Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Trans New
Trans New
Uploaded by
Sharan SaarsarOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Trans New
Trans New
Uploaded by
Sharan SaarsarCopyright:
Available Formats
Lessons Learnt
Roll Cage
1. Poor weight transfer due to highly stiff roll cage
2. Complex geometry for suspension arm mountings
3. Large clearance from driver’s head to the top
member
4. Better integration with engine assembly
5. Large errors in 3D bending of tubes
6. Better fixtures for manufacture of roll cage
Powertrain
1. Tuning of CVT must be done accurately as it affects
vehicle performance
2. Loss of traction due to high gear ratio
3. Non-compliance of CV axle at high articulation
angles
4. Mechanism is needed to reduce heating of cvt
5. Gearbox heating lead to high pressure built up
6. CV axle hindered with suspension arms
Suspension and Steering
1. Stiff and light arms and joints should be
preferred. Fig.(a)
2. Accuracy in manufacturing to avoid play
3. Avoid toggle position in steering mechanism
4. Proper clearance to avoid hindrance to
shockers
5. Proper clearance between rear suspension
arms and CV axle required
6. To compact the front wheel hub assembly, Stub
axle assembly is suggested. Fig.(b)
7. To avoid the tie rod failure, proper orientation
is needed with material of more fractural Fig.(a) Fig.(b)
rigidity.
Braking
1. To increase FOS in FEA analysis
2. To maintain proper height of brake pedal from
base
3. To maintain proper clearance between rims and
calipers. Fig.(c)
4. Manufacturability of master cylinder and its
affordability
Fig.(c)
Comparative Analysis
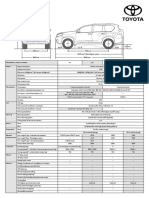
Parameter Old vehicle New vehicle Parameter Old Vehicle New Vehicle
Length 77’’ 77” Maximum 7.355 KW (10
7.355 KW (10 HP)
Width 58” 56'' Power HP)
56” Maximum
Height 55.8” Torque 19.66 N-m 19.66 N-m
Wheelbase 57” 55'' CVT (CVTech),
Track Width 52” ratio 0.43:1 to CVT (CVTech),
50''
(front) 3:1 ratio 0.43:1 to
Track Width (rear) 46” 48'' Transmission Custom 3.0:1
Performance specifications
Gearbox, Custom Gearbox,
Design Ground Clearance 11” 12''
Reduction Reduction 8.89:1
Kerb Weight 161 kg 150 kg
11.6:1
Weight 46.0 : 54.0 (F:R) 42.0 : 58.0 (F:R) Maximum
Acceleration 6.8 m/s 5.37 m/s2
2
Distribution
17.01” (height) 17.87” (height) Top Speed 54.9 kmph 56 kmph
Technical Specifications
COG Coordinates 30.75”( front axle) 31.9”( front axle) Gradeability 64.90% 64.9%
26.25”(rear axle) 23.1”(rear axle)
22”x8”-10” Front; 22”x8”-10” Front;
Tyre Size 22”x8”-10” Rear 22”x8”-10” Rear
Independent,
Front Suspension Double Wishbone Independent,
Double Wishbone
Power to
Suspension Rear Suspension Independent, Independent, Weight Ratio 32.42 W/kg 33.89 W/kg
& Steering H – Frame Lower H – Frame Lower
Steering Type Rack & Pinion Rack & Pinion Comparison
Turning Radius 106.30” (2.7m) 94.49"(2.4 m)
Front Disc Brakes Disc Brakes
Braking
Rear Disc Brakes Disc Brakes
BAJA 2017 BAJA 2018
Power Train
Design
Design constraints|
constraints| Application
Application |Weight
|Weight |Manufacturability
