Professional Documents
Culture Documents
AccHor 7e CH 23
AccHor 7e CH 23
Uploaded by
Muh Bilal0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
5 views24 pagesOriginal Title
PPT AccHor 7e ch 23
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
5 views24 pagesAccHor 7e CH 23
AccHor 7e CH 23
Uploaded by
Muh BilalCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 24
Flexible Budgets and Standard Costs
Chapter 23
Copyright © 2007 Prentice-Hall. All rights reserved
In a flexible budget, which parameter is varied?
1. Fixed cost
2. Sales volume
3. Unit variable cost
4. Unit revenue
Copyright © 2007 Prentice-Hall. All rights reserved
Answer: 2
Copyright © 2007 Prentice-Hall. All rights reserved
In a flexible budget, as sales volume increases
1. Total fixed costs rise
2. Total variable costs decrease
3. Operating income increases
4. Relevant range increases
Copyright © 2007 Prentice-Hall. All rights reserved
Answer: 3
Copyright © 2007 Prentice-Hall. All rights reserved
The flexible budget variance shows
1. Actual results for actual sales volume
2. Actual results for budgeted volume
3. Budgeted results for budgeted volume
4. Budgeted results for actual volume
Copyright © 2007 Prentice-Hall. All rights reserved
Answer: 4
Copyright © 2007 Prentice-Hall. All rights reserved
Standard costs are used to
1. Control expenditures for direct materials
2. Estimate labor rates
3. Allocate management overhead costs
4. All of the above
Copyright © 2007 Prentice-Hall. All rights reserved
Answer: 4
Copyright © 2007 Prentice-Hall. All rights reserved
5. A carefully predetermined cost that usually is
expressed on a per unit basis is called a(n):
1. applied cost
2. standard cost
3. flexible cost
4. fixed cost
Copyright © 2007 Prentice-Hall. All rights reserved
Answer: 2
Copyright © 2007 Prentice-Hall. All rights reserved
The cost incurred to have inventory shipping in
1. is included in the standard cost of direct
materials
2. is not included in the standard cost of direct
materials
3. is a selling expense
4. is ignored in a standard cost system
Copyright © 2007 Prentice-Hall. All rights reserved
Answer: 1
Copyright © 2007 Prentice-Hall. All rights reserved
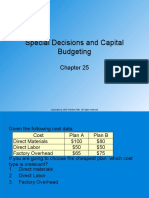
Given the following direct labor cost results:
Actual cost @ actual volume = $1,800
Standard cost @ actual volume = $1,300
Standard cost @ Standard volume = $1,100
Calculate the cost variance for direct labor
Copyright © 2007 Prentice-Hall. All rights reserved
Answer:
Cost variance = $1,800 - $1,300 = $500 (U)
Copyright © 2007 Prentice-Hall. All rights reserved
Given the following direct labor cost results:
Actual cost @ actual volume = $1,800
Standard cost @ actual volume = $1,300
Standard cost @ standard volume = $1,100
Calculate the efficiency variance for direct labor
Copyright © 2007 Prentice-Hall. All rights reserved
Answer:
Efficiency Variance = $1,300 - $1100 = $200 (U)
Copyright © 2007 Prentice-Hall. All rights reserved
Given:
Actual total overhead cost for actual volume = $22,000
Standard total overhead cost for actual volume = $20,000
Calculate total manufacturing overhead variance
Copyright © 2007 Prentice-Hall. All rights reserved
Answer:
Total manufacturing overhead variance =
$22,000 - $20,000 = $2,000 (U)
Copyright © 2007 Prentice-Hall. All rights reserved
An unfavorable materials quantity variance occurs when
1. actual amounts of materials used are greater than the
standard amounts allowed
2. actual amounts of materials used are less than the
standard amounts allowed
3. actual costs of materials used are greater than the
standard costs allowed
4. actual costs of materials used are less than the standard
costs allowed
Copyright © 2007 Prentice-Hall. All rights reserved
Answer: 1
Copyright © 2007 Prentice-Hall. All rights reserved
To record purchase of direct materials in a
standard cost system, debit direct material
inventory at:
1. Actual cost, actual quantity
2. Actual cost, standard quantity
3. Standard cost, actual quantity
4. Standard, standard quantity
Copyright © 2007 Prentice-Hall. All rights reserved
Answer: 3
Purchase of inventory is recorded at standard cost
for the actual quantity purchased.
