure.
HUAWEI TECHNOLOGIES CO., LTD. All rights reserved Page 2
References
3GPP protocol 23060
3GPP protocol 29060
3GPP protocol 24008
HUAWEI TECHNOLOGIES CO., LTD. All rights reserved Page 3
Upon completion of this course, you
will be able to:
Describe the GPRS networking
structure
Describe the GPRS mobility
management procedure
Describe the GPRS session
management procedure
HUAWEI TECHNOLOGIES CO., LTD. All rights reserved Page 4
Chapter 1 GPRS Network Structure
Chapter 2 Mobility Management
Chapter 3 Radio Resource Management
Chapter 4 Session Management
HUAWEI TECHNOLOGIES CO., LTD. All rights reserved Page 5
GPRS Network Structure
What is GPRS?
General Packet Radio Service
What is the function of GPRS?
In order to provide the data service out the scope of the fixed network
GPRS network classification
GSM GPRS
UMTS GPRS
GPRS network background
GSM GPRS network reuse the existed GSM network
UMTS GPRS network just change the RAN side
HUAWEI TECHNOLOGIES CO., LTD. All rights reserved Page 6
GPRS Network Structure
MSC/VLR
MSC/VLR SMS-GMSC
SMS-GMSC SCP
SCP GMLC
GMLC HLR
HLR EIR
EIR
SMS-IWMSC
SMS-IWMSC
SS7
Gs Gd Ge Lg Gr Gf Gc
Gn
BSS
BSS FR SGSN
SGSN GGSN
GGSN
PDN TE
TE
ATM Gi
Um Gb GPRS
DDN
Gn Backbone
ISDN Ga
Ethernet.etc
UTRAN
UTRAN SGSN
SGSN Ga CG
CG
ATM
Um Iu
BG
BG
Gp
HUAWEI TECHNOLOGIES CO., LTD. All rights reserved Page 7
GPRS Network Structure
Some Abbreviation
GPRS: General Packet Radio Service
BSS: Base Station Subsystem
UTRAN: UMTS Terrestrial Radio Access Network
SGSN: Service GPRS Support Node
GGSN: Gateway GPRS Support Node
CG: Charging Gateway
BG: Bordering Gateway
PDN: Packet Data Network
HUAWEI TECHNOLOGIES CO., LTD. All rights reserved Page 8
GPRS Network Structure
Abbreviations:
MSC/VLR: Mobile Switch Center/Visitor Location Register
SMS-GMSC: Gateway MSC For Short Message Service
SMS-IWMSC: Short Message Service Interworking MSC
SCP: Service Control Point
GMLC: Gateway Mobile Location Center
HLR: Home Location Register
EIR: Equipment Identity Register
HUAWEI TECHNOLOGIES CO., LTD. All rights reserved Page 9
GPRS Network Structure
Important Entity Function: SGSN
Mobility management
− The MM functions are used to keep track of the current location of
an MS within the PLMN or within another PLMN.
Session management
− SM function manages the PDP context of MS.
Routing and transfer
− SGSN performs routing and forwarding of service data between
MS and GGSN.
Charging
− SGSN can generate, store, convert and send CDRs.
Lawful Interception
NTP
HUAWEI TECHNOLOGIES CO., LTD. All rights reserved Page 10
GPRS Network Structure
Important Entity Function : GGSN
Session management
− SM function manages the PDP context of MS.
Routing and transfer
− GGSN performs routing and forwarding of service data
between MS and internet.
Charging
− GGSN can generate, store, convert and send CDRs.
Dynamic IP allocation
Service management
− Manage APN
HUAWEI TECHNOLOGIES CO., LTD. All rights reserved Page 11
GPRS Network Structure
Important Entity Function: CG
Real-time collection of GPRS CDRs
Temporary storage and buffering of GPRS CDRs
Pre-processing of GPRS CDRs
Sending GPRS CDRs to the billing center
HUAWEI TECHNOLOGIES CO., LTD. All rights reserved Page 12
GPRS Network Structure
Important Entity Function: DNS
SGSN GGSN(A)
ISP
ISP A
A
GPRS
GPRS backbone
backbone
ISP
ISP B
B
BSS
DNS Internet/
GGSN(B) Intranet
MS Resolve the APN to a GGSN IP in the PDP active procedure
Resolve the RAI to a SGSN IP in the inter-SGSN RAU procedure
Resolve the RNCID to a SGSN IP in the relocation procedure (UMTS)
HUAWEI TECHNOLOGIES CO., LTD. All rights reserved Page 13
GPRS Network Structure
Important Entity Function: HLR/AUC
Saving and updating GPRS subscriber subscription data
User authentication
Providing location/routing information and processing
needed in mobility management and routing, for example
− Saving and updating user service SGSN number and
address
− GPRS user location deletion indication
− Whether MS is reachable
HUAWEI TECHNOLOGIES CO., LTD. All rights reserved Page 14
Typical Application
E-mail from mobile to fixed network
HLR
BTS/No BSC/R GGSN
SGSN
deB NC Backbone
Access
MS server
ISP
Mail
server
e-mail
HUAWEI TECHNOLOGIES CO., LTD. All rights reserved Page 15
Typical Application
E-mail from fixed to mobile network
HLR
BTS/No BSC/R GGSN
SGSN
deB NC Backbone
Access
MS server
ISP
Mail
server
e-mail
HUAWEI TECHNOLOGIES CO., LTD. All rights reserved Page 16
Summary
GPRS network provides data service to the mobile subscribers.
GPRS network is composed of SGSN, GGSN and CG. BG and
DNS provide special function during the data service.
HUAWEI TECHNOLOGIES CO., LTD. All rights reserved Page 17
Chapter 1 GPRS Network Structure
Chapter 2 Mobility Management
Chapter 3 Radio Resource Management
Chapter 4 Session Management
HUAWEI TECHNOLOGIES CO., LTD. All rights reserved Page 18
Chapter 2 Mobility Management
2.1 Basic concepts
2.2 Attach and Detach
2.3 Security Function
2.4 Loaction Management
2.5 Service Request (UMTS only)
HUAWEI TECHNOLOGIES CO., LTD. All rights reserved Page 19
GMM (GPRS Mobility Management)
Function of the Mobility Management
keep track of the current location of an MS within the PLMN
or within another PLMN
Subscription data management
MS states management
HUAWEI TECHNOLOGIES CO., LTD. All rights reserved Page 20
GMM (GPRS Mobility Management)
GMM main procedures
Attach procedure
RAU and periodic procedure
Detach procedure
GMM other procedures
P-TMSI reallocation procedure
Authentication procedure
Identification procedure
Subscriber management procedure
HUAWEI TECHNOLOGIES CO., LTD. All rights reserved Page 21
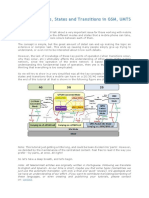
GMM States
IDLE IDLE
GPRS Detach
GPRS Attach GPRS Detach GPRS Attach or
Cancel Location
READY Implicit Detach READY
or
Cancel Location
READY timer expiry
READY timer expiry or
or PDU transmission PDU reception
Force to STANDBY
Force to STANDBY or
Abnormal RLC condition
STANDBY STANDBY
MM State Model of MS MM State Model of SGSN
HUAWEI TECHNOLOGIES CO., LTD. All rights reserved Page 22
PMM (Packet Mobility Management)
The function of PMM is similar to GMM.
PMM other procedures PMM main procedures
P-TMSI reallocation Attach
Authentication RAU and periodic RAU
Identification Detach
Subscriber management Service request
SRNS relocation
HUAWEI TECHNOLOGIES CO., LTD. All rights reserved Page 23
PMM States
PM M- PMM-
D ETACH ED D ETAC H ED
Detach, D etach,
P S D etach PS Attach R eject, P S D etach PS Attach Reject,
PS Attach RAU Rej ect PS Attach RA U R eject
P S S ignalling PS S ignalling
Connection Releas e PMM- Connection Releas e PMM-
P MM-IDL E CONNE CTE D P MM-IDL E CONNE CTE D
SM-A CT IVE or S M-ACT IV E or SM-A CT IVE or S M-ACT IV E or
INA CT IVE P S S ignalling INACTIV E INA CT IVE PS S ignalling INAC TIV E
Connection Establish Connection Establish
Serving RNC
reloc ation
MS MM States 3G-SGSN MM States
HUAWEI TECHNOLOGIES CO., LTD. All rights reserved Page 24
Mobility Management Timer Functions
READY Timer Function (GSM only)
The READY timer controls the time an MS remains in READY
state in the MS and the SGSN. When the READY timer expires,
the MS and SGSN MM contexts shall return to STANDBY state.
