Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Z00820040220174212Z00820010220154080COMP6048Pert12 - Introduction To Binary Search Tree and Threaded Binary Tree Rev
Uploaded by
riyan0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2 views30 pagesThis document discusses binary search trees and threaded binary trees. It defines a binary search tree as a binary tree where every node contains a unique key and the left subtree of a node contains keys smaller than the node's key and the right subtree contains larger keys. It also describes the basic operations of search, insertion, and deletion in a binary search tree. A threaded binary tree is similar to a binary tree but stores pointers to predecessors and successors instead of null pointers to allow linear traversal.
Original Description:
Original Title
Z00820040220174212Z00820010220154080COMP6048Pert12 - Introduction to Binary Search Tree and Threaded Binary Tree Rev
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document discusses binary search trees and threaded binary trees. It defines a binary search tree as a binary tree where every node contains a unique key and the left subtree of a node contains keys smaller than the node's key and the right subtree contains larger keys. It also describes the basic operations of search, insertion, and deletion in a binary search tree. A threaded binary tree is similar to a binary tree but stores pointers to predecessors and successors instead of null pointers to allow linear traversal.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2 views30 pagesZ00820040220174212Z00820010220154080COMP6048Pert12 - Introduction To Binary Search Tree and Threaded Binary Tree Rev
Uploaded by
riyanThis document discusses binary search trees and threaded binary trees. It defines a binary search tree as a binary tree where every node contains a unique key and the left subtree of a node contains keys smaller than the node's key and the right subtree contains larger keys. It also describes the basic operations of search, insertion, and deletion in a binary search tree. A threaded binary tree is similar to a binary tree but stores pointers to predecessors and successors instead of null pointers to allow linear traversal.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 30
Course : COMP6048 – DATA STRUCTURE
Year : 2017
Introduction to Binary Search
Tree and Threaded Binary Tree
Learning Outcomes
At the end of this session, student will be able to:
• Demonstrate construction process of binary search tree (LO1 &
LO3)
COMP6048 - Data Structure 2
Sub Topics
Binary Search Tree:
- Binary Search Tree Concept
- Operations: Search, Insertion, Deletion
- Threaded Binary Tree Concept
- Advantages
COMP6048 - Data Structure 3
Binary Search Tree Concept
Binary Search Tree (BST) is a binary tree with the following
properties:
– Every node has a key and no two nodes have the
same key (keys are unique).
– The keys in left sub tree are smaller than the key in
the root of the sub tree.
– The keys in right sub tree are larger than the key in
the root of the sub tree.
– The left and right sub trees are also binary search
tree (recursively).
COMP6048 - Data Structure 4
Binary Search Tree Concept
Pay attention to the keys stored in each node
COMP6048 - Data Structure 5
Binary Search Tree Operations
Binary Search Tree has the following basic operations:
– find(x) : find key x in the BST
– insert(x) : insert new key x into BST
– remove(x) : remove key x from BST
COMP6048 - Data Structure 6
Operations: Search
• Because of the property of BST, finding/searching in BST is
easy.
• Let the key that we want to search is X.
– We begin at root
– If the root contains X then search terminates
successfully.
– If X is less than root’s key then search recursively on left
sub tree, otherwise search recursively on right sub tree.
COMP6048 - Data Structure 7
Operations: Insertion
• Inserting into BST is done recursively.
• Let the new node’s key be X,
– Begin at root
– If X is less than node’s key then insert X into left
sub tree, otherwise insert X into right sub tree
– Repeat until we found an empty node to put X (X
will always be a new leaf)
COMP6048 - Data Structure 8
Operations: Insertion – Example
Inserting new
key (35)
COMP6048 - Data Structure 9
Operations: Insertion – Example
COMP6048 - Data Structure 10
Operations: Insertion – Example
COMP6048 - Data Structure 11
Operations: Insertion – Example
COMP6048 - Data Structure 12
Operations: Deletion
• There are 3 cases which should be considered:
– If the key is in a leaf, just delete that node
– If the key is in a node which has one child, delete
that node and connect its child to its parent
– If the key is in a node which has two children,
find the right most child of its left sub tree (node
P), replace its key with P’s key and remove P
recursively. (or alternately you can choose the left
most child of its right sub tree)
COMP6048 - Data Structure 13
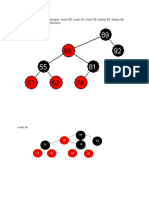
Operations: Deletion – Example
Deleting key (21)
COMP6048 - Data Structure 14
Operations: Deletion – Example
Deleting key (21),
(continue)
COMP6048 - Data Structure 15
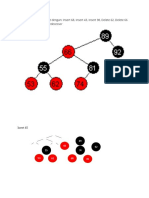
Operations: Deletion – Example
Deleting key (37)
COMP6048 - Data Structure 16
Operations: Deletion – Example
Deleting key (37),
(continue)
COMP6048 - Data Structure 17
Operations: Deletion – Example
Deleting key (30)
COMP6048 - Data Structure 18
Operations: Deletion – Example
Deleting key (30),
(continue)
COMP6048 - Data Structure 19
Threaded Binary Tree Concept
• A threaded binary tree is same as that of a binary tree but
with a difference in storing NULL pointers.