|Manufacturability |Safety
|Safety |Aesthetics
|Aesthetics |Cost
|Cost
DESIGN PROCESS Vehicle Performance
Acceleration 5.37 m2/s
Literature study and Benchmarking
Grade-ability 64.9%
Deciding vehicle parameters
Top Speed 56 Kmph
CVT selection
Power to Weight 33.89 W/Kg
Calculation
Gearbox design
ENGINE
Validation
Max. Power 10 HP at 3600
Design Review
Max. Torque 19.66Nm at
2800rpm
• Flat assembly Transmission Type
• Use of DAQ system for tuning the CVT Constant Velocity CV-Tech CVT
• Use of fan based air cooling system Transmission (Gear ratio
• Improved gear ratio as compared to (CVT) 0.43:1 to
last year 3.0:1)
• Modified Half-shaft
• Neoprene cylindrical dampers Coupled with a Gear Ratio
• single gear 8.89:1
Custom gearbox reduction custom
• No differential used to overcome gearbox
shortcomings of open differential
You might also like
- JSA SplicingDocument3 pagesJSA Splicingluis100% (4)
- Case Memo InstructionsDocument4 pagesCase Memo InstructionsVish KamdarNo ratings yet
- CNC ReportDocument39 pagesCNC Reportrasaiya69% (13)
- FinalDocument10 pagesFinalSharan SaarsarNo ratings yet
- Iit JodhpurDocument13 pagesIit JodhpurSharan SaarsarNo ratings yet
- 2005 LEXUS RX Specifications: KnowledgeDocument4 pages2005 LEXUS RX Specifications: KnowledgeDani SoNo ratings yet
- All-New 2024 Ford Ranger Technical SpecificationsDocument4 pagesAll-New 2024 Ford Ranger Technical Specificationsluke.christianNo ratings yet
- 2015 Escape Specs PDFDocument2 pages2015 Escape Specs PDFNelson CalizNo ratings yet
- rtx450 Ride Utility Trencher Spec Sheet Updated 2023Document2 pagesrtx450 Ride Utility Trencher Spec Sheet Updated 2023RojasNo ratings yet
- Galion 150FDocument6 pagesGalion 150FLuis avitia ortegaNo ratings yet
- 2017 Kia Rio Especificaciones: LX EXDocument1 page2017 Kia Rio Especificaciones: LX EXerick muñico alejoNo ratings yet
- 2013 FORD C-MAX Technical SpecificationsDocument3 pages2013 FORD C-MAX Technical SpecificationsMaverick SergNo ratings yet
- Technical Specifications: Ford RangerDocument4 pagesTechnical Specifications: Ford RangerStefany AyalaNo ratings yet
- 1984 Chevrolet Corvette Specs and OptionsDocument8 pages1984 Chevrolet Corvette Specs and OptionsRomanvi1980No ratings yet
- 2018 BMW X5 M Specifications 06122017Document2 pages2018 BMW X5 M Specifications 06122017ahmed.mohamed021No ratings yet
- R7e 1 PDFDocument16 pagesR7e 1 PDFMichaelStoneNo ratings yet
- TR Ac TorDocument6 pagesTR Ac TorTomas MigilinskasNo ratings yet
- bc900xl Brush Chipper Spec Sheet Updated Sep 2021Document2 pagesbc900xl Brush Chipper Spec Sheet Updated Sep 2021SavindaNo ratings yet
- 1985 Chevrolet Corvette Specs and OptionsDocument8 pages1985 Chevrolet Corvette Specs and OptionsRomanvi1980No ratings yet
- 20 2 1 LX 570 PR Oduct Specifications: Exterior DimensionsDocument5 pages20 2 1 LX 570 PR Oduct Specifications: Exterior Dimensionsbestbest07No ratings yet
- SpecificationsDocument1 pageSpecificationsPabloNo ratings yet
- SpecificationsDocument1 pageSpecificationselchin mahmudovNo ratings yet
- 2015 Legacy SpecsDocument2 pages2015 Legacy Specstransman76No ratings yet