Periodic RA Update Timer Function
Upon expiry of the periodic RA update timer, the MS shall start a
periodic routeing area update procedure.
Mobile Reachable Timer Function
If the mobile reachable timer expires, the SGSN shall clear PPF.
After expiry of the mobile reachable timer the SGSN may
perform an implicit detach.
HUAWEI TECHNOLOGIES CO., LTD. All rights reserved Page 25
MS Operation Modes for GSM
Class‑A mode of operation: The MS is attached to both GPRS
and other GSM services, and the MS supports simultaneous
operation of GPRS and other GSM services.
Class‑B mode of operation: The MS is attached to both GPRS
and other GSM services, but the MS can only operate one set of
services at a time.
Class‑C mode of operation: The MS is exclusively attached to
GPRS services.
HUAWEI TECHNOLOGIES CO., LTD. All rights reserved Page 26
UE Operation Modes for UMTS
PS/CS mode of operation: The MS is attached to both the PS
domain and CS domain, and the MS is capable of simultaneously
operating PS services and CS services.
PS mode of operation: The MS is attached to the PS domain only
and may only operate services of the PS domain. However, this
does not prevent CS-like services to be offered over the PS domain
(e.g. VoIP).
CS mode of operation: The MS is attached to the CS domain only
and may only operate services of the CS domain. However, this
does not prevent PS-like service to be offered over the CS domain.
HUAWEI TECHNOLOGIES CO., LTD. All rights reserved Page 27
Network Operation Modes for GSM
Mode Circuit Paging GPRS Paging Paging co-
Channel Channel ordination
Packet Paging Packet Paging
Channel Channel
CCCH Paging CCCH Paging
I Yes
Channel Channel
Packet Data Not Applicable
Channel
CCCH Paging CCCH Paging
II No
Channel Channel
CCCH Paging Packet Paging
Channel Channel
III No
CCCH Paging CCCH Paging
Channel Channel
HUAWEI TECHNOLOGIES CO., LTD. All rights reserved Page 28
Network Operation Modes for UMTS
Mode Network configuration Combined procedure
by MT
I Gs interface is present Yes
II Gs interface is not present No
HUAWEI TECHNOLOGIES CO., LTD. All rights reserved Page 29
Chapter 2 Mobility Management
2.1 Basic concepts
2.2 Attach and Detach
2.3 Security Function
2.4 Loaction Management
2.5 Service Request (UMTS only)
HUAWEI TECHNOLOGIES CO., LTD. All rights reserved Page 30
Attach Procedure
Function
An MS/UE shall perform a GPRS Attach to the SGSN
in order to obtain access to the GPRS services.
If the MS/UE is connected via a GSM radio, it shall
perform a GSM GPRS Attach procedure.
If the MS/UE is connected via a UMTS radio access
network, it shall perform a UMTS GPRS Attach
procedure
HUAWEI TECHNOLOGIES CO., LTD. All rights reserved Page 31
Attach Procedure
(IMSI or PTMSI+RAI) (PTMSI)
(IMSI)
(Identity Type = IMSI)
(IMSI)
HUAWEI TECHNOLOGIES CO., LTD. All rights reserved Page 32
Attach Procedure
HUAWEI TECHNOLOGIES CO., LTD. All rights reserved Page 33
Attach Procedure
Results after any attach procedure:
SGSN get subscriber data from HLR
HLR recorded the MS’s serving SGSN number
SGSN and MS create MM context for the MS
MS can request Session Management services
HUAWEI TECHNOLOGIES CO., LTD. All rights reserved Page 34
Reject Caused by GPRS Core Network
Cause in attach reject Actions in PS domain Actions in CS domain
Illegal MS The MS shall set the GPRS update status to If the MS is IMSI attached, the MS
GU3 ROAMING NOT ALLOWED The shall in addition set the update
Illegal ME
SIM/USIM shall be considered as invalid for status to U3 ROAMING NOT
GPRS services until switching off or the ALLOWED, shall delete any TMSI,
SIM/USIM is removed LAI and ciphering key sequence
number
GPRS services not allowed The MS shall set the GPRS update status to no effect
GU3 ROAMING NOT ALLOWED; The
SIM/USIM shall be considered as invalid for
GPRS services until switching off or the
SIM/USIM is removed.
GPRS services not allowed in this shall set the GPRS update status to GU3
PLMN ROAMING NOT ALLOWED
PLMN not allowed shall set the GPRS update status to GU3 The MS shall perform a PLMN
ROAMING NOT ALLOWED), shall reset the selection
Location area not allowed
GPRS attach attempt counter and shall
Roaming not allowed in this location change to state GMM-DEREGISTERED
area
No Suitable Cells In Location Area shall set the GPRS update status to GU3 The MS shall search for a suitable
ROAMING NOT ALLOWED cell in another location area in the
same PLMN
HUAWEI TECHNOLOGIES CO., LTD. All rights reserved Page 35
MM Context
Field Description A/Gb Iu mode
mode
IMSI IMSI is the main reference key. X X
MM State Mobility management state, IDLE, STANDBY, READY, PMM‑DETACHED, PMM‑IDLE, or X X
PMM‑CONNECTED.
P‑TMSI Packet Temporary Mobile Subscriber Identity. X X
P‑TMSI Signature A signature used for identification checking purposes. X X
IMEI International Mobile Equipment Identity X X
MSISDN The basic MSISDN of the MS. X X
Routeing Area Current routeing area. X X
Cell Identity Current cell in READY state, last known cell in STANDBY or IDLE state. X
Cell Identity Age Time elapsed since the last LLC PDU was received from the MS at the SGSN. X
Service Area Code Last known SAC when initial UE message was received or Location Reporting procedure was X
executed.
Service Area Code Age Time elapsed since the last SAC was received at the 3G‑SGSN. X
VLR Number The VLR number of the MSC/VLR currently serving this MS. X X
New SGSN Address The IP address of the new SGSN where buffered and not sent N‑PDUs should be forwarded to. X X
Authentication Vectors Authentication and ciphering parameters (authentication triplets or quintets). X X
Kc Currently used A/Gb mode ciphering key. X 2)
CKSN Ciphering key sequence number of Kc. X 2)
Ciphering algorithm Selected ciphering algorithm (GEA). X X
CK Currently used Iu mode ciphering key. 1) X
HUAWEI TECHNOLOGIES CO., LTD. All rights reserved Page 36
MM Context
IK Currently used Iu mode integrity key. 1) X
KSI Key Set Identifier. 1) X
MS Radio Access Capability MS radio access capabilities. X
MS Network Capability MS network capabilities. X X
DRX Parameters Discontinuous reception parameters. X X
Radio Priority SMS The RLC/MAC radio priority level for uplink SMS transmission. X
MNRG Indicates whether activity from the MS shall be reported to the HLR. X X
NGAF Indicates whether activity from the MS shall be reported to the MSC/VLR. X X
PPF Indicates whether paging for PS and CS services can be initiated. X X
Subscribed Charging Characteristics The charging characteristics for the MS, e.g. normal, prepaid, flat-rate, and/or hot billing X X
subscription.
SMS Parameters SMS-related parameters, e.g. operator-determined barring. X X
Recovery Indicates if HLR or VLR is performing database recovery. X X
GPRS‑CSI Optional GPRS CAMEL subscription information, see 3GPP TS 23.016 X X
ODB for PS parameters Indicates that the status of the operator determined barring for packet oriented services. X X
The information marked with a "1)" may be maintained if authentication is performed by the UMTS
authentication procedure.
