Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Conduction, Convection and Radiation-1
Uploaded by
Alvin Jacob0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
19 views19 pagesOriginal Title
conduction, convection and radiation-1
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
19 views19 pagesConduction, Convection and Radiation-1
Uploaded by
Alvin JacobCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 19
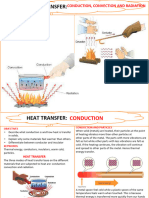
HEAT TRANSFER:
Convection, Conduction and
Radiation
CONDUCTION
• Heat energy can move through a substance by
conduction.
• Conduction is the transfer of thermal energy
through direct contact between particles
of a substance, without moving the particles t
o a new location
• When heat is supplied to one end, molecules
at that end start to move more quickly
• In the process, they bump into their
neighbors, transferring the kinetic energy
GOOD AND BAD CONDUCTORS
• Metals are generally good conductors of heat
• Non-metals and gases are usually poor
conductors of heat, also called insulators.
How is heat transferred?
• Good conductors are those materials whose
electrons can leave their atoms and move
about freely. Metals, for example are
considered to be good conductors of heat
because their electrons are able to move
freely around the metal. The parts of the
metal left behind will then be charged metal
ions.
…ions!
• Ions are close together and continually
vibrate. The hotter the metal, the more kinetic
energy these vibrations have.
• Kinetic energy is transferred by the free
electrons from hot parts of the metal to cooler
parts. These move through the structure of
the metal, colliding with ions as they go.
Examples
Good conductors of heat are:
-copper
-aluminium
-platinum
-gold
-silver
-water
-people and animals
-trees
Examples
Insulators (materials through which heat does
not transfer):
-plastic
-wood
-glass
-porcelain
-rubber
Diagram
Convention
• Convection is the transfer of thermal energy, which
moves particles from one place to another.
• Convection relies on the circulating motion of
molecules to transfer heat.
• Convection’s heat transfer moves from hot to cold
areas.
• Convection is more likely to be found in liquids or
gases.
How is heat transferred? (with example)
– The hot radiator transfers heat to the nearby air when air molecules
collide with the radiator surface.
– The hot air near to the radiator expands and increases in volume. Hot
air expands because the particles move further apart as they get hotter
– This makes the density of the hot air decrease and it starts to rise
upwards
– The colder air above it gets pushed along to the right and then
circulates as shown by the arrows
– The arrows show how the convention current move
– As the hot air moves around the room, it loses its heat by collision with
the walls, ceiling and the objects in the room
– Finally the colder air circulates near to the radiator where it is heated
and the whole process repeats itself.
Diagram
RADIATION
• The energy that comes from a source and
travels through material or space.
• Light, heat and sound are types of radiation.
• Radiation can produce charged particles (ions)
in matter.
• Examples of radiation is the heat from the sun,
or heat released from the filament of a light
bulb.
How is heat transferred?
• Radiation is a method of heat transfer that
does not rely upon any contact between the
heat source and the heated object as is the
case with conduction and convection.
• Heat can be transmitted through empty space
by thermal radiation often called infrared
radiation. This is a type of electromagnetic
radiation. No mass is exchanged and no
medium is required in the process of radiation.