• Binary Tree:
COMP6048 - Data Structure 20
Threaded Binary Tree Concept
In the linked representation, a number of nodes contain a
NULL pointer either in their left or right fields or in both.
This space that is wasted in storing a NULL pointer can be
efficiently used to store some other useful peace of
information.
COMP6048- Data Structure 21
Threaded Binary Tree Concept
For example, the NULL entries can be replaced to store a
pointer to the in-order predecessor, or the in-order successor
of the node. These special pointers are called thread and
binary trees containing thread are called threaded trees.
In the linked representation of a threaded binary tree,
threads will be denoted using dotted lines
COMP6048 - Data Structure 22
Threaded Binary Tree Concept
• Binary Tree without threading
• Linked
• representation of
• the binary tree
COMP6048 - Data Structure 23
Threaded Binary Tree Concept
• In one way threading, a thread will appear either in the right field
or the left field of the node.
• A one way threaded tree is also called a single threaded tree.
• If the thread appears in the left field, then the left field will be
made to point to the in-order predecessor of the node.
• Such a one way threaded tree is called a left threaded binary tree.
• On the contrary, if the thread appears in the right field, then it will
point to the in-order successor of the node. Such a one way
threaded tree is called a right threaded binary tree.
COMP6048 - Data Structure 24
Threaded Binary Tree Example
Binary tree with
one-way
threading
COMP6048 - Data Structure 25
Threaded Binary Tree Example
Binary tree with
two-way
threading
COMP6048 - Data Structure 26
Advantages
• It enables linear traversal of elements in the tree
• Linear traversal eliminates the use of stacks which in turn
consume a lot of memory space and computer time
• It enables to find the parent of a given element without
explicit use of parent pointers
• Since nodes contain pointers to in-order predecessor and
successor, the threaded tree enables forward and backward
traversal of the nodes as given by in-order fashion
COMP6048 - Data Structure 27
Summary
• Binary Search Tree (BST) is a binary tree with properties:
– Every node has a key and no two nodes have the
same key (keys are unique).
– Left sub tree’s keys are smaller than root’s key.
– Right sub tree’s keys are larger than root’s key.
– The left and right sub trees are also binary search tree
(recursively).
• A threaded binary tree is same as that of a binary tree but
with a difference in storing NULL pointers
COMP6048 - Data Structure 28
References
• Reema Thareja,. 2014. Data structures using C. OXFOR. New
Delhi. ISBN:978-0-19-809930-7 Chapter 10
• Threaded Binary Tree
http://quiz.geeksforgeeks.org/threaded-binary-tree/
COMP6048 - Data Structure 29
END
Introduction to Binary Search Tree
and Threaded Binary Tree
COMP6048 - Data Structure 30
You might also like
- DS Unit 2Document32 pagesDS Unit 2Subathra Devi MourouganeNo ratings yet
- Final Exam SheetDocument2 pagesFinal Exam Sheetbobtheblob94No ratings yet
- COMP6048 - Balanced BST InsertionDocument52 pagesCOMP6048 - Balanced BST InsertionCanon RockNo ratings yet
- PPT6 - Binary Search TreeDocument33 pagesPPT6 - Binary Search TreeRapik HardiantoNo ratings yet
- Z00820040220174212Z00820010220154080COMP6048Pert14 - Binary Search TreeDocument26 pagesZ00820040220174212Z00820010220154080COMP6048Pert14 - Binary Search TreeriyanNo ratings yet
- Binary Search TreeDocument36 pagesBinary Search Treeapi-237335979No ratings yet