The information marked with a "2)" may be maintained if authentication is performed by the GSM
authentication procedure.
HUAWEI TECHNOLOGIES CO., LTD. All rights reserved Page 37
Detach Procedure
Function
The GPRS Detach procedure allows an MS to inform the network
that it does not want to access the SGSN-based services any
longer
The GPRS Detach procedure allows the network to inform an MS
that it does not have access to the SGSN-based services any more
The following three entity can initiate the detach procedure
MS
SGSN
HLR
HUAWEI TECHNOLOGIES CO., LTD. All rights reserved Page 38
Detach Procedure
Results after any Detach procedure:
The SGSN shall not service the detached MS, unless reattach
The MS is in idle or PMM-DETACHED state
The MS is detached either explicitly or implicitly:
Explicit detach: The network or the MS explicitly requests detach
Implicit detach: The network detaches the MS, without notifying the
MS, a configuration-dependent time after the mobile reachable timer
expired, or after an irrecoverable radio error causes disconnection of
the logical link.
HUAWEI TECHNOLOGIES CO., LTD. All rights reserved Page 39
Detach Types
The different types of detach are:
IMSI detach;
GPRS detach;
combined GPRS / IMSI detach (MS-initiated only).
The MS can make an IMSI detach in one of two ways depending on
whether it is GPRS-attached or not:
A GPRS-attached MS sends a Detach Request message to the SGSN,
indicating an IMSI detach. This can be made in combination with GPRS
detach.
An MS that is not GPRS-attached makes the IMSI detach as already
defined in A/Gb mode or UMTS.
HUAWEI TECHNOLOGIES CO., LTD. All rights reserved Page 40
Detach Procedure (MS Initiated)
MS BSS/UTRAN SGSN GGSN MSC/VLR
1. Detach Request
2. Delete PDP Context Request
2. Delete PDP Context Response
C1
3. IMSI Detach Indication
4. GPRS Detach Indication
5. Detach Accept C2
6. PS Signalling Connection Release
HUAWEI TECHNOLOGIES CO., LTD. All rights reserved Page 41
Detach Type IE of Detach Request
Type of detach (octet 1)
In the MS to network direction:
8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 Bits
3 2 1
Detach type Power Type of detach 0 0 1 GPRS detach
IEI off
0 1 0 IMSI detach
0 1 1 Combined GPRS/IMSI detach
All other values are interpreted as Combined
Power off (octet 1) GPRS/IMSI detach by this version of the
protocol.
In the MS to network direction:
Bit
In the network to MS direction:
4
Bits
0 normal detach
3 2 1
1 power switched off
0 0 1 re-attach required
In the network to MS direction the Power off 0 1 0 re-attach not required
bit shall be spare and set to zero.
0 1 1 IMSI detach (after VLR failure)
All other values are interpreted as re-attach not
required by this version of the protocol.
HUAWEI TECHNOLOGIES CO., LTD. All rights reserved Page 42
Detach Procedure (SGSN Initiated)
MS BSS/UTRAN SGSN GGSN MSC/VLR
1. Detach Request
2. Delete PDP Context Request
2. Delete PDP Context Response
C1
3. GPRS Detach Indication
4. Detach Accept
C2
5. PS Signalling Connection Release
HUAWEI TECHNOLOGIES CO., LTD. All rights reserved Page 43
Detach Procedure (HLR Initiated)
MS BSS/UTRAN SGSN GGSN HLR MSC/VLR
1. Cancel Location
2. Detach Request
3. Delete PDP Context Request
3. Delete PDP Context Response
C1
4. GPRS Detach Indication
5. Detach Accept
C2
6. Cancel Location Ack
7. PS Signalling Connection Release
HUAWEI TECHNOLOGIES CO., LTD. All rights reserved Page 44
Purge Function
Function
The Purge function allows an SGSN to inform the HLR that it
has deleted the MM and PDP contexts of a detached MS
After the MS detach from the network:
The SGSN may delete the MM/PDP context immediately
the SGSN may keep the MM/PDP context for some time of the
detached MS
Purge Timer Function
Allows the SGSN to inform the HLR that it has deleted the MM
and PDP contexts of a detached MS.
The purge timer is set longer than the mobile reachable timer
HUAWEI TECHNOLOGIES CO., LTD. All rights reserved Page 45
Purge Function
SGSN HLR
1. Purge MS
2. Purge MS Ack
HUAWEI TECHNOLOGIES CO., LTD. All rights reserved Page 46
Chapter 2 Mobility Management
2.1 Basic concepts
2.2 Attach and Detach
2.3 Security Function
2.4 Loaction Management
2.5 Service Request (UMTS only)
HUAWEI TECHNOLOGIES CO., LTD. All rights reserved Page 47
Authentication Function
Function
Permit the network to check whether the identity provided
by the mobile station is acceptable or not;
Provide parameters enabling the mobile station to calculate
a new ciphering key ; ( UMTS and GSM )
Provide parameters enabling the mobile station to calculate
a new UMTS integrity key; ( UMTS only )
Permit the mobile station to authenticate the network.
( UMTS only )
HUAWEI TECHNOLOGIES CO., LTD. All rights reserved Page 48
Authentication Function
Authentication types:
GSM Authentication
− Using triplet: RAND, SRES, Kc
− Using GPRS Encryption Algorithm (GEA)
UMTS Authentication
− Using quintet: RAND, XRES, AUTN, CK, IK
▪ AUTN: for UE authenticate network
▪ IK: for data integrity function
− Using UMTS Encryption Algorithm (UEA)
These procedures are used independent of the GSM or UTRAN
RANs, i.e. each procedure may be executed in A/Gb mode or in Iu
mode.
HUAWEI TECHNOLOGIES CO., LTD. All rights reserved Page 49
Authentication Function
MS BSS/UTRAN SGSN HLR/Auc
1a. Send Authentication Info
1b . Send Authentication Info ack
2a. Authentication and Ciphering Request
2b. Authentication and Ciphering Response
HUAWEI TECHNOLOGIES CO., LTD. All rights reserved Page 50
Authentication Function(3G)
MS VLR/SGSN HE/HLR
Authentication data request
Generate authentication
Distribution of vectors AV(1..n)
authentication
vectors from HE
to SN Authentication data response
AV(1..n)
Store authentication vectors
Select authentication vector AV(i)
User authentication request
RAND(i) || AUTN(i)
Verify AUTN(i)
Compute RES(i)
Authentication and
key establishment
User authentication response
RES(i)
Compare RES(i) and XRES(i)
Compute CK(i) and IK(i) Select CK(i) and IK(i)
HUAWEI TECHNOLOGIES CO., LTD. All rights reserved Page 51
Authentication Function (2G-3G)
Release 99+ Release 98- or Release 99+
CK, IK Kc
HLR/AuC RES SRES HLR/AuC
Quintets Triplets Triplets Triplets
Release 99+ VLR/SGSN Release 98- Release 99+ Release 98-
VLR/SGSN VLR/SGSN VLR/SGSN
CK, IK Kc
CK, IK Kc RES SRES Kc CK, IK
CK [Kc] [Kc] [Kc] CK [Kc] [Kc] [Kc]
IK IK
UTRAN GSM BSS UTRAN GSM BSS
RAND RAND RAND RAND RAND RAND RAND RAND
AUTN AUTN [AUTN] SRES
SRES SRES SRES SRES
RES RES SRES
ME capable of ME not ME
UMTS AKA
capable of UMTS R99+ UE R98- UE R99+ UE
AKA or
Kc CK, IK R98- UE
CK, IK CK, IK Kc Kc
Kc Kc Kc Kc Kc Kc
CK, IK Kc CK, IK Kc CK, IK Kc CK, IK Kc
RES SRES RES SRES
SIM
USIM
UMTS security GSM security GSM security context
context context
HUAWEI TECHNOLOGIES CO., LTD. All rights reserved Page 52
Scope and Start of Ciphering
In A/Gb mode, the scope of ciphering is from the ciphering function
in the SGSN to the ciphering function in the MS.
In Iu mode, the scope of ciphering is from the ciphering function in
the UTRAN to the ciphering function in the MS.
