Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Pituitary Gland: Anterior Lobe Posterior Lobe
Uploaded by
waqar0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
4 views5 pagesOriginal Title
Pituitary Gland
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
4 views5 pagesPituitary Gland: Anterior Lobe Posterior Lobe
Uploaded by
waqarCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 5
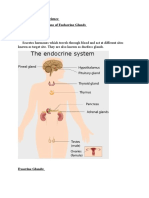
PITUITARY GLAND
•The pituitary gland is small and oval-shaped. It’s located behind your
nose, near the underside of your brain. It’s attached to
the hypothalamus by a stalk like structure.
• Size of a pea and weighing 0.5 g
•The hypothalamus is a small area of your brain. It’s very important in
controlling the balance of your bodily functions. It controls the release of
hormones from the pituitary gland.
•The pituitary gland can be divided into two different parts: the anterior
and posterior lobes.
• AnteriorLobe
• Posterior Lobe
Anterior pituitary is composed of 3 regions:
Pars distalis – it comprises majority of anterior pituitary
greater amount of pituitary hormone production occurs here
Pars tuberalis – it forms casing around pituitary stalk
Pars intermedia – It sits between pars distalis and posterior pituitary
Anterior Lobe Hormones:
Adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH): ACTH stimulates the adrenal glands
to produce hormones.
Follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH): FSH works with LH to ensure normal
functioning of the ovaries and testes.
Growth hormone (GH): GH is essential in early years to maintaining a healthy body
composition and for growth in children. In adults, it aids healthy bone and muscle mass
and affects fat distribution.
Luteinizing hormone (LH): LH works with FSH to ensure normal functioning of the ovaries and
testes.
Prolactin: Prolactin stimulates breast milk production.
Thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH): TSH stimulates the thyroid gland to produce hormones.
Posterior Gland:
The posterior pituitary (or neurohypophysis) is the posterior lobe of the pituitary
gland which is part of the endocrine system. The posterior pituitary is not glandular as is
the anterior pituitary. Instead, it is largely a collection of axonal projections from
the hypothalamus that terminate behind the anterior pituitary, and serve as a site for the
secretion of neurohypophysial hormones (oxytocin and vasopressin) directly into the
blood.
Diagram:
Relations
Anteriorly: sphenoid sinus
Posteriorly: dorsum sellae, basilar artery, pons
Superiorly: diaphragma sellae
Inferiorly: body of sphenoid
Main Function Of Pituitary Gland:
Its main function is to secrete hormones into your
bloodstream.
These hormones can affect other organs and glands.
You might also like
- A Simple Guide to Pituitary Disorders, Diagnosis, Treatment and Related ConditionsFrom EverandA Simple Guide to Pituitary Disorders, Diagnosis, Treatment and Related ConditionsNo ratings yet
- The Endocrine System and Key Glands Like the PituitaryDocument8 pagesThe Endocrine System and Key Glands Like the PituitaryPing KyNo ratings yet
- Mhs-1Pituitary Gland PresentationDocument34 pagesMhs-1Pituitary Gland PresentationAyi Abdul BasithNo ratings yet
- Pituitary Gland, Functions, Diseases, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsFrom EverandPituitary Gland, Functions, Diseases, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (1)
- Unit2-Hypothalamus and PituitaryDocument80 pagesUnit2-Hypothalamus and Pituitarypranutan739No ratings yet
- Thyroid Health: The Thyroid Solution Diet ExposedFrom EverandThyroid Health: The Thyroid Solution Diet ExposedRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (2)
- The Pituitary GlandDocument3 pagesThe Pituitary Glandshrabasti89No ratings yet
- The Endocrine System in 40 CharactersDocument34 pagesThe Endocrine System in 40 CharactersNeil VelascoNo ratings yet
- Behavioural Neuro ScienceDocument8 pagesBehavioural Neuro ScienceFaisal AwanNo ratings yet
- Science 10 A2.2 Pituitary and Hypothalamus The Bodys Control CentersDocument40 pagesScience 10 A2.2 Pituitary and Hypothalamus The Bodys Control CentersKhobie PabilicoNo ratings yet
- Pituitary and Hypothalamus: The Body's Control Center: Lesson A2.2Document40 pagesPituitary and Hypothalamus: The Body's Control Center: Lesson A2.2Khobie PabilicoNo ratings yet
- Hypothalamus and Pituitary Gland Control Endocrine SystemDocument13 pagesHypothalamus and Pituitary Gland Control Endocrine SystemUmer Shahzad ANSERNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 Part 1 Patho 2 Kmu IhsanDocument33 pagesUnit 2 Part 1 Patho 2 Kmu IhsanRehan Khan RkNo ratings yet
- The Endocrine System: Glands and Hormones that Regulate the BodyDocument27 pagesThe Endocrine System: Glands and Hormones that Regulate the Bodydaphnereeze100% (1)
- Endocrine SystemDocument3 pagesEndocrine Systemyessii_rahmawatiNo ratings yet