Copyright © 2007 Prentice-Hall. All rights reserved
Copyright © 2007 Prentice-Hall. All rights reserved
You might also like
- Ch02 Harrison 8e GE SMDocument96 pagesCh02 Harrison 8e GE SMMuh BilalNo ratings yet
- Job Order Costing: Patrick Louie E. Reyes, CTT, Micb, Rca, CpaDocument45 pagesJob Order Costing: Patrick Louie E. Reyes, CTT, Micb, Rca, CpaClaudette Clemente100% (1)
- FRM Lecture2Document117 pagesFRM Lecture2Dang Thi Tam AnhNo ratings yet
- Quizz C3Document10 pagesQuizz C3Thanh NgânNo ratings yet
- CH 01Document4 pagesCH 01sompon12383% (6)
- Standard Costing and Variance AnalysisDocument13 pagesStandard Costing and Variance AnalysisSigei Leonard100% (1)
- KRI Library Proposal - IndiaDocument11 pagesKRI Library Proposal - IndiaRahul BhanNo ratings yet
- Management Accounting: Decision-Making by Numbers: Business Strategy & Competitive AdvantageFrom EverandManagement Accounting: Decision-Making by Numbers: Business Strategy & Competitive AdvantageRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- AccHor 7e CH 19Document28 pagesAccHor 7e CH 19Muh BilalNo ratings yet
- AccHor 7e CH 25Document24 pagesAccHor 7e CH 25Muh BilalNo ratings yet
- COMA - 04 Variaance PDFDocument49 pagesCOMA - 04 Variaance PDFAbhishekNo ratings yet
- 1314 IBMS-IBO-FIN Lecture Week 3Document27 pages1314 IBMS-IBO-FIN Lecture Week 3LucaBoselliNo ratings yet
- Input 5Document4 pagesInput 5Trizia Anne Dapon NeflasNo ratings yet
- Chapter Eleven: Standard Costs and Variance AnalysisDocument43 pagesChapter Eleven: Standard Costs and Variance AnalysisnnonscribdNo ratings yet
- An Introduction To Cost Terms and Purposes: © 2012 Pearson Prentice Hall. All Rights ReservedDocument30 pagesAn Introduction To Cost Terms and Purposes: © 2012 Pearson Prentice Hall. All Rights ReservedSubha ManNo ratings yet
- An Introduction To Cost Terms and PurposesDocument18 pagesAn Introduction To Cost Terms and PurposesAlina KhanNo ratings yet
- Inventory Costing and Capacity Analysis: © 2009 Pearson Prentice Hall. All Rights ReservedDocument22 pagesInventory Costing and Capacity Analysis: © 2009 Pearson Prentice Hall. All Rights ReservedUmar FarooqNo ratings yet
- AccHor 7e CH 17Document24 pagesAccHor 7e CH 17Muh BilalNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1. Introduction To Cost TermsDocument17 pagesChapter 1. Introduction To Cost TermsfekadeNo ratings yet
- STD CSTGDocument42 pagesSTD CSTGsanam20191No ratings yet
- CH 11Document48 pagesCH 11Amanda SaffouriNo ratings yet
- Group 3 - Job Order CostingDocument33 pagesGroup 3 - Job Order CostingJeonNo ratings yet
- Acca Ma1 CH 3.Document11 pagesAcca Ma1 CH 3.Muhammad Haris AbbasNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Solutions: Solutions To Questions For Review and DiscussionDocument31 pagesChapter 2 Solutions: Solutions To Questions For Review and DiscussionAlbert CruzNo ratings yet
- Cost ManagementDocument9 pagesCost ManagementVikkuNo ratings yet
- Chapter 03Document74 pagesChapter 03Kent Raysil PamaongNo ratings yet
- Standard Cost Variance AnalysisDocument48 pagesStandard Cost Variance AnalysisLight knightNo ratings yet