Diagram
Examples of Radiation
• Infrared light
• Microwaves
• Low frequency waves
• Radio waves
• Waves produced by mobile phones
• Power lines
• Strong magnets
• MRI
• Lasers
• Light bulbs
• Light from the sun
• Remote controls
• Cordless phones
• X-rays
• Sterilization of medical tools
• Nuclear power production
COMPARISON
…CONTINUING COMPARISON
BIBLIOGRAPHY
• http://schoolworkhelper.net/thermal-energy-
transfer-conduction-convection-radiation/
• http://examples.yourdictionary.com/examples-of-
convection.html
• http://www.softschools.com/examples/science/c
onvection_examples/8/
• http://examples.yourdictionary.com/examples-of-
radiation.html
• http://www.epa.gov/radiation/understand/
You might also like
- Quantum Magick Reconfiguring The Field, A Powerful Companion To Mind Magic Methods (The Mind Magic System Book 2) (Merlin Starlight) (Z-Library)Document225 pagesQuantum Magick Reconfiguring The Field, A Powerful Companion To Mind Magic Methods (The Mind Magic System Book 2) (Merlin Starlight) (Z-Library)Raynald Sumampouw100% (1)
- Conduction Convection Radiation PowerpointDocument27 pagesConduction Convection Radiation PowerpointFitz Baniqued100% (3)
- Conduction Convection Radiation PowerpointDocument27 pagesConduction Convection Radiation PowerpointApet Satusembilansembilan JieNo ratings yet
- Conduction, Convection, & RadiationDocument14 pagesConduction, Convection, & Radiationyuvionfire100% (1)
- Physics Fundamentals 1 Reviewer P1&2Document56 pagesPhysics Fundamentals 1 Reviewer P1&2roxy8marie8chan100% (2)
- Two DimensionsDocument7 pagesTwo Dimensionsalex murker100% (1)
- Conduction Convection RadiationDocument32 pagesConduction Convection RadiationShalini Kulshrestha100% (2)
- Homework SolutionDocument25 pagesHomework SolutionHirman De NovaNo ratings yet
- Performance of Heat ExchangersDocument10 pagesPerformance of Heat ExchangersJusztinAquinoNo ratings yet
- Article Balancing of Rotor BladesDocument5 pagesArticle Balancing of Rotor BladesAhmedFaissalNo ratings yet
- Conduction Convection Radiation PowerpointDocument18 pagesConduction Convection Radiation PowerpointRavichandran G100% (1)
- Advanced Linear and Nonlinear Control DesignDocument15 pagesAdvanced Linear and Nonlinear Control Designdenise_meira_2100% (1)
- 1-Introduction and Basic Concepts PDFDocument18 pages1-Introduction and Basic Concepts PDFsara sofeaNo ratings yet
- Transfer of Thermal EnergyDocument9 pagesTransfer of Thermal Energycontroller playerNo ratings yet
- ConductionDocument9 pagesConductionaneeqa StudentNo ratings yet
- AnotherDocument6 pagesAnotherIrram RanaNo ratings yet
- Thermal ProcessesDocument5 pagesThermal Processestrsilas24No ratings yet
- Interface Mass TraDocument26 pagesInterface Mass TraWahid AliNo ratings yet
- Methods of Heat TransferDocument29 pagesMethods of Heat TransferRodriguez ArthursNo ratings yet
- Heat Transfer PDFDocument3 pagesHeat Transfer PDFTahmeed AzizNo ratings yet
- Document 10Document5 pagesDocument 10shookookie 101No ratings yet
- HeatDocument2 pagesHeatEvangeline BocasasNo ratings yet
- Basa HTBCDocument10 pagesBasa HTBCErhiecka BasaNo ratings yet
- Heat Transfer Methods 2017 Class Notes AutosavedDocument39 pagesHeat Transfer Methods 2017 Class Notes AutosavedItsMe SirMJNo ratings yet
- PhysicssDocument5 pagesPhysicsschionumaraliaNo ratings yet
- CorrectDocument2 pagesCorrectjadonallen2007No ratings yet