MS BSS/UTRAN SGSN
Scope of GSM GPRS ciphering
Scope of UMTS ciphering
In A/Gb mode, the MS starts ciphering after sending the
Authentication and Ciphering Response message.
In Iu mode, the start of ciphering is controlled by the security mode
procedure after authentication procedure.
HUAWEI TECHNOLOGIES CO., LTD. All rights reserved Page 53
Identity Check
Function
Get IMSI from MS
Check the IMEI
MS BSS/UTRAN SGSN EIR
1. Identity Request
1. Identity Response
2. Check IMEI
2. Check IMEI Ack
HUAWEI TECHNOLOGIES CO., LTD. All rights reserved Page 54
P‑TMSI Reallocation
Function
The SGSN may reallocate the P‑TMSI at any time
The reallocation procedure can be performed by the
P‑TMSI Reallocation procedure
The P‑TMSI can be included in the Attach or Routeing Area
Update procedures.
MS BSS/UTRAN SGSN
1. P-TMSI Reallocation Command
2. P-TMSI Reallocation Complete
HUAWEI TECHNOLOGIES CO., LTD. All rights reserved Page 55
Chapter 2 Mobility Management
2.1 Basic concepts
2.2 Attach and Detach
2.3 Security Function
2.4 Loaction Management
2.5 Service Request (UMTS only)
HUAWEI TECHNOLOGIES CO., LTD. All rights reserved Page 56
Location Management
Function
A mechanisms for cell and PLMN selection;
A mechanism for the network to know the Routeing Area for MSs
in STANDBY, PMM‑IDLE, READY, and PMM‑CONNECTED
states;
A mechanism for the 2G‑SGSN to know the cell identity for MSs in
READY state;
A mechanism for the UTRAN to know the URA identity or cell
identity for MSs in PMM‑CONNECTED state;
A mechanism for the UTRAN to indicate to an MS in RRC
Connected mode when a Routeing Area Update procedure shall
be performed by providing the RAI;
A mechanism for the network to know the address of the serving
RNC handling an MS in PMM‑CONNECTED state. This
mechanism is the serving RNC relocation procedure
HUAWEI TECHNOLOGIES CO., LTD. All rights reserved Page 57
Layered Location Management Mode (2G)
•HLR
•SGSN
•SGSN number
•BSS
•ready state: cell number
•MS •Standby state: RAI
HUAWEI TECHNOLOGIES CO., LTD. All rights reserved Page 58
Layered Location Management Mode (3G)
•HLR
•SGSN
•SGSN number
•RNC
•PMM-connect state: RNCID,RAI,SAI
•MS •PMM-idle: RAI
HUAWEI TECHNOLOGIES CO., LTD. All rights reserved Page 59
Network Architecture
PDN
Routeing area update Gi
GGSN
procedure
SGSN can manage the old SGSN
Gn/Gp Gn/Gp
new SGSN
MS location Gn
information via RAU
Gr
procedure in RAI level Iu
Iu
Gr
IU
IU
Relocation procedure
(UMTS only) RNC2
Iur RNC1 HLR/AUC
RNC4 RNC3
Move the Iu interface
to the other RNC RA4 RA5 RA9 RA10
Handover procedure RA1 RA2 RA3
RA6 RA7 RA9
Move the radio link to
the other BTS/NodeB
MS
HUAWEI TECHNOLOGIES CO., LTD. All rights reserved Page 60
Routeing Area Update Procedure
RAU procedure will happen in the following two case:
MS entered a new Route Area
Periodic RAU ( after periodic timer expires)
In the viewpoint of SGSN:
intra-SGSN RAU
Inter-SGSN RAU
HUAWEI TECHNOLOGIES CO., LTD. All rights reserved Page 61
Routeing Area Update Procedure
Gn
SGSN SGSN
RAI 1 RAI 2 RAI 3 RAI 4
cell
Inter SGSN -RAU
Intra SGSN-RAU
MS
HUAWEI TECHNOLOGIES CO., LTD. All rights reserved Page 62
Inter-SGSN RAU Procedure (2G)
HUAWEI TECHNOLOGIES CO., LTD. All rights reserved Page 63
Inter-SGSN RAU Procedure (2G)
HUAWEI TECHNOLOGIES CO., LTD. All rights reserved Page 64
Inter-SGSN RAU Procedure (3G)
HUAWEI TECHNOLOGIES CO., LTD. All rights reserved Page 65
Inter-SGSN RAU Procedure (3G)
HUAWEI TECHNOLOGIES CO., LTD. All rights reserved Page 66
Serving RNS Relocation Procedure
HLR/AuC HLR/AuC
GGSN GGSN
old MSC/VLR old SGSN new SGSN new MSC/VLR old MSC/VLR old SGSN new SGSN new MSC/VLR
source SRNC target RNC source RNC target SRNC
LA1, RA1 LA2, RA2 LA1, RA1 LA2, RA2
MS MS
Before relocation After relocation
HUAWEI TECHNOLOGIES CO., LTD. All rights reserved Page 67
Serving RNS Relocation Procedure
Source Target Old New
MS GGSN
RNC RNC SGSN SGSN
1. Decision to perform
SRNS relocation
2. Relocation Required
3. Forward Relocation Request
4. Relocation Request
Establishment of Radio Access Bearers
4. Relocation Request Acknowledge
5. Forward Relocation Response
C1
6. Relocation Command
7. Forwarding of data
8. Relocation Commit
9. Relocation Detect
10. UTRAN Mobility Information 11. Update PDP Context Request
10. UTRAN Mobility Information Confirm 11. Update PDP Context Response
12. Relocation Complete
12. Forward Relocation Complete
12. Forward Relocation Complete Acknowledge
13. Iu Release Command
13. Iu Release Complete
14. Routing Area Update C2
C3
HUAWEI TECHNOLOGIES CO., LTD. All rights reserved Page 68
Chapter 2 Mobility Management
2.1 Basic concepts
2.2 Attach and Detach
2.3 Security Function
2.4 Loaction Management
2.5 Service Request (UMTS only)
HUAWEI TECHNOLOGIES CO., LTD. All rights reserved Page 69
Service Request Procedure
The Service Request procedure is used by a 3G‑MS in PMM‑IDLE
state to request the establishment of a secure connection to a
3G‑SGSN.
The MS in PMM‑IDLE state initiates this procedure in order to send
uplink signalling messages (e.g. Activate PDP Context Request),
user data, or as paging response, or after the MS has regained
radio coverage.
This procedure is also used by an MS in PMM‑CONNECTED state
to request resource reservation for active PDP contexts.
HUAWEI TECHNOLOGIES CO., LTD. All rights reserved Page 70
Service Request Procedure –MS initiated
M S R N C S G S N H LR G G S N
1 . R R C C o n n e c t io n R e q u e s t
1 . R R C C o n n e c t io n S e tu p
2 . S e r v ic e R e q u e s t
3 . S e c u r ity F u n c tio n s
4 . S e r v ic e A c c e p t
4 . R a d io A c c e s s B e a r e r A s s ig n m e n t
R equest
5 . R a d io B e a r e r S e tu p
6 . R a d io B e a r e r S e tu p
C o m p le t e
6 . R a d io A c c e s s B e a r e r A s s ig n m e n t
R esponse
7 . S G S N - I n it ia t e d P D P C o n t e x t M o d if ic a t io n
8 . U p lin k P D U
HUAWEI TECHNOLOGIES CO., LTD. All rights reserved Page 71
Service Request Procedure - network
initiated
MS RNC SGSN HLR GGSN
1. Downlink PDU
2. Paging
2. Paging
3. RRC Connection Request
3. RRC Connection Setup
4. Service Request
5. Security Functions
6. Radio Access Bearer Assignment
6. Radio Bearer Setup Request
6. Radio Bearer Setup
Complete 6. Radio Access Bearer Assignment
Response
7. SGSN-Initiated PDP Context Modification Procedure
8. Downlink PDU
HUAWEI TECHNOLOGIES CO., LTD. All rights reserved Page 72
Service Type IE of Service Request Msg.
MS initiated
Service type= signalling.
Service type= data.