- MS Quiz-ReviewDocument12 pagesMS Quiz-ReviewJnen MayNo ratings yet
- CMA II - Chapter 3, Flexible Budgets & StandardsDocument77 pagesCMA II - Chapter 3, Flexible Budgets & StandardsLakachew Getasew0% (1)
- Accg200 L12Document11 pagesAccg200 L12Nikita Singh DhamiNo ratings yet
- An Introduction To Cost Terms and PurposesDocument22 pagesAn Introduction To Cost Terms and PurposesMegawati MediyaniNo ratings yet
- 09 Standard CostingDocument5 pages09 Standard CostingabcdefgNo ratings yet
- Flexible Budgets, Direct-Cost Variances, and Management ControlDocument21 pagesFlexible Budgets, Direct-Cost Variances, and Management ControlIrfanNo ratings yet
- Manajemen OperasionalDocument35 pagesManajemen Operasionalikarus halNo ratings yet
- Part 2 - StudentsDocument77 pagesPart 2 - StudentsĐỉnh Kout NamNo ratings yet
- Solution Manual For Microeconomics Principles Applications and Tools 10th Edition Arthur Osullivan Steven Sheffrin Stephen Perez 10 013Document12 pagesSolution Manual For Microeconomics Principles Applications and Tools 10th Edition Arthur Osullivan Steven Sheffrin Stephen Perez 10 013louisdienek3100% (21)
- Midterm ExaminationDocument20 pagesMidterm ExaminationEmmanuel VillafuerteNo ratings yet
- Full Costing Book - CA Sanjeev MittalDocument206 pagesFull Costing Book - CA Sanjeev Mittalsubroshakar gamer100% (1)
- Standard Costing and Variance AnalysisDocument26 pagesStandard Costing and Variance AnalysisFidelina CastroNo ratings yet
- Costs Terms, Concepts and ClassificationsDocument32 pagesCosts Terms, Concepts and Classificationsjeela1No ratings yet
- Afm102 Exam Aid FinalDocument128 pagesAfm102 Exam Aid FinalVanessa LawsonNo ratings yet
- STANDARD COSTING and Variance AnalysisDocument28 pagesSTANDARD COSTING and Variance AnalysisDanica VillaganteNo ratings yet
- Job Order, Operation and Life Cycle Costing Job Order CostingDocument19 pagesJob Order, Operation and Life Cycle Costing Job Order Costingjessa mae zerdaNo ratings yet
- Local Media5868281332441447836Document3 pagesLocal Media5868281332441447836RolandNo ratings yet
- An Introduction To Cost Terms and Purposes: © 2012 Pearson Education. All Rights ReservedDocument30 pagesAn Introduction To Cost Terms and Purposes: © 2012 Pearson Education. All Rights ReservedAmaliaAmelNo ratings yet
- Colegio de San Gabriel Arcangel: Learning Module in Strategic Cost Management Unit TitleDocument8 pagesColegio de San Gabriel Arcangel: Learning Module in Strategic Cost Management Unit TitleC XNo ratings yet
- Absorption Costing - OverviewDocument24 pagesAbsorption Costing - OverviewEdwin LawNo ratings yet
- RWD 03 Standard CostingDocument52 pagesRWD 03 Standard Costinghamba allahNo ratings yet
- Cost Concepts and Behaviors-EEP-lec5Document25 pagesCost Concepts and Behaviors-EEP-lec5Ramendra KumarNo ratings yet
- Sva - Student Copy P1Document101 pagesSva - Student Copy P1Joyce MamokoNo ratings yet
- Standard Cost SystemDocument39 pagesStandard Cost SystemTricia Marie TumandaNo ratings yet
- Microeconomics Principles Applications and Tools 9th Edition Osullivan Solutions ManualDocument11 pagesMicroeconomics Principles Applications and Tools 9th Edition Osullivan Solutions Manualanagogegirdler.kycgr100% (26)