- Pettibone Cary Lift 204Document2 pagesPettibone Cary Lift 204JonathanDavidDeLosSantosAdornoNo ratings yet
- Sae Baja Hand BookDocument16 pagesSae Baja Hand Booksampath siddamNo ratings yet
- 1993 Chevrolet Corvette Specs and OptionsDocument10 pages1993 Chevrolet Corvette Specs and OptionsRomanvi1980No ratings yet
- 2015 Focus SpecsDocument3 pages2015 Focus SpecsDaniel RamirezNo ratings yet
- 2014 Cayman Technical SpecificationsDocument2 pages2014 Cayman Technical SpecificationsGheorghe Gabriel CerneanNo ratings yet
- 1988 Chevrolet Corvette Specs and OptionsDocument9 pages1988 Chevrolet Corvette Specs and OptionsRomanvi1980No ratings yet
- Orv Atv My23 Spec Can Am Out Max 450 570 en HRDocument1 pageOrv Atv My23 Spec Can Am Out Max 450 570 en HRJuan Pablo CastroNo ratings yet
- 4front™ FrontDocument2 pages4front™ FrontNontonFilemNo ratings yet
- Vermeer RT 100 Trencher SpecsDocument4 pagesVermeer RT 100 Trencher SpecsRicardo FronteiraNo ratings yet
- Carrera Coupe Specs 2006Document2 pagesCarrera Coupe Specs 2006JohnNo ratings yet
- Prado: Mechanical SpecificationsDocument3 pagesPrado: Mechanical SpecificationsMark MendozaNo ratings yet
- Baja SAE India Virtual PresentationDocument14 pagesBaja SAE India Virtual PresentationSwapnil FagareNo ratings yet
- Kitfox2 Owners ManualDocument19 pagesKitfox2 Owners ManualNofriagara Davit HarnawanNo ratings yet
- 2020TiguanTechSpecsFINALDocument2 pages2020TiguanTechSpecsFINALxgajaxNo ratings yet
- bc900xl Brush Chipper Spec Sheet UpdatedDocument2 pagesbc900xl Brush Chipper Spec Sheet UpdatedJulio Gonzalez SzNo ratings yet
- B000110 Attachment 2 535i Sedan Technical DataDocument2 pagesB000110 Attachment 2 535i Sedan Technical Datatho huynhtanNo ratings yet
- 2011 Models Specifications Cayenne Cayenne SDocument3 pages2011 Models Specifications Cayenne Cayenne Ssanja721No ratings yet
- 2010 GX 460 Product InfoDocument9 pages2010 GX 460 Product InfoTetsunari KodaNo ratings yet
- Prado: Mechanical SpecificationsDocument3 pagesPrado: Mechanical SpecificationsCarlo AmbrosiniNo ratings yet
- 2023 Sportage HEV SpecificationsDocument6 pages2023 Sportage HEV SpecificationsbitadminaccNo ratings yet
- 2023 klr650 Adventure en Us Spec SheetDocument1 page2023 klr650 Adventure en Us Spec SheetFernando GuimarãesNo ratings yet
- FUSO Canter LeafletDocument6 pagesFUSO Canter LeafletComercial AlfaOmega LimitadaNo ratings yet
- 600 CCDocument47 pages600 CCMochamad FebriNo ratings yet
- ORV-MY22-TechSpecs-Outlander XT 650 T-LR-ENDocument1 pageORV-MY22-TechSpecs-Outlander XT 650 T-LR-ENTC Türkoğlu İbrahim ZararsızNo ratings yet
- Design Presentation: Virtual Baja Saeindia 2015Document12 pagesDesign Presentation: Virtual Baja Saeindia 2015goldencomet100% (1)
- TB070Document2 pagesTB070Srdjan NikolicNo ratings yet
- Dieci Zeus Telehandler 3.3 - 4 T / 7 - 10.6 MDocument4 pagesDieci Zeus Telehandler 3.3 - 4 T / 7 - 10.6 MRoma RubanNo ratings yet
- Dieci Zeus 33.11 35.10 & 40.7 Spec SheetDocument4 pagesDieci Zeus 33.11 35.10 & 40.7 Spec SheetNash ServiceNo ratings yet