- BST Operations and TraversalsDocument36 pagesBST Operations and TraversalsarulrajmeNo ratings yet
- DS - Binary Tree - 214044Document10 pagesDS - Binary Tree - 214044Sarthak LonkarNo ratings yet
- Bachelor of Engineering Subject Code: 3130702 Semester - III Subject Name: Data StructuresDocument70 pagesBachelor of Engineering Subject Code: 3130702 Semester - III Subject Name: Data StructuresRutvik SakhavalaNo ratings yet
- Search Trees: Binary and AVL StructuresDocument42 pagesSearch Trees: Binary and AVL StructuresMotseilekgoaNo ratings yet
- DSP PR 20Document12 pagesDSP PR 20Dhvanil TantiNo ratings yet
- DS Trees Short NotesDocument12 pagesDS Trees Short Notessathvikag001No ratings yet
- Advanced Data Structures: Binary Search TreeDocument14 pagesAdvanced Data Structures: Binary Search TreePushpa Latha MNo ratings yet
- DSA Interview QuestionsDocument8 pagesDSA Interview QuestionsAshutosh Kumar ShahiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 19 - Binary TreesDocument39 pagesChapter 19 - Binary TreesMuhammad Farooq Azam KhanNo ratings yet
- Binary Search Trees GuideDocument47 pagesBinary Search Trees Guidemilestone inventionsNo ratings yet
- 2 - 4 Expression Trees and BSTDocument6 pages2 - 4 Expression Trees and BSTbhavya mittalNo ratings yet
- CS301FinaltermMCQsbyDr TariqHanifDocument15 pagesCS301FinaltermMCQsbyDr TariqHanifRizwanIlyasNo ratings yet
- Data StructuresDocument17 pagesData Structuresnaveen rajNo ratings yet
- Dsa Viva Questions - Coders LodgeDocument12 pagesDsa Viva Questions - Coders LodgeGulchetan SinghNo ratings yet
- Data Structures: 10 Lecture - Binary Search TreeDocument22 pagesData Structures: 10 Lecture - Binary Search TreeHard FuckerNo ratings yet
- Module 2 - Binary Tree - Binary Search TreeDocument39 pagesModule 2 - Binary Tree - Binary Search TreelejmcguzansveuykbuNo ratings yet
- BSTDocument20 pagesBSTPulkit AggarwalNo ratings yet
- Binary Search TreeDocument35 pagesBinary Search TreeMax WongNo ratings yet
- Python Advanced Data StructureDocument61 pagesPython Advanced Data StructureTse ChrisNo ratings yet
- Binary Tree TahsinDocument14 pagesBinary Tree TahsinRojot SahaNo ratings yet
- DS and Algorithm Session 14Document107 pagesDS and Algorithm Session 14Soumya RanjanNo ratings yet
- Find Smallest, Largest Nodes in BSTsDocument22 pagesFind Smallest, Largest Nodes in BSTsAruna RajNo ratings yet
- CS301 Today PaperDocument9 pagesCS301 Today PaperJibran HayatNo ratings yet
- Binary Search TreesDocument39 pagesBinary Search Treesআরব বেদুঈনNo ratings yet
- DSA Lab Report 11 Anas ZohrabDocument9 pagesDSA Lab Report 11 Anas ZohrabAnasAbbasiNo ratings yet
- Top 50 Data Structures Interview Questions & Answers: 1) What Is Data Structure?Document8 pagesTop 50 Data Structures Interview Questions & Answers: 1) What Is Data Structure?Sudhanshu RanjanNo ratings yet
- JEDI Slides-DataSt-Chapter04-Binary Trees - SxiDocument36 pagesJEDI Slides-DataSt-Chapter04-Binary Trees - SxiAbdreyll GerardNo ratings yet
- Define data structure 2023 question paper with solutionDocument35 pagesDefine data structure 2023 question paper with solutionBrijesh C.GNo ratings yet
- Data StructuresDocument8 pagesData StructuresJordi WestNo ratings yet
- C++: Basics and BeyondDocument11 pagesC++: Basics and Beyondujjwal jhaNo ratings yet
- Hashing Refers To The Process of Generating A Fixed-Size Output From An Input of Variable SizeDocument10 pagesHashing Refers To The Process of Generating A Fixed-Size Output From An Input of Variable SizeManthena Narasimha RajuNo ratings yet