Network initiated
Service type= paging response
HUAWEI TECHNOLOGIES CO., LTD. All rights reserved Page 73
Summary
Attach, location management, security function and detach
procedures are the main procedures in PS core network.
SRNS relocation procedure and Service request procedure are
newly added in UMTS PS core network.
HUAWEI TECHNOLOGIES CO., LTD. All rights reserved Page 74
Chapter 1 GPRS Network Structure
Chapter 2 Mobility Management
Chapter 3 Radio Resource Management
Chapter 4 Session Management
HUAWEI TECHNOLOGIES CO., LTD. All rights reserved Page 75
Paging Summary
The MM state in SGSN and MS before paging:
PMM-IDLE
STANDBY mode
Change MM state in MS to PMM-Connected or Ready after
successful paging.
Identification of MS in Paging message:
P-TMSI is used to identify the MS
If P-TMSI is invalid or MS not respond ,then use IMSI
HUAWEI TECHNOLOGIES CO., LTD. All rights reserved Page 76
Paging for GPRS (2G)
Function
An MS in STANDBY state is paged by the SGSN before a
downlink transfer to that MS
Paging move the MS state from STANDBY to READY.
Any uplink data from MS is a valid response to paging
HUAWEI TECHNOLOGIES CO., LTD. All rights reserved Page 77
Paging for GPRS (2G)
MS BSS SGSN
1. PDP PDU
STANDBY 2. Paging Request
3. GPRS Paging Request
(IMSI, P‑TMSI,
Area, Channel
4. Any LLC Frame
Needed, QoS,
(Receive Ready or 5. Any LLC Frame DRX
Information frame) Parameters)
READY
HUAWEI TECHNOLOGIES CO., LTD. All rights reserved Page 78
Paging Initiated by CN (3G)
PS Paging Initiated by 3G‑SGSN without RRC Connection for CS
A CN node requests paging only for MSs in PMM‑IDLE state
The RNS controls whether the MS has an established RRC
connection or not
MS has no RRC connection
Paging Type 1 is transferred on the Paging channel
HUAWEI TECHNOLOGIES CO., LTD. All rights reserved Page 79
Paging Initiated by CN (3G)
PS Paging Initiated by 3G‑SGSN without RRC Connection for CS
MS RNS MSC/VLR
3G-SGSN
1. PDP PDU or
PMM IDLE Downlink signaling
2. Paging
3. Paging Type1 (PCH paging)
(IMSI, P‑TMSI,
4. Service Request Area, CN
4. Service Request Domain
Indicator, DRX
PMM parameters)
CONNECTED
HUAWEI TECHNOLOGIES CO., LTD. All rights reserved Page 80
Paging Initiated by CN (3G)
PS Paging Initiated by 3G‑SGSN with RRC Connection for CS
A CN node requests paging only for MSs in PMM‑IDLE state
The RNS controls whether the MS has an established RRC
connection or not
In this case, MS has an established RRC connection for CS service
Paging Type 2 is base on the establish RRC connection
HUAWEI TECHNOLOGIES CO., LTD. All rights reserved Page 81
Paging Initiated by CN (3G)
PS Paging Initiated by 3G‑SGSN with RRC Connection for CS
MS RNS MSC/VLR
Connection Established
3G-SGSN
1. PDP PDU or
PMM IDLE Downlink signalling
2. Paging
3. Paging Type2 (RRC paging)
(IMSI, P‑TMSI,
4. Service Request Area, CN
4. Service Request Domain
Indicator, DRX
PMM parameters)
CONNECTED
HUAWEI TECHNOLOGIES CO., LTD. All rights reserved Page 82
CS Paging (GSM only)
When an MS is both IMSI and GPRS-attached in a network that
operates in mode I, the MSC/VLR executes paging for circuit-
switched services via the SGSN. If the MS is in STANDBY state, it
is paged in the routeing area and in the null routeing area (see
clause "Routeing Area Identity “ of TS23060). If the MS is in READY
state, it is paged in the cell. The SGSN converts the MSC paging
message into an SGSN paging message.
MS BSS SGSN MSC/VLR
1. Page
2. Paging Request
3. Paging Request
4. SABM (Paging Response)
5. SCCP Connection Request (Paging Response)
HUAWEI TECHNOLOGIES CO., LTD. All rights reserved Page 83
CS Paging (UMTS only)
When an MS is both IMSI- and GPRS-attached in a network that
operates in mode I, the MSC/VLR executes paging for circuit-
switched services via the SGSN.
In the MSC, a paging timer supervises the paging procedure.
MS RNS 3G-SGSN MSC/VLR
1. Page
2. Paging
3. Paging Request
4. RRC Initial Direct Transfer (Paging Response)
5. RANAP Initial UE (Paging Response)
HUAWEI TECHNOLOGIES CO., LTD. All rights reserved Page 84
Summary
In UMTS, Paging type 1 for UE without RRC connection with
RNC, Paging type 2 for UE with RRC connection with RNC.
CS paging can be executed via PS.
HUAWEI TECHNOLOGIES CO., LTD. All rights reserved Page 85
Chapter 1 GPRS Network Structure
Chapter 2 Mobility Management
Chapter 3 Radio Resource Management
Chapter 4 Session Management
HUAWEI TECHNOLOGIES CO., LTD. All rights reserved Page 86
Chapter 4 Session Management
4.1 Basic concepts
4.2 PDP Context Activation Procedure
4.3 PDP Context Modification Procedure
4.4 PDP Context Deactivation Procedure
4.5 Preservation Procedure (UMTS only)
HUAWEI TECHNOLOGIES CO., LTD. All rights reserved Page 87
Session Management
Function
Establish and monitor a packet tunnel from MS to GGSN, and
allocate system resource for the packet service.
Important Procedure
PDP Context Activation
PDP Context Modification
PDP Context Deactivation
HUAWEI TECHNOLOGIES CO., LTD. All rights reserved Page 88
PDP Context
PDP Context: Packet Data Protocol context
PDP context contains all the information needed to transfer user
data between MS and GGSN.
The context includes parameters such as Routing, QoS (Quality
of Service), Charging ID etc.
PDP context exists in MS, SGSN, GGSN.
HUAWEI TECHNOLOGIES CO., LTD. All rights reserved Page 89
PDP Context
Each MM context contains zero or more of the following PDP contexts:
Field Description A/Gb mode Iu mode
PDP Context Identifier Index of the PDP context. X X
PDP State Packet data protocol state, INACTIVE or ACTIVE. X X
PDP Type PDP type, e.g. PPP or IP. X X
PDP Address PDP address, e.g. an IP address. X X
APN Subscribed The APN received from the HLR. X X
APN in Use The APN currently used. This APN shall be composed of the APNNetwork X X
Identifier and the APN Operator Identifier.
NSAPI Network layer Service Access Point Identifier. X X
TI Transaction Identifier. X X
TEID for Gn/Gp Tunnel Endpoint Identifier for the Gn and Gp interfaces. X X
TEID for Iu Tunnel Endpoint Identifier for the Iu interface. X
GGSN Address in Use The IP address of the GGSN currently used. X X
VPLMN Address Allowed Specifies whether the MS is allowed to use the APN in the domain of the X X
HPLMN only, or additionally the APN in the domain of the VPLMN.
QoS Profile Subscribed The quality of service profile subscribed. X X
HUAWEI TECHNOLOGIES CO., LTD. All rights reserved Page 90
PDP Context
QoS Profile Requested The quality of service profile requested. X X
QoS Profile Negotiated The quality of service profile negotiated. X X
Radio Priority The RLC/MAC radio priority level for uplink user data transmission. X
Packet Flow Id Packet flow identifier. X
Aggregate BSS QoS Profile The aggregate BSS quality of service profile negotiated for the packet flow that X
Negotiated this PDP context belongs to.
Send N‑PDU Number SNDCP sequence number of the next downlink N‑PDU to be sent to the MS. X
Receive N‑PDU Number SNDCP sequence number of the next uplink N‑PDU expected from the MS. X
GTP‑SND GTP‑U sequence number of the next downlink N‑PDU to be sent to the MS. X X
GTP‑SNU GTP‑U sequence number of the next uplink N‑PDU to be sent to the GGSN. X X
PDCP‑SND Sequence number of the next downlink in-sequence PDCP‑PDU to be sent to X
the MS.