- Introduction HTDocument29 pagesIntroduction HTGoutam VijNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2Document10 pagesLecture 2Aarzoo JobanputraNo ratings yet
- Heat and Temperature - 4Document28 pagesHeat and Temperature - 4Endar MadesaNo ratings yet
- Students Unit 2 PHYSICS Energy and HeatDocument74 pagesStudents Unit 2 PHYSICS Energy and HeatAnnalisa ChenNo ratings yet
- Forging New Generations of EngineersDocument28 pagesForging New Generations of EngineersDarshan MbNo ratings yet
- Heatvs Tem2Document18 pagesHeatvs Tem2Ross Adrales GeleraNo ratings yet
- (2.3) A - Transfer of Thermal Energy - ConductionDocument2 pages(2.3) A - Transfer of Thermal Energy - Conductionzahra1No ratings yet
- Part 2Document14 pagesPart 2api-298420434No ratings yet
- Different Kinds of Method of Heat TransferDocument9 pagesDifferent Kinds of Method of Heat TransferJohn Gabriel JimenezNo ratings yet
- Different Kinds of Method of Heat TransferDocument9 pagesDifferent Kinds of Method of Heat TransferJohn Gabriel JimenezNo ratings yet
- Activity No. 1: Modes of Heat TransferDocument7 pagesActivity No. 1: Modes of Heat TransferSquidward TentaclesNo ratings yet
- Transmission of Heat: Presented by V.Rajalakshmi II-B.Sc (Physics) 13UPHY024Document11 pagesTransmission of Heat: Presented by V.Rajalakshmi II-B.Sc (Physics) 13UPHY024shajmalikNo ratings yet
- Heat TransfeerDocument26 pagesHeat TransfeerRonald AlisingNo ratings yet
- Conduction, Convection, RadiationDocument11 pagesConduction, Convection, RadiationKuruluş OsmanNo ratings yet
- Heat TransferDocument47 pagesHeat TransferMuthukrishagalsNo ratings yet
- Module 2 Understanding Conduction Convection RadiationDocument29 pagesModule 2 Understanding Conduction Convection RadiationVishnupriya B.No ratings yet
- Heat Transfer and Thermal Performance of Wall & Roof: Submitted by Darshini.MDocument17 pagesHeat Transfer and Thermal Performance of Wall & Roof: Submitted by Darshini.MDarshini manoharanNo ratings yet
- Heat 1 PDFDocument22 pagesHeat 1 PDFHendrik Ongki S 921224No ratings yet
- Thermal Effects - Do Now!: - Make A List of Good and Bad Conductors of HeatDocument50 pagesThermal Effects - Do Now!: - Make A List of Good and Bad Conductors of HeatErna GampalNo ratings yet
- Transfer of Thermal EnergyDocument3 pagesTransfer of Thermal EnergyPeter KachouhNo ratings yet
- Heat TransferDocument2 pagesHeat TransferRitishBoodhunNo ratings yet
- Transfer of Thermal Energy - Conduction - Convection - Radiation - Applications of Thermal Energy TransferDocument47 pagesTransfer of Thermal Energy - Conduction - Convection - Radiation - Applications of Thermal Energy TransfervaishnaviNo ratings yet
- Radiation Heat Transfer: Lecture By:-A.Bari (Msc. Thermal Eng'G)Document20 pagesRadiation Heat Transfer: Lecture By:-A.Bari (Msc. Thermal Eng'G)tsegayNo ratings yet
- P2.1 Energy Transfer by ConductionDocument17 pagesP2.1 Energy Transfer by ConductionchrisNo ratings yet
- Heat Transfer ProjectDocument7 pagesHeat Transfer Projectapi-215058027No ratings yet
- Conduction Convection Radiation NotesDocument29 pagesConduction Convection Radiation NotesAnosha AminNo ratings yet
- Transfer of Thermal Energy: Physics Notes GCE Study BuddyDocument20 pagesTransfer of Thermal Energy: Physics Notes GCE Study Buddyanwar9602020No ratings yet