- Endocrinol Pred 02Document7 pagesEndocrinol Pred 02api-3706483No ratings yet
- PituartaryDocument3 pagesPituartarynancy dasNo ratings yet
- The Pituitary Gland: An Overview of Its Anatomy and Major HormonesDocument3 pagesThe Pituitary Gland: An Overview of Its Anatomy and Major Hormonesfrechel kimNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology of the Endocrine System in 40 CharactersDocument14 pagesAnatomy and Physiology of the Endocrine System in 40 Charactersyolanda merinskyNo ratings yet
- The Miracle of The Pituitary GlandDocument7 pagesThe Miracle of The Pituitary GlandHossam Farouk HassanNo ratings yet
- The Structure and Function of Central and Peripheral HormonDocument34 pagesThe Structure and Function of Central and Peripheral HormonrichardiaNo ratings yet
- Pituitary Gland 1Document3 pagesPituitary Gland 1iiout346No ratings yet
- Illustration of The Endocrine SystemDocument7 pagesIllustration of The Endocrine SystemMohammed MohammedNo ratings yet
- Pituitary GlandDocument1 pagePituitary GlandPCRNo ratings yet
- Endocrine GlandsDocument36 pagesEndocrine GlandsnasyitahnorzlanNo ratings yet
- Pituitary GlandDocument22 pagesPituitary GlandSara Musavi100% (2)
- Endocrine System and Endocrine GlandsDocument7 pagesEndocrine System and Endocrine GlandsMr.VivStarNo ratings yet
- The Role and Functions of the HypothalamusDocument12 pagesThe Role and Functions of the Hypothalamusshahad hamedNo ratings yet
- The Pituitary Gland Phamela Joy S. Alvarez Anatomic and Physiologic OverviewDocument27 pagesThe Pituitary Gland Phamela Joy S. Alvarez Anatomic and Physiologic OverviewEdelrose LapitanNo ratings yet
- Hormones: and The That Are Need To The Our Body To Function WellDocument2 pagesHormones: and The That Are Need To The Our Body To Function WellGian Georgette SalcedoNo ratings yet
- LECTURE 1 Endocrine Diseases Lecture 1 January 10-020Document68 pagesLECTURE 1 Endocrine Diseases Lecture 1 January 10-020aleen qawareetNo ratings yet
- Endocrine Gland - WikipediaDocument29 pagesEndocrine Gland - WikipediaSumaya FarheenNo ratings yet
- Corticotropins and GonadotropinsDocument39 pagesCorticotropins and GonadotropinsSudhakar LakavathNo ratings yet
- Worksheet 1, AnaphyDocument3 pagesWorksheet 1, AnaphycelynjasminegNo ratings yet
- Nervous System ReportDocument5 pagesNervous System ReportsharkNo ratings yet
- Hypothalamus, Pituitary, Thyroid & Parathyroid Glands-3Document70 pagesHypothalamus, Pituitary, Thyroid & Parathyroid Glands-3Benard NyaumaNo ratings yet
- HypothalamusDocument3 pagesHypothalamustewogbadeomobuwajo005No ratings yet
- Endocrine System IDocument19 pagesEndocrine System IMarbahun Jala KharbhihNo ratings yet
- The Endocrine System - Integral PartsDocument3 pagesThe Endocrine System - Integral PartsDavid TanNo ratings yet
- Endocrine SystemDocument58 pagesEndocrine SystemBeBs jai SelasorNo ratings yet
- Hypopituitarism Group F BSN 3Document21 pagesHypopituitarism Group F BSN 3Mari IllustriousNo ratings yet
- Grow Taller: © Dr. Laura de Giorgio All Rights ReservedDocument12 pagesGrow Taller: © Dr. Laura de Giorgio All Rights ReservednepplutoNo ratings yet
- EndocrineDocument6 pagesEndocrineShreyasi PatankarNo ratings yet
- Endocrine SystemDocument18 pagesEndocrine SystemDioh EmmanuelNo ratings yet
- The Endocrine System - Hormones Control Growth and HomeostasisDocument12 pagesThe Endocrine System - Hormones Control Growth and HomeostasisBai Donna S. AlimanNo ratings yet
- V3 Unit 9B_ Human Regulation and ReproductionDocument16 pagesV3 Unit 9B_ Human Regulation and ReproductionNellNo ratings yet
- Local Media2182658933713495317Document129 pagesLocal Media2182658933713495317JAYMAYMA ELGARIONo ratings yet
- What Is The Endocrine System?: HormonesDocument7 pagesWhat Is The Endocrine System?: HormonesGhezyl LascoNo ratings yet
- Endocrine System IntroductionDocument8 pagesEndocrine System IntroductionAlchemi Mij PoolscanNo ratings yet
- The Endocrine System: Regulating Bodily Functions Through HormonesDocument41 pagesThe Endocrine System: Regulating Bodily Functions Through HormonesAtteya Mogote AbdullahNo ratings yet
- BiologyDocument21 pagesBiologynitesh.th15005No ratings yet
- ENDOCRINE SYSTEM ReportDocument21 pagesENDOCRINE SYSTEM ReportAdelfa LibanonNo ratings yet
- Seminor On Hormons Slide2 by Prof - Dr.HariharDocument49 pagesSeminor On Hormons Slide2 by Prof - Dr.Hariharhariharb999_23960100No ratings yet
- HormonesDocument29 pagesHormonesCandy Chieng67% (3)
- What Is The Hypothalamus?Document4 pagesWhat Is The Hypothalamus?Jae Em DiestroNo ratings yet
- Chapter 11 - HormonesDocument8 pagesChapter 11 - Hormonesbussniesm05No ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology - Endocrine SystemDocument8 pagesAnatomy and Physiology - Endocrine Systemcn351073No ratings yet
- Science Endocrine System NotesDocument6 pagesScience Endocrine System Notesstephanie adorioNo ratings yet
- Unit 13 Endocrine GlandDocument73 pagesUnit 13 Endocrine GlandChandan ShahNo ratings yet