PDCP‑SNU Sequence number of the next uplink in-sequence PDCP‑PDU expected from the X
MS.
Charging Id Charging identifier, identifies charging records generated by SGSN and GGSN. X X
PDP Context Charging The charging characteristics of this PDP context, e.g. normal, prepaid, flat-rate, X X
Characteristics and/or hot billing.
RNC Address in Use The IP address of the RNC currently used. X
HUAWEI TECHNOLOGIES CO., LTD. All rights reserved Page 91
MM Context and PDP Context
HLR
MS BSC SGSN GGSN
Uu Gb/ Iu Gn
or RNC
MM context PDP context #1
MM context
PDP context #1 PDP context #1 .
. . .
. . .
PDP context #n PDP context #n PDP context #n
HUAWEI TECHNOLOGIES CO., LTD. All rights reserved Page 92
PDP State
INACTIVE
Deactivate PDP Context
Activate PDP or
Context MM state change to IDLE
or PMM-DETACHED
PDP state ACTIVE
inactive : cannot transmit data
active : can transmit data
HUAWEI TECHNOLOGIES CO., LTD. All rights reserved Page 93
PDP Type and PDP Address
PDP Type
IPV4
IPV6
PPP
PDP Address
Static IP
− Public IP
− Allocate by the operator
Dynamic IP
− Private IP
− Allocate by GGSN, DNCP or Radius
HUAWEI TECHNOLOGIES CO., LTD. All rights reserved Page 94
QoS
QoS: quality of service
It is a group of parameters that can define the network
ability, such as the bit rate for downlink or uplink data
transmission and the reliability class and so on
It is end to end concept
HUAWEI TECHNOLOGIES CO., LTD. All rights reserved Page 95
APN
APN structure: APN-NI+APN-OI
huawei.com.cn.mnc<MNC>.mcc<MCC>.gprs
APN APN
Network ID Operator ID
•Operator ID : fixed extension, must end with “.gprs”
•Network ID shall not end with “.gprs”
HUAWEI TECHNOLOGIES CO., LTD. All rights reserved Page 96
APN
APN1
IP1 GGSN1
APN1
APN2 MS APN SGSN GGSN2
APN2
APN3
APN GGSN IP
GGSN3
APN3
DNS APN1=GGSN1 IP1
APN2=GGSN2 IP2
APN3=GGSN3 IP3
HUAWEI TECHNOLOGIES CO., LTD. All rights reserved Page 97
APN
•internet General APN
GGSN GGSN
•GuangDong province
SGSN SGSN
APN:CMNET
MS MS
Roaming
HUAWEI TECHNOLOGIES CO., LTD. All rights reserved Page 98
APN
Local APN
VPN tunnel
GGSN GGSN
Province 1 Province 2
SGSN SGSN
APN:test.xy
MS MS
Roaming
HUAWEI TECHNOLOGIES CO., LTD. All rights reserved Page 99
APN
BTS BSC
/NodeB /RNC
ISP A
GGSN (A) ISP B
MS
•APN-NI/
SGSN GGSN (B)
Backbone Corp.
•Or APN-NI+APN-OI DNS Network
•APN-NI
DNS DNS
•APN-NI+APN-OI =
GGSN IP address
HUAWEI TECHNOLOGIES CO., LTD. All rights reserved Page 100
Chapter 4 Session Management
4.1 Basic concepts
4.2 PDP Context Activation Procedure
4.3 PDP Context Modification Procedure
4.4 PDP Context Deactivation Procedure
4.5 Preservation Procedure (UMTS only)
HUAWEI TECHNOLOGIES CO., LTD. All rights reserved Page 101
Activation Procedure
PDP context activation procedure
To establish a PDP context between the MS and the SGSN,
the GGSN
Activation procedure types:
PDP context activation procedure
Secondary PDP Context Activation Procedure
Network-Requested PDP Context Activation Procedure
HUAWEI TECHNOLOGIES CO., LTD. All rights reserved Page 102
PDP Context Activation Procedure (2G)
MS BSS 2G-SGSN 2G-GGSN
1. Activate PDP Context Request
C1
2. Security Functions
3. Create PDP Context Request
3. Create PDP Context Response
4. BSS Packet Flow Context Procedures
C2
5. Activate PDP Context Accept
HUAWEI TECHNOLOGIES CO., LTD. All rights reserved Page 103
PDP Context Activation Procedure (3G)
MS UTRAN 3G-SGSN 3G-GGSN
1. Activate PDP Context Request
(PDP Type, PDP Address, Access Point Name,
QoS Requested) C1
2. Create PDP Context Request
3. Create PDP Context Response
4. Radio Access Bearer Setup ( Qo
Charging ID allocation
s)
IP address
5. Update PDP Context Request
6. Update PDP Context Response
C2
7. Activate PDP Context Accept
HUAWEI TECHNOLOGIES CO., LTD. All rights reserved Page 104
Handling in MS
MS start and send “Active PDP context request” to SGSN
Provide QoS parameter
Provide a APN-NI
Provide a static IP or null
Receive ACCEPT from SGSN
If the QoS not accept by MS, then starts delete PDP context
procedure.
HUAWEI TECHNOLOGIES CO., LTD. All rights reserved Page 105
Handling in SGSN
Check subscriber data
APN selection
According to TS 23.060
default APN, APN provide from MS and the APN subscribed in HLR
APN-NI.APN-OI
Interrogate DNS
Hostfile/Cache/DNS server
QoS negotiation
QoS provided from MS, default QoS ,QoS subscribed in HLR
Send message “Create PDP context request” to GGSN
RAB assignment (UMTS only)
Send message “Active PDP context accept” to MS
Dynamic IP address
QoS
HUAWEI TECHNOLOGIES CO., LTD. All rights reserved Page 106
Handling in GGSN
Check the APN provided by SGSN
QoS negotiation
Allocate a dynamic IP to the MS
Allocate a charging ID for the PDP context
Return a CREATE PDP CONTEXT ACCEPT message to SGSN
Dynamic IP
QoS
Charging ID
Other information
Update PDP context
HUAWEI TECHNOLOGIES CO., LTD. All rights reserved Page 107
Handling in RNC
RAB assignment
MS SGSN GGSN
RAB assignment
RNC (Final negotiated
Qos)
Allocate radio resource Allocate Iu interface resource
HUAWEI TECHNOLOGIES CO., LTD. All rights reserved Page 108
Secondary PDP Context Activation Procedure
The Secondary PDP Context Activation procedure may be used to
activate a PDP context while reusing the PDP address and other
PDP context information from an already active PDP context, but
with a different QoS profile.
Procedures for APN selection and PDP address negotiation are not
executed.
A unique TI and a unique NSAPI shall identify each PDP context
sharing the same PDP address and APN.
HUAWEI TECHNOLOGIES CO., LTD. All rights reserved Page 109
Secondary PDP Context Activation Procedure
For GPRS
MS BSS 2G-SGSN 2G-GGSN
1. Activate Secondary PDP Context Request
C1
2. Security Functions
3. Create PDP Context Request
3. Create PDP Context Response
5. BSS Packet Flow Context Procedures
C2
7. Activate Secondary PDP Context Accept
HUAWEI TECHNOLOGIES CO., LTD. All rights reserved Page 110
Secondary PDP Context Activation Procedure
For UMTS
MS UTRAN 3G-SGSN 3G-GGSN
1. Activate Secondary PDP Context Request
C1
3. Create PDP Context Request
3. Create PDP Context Response
4. Radio Access Bearer Setup
6. Update PDP Context Request
6. Update PDP Context Response
C2
7. Activate PDP Context Accept
HUAWEI TECHNOLOGIES CO., LTD. All rights reserved Page 111
Network-Requested PDP Context
Activation Procedure
MS SGSN HLR GGSN
1. PDP PDU
2. Send Routeing Info for GPRS
2. Send Routeing Info for GPRS Ack
3. PDU Notification Request
3. PDU Notification Response
4. Request PDP Context Activation
5. PDP Context Activation procedure
HUAWEI TECHNOLOGIES CO., LTD. All rights reserved Page 112
Chapter 4 Session Management
4.1 Basic concepts
4.2 PDP Context Activation Procedure
4.3 PDP Context Modification Procedure
4.4 PDP Context Deactivation Procedure
4.5 Preservation Procedure (UMTS only)
HUAWEI TECHNOLOGIES CO., LTD. All rights reserved Page 113
Modification Procedures
Modification procedures modify parameters that were negotiated
during an activation procedure for one or several PDP contexts.