- An Introduction To Cost Terms and Purposes: © 2009 Pearson Prentice Hall. All Rights ReservedDocument30 pagesAn Introduction To Cost Terms and Purposes: © 2009 Pearson Prentice Hall. All Rights ReservednishulalwaniNo ratings yet
- Variance Analysis - Patubo, Ma. Angelli M.Document21 pagesVariance Analysis - Patubo, Ma. Angelli M.Ma Angelli PatuboNo ratings yet
- Cost Sheet 2Document13 pagesCost Sheet 2Nandan Kumar JenaNo ratings yet
- Cost ConceptsDocument35 pagesCost ConceptsAngela Miles DizonNo ratings yet
- SummaryDocument8 pagesSummarySittiehaina GalmanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 9 - Inventory Costing and Capacity AnalysisDocument40 pagesChapter 9 - Inventory Costing and Capacity AnalysisBrian SantsNo ratings yet
- CH 10Document15 pagesCH 10JesseEwingNo ratings yet
- (Mas) 04 - Standard Costing and Variance AnalysisDocument7 pages(Mas) 04 - Standard Costing and Variance AnalysisCykee Hanna Quizo Lumongsod0% (1)
- AnswerDocument31 pagesAnswerJabeth IbarraNo ratings yet
- Hhofma3ech23inst 140930122004 Phpapp02Document56 pagesHhofma3ech23inst 140930122004 Phpapp02RaoNo ratings yet
- AccHor 7e CH 21Document25 pagesAccHor 7e CH 21Muh BilalNo ratings yet
- AccHor 7e CH 22Document28 pagesAccHor 7e CH 22Muh BilalNo ratings yet
- AccHor 7e CH 01Document32 pagesAccHor 7e CH 01Muh BilalNo ratings yet
- AccHor 7e CH 02Document28 pagesAccHor 7e CH 02Muh BilalNo ratings yet
- Ch12 Harrison 8e GE SMDocument87 pagesCh12 Harrison 8e GE SMMuh BilalNo ratings yet
- Ch08 Harrison 8e GE SM (Revised)Document102 pagesCh08 Harrison 8e GE SM (Revised)Muh BilalNo ratings yet
- AccHor 7e CH 18Document22 pagesAccHor 7e CH 18Muh BilalNo ratings yet
- AccHor 7e CH 14Document22 pagesAccHor 7e CH 14Muh BilalNo ratings yet
- Ch07 Harrison 8e GE SMDocument87 pagesCh07 Harrison 8e GE SMMuh BilalNo ratings yet
- AccHor 7e CH 17Document24 pagesAccHor 7e CH 17Muh BilalNo ratings yet
- Chap 023Document19 pagesChap 023Muh BilalNo ratings yet
- Ch06 Harrison 8e GE SMDocument87 pagesCh06 Harrison 8e GE SMMuh BilalNo ratings yet
- Ch03 Harrison 8e GE SMDocument113 pagesCh03 Harrison 8e GE SMMuh BilalNo ratings yet
- Risk Management: Fundamentals of Corporate FinanceDocument24 pagesRisk Management: Fundamentals of Corporate FinanceMuh BilalNo ratings yet
- Ch04 Harrison 8e GE SMDocument73 pagesCh04 Harrison 8e GE SMMuh BilalNo ratings yet
- Ch01 Harrison 8e GE SMDocument63 pagesCh01 Harrison 8e GE SMMuh BilalNo ratings yet
- Ch05 Harrison 8e GE SMDocument73 pagesCh05 Harrison 8e GE SMMuh BilalNo ratings yet
- Financial Statement Analysis: Fundamentals of Corporate FinanceDocument23 pagesFinancial Statement Analysis: Fundamentals of Corporate FinanceMuh BilalNo ratings yet
- Chap 022Document23 pagesChap 022Muh BilalNo ratings yet
- Long-Term Financial Planning: Fundamentals of Corporate FinanceDocument17 pagesLong-Term Financial Planning: Fundamentals of Corporate FinanceMuh BilalNo ratings yet
- Short-Term Financial Planning: Fundamentals of Corporate FinanceDocument26 pagesShort-Term Financial Planning: Fundamentals of Corporate FinanceMuh BilalNo ratings yet