- 2022 klr650 Adventure en Us Spec SheetDocument1 page2022 klr650 Adventure en Us Spec SheetKevin BuiNo ratings yet
- Engine: Tce 155 Edc Engine 1.3 Tce 155Document5 pagesEngine: Tce 155 Edc Engine 1.3 Tce 155sopedalleyNo ratings yet
- MMMDocument6 pagesMMMAbdelkader DraïNo ratings yet
- Kobelco Hydraulic Crawler Crane Ck1600 II Spec BookDocument3 pagesKobelco Hydraulic Crawler Crane Ck1600 II Spec Bookmanuel100% (49)
- 856h Spec Sheet R1.5a0350c55ae44Document2 pages856h Spec Sheet R1.5a0350c55ae44Ko ZayNo ratings yet
- Horizontal Directional Drill: Durable Hydraulic Circuit. Stay Productive. Work in ComfortDocument2 pagesHorizontal Directional Drill: Durable Hydraulic Circuit. Stay Productive. Work in ComfortkennymontenegroNo ratings yet
- Ultra Bee - Surron CanadaDocument1 pageUltra Bee - Surron CanadaGanesh NAGARAJANNo ratings yet
- Ab14ej (Ab460ej) Ab16ej (Ab520ej)Document2 pagesAb14ej (Ab460ej) Ab16ej (Ab520ej)AnaMariaDavidNo ratings yet
- Prado: Mechanical Specifications GX GXL VX Kakadu EngineDocument2 pagesPrado: Mechanical Specifications GX GXL VX Kakadu EngineWilliam SelokaNo ratings yet
- Dayton Pallet Catalogo RodosDocument1 pageDayton Pallet Catalogo RodosLenin RodriguezNo ratings yet
- Volvo Articulated HaulerDocument6 pagesVolvo Articulated HaulerAndrea797No ratings yet
- Baja Individual Boxes DetailsDocument3 pagesBaja Individual Boxes DetailsSharan SaarsarNo ratings yet
- FinalDocument10 pagesFinalSharan SaarsarNo ratings yet
- Powertrain Design ReportDocument3 pagesPowertrain Design ReportSharan SaarsarNo ratings yet
- 06 Service Level & Fill RateDocument10 pages06 Service Level & Fill RateSharan SaarsarNo ratings yet
- Shreya Rathi Section HDocument3 pagesShreya Rathi Section HSharan SaarsarNo ratings yet
- Linking Operations With Finance CaseDocument2 pagesLinking Operations With Finance CaseSharan SaarsarNo ratings yet
- Corporate Comm AssignementDocument4 pagesCorporate Comm AssignementSharan SaarsarNo ratings yet
- Iit JodhpurDocument13 pagesIit JodhpurSharan SaarsarNo ratings yet
- Lessons Learnt RollDocument1 pageLessons Learnt RollSharan SaarsarNo ratings yet
- Powertrain (Drivetrain) : Previous Year's Design: New DesignDocument1 pagePowertrain (Drivetrain) : Previous Year's Design: New DesignSharan SaarsarNo ratings yet
- Operations Management Assignment Don't Bother Me I Can't CopeDocument3 pagesOperations Management Assignment Don't Bother Me I Can't CopeSharan SaarsarNo ratings yet
- Operations Good (Sharan) : I Need To Work On The Estimates For The Productivity and Idle TimeDocument1 pageOperations Good (Sharan) : I Need To Work On The Estimates For The Productivity and Idle TimeSharan SaarsarNo ratings yet
- Product Launch at VMPCDocument1 pageProduct Launch at VMPCSharan SaarsarNo ratings yet
- Dhaka Bank UncompleteDocument40 pagesDhaka Bank UncompleteAbir HasanNo ratings yet
- Partnerships: Formation, Operation, and Changes in MembershipDocument39 pagesPartnerships: Formation, Operation, and Changes in MembershipVino VillegasNo ratings yet
- Action Plan in Science Jaja VersionDocument4 pagesAction Plan in Science Jaja VersionJaja Carlina100% (1)