- 2.3 Thermal ProcessesDocument6 pages2.3 Thermal ProcesseshaiderNo ratings yet
- Heat 1Document22 pagesHeat 1Hendrik Ongki S 921224No ratings yet
- Heat Transfer Chapter OneDocument36 pagesHeat Transfer Chapter OneteddiyfentawNo ratings yet
- Physics STPM HEAT TRANSFERDocument23 pagesPhysics STPM HEAT TRANSFERRed Jagung Fish100% (3)
- Heat Transfer ANTONIO VIDA VDocument40 pagesHeat Transfer ANTONIO VIDA Vshahanajmunni178No ratings yet
- Heat Transfer 1Document33 pagesHeat Transfer 1JATIN DALMIANo ratings yet
- Lesson 7: Thermal EnergyDocument19 pagesLesson 7: Thermal EnergyAthena ArevaloNo ratings yet
- 1 Fundamental of Heat TransferDocument20 pages1 Fundamental of Heat Transferred18ggmuNo ratings yet
- CH 15 LogoDocument45 pagesCH 15 LogoThaw ThawNo ratings yet
- AND Modes of Heat TransferDocument41 pagesAND Modes of Heat TransferKushNo ratings yet
- HEATDocument16 pagesHEATHoney Mae CarvajalNo ratings yet
- G8 - Light& Heat and TemperatureDocument49 pagesG8 - Light& Heat and TemperatureJhen BonNo ratings yet
- V. Bernoulli EquationDocument31 pagesV. Bernoulli EquationNugraha RizkiNo ratings yet
- Grade 7 Daily Lesson Plan: I. ObjectivesDocument3 pagesGrade 7 Daily Lesson Plan: I. ObjectivesJanecil A. BonzaNo ratings yet
- Geankoplis 2.6-4 2.7-4Document7 pagesGeankoplis 2.6-4 2.7-4BenePicarNo ratings yet
- Ag Cu inDocument8 pagesAg Cu inReda TammamNo ratings yet
- Some Interesting Facts About: Mechanical EngineeringDocument9 pagesSome Interesting Facts About: Mechanical EngineeringHaraprasad SNo ratings yet
- Electron StructureDocument13 pagesElectron Structuredejla67No ratings yet
- Efflux Time: TOGUN Iyanuoluwa JohnDocument24 pagesEfflux Time: TOGUN Iyanuoluwa JohnJohnNo ratings yet
- Dawson College: Department of MathematicsDocument14 pagesDawson College: Department of Mathematicsadcyechicon123No ratings yet
- شيت مختبر الاسس PDFDocument23 pagesشيت مختبر الاسس PDFMohamad AlhadithyNo ratings yet
- Science 2004Document5 pagesScience 2004yilongwei.comNo ratings yet
- Inertia PictureDocument20 pagesInertia PictureMohd Sabri NorNo ratings yet
- Relativity VIC McqsDocument3 pagesRelativity VIC McqsLasnthaBandara75% (4)
- Assignment 1 - MagnetismDocument3 pagesAssignment 1 - MagnetismAnanya SinghNo ratings yet
- GP1 - Q2 - Week 8Document5 pagesGP1 - Q2 - Week 8Shekaina Faith Cuizon LozadaNo ratings yet
- PosDocument3 pagesPosAndre De VillaNo ratings yet
- Meherwan P Boyce - Gas Turbine Engineering Handbook-Elsevier Butterworth-Heinemann (2012) 27Document5 pagesMeherwan P Boyce - Gas Turbine Engineering Handbook-Elsevier Butterworth-Heinemann (2012) 27amir moniriNo ratings yet
- QUIZDocument26 pagesQUIZKieron Ivan Mendoza GutierrezNo ratings yet
- Cell Type UR18650F: SpecificationsDocument5 pagesCell Type UR18650F: SpecificationsIskandar WirawanNo ratings yet
- Time: 2 Hours Maximum Marks - 208: Physics Test (Electrostatics)Document11 pagesTime: 2 Hours Maximum Marks - 208: Physics Test (Electrostatics)ZomatoswiggyNo ratings yet
- UNITS AND MEASUREMENTS Assignment PDFDocument3 pagesUNITS AND MEASUREMENTS Assignment PDFvanshika MorNo ratings yet
- 09 - Chapter 2 PDFDocument34 pages09 - Chapter 2 PDFrajkumarNo ratings yet
- Engineering Drawing TangencyDocument11 pagesEngineering Drawing TangencyEmijo.ANo ratings yet
- Module 13 (Trusses Sections)Document13 pagesModule 13 (Trusses Sections)Vincent John MendezNo ratings yet