An MS, a GGSN, an SGSN, or an RNC can request a modification
procedure.
The following parameters can be modified:
QoS Negotiated;
Radio Priority;
Packet Flow Id;
PDP Address (in case of the GGSN-initiated modification
procedure);
TFT (in case of MS-initiated modification procedure).
HUAWEI TECHNOLOGIES CO., LTD. All rights reserved Page 114
SGSN-Initiated Modification Procedure
MS UTRAN SGSN GGSN
1. Update PDP Context Request
2. Update PDP Context Response
3. Modify PDP Context Request
4. Modify PDP Context Accept
C1
5. Radio Access Bearer Modification
6. Invoke Trace
HUAWEI TECHNOLOGIES CO., LTD. All rights reserved Page 115
GGSN-Initiated Modification Procedure
MS UTRAN SGSN GGSN
1. Update PDP Context Request
2. Modify PDP Context Request
3. Modify PDP Context Accept
4. Radio Access Bearer Modification
5. Update PDP Context Response
C1
HUAWEI TECHNOLOGIES CO., LTD. All rights reserved Page 116
MS-Initiated Modification Procedure
MS UTRAN SGSN GGSN
1. Modify PDP Context Request
2. Update PDP Context Request
3. Update PDP Context Response
4. Radio Access Bearer Modification
5. Modify PDP Context Accept
C1
HUAWEI TECHNOLOGIES CO., LTD. All rights reserved Page 117
RNC-initiated RAB Modification Procedure
RNC modify RAB may cause SGSN modify PDP context.
MS RNC SGSN GGSN
1. RAB Modify Request
2. SGSN initiated PDP Context Modification Procedure
HUAWEI TECHNOLOGIES CO., LTD. All rights reserved Page 118
Chapter 4 Session Management
4.1 Basic concepts
4.2 PDP Context Activation Procedure
4.3 PDP Context Modification Procedure
4.4 PDP Context Deactivation Procedure
4.5 Preservation Procedure (UMTS only)
HUAWEI TECHNOLOGIES CO., LTD. All rights reserved Page 119
MS Initiated Deactivation Procedure
For GPRS
MS 2G-SGSN 2G-GGSN
1. Deactivate PDP Context Request
C1
2. Security Functions
3. Delete PDP Context Request
3. Delete PDP Context Response
4. Deactivate PDP Context Accept
HUAWEI TECHNOLOGIES CO., LTD. All rights reserved Page 120
MS Initiated Deactivation Procedure
For UMTS
MS UTRAN 3G-SGSN 3G-GGSN
1. Deactivate PDP Context Request
C1
3. Delete PDP Context Request
3. Delete PDP Context Response
4. Deactivate PDP Context Accept
5. Radio Access Bearer Release
HUAWEI TECHNOLOGIES CO., LTD. All rights reserved Page 121
SGSN-initiated Deactivation Procedure
MS UTRAN SGSN GGSN
C1
1. Delete PDP Context Request
1. Delete PDP Context Response
2. Deactivate PDP Context Request
2. Deactivate PDP Context Accept
3. Radio Access Bearer Release
HUAWEI TECHNOLOGIES CO., LTD. All rights reserved Page 122
GGSN-initiated Deactivation Procedure
MS UTRAN SGSN GGSN
1. Delete PDP Context Request
C1
2. Deactivate PDP Context Request
2. Deactivate PDP Context Accept
3. Delete PDP Context Response
4. Radio Access Bearer Release
HUAWEI TECHNOLOGIES CO., LTD. All rights reserved Page 123
Chapter 4 Session Management
4.1 Basic concepts
4.2 PDP Context Activation Procedure
4.3 PDP Context Modification Procedure
4.4 PDP Context Deactivation Procedure
4.5 Preservation Procedure (UMTS only)
HUAWEI TECHNOLOGIES CO., LTD. All rights reserved Page 124
Preservation Procedures
By sending a RAB Release Request or Iu Release Request
message to the SGSN, UTRAN initiates the release of one or more
RABs.
The preservation procedure allows the active PDP contexts
associated with the released RABs to be preserved without
modification in the CN, and the RABs can then be re-established at
a later stage (e.g. by service request procedure).
UTRAN uses the Iu Release Request to request release of all RABs
of an MS, and the RAB Release Request in other cases.
HUAWEI TECHNOLOGIES CO., LTD. All rights reserved Page 125
RAB Release Procedure
UTRAN initiates a RAB release procedure to release one or several
RABs.
MS UTRAN 3G-SGSN 3G-GGSN
1. RAB Release Request
2. RAB Assignment Request
3. Release Radio
Bearer(s)
4. RAB Assignment Response
HUAWEI TECHNOLOGIES CO., LTD. All rights reserved Page 126
Iu Release Procedure
UTRAN initiates an Iu release procedure to release all RABs of an
MS and the Iu connection.
MS UTRAN 3G-SGSN 3G-GGSN
1. Iu Release Request
2. Iu Release Command
3. Release of RRC Connection
4. Iu Release Complete
HUAWEI TECHNOLOGIES CO., LTD. All rights reserved Page 127
PDP Context Modification after RAB Release
After RAB/Iu Release the PDP contexts are modified as follows:
Background or interactive traffic class PDP context:
Be preserved with no modifications in UE, SGSN and GGSN.
Streaming or conversational traffic class PDP context:
Be preserved, but the maximum bit rate is downgraded to
0 kbit/s (for both uplink and downlink) in UE, SGSN and GGSN.
HUAWEI TECHNOLOGIES CO., LTD. All rights reserved Page 128
Re-establishment of RABs
In case of uplink data to be transfer for the active PDP context
without RAB:
Background or interactive traffic class PDP context:
− UE initiates the Service Request procedure (Service Type =
Data) to re-establish PDP context.
Streaming or conversational traffic class PDP context:
− UE initiates the PDP context modification procedure to re-
establish PDP context, or deactivation procedure to delete
the PDP context.
In case of downlink data to be transfer for the active PDP context
without RAB: CN must first page the UE, then re-establish the RAB
by network-initiated service request procedure.
HUAWEI TECHNOLOGIES CO., LTD. All rights reserved Page 129
Summary
The session management function includes the flowing functions:
PDP context activation function;
PDP context modification function;
PDP context deactivation function;
PDP context preservation function.
HUAWEI TECHNOLOGIES CO., LTD. All rights reserved Page 130
Course Summary
MM and SM function are the most
important function of GPRS/UMTS PS
core network.
HUAWEI TECHNOLOGIES CO., LTD. All rights reserved Page 131
Thank you
www.huawei.com
Copyright©2007 Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. All Rights Reserved.
The information contained in this document is for reference purpose only, and is subject to
change or withdrawal according to specific customer requirements and conditions.