- Systems": General Ledger Systems ShouldDocument2 pagesSystems": General Ledger Systems ShouldKaren CaelNo ratings yet
- Stop Simping - Stop Simping - Phone Case TeePublic PDFDocument1 pageStop Simping - Stop Simping - Phone Case TeePublic PDFboss_amitNo ratings yet
- ATR Ata - 24 - Electrical - PowerDocument151 pagesATR Ata - 24 - Electrical - PowerJesús Montalvo Fernández100% (1)
- Healthmedicinet I 2017 2Document598 pagesHealthmedicinet I 2017 2tuni santeNo ratings yet
- AGW 615/3 Advanced Business Statistics: Statistical Analysis ReportDocument10 pagesAGW 615/3 Advanced Business Statistics: Statistical Analysis ReportNida AmriNo ratings yet
- Public Health ResearchDocument124 pagesPublic Health ResearchAsmitNo ratings yet
- Excavator O&KDocument8 pagesExcavator O&Keknasius iwan sugoro100% (2)
- Ipe1735v2 1610 1 0 d01Document6 pagesIpe1735v2 1610 1 0 d01li nuohaiNo ratings yet
- Faculty Mentor: Dr. PRABIR Jana Mr. Deepak Panghal Industry Mentor: Mr. UDAY N B (Sales & Technical Manager)Document2 pagesFaculty Mentor: Dr. PRABIR Jana Mr. Deepak Panghal Industry Mentor: Mr. UDAY N B (Sales & Technical Manager)Varun MehrotraNo ratings yet
- 3 Professional Practice of Civil Engineers (Revised Assignments 1)Document2 pages3 Professional Practice of Civil Engineers (Revised Assignments 1)Angelo John R. JavinezNo ratings yet
- Datasheet AEAT-6600Document11 pagesDatasheet AEAT-6600ArminNo ratings yet
- Physician-Induced Demand: EM Johnson, Massachusetts Institute of Technology, Cambridge, MA, USADocument6 pagesPhysician-Induced Demand: EM Johnson, Massachusetts Institute of Technology, Cambridge, MA, USAAnonymous mDkBoIyhjlNo ratings yet
- Gcse Pe Coursework 6 Week Training ProgrammeDocument7 pagesGcse Pe Coursework 6 Week Training Programmeirugqgajd100% (2)
- Shivam 5555@yahoo Dotco DotinDocument3 pagesShivam 5555@yahoo Dotco DotinsupriyaNo ratings yet
- Determine The Equivalent Spring Constant of SystemDocument8 pagesDetermine The Equivalent Spring Constant of SystemKornwipa MongkonkehaNo ratings yet
- The Essential Guide For EntrepreneursDocument77 pagesThe Essential Guide For Entrepreneurselom100% (1)
- CO KEU1 JPN Create Actual Assessment CycleDocument85 pagesCO KEU1 JPN Create Actual Assessment CyclenguyencaohuyNo ratings yet
- WarmAir Family BrochureDocument8 pagesWarmAir Family BrochureFiqran Septeo RozzyNo ratings yet
- Syllabus - Momentum Transfer Lec and LabDocument6 pagesSyllabus - Momentum Transfer Lec and LabKzenetteNo ratings yet
- Tensorflow InternalDocument17 pagesTensorflow InternalNJNo ratings yet
- Black BookDocument80 pagesBlack Book148 Kanchan SasaneNo ratings yet
- Call For Interest Establishing "Gomal University Distance Education Study Centers"Document22 pagesCall For Interest Establishing "Gomal University Distance Education Study Centers"hubdar aliNo ratings yet
- Kodak Bankruptcy AffidavitDocument96 pagesKodak Bankruptcy AffidavitrachbarnhartNo ratings yet
- 1306-E87T IOPU 140kW (PN1623 75th)Document2 pages1306-E87T IOPU 140kW (PN1623 75th)John GarnetNo ratings yet