- DSA Short NotesDocument4 pagesDSA Short NotesJitendra ChoudharyNo ratings yet
- BCS304-DSA Notes M-4Document25 pagesBCS304-DSA Notes M-4sagar2024kNo ratings yet
- CSCE 3110 Data Structures & Algorithm Analysis: Binary Search Trees Reading: Chap. 4 (4.3) WeissDocument29 pagesCSCE 3110 Data Structures & Algorithm Analysis: Binary Search Trees Reading: Chap. 4 (4.3) WeissPradeep Kumar Reddy ReddyNo ratings yet
- 01 Intro To Course DSADocument35 pages01 Intro To Course DSAHaseeb MuhammadNo ratings yet
- EE2204 DSA 100 2marksDocument18 pagesEE2204 DSA 100 2marksVinod DeenathayalanNo ratings yet
- Codebix: Live Class SyllabusDocument21 pagesCodebix: Live Class SyllabusmacrithvikyadavNo ratings yet
- ProjectdocDocument12 pagesProjectdocMohammad QassasNo ratings yet
- Cache Memory: CS 322M Digital Logic & Computer ArchitectureDocument16 pagesCache Memory: CS 322M Digital Logic & Computer ArchitectureUjjawalRanjanNo ratings yet
- 4 - Binary TreesDocument39 pages4 - Binary TreesAnonymous zK1oHu0zNo ratings yet
- Binary Search TreesDocument28 pagesBinary Search TreesPriya SharmaNo ratings yet
- cs2110 15 TreesDocument42 pagescs2110 15 TreesSteve McCnamyNo ratings yet
- Practice Problems AnsDocument16 pagesPractice Problems AnsSanskar SinghalNo ratings yet
- Indexing in Main Memory: T-Trees, CSS-Trees and CSB+-TreesDocument6 pagesIndexing in Main Memory: T-Trees, CSS-Trees and CSB+-TreesGeorge SemionoNo ratings yet
- Data Structure Lecture 7 TreeDocument49 pagesData Structure Lecture 7 TreeSweetMainaNo ratings yet
- Binary Search TreesDocument49 pagesBinary Search TreesAbdurezak ShifaNo ratings yet
- 10 - DS and Algorithm - Session - 14.ppsDocument107 pages10 - DS and Algorithm - Session - 14.ppsAjai KumarNo ratings yet
- Binary Search TreeDocument3 pagesBinary Search TreeRavi KumarNo ratings yet
- Lab 11: Implementation of The BINARY SEARCH TREE Data Structure With The Help of AlgorithmsDocument4 pagesLab 11: Implementation of The BINARY SEARCH TREE Data Structure With The Help of Algorithmshashir mahboobNo ratings yet
- Imp - Data-Structures QuestionsDocument16 pagesImp - Data-Structures QuestionsBLACK xDEMONNo ratings yet
- Multilevel Indexing and B+ TreesDocument33 pagesMultilevel Indexing and B+ TreesRussel PonferradaNo ratings yet
- Data StructuresDocument6 pagesData StructuresArkadeep RoyNo ratings yet
- Lecture 9 Binary Search TreesDocument28 pagesLecture 9 Binary Search TreesMuhammad Owais khanNo ratings yet
- Ds With Python Week11-1Document11 pagesDs With Python Week11-1tanushaNo ratings yet
- Exercise 4: Consider The Following Stack With Top 4Document20 pagesExercise 4: Consider The Following Stack With Top 4hamA lolNo ratings yet
- RBT SimulationDocument2 pagesRBT SimulationriyanNo ratings yet
- Simulasikan Tree Tersebut Dengan: Insert 68, Insert 43, Insert 98, Delete 62, Delete 66 Gunakan Pendekatan PredecessorDocument2 pagesSimulasikan Tree Tersebut Dengan: Insert 68, Insert 43, Insert 98, Delete 62, Delete 66 Gunakan Pendekatan PredecessorriyanNo ratings yet
- Z00820040220174212Z00820010220154080COMP6048Pert15-16 - Material Review I (T)Document3 pagesZ00820040220174212Z00820010220154080COMP6048Pert15-16 - Material Review I (T)riyanNo ratings yet
- RBT SimulationDocument2 pagesRBT SimulationriyanNo ratings yet
- Z00820040220174212Z00820010220154080COMP6048Pert15-16 - Material Review I (T)Document3 pagesZ00820040220174212Z00820010220154080COMP6048Pert15-16 - Material Review I (T)riyanNo ratings yet