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (895)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (588)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (120)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- RAN16.0 RTWP Controllable Optimization v2.0Document29 pagesRAN16.0 RTWP Controllable Optimization v2.0anthonyNo ratings yet
- UL Power Congestion Due To Issue On High TrafficDocument3 pagesUL Power Congestion Due To Issue On High TrafficanthonyNo ratings yet
- Security Level RTWP Troubleshooting UideDocument57 pagesSecurity Level RTWP Troubleshooting UideanthonyNo ratings yet
- APC ManifestoDocument40 pagesAPC ManifestoDon EmekaNo ratings yet
- A 2133034114Document6 pagesA 2133034114Ashish ShuklaNo ratings yet
- PS Drop Rate Improvement in Whole Network After Optimization of RNC Level SwitchDocument7 pagesPS Drop Rate Improvement in Whole Network After Optimization of RNC Level SwitchanthonyNo ratings yet
- Mute Call Root Analysis Doc - JamesDocument4 pagesMute Call Root Analysis Doc - JamesanthonyNo ratings yet
- CDR Improvement by Changing RL MinpowermaxDocument5 pagesCDR Improvement by Changing RL MinpowermaxanthonyNo ratings yet
- BSS Counter Name Counter NumberDocument27 pagesBSS Counter Name Counter NumberanthonyNo ratings yet
- BSS Counter Name Counter NumberDocument27 pagesBSS Counter Name Counter NumberanthonyNo ratings yet
- OWP112020 WCDMA Radio Network Capacity Dimensioning ISSUE1.24Document107 pagesOWP112020 WCDMA Radio Network Capacity Dimensioning ISSUE1.24anthonyNo ratings yet
- PS Drop Rate Improvement in Whole Network After Optimization of RNC Level SwitchDocument7 pagesPS Drop Rate Improvement in Whole Network After Optimization of RNC Level SwitchanthonyNo ratings yet
- Co-BCCH & DCS1800 Implementation Reference GuideDocument10 pagesCo-BCCH & DCS1800 Implementation Reference GuideanthonyNo ratings yet
- GSM&UMTS Training Course 10-Analysis of RRC&RAB Access Problems and Cases 20111130-A-V1.0Document51 pagesGSM&UMTS Training Course 10-Analysis of RRC&RAB Access Problems and Cases 20111130-A-V1.0anthonyNo ratings yet
- 3GPP Release and Main FeaturesDocument41 pages3GPP Release and Main FeaturesanthonyNo ratings yet
- GENEXCloud Platform UMTS Engineer Parameter TemplateDocument9 pagesGENEXCloud Platform UMTS Engineer Parameter TemplateanthonyNo ratings yet
- What Are ModesDocument25 pagesWhat Are ModesNeoRa Ndivo RamsNo ratings yet
- CEDocument313 pagesCEanthonyNo ratings yet
- 60 Things God Said About Sex Lester SumrallDocument174 pages60 Things God Said About Sex Lester SumrallMugisa100% (3)
- High Call Drop Ratio Caused by Frequent MAHHO SearchingDocument4 pagesHigh Call Drop Ratio Caused by Frequent MAHHO SearchinganthonyNo ratings yet
- 04 ESRVCC Issue Troubleshooting Based On SEQ Platform - NewDocument6 pages04 ESRVCC Issue Troubleshooting Based On SEQ Platform - NewanthonyNo ratings yet
- Action 1: Determine The Scope of ProblemsDocument84 pagesAction 1: Determine The Scope of ProblemsanthonyNo ratings yet
- Optimization Guidelines ACCESSIBILITY Ericsson Rev01Document27 pagesOptimization Guidelines ACCESSIBILITY Ericsson Rev01Ömer AlbatNo ratings yet
- eRAN11.1KPI ReferenceDocument28 pageseRAN11.1KPI ReferenceanthonyNo ratings yet
- Configuring Dynamic CE Resource Management: PrerequisitesDocument2 pagesConfiguring Dynamic CE Resource Management: PrerequisitesanthonyNo ratings yet
- SRAN10.0 Multi-Band, Multimode, and Multi-Antenna Network Planning and Optimization SolutionDocument106 pagesSRAN10.0 Multi-Band, Multimode, and Multi-Antenna Network Planning and Optimization SolutionanthonyNo ratings yet
- Lac Tac MappingDocument299 pagesLac Tac MappinganthonyNo ratings yet
- LTE Parameters Commonly Used For Optimization RecommendationsDocument8 pagesLTE Parameters Commonly Used For Optimization RecommendationsBhaskar SharmaNo ratings yet
- Transmission Data ChecksDocument43 pagesTransmission Data ChecksanthonyNo ratings yet
- Forsk Presentation February 2016Document16 pagesForsk Presentation February 2016Dabin ClovisNo ratings yet
- Dip Electrical 2022 220919 213608Document9 pagesDip Electrical 2022 220919 213608TsoloNo ratings yet
- Yeastar Discoutned Retail Pricing v1.5Document1 pageYeastar Discoutned Retail Pricing v1.5Anonymous hywwi19lNo ratings yet
- Case Study On SDR: Software Defined Radio: Dr. S. JayakumarDocument9 pagesCase Study On SDR: Software Defined Radio: Dr. S. JayakumarUday KrishnaNo ratings yet
- Cs Core - Call FlowsDocument16 pagesCs Core - Call FlowsAhmad HassanNo ratings yet
- WB AMR TestingDocument6 pagesWB AMR TestingrakeshMozaNo ratings yet
- GSM PresentacionDocument81 pagesGSM PresentacionRoberto RuizNo ratings yet
- Lte Poster2013 Web PDFDocument1 pageLte Poster2013 Web PDFkentck86No ratings yet
- UMTS Interview Questions and AnswerDocument24 pagesUMTS Interview Questions and AnswervikydilseNo ratings yet
- Umts Wcdma Evolution 3gDocument15 pagesUmts Wcdma Evolution 3gA.K.M.TOUHIDUR RAHMANNo ratings yet
- SMS Call Flow - BasicDocument3 pagesSMS Call Flow - BasicarunmathewleoNo ratings yet
- Exercise - 5G KaviDocument2 pagesExercise - 5G Kavikavi manimaranNo ratings yet
- Mannar Mannan PallaviDocument76 pagesMannar Mannan PallavisomroNo ratings yet
- SGSN - HO.3G-3G.Iu SGSN - HO.3G-3G.Gn: MS Source RNC Target RNC Old SGSN New SGSN GGSNDocument1 pageSGSN - HO.3G-3G.Iu SGSN - HO.3G-3G.Gn: MS Source RNC Target RNC Old SGSN New SGSN GGSNXuân ToànNo ratings yet
- 01 Rn31551en30gla0 Warming UpDocument32 pages01 Rn31551en30gla0 Warming UpSalman ZaheerNo ratings yet
- LTE Technical SpecificationDocument337 pagesLTE Technical Specificationspiros09No ratings yet
- Deployment of Mobile WimaxDocument6 pagesDeployment of Mobile WimaxsaintdevilzNo ratings yet
- Gprs/Umts: IAB Workshop February 29 - March 2, 2000 Jonne Soininen NokiaDocument34 pagesGprs/Umts: IAB Workshop February 29 - March 2, 2000 Jonne Soininen NokiaSajid HussainNo ratings yet
- LTE Cell Planning 2.0Document47 pagesLTE Cell Planning 2.0Dede100% (1)
- Celcom Swap 3G Health Check - Rev2.0Document9 pagesCelcom Swap 3G Health Check - Rev2.0dhanamiwsNo ratings yet
- Curr Mob Voucher PDFDocument3 pagesCurr Mob Voucher PDFvipNo ratings yet
- GNSS-SDRLIB: An Open-Source and Real-Time GNSS Software Defined Radio LibraryDocument12 pagesGNSS-SDRLIB: An Open-Source and Real-Time GNSS Software Defined Radio Librarygeorge jiNo ratings yet
- Hexylon Datasheet (En)Document2 pagesHexylon Datasheet (En)Carlos A. Galeano A.No ratings yet
- Albert TensuinDocument4 pagesAlbert Tensuinbhargavs tiriveedhiNo ratings yet
- Huawei Me906eDocument1 pageHuawei Me906ekindboomerNo ratings yet
- NHM 5 SchematicsDocument7 pagesNHM 5 SchematicsRomanNo ratings yet
- Overview of 3GPP Release 99Document61 pagesOverview of 3GPP Release 99ilyamNo ratings yet
- 3GPP TS 36.300: Technical SpecificationDocument147 pages3GPP TS 36.300: Technical SpecificationLAVANYA MURALINo ratings yet
- Intermediate004security 180101111938Document52 pagesIntermediate004security 180101111938MohamedNasser Gad El MawlaNo ratings yet
- 1 - 4 Evolution - 4G - LTEDocument25 pages1 - 4 Evolution - 4G - LTEKOMBOLCHA DRYPORTTERMINALNo ratings yet