- Municipal Account ManualDocument164 pagesMunicipal Account ManualShyam SNo ratings yet
- Option GreeksDocument7 pagesOption GreeksNIDHI ANN FRANCIS 20121024No ratings yet
- Gov Acc Chapter 2Document7 pagesGov Acc Chapter 2imsana minatozakiNo ratings yet
- Public Notice 20 of 2021 First Quarter Provisional Income TaxDocument3 pagesPublic Notice 20 of 2021 First Quarter Provisional Income TaxTim StockwellNo ratings yet
- Syllabus-Prba154 CREDIT AND COLLECTIONDocument7 pagesSyllabus-Prba154 CREDIT AND COLLECTIONKass Kaye HR100% (1)
- Payment Receipt PDFDocument1 pagePayment Receipt PDFJay YadavNo ratings yet
- Debt Settlement AgreementDocument19 pagesDebt Settlement AgreementMuhammad DafisNo ratings yet
- Commission On Audit: Cfficular No DateDocument18 pagesCommission On Audit: Cfficular No DateMaria Teresa TampisNo ratings yet
- FX Trading: Key Benefits For Spot TradersDocument2 pagesFX Trading: Key Benefits For Spot Tradersarif tantoNo ratings yet
- Buying Winners and Selling LosersDocument3 pagesBuying Winners and Selling LosersLeynard ColladoNo ratings yet
- Amcon Act 2010Document35 pagesAmcon Act 2010Idemudia Bright AigbeNo ratings yet
- Unaudited 3m Condensed Combined Financial StatementsDocument40 pagesUnaudited 3m Condensed Combined Financial StatementsValtteri ItärantaNo ratings yet
- Master in Trading BrochureDocument17 pagesMaster in Trading Brochureace187No ratings yet
- Solution Ch16Document5 pagesSolution Ch16Amanda AyarinovaNo ratings yet
- Brand ValuationDocument11 pagesBrand ValuationDivya Divzz RanaNo ratings yet
- Anna University Tiruchirappalli Tiruchirappalli - 620 024Document64 pagesAnna University Tiruchirappalli Tiruchirappalli - 620 024haiitskarthickNo ratings yet
- r6 15 Mca Accounting and Financial Management Set1Document2 pagesr6 15 Mca Accounting and Financial Management Set1SRINIVASA RAO GANTANo ratings yet
- Nyse Kim 2018Document138 pagesNyse Kim 2018Swapna Wedding Castle EramaloorNo ratings yet
- Atal Pension Yojana (Apy) - Subscriber Registration FormDocument1 pageAtal Pension Yojana (Apy) - Subscriber Registration FormpraveenaNo ratings yet
- Chapter - 7 Assets and Liabilities ManagementDocument10 pagesChapter - 7 Assets and Liabilities Managementsahil ShresthaNo ratings yet
- Aggregate Demand and Supply Plotted Against InflationDocument13 pagesAggregate Demand and Supply Plotted Against Inflationapi-3825580No ratings yet
- Module 2A - Presentation of Financial StatementsDocument6 pagesModule 2A - Presentation of Financial StatementsJaquelyn ClataNo ratings yet
- Banking Sector ReformsDocument16 pagesBanking Sector ReformsDivya JainNo ratings yet
- Customer StatementDocument13 pagesCustomer StatementSophia GraysonNo ratings yet
- Danashmand Quotn. 16-17-MAP-PL-130117ADocument1 pageDanashmand Quotn. 16-17-MAP-PL-130117ASandip ChaudhariNo ratings yet
- ICO Platform Investment MemoDocument5 pagesICO Platform Investment MemosvictorNo ratings yet
- Commodity Daily Briefing 102634710Document9 pagesCommodity Daily Briefing 102634710jasonkstearnsNo ratings yet