Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Microprocessor Operation 1
Uploaded by
Aisha Sarin0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
19 views4 pagesThe microprocessor contains an ALU to perform arithmetic and logic operations on data stored in registers or memory. It also has a register array to temporarily store data and addresses during program execution. A control unit provides timing and control signals to coordinate data flow between the microprocessor, memory, and peripherals. The microprocessor reads instructions and data from memory to perform computations in its ALU, storing results back in memory or outputting them.
Original Description:
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe microprocessor contains an ALU to perform arithmetic and logic operations on data stored in registers or memory. It also has a register array to temporarily store data and addresses during program execution. A control unit provides timing and control signals to coordinate data flow between the microprocessor, memory, and peripherals. The microprocessor reads instructions and data from memory to perform computations in its ALU, storing results back in memory or outputting them.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
19 views4 pagesMicroprocessor Operation 1
Uploaded by
Aisha SarinThe microprocessor contains an ALU to perform arithmetic and logic operations on data stored in registers or memory. It also has a register array to temporarily store data and addresses during program execution. A control unit provides timing and control signals to coordinate data flow between the microprocessor, memory, and peripherals. The microprocessor reads instructions and data from memory to perform computations in its ALU, storing results back in memory or outputting them.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 4
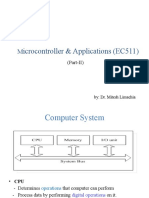
Microprocessor Architecture & Operation
Microprocessor Architecture & Operation
• ALU (Arithmetic/Logic Unit) – It performs such arithmetic operations
as addition and subtraction, and such logic operations as AND, OR,
and XOR. Results are stored either in registers or in memory.
•
• Register Array – It consists of various registers identified by letter
such as B, C, D, E, H, L, IX, and IY. These registers are used to store
data and addresses temporarily during the execution of a program.
•
• Control Unit – The control unit provides the necessary timing and
control signals to all the operations in the microcomputer. It controls
the flow of data between the microprocessor and memory and
peripherals.
Microprocessor Architecture & Operation
• Input – The input section transfers data and instructions in binary
from the outside world to the microprocessor. It includes such
devices as a keyboard, switches, a scanner, and an analog-to-digital
converter.
• Output – The output section transfers data from the microprocessor
to such output devices as LED, CRT, printer, magnetic tape, or another
computer.
• Memory – It stores such binary information as instructions and data,
and provides that information to the microprocessor. To execute
programs, the microprocessor reads instructions and data from
memory and performs the computing operations in its ALU section.
Results are either transferred to the output section for display or
stored in memory for later use.
System bus
• System bus – It is a communication path
between the microprocessor and peripherals.
The microprocessor communicates with only
one peripheral at a time. The timing is
provided by the control unit of the
microprocessor.
You might also like
- CS 208-1-3 Organization of A Microcomputer by Baldev Ram MaliDocument12 pagesCS 208-1-3 Organization of A Microcomputer by Baldev Ram MaliINFINITY GAmErNo ratings yet
- Computer ArchitectureDocument29 pagesComputer ArchitectureIfLah IToo100% (1)
- CO Unit 1Document43 pagesCO Unit 1Dinkesh JainNo ratings yet
- PLC 2021 ArchitectureDocument62 pagesPLC 2021 ArchitectureJosephNo ratings yet
- MP 8085 NotesDocument37 pagesMP 8085 NotesSaddam AnsariNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 - Central Processing Unit - PPTDocument92 pagesUnit 1 - Central Processing Unit - PPTPulihora Kat RajaNo ratings yet
- Introduction To The 68Hc12 MicrocontrollerDocument28 pagesIntroduction To The 68Hc12 Microcontrollerahetdhaezh100% (2)
- Microprocessor Notes Pruvanchal UniversityDocument84 pagesMicroprocessor Notes Pruvanchal UniversityNika Unav100% (1)
- CISE414 - Unit 01 IntroductionDocument50 pagesCISE414 - Unit 01 Introductionمحمد حمدNo ratings yet
- Arm ProgrammingDocument84 pagesArm ProgrammingmnmnNo ratings yet
- MicroprocessorDocument51 pagesMicroprocessorBishal TiwariNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 - Classification of ComputerDocument46 pagesChapter 2 - Classification of ComputerDev ShahNo ratings yet
- Microprocessor AllDocument84 pagesMicroprocessor Allcodingwallah0No ratings yet
- Unit 01: BEE-15ADocument22 pagesUnit 01: BEE-15APrashant SinghNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 IntroductionDocument54 pagesUnit 1 IntroductionNikhil DeshmukhNo ratings yet
- 57 Ma NotesDocument21 pages57 Ma NotesKajal GoudNo ratings yet
- Embedded SystemsDocument136 pagesEmbedded Systemsjapheth louie m. gofredoNo ratings yet
- Unit IV - MechatronicsDocument46 pagesUnit IV - Mechatronicsvivekananthan.mechNo ratings yet
- DLD Lecture 1Document14 pagesDLD Lecture 1Muhammad RehanNo ratings yet
- Computer and MircroprocessorDocument28 pagesComputer and MircroprocessorPhongNo ratings yet
- Microprocessor and ControllerDocument18 pagesMicroprocessor and ControllerSai Murali SirapuNo ratings yet
- Microprocessor CH 01Document56 pagesMicroprocessor CH 01hari kcNo ratings yet
- Module 1Document33 pagesModule 1yadvendra dhakadNo ratings yet
- MCA Sessional1 2023 24Document87 pagesMCA Sessional1 2023 24Jayraj SONINo ratings yet
- Introduction To Micro Lect3Document21 pagesIntroduction To Micro Lect3Annalyn SoriaNo ratings yet
- Module 3 Basic Structure of ComputersDocument76 pagesModule 3 Basic Structure of ComputersMadhuNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document46 pagesChapter 1Temesgen MekonenNo ratings yet
- Ppts FinalDocument223 pagesPpts Final1553No ratings yet
- Microproessor - Microprocessor and Its Components - : Qisthi Al Hazmi HR., S.T., M.TDocument21 pagesMicroproessor - Microprocessor and Its Components - : Qisthi Al Hazmi HR., S.T., M.TChuenk NeutronNo ratings yet
- Coa Module 1Document79 pagesCoa Module 1B G JEEVANNo ratings yet
- Co-1 - CoaDocument112 pagesCo-1 - CoaDAVU REVANTH NAGNo ratings yet
- 3 MicrocontrollersDocument28 pages3 MicrocontrollersRynefel ElopreNo ratings yet
- CPEN 100 Structural Components of Microprocessor and Microcontroller.1Document35 pagesCPEN 100 Structural Components of Microprocessor and Microcontroller.1Jiever AustriaNo ratings yet
- CH-6 Basics of MicroprocessorsDocument38 pagesCH-6 Basics of MicroprocessorsbelaynehNo ratings yet
- New Chapter 1Document18 pagesNew Chapter 1Amzar ShukriNo ratings yet
- Unit 1: Computers, Microprocessors and MicrocontrollersDocument65 pagesUnit 1: Computers, Microprocessors and MicrocontrollersHARSHITHA BHAVISETTINo ratings yet
- Lecture OneDocument36 pagesLecture OneMworozi DicksonNo ratings yet
- Embedded System Unit 1 (VTU)Document20 pagesEmbedded System Unit 1 (VTU)GucciNo ratings yet
- UNIT-3: Processor and Control Unit by Anoop GuptaDocument35 pagesUNIT-3: Processor and Control Unit by Anoop GuptaMingma Kanchhi SherpaNo ratings yet
- PLC - Docx NiterDocument17 pagesPLC - Docx NiterRanju Marma RmsNo ratings yet
- MP Manual BscitDocument135 pagesMP Manual BscitSubir ShresthaNo ratings yet
- Dfc2053 Computer System ArchitectureDocument54 pagesDfc2053 Computer System ArchitectureHasif AimanNo ratings yet
- Computer Systems HARDWARE L2Document102 pagesComputer Systems HARDWARE L2trevorNo ratings yet
- Computer Arch NotesDocument9 pagesComputer Arch NoteszomukozaNo ratings yet
- 18Csc203J:Computer Organization and ArchitectureDocument56 pages18Csc203J:Computer Organization and ArchitectureSENTHIL RNo ratings yet
- Computer Hardware ComponentsDocument20 pagesComputer Hardware ComponentsMJ Mackie TanNo ratings yet
- Microprocessor Systems Chapter 1 1Document39 pagesMicroprocessor Systems Chapter 1 1Johnbob ToveraNo ratings yet
- University of Salahaddin College of Engineering Software & Informatics DepDocument26 pagesUniversity of Salahaddin College of Engineering Software & Informatics DepZayto SaeedNo ratings yet
- Ecpc-308 15Document140 pagesEcpc-308 15chinusood08No ratings yet
- Microprocessor Lec No.1Document26 pagesMicroprocessor Lec No.1bashirahmed bashirahmedNo ratings yet
- 18csc203j Coa Unit1Document216 pages18csc203j Coa Unit1bobNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Mechatronics: Microcontrollers and MicroprocessorsDocument12 pagesIntroduction To Mechatronics: Microcontrollers and MicroprocessorsAmanuel tadiwosNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of C 1Document20 pagesFundamentals of C 1yzNo ratings yet
- COA Module3Document35 pagesCOA Module3Aditya Dhanaraj KunduNo ratings yet
- Von Neumann Architecture PDFDocument4 pagesVon Neumann Architecture PDFpreetarora2k18No ratings yet
- (RB) COA - Notes UNIT-1Document20 pages(RB) COA - Notes UNIT-1aryanraj22760No ratings yet
- Functional UnitsDocument13 pagesFunctional UnitsAnu PriyaNo ratings yet
- Microprocessor - ECE312: Introduction ClassDocument17 pagesMicroprocessor - ECE312: Introduction Classblooms116No ratings yet
- TOPIC - 1 MicroprocessorDocument38 pagesTOPIC - 1 MicroprocessorPrevenaManiamNo ratings yet
- Digital Electronics, Computer Architecture and Microprocessor Design PrinciplesFrom EverandDigital Electronics, Computer Architecture and Microprocessor Design PrinciplesNo ratings yet
- 9 Data Communication and Computer NetworkDocument71 pages9 Data Communication and Computer NetworkAisha SarinNo ratings yet
- Block Diagram of 8085.Pptx1ENDDocument32 pagesBlock Diagram of 8085.Pptx1ENDAisha SarinNo ratings yet
- Internal Organization Register1Document12 pagesInternal Organization Register1Aisha SarinNo ratings yet
- Microprocessor and Its TypesDocument16 pagesMicroprocessor and Its TypesAisha SarinNo ratings yet