- Z00820040220174212Z00820010220154080COMP6048Pert12 - Introduction To Binary Search Tree and Threaded Binary Tree RevDocument30 pagesZ00820040220174212Z00820010220154080COMP6048Pert12 - Introduction To Binary Search Tree and Threaded Binary Tree RevriyanNo ratings yet
- Z00820040220174212Z00820010220154080COMP6048Pert15-16 - Material Review I (T)Document3 pagesZ00820040220174212Z00820010220154080COMP6048Pert15-16 - Material Review I (T)riyanNo ratings yet
- GATE CS Topic Wise Preparation Notes - GeeksforGeeksDocument21 pagesGATE CS Topic Wise Preparation Notes - GeeksforGeeksRanu RawatNo ratings yet
- CZ4032 Data Analytics & Mining NotesDocument16 pagesCZ4032 Data Analytics & Mining NotesFeng ChengxuanNo ratings yet
- Chapter-4 AP - FormattedDocument25 pagesChapter-4 AP - FormattedMaxy GiuliNo ratings yet
- A357460420 - 22393 - 2 - 2018 - String MatchingDocument27 pagesA357460420 - 22393 - 2 - 2018 - String MatchingkalpeshNo ratings yet
- Multi Level CPU SchedulingDocument5 pagesMulti Level CPU SchedulingPawanPaagalNo ratings yet
- Artificial Intelligence and Machine LearningDocument11 pagesArtificial Intelligence and Machine LearningPa Krishna Sankar100% (1)
- DAA Module 3 Power Point-S.MercyDocument56 pagesDAA Module 3 Power Point-S.MercyIshita SinghalNo ratings yet
- Assignment MLDocument3 pagesAssignment MLRamaadyuti BattabyalNo ratings yet
- DSC Programs 2015Document37 pagesDSC Programs 2015Arpit KumarNo ratings yet
- 2 Uninformed SearchDocument41 pages2 Uninformed SearchPratyushNo ratings yet
- Data Structures Question BankDocument32 pagesData Structures Question BankMuhammad Anas RashidNo ratings yet
- Prime Algorithms ComparisonDocument15 pagesPrime Algorithms ComparisonVignesh DevamullaNo ratings yet
- LECTURE B 1 FSM Minimization IntroDocument18 pagesLECTURE B 1 FSM Minimization IntroBharadwaja PisupatiNo ratings yet
- 4 Big M Method Min N Max Up Cross 2023Document28 pages4 Big M Method Min N Max Up Cross 2023Mohammad Ishraq HossainNo ratings yet
- MCA-4sem Microprocessor and Systems SoftwareDocument34 pagesMCA-4sem Microprocessor and Systems Softwareatul211988No ratings yet
- Dsu SolutionDocument30 pagesDsu Solutionvaishali raneNo ratings yet
- Analysis of Algorithms - Set 1 (Asymptotic Analysis)Document2 pagesAnalysis of Algorithms - Set 1 (Asymptotic Analysis)Mir ArifaNo ratings yet
- hw2 SoluDocument9 pageshw2 SoluRegner Muñoz SantillanNo ratings yet
- 4x4 - Useful Last 2 Edge AlgorithmsDocument1 page4x4 - Useful Last 2 Edge AlgorithmsKattya Enciso QuispeNo ratings yet
- Understanding Probability 3rd Edition. Henk Tijms. Cambridge University Press 2012.Document6 pagesUnderstanding Probability 3rd Edition. Henk Tijms. Cambridge University Press 2012.Chavobar0% (2)
- CS 3870: Exercise Solutions: Week 1, Part 2Document5 pagesCS 3870: Exercise Solutions: Week 1, Part 2Asadullah Tariq TariqNo ratings yet
- Presentacion Capitulo 8 (Abstraciones de Datos)Document25 pagesPresentacion Capitulo 8 (Abstraciones de Datos)chapuzas22No ratings yet
- 1 Shortest Paths (Continued) : 1.1 Dijkstra's Algorithm (Continued)Document2 pages1 Shortest Paths (Continued) : 1.1 Dijkstra's Algorithm (Continued)Duaa Al-HasanNo ratings yet
- DS Lab Record PDFDocument146 pagesDS Lab Record PDFJishnuNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5: Unfolding: Keshab K. ParhiDocument13 pagesChapter 5: Unfolding: Keshab K. Parhisushant sahooNo ratings yet
- Jacobi MethodDocument2 pagesJacobi Methodapi-3839714100% (1)
- Nelder Mead ProofDocument8 pagesNelder Mead ProofSuresh KumarNo ratings yet
- CSE 2201 Algorthm Analysis & Design: Solving RecurrenceDocument22 pagesCSE 2201 Algorthm Analysis & Design: Solving RecurrenceRomNo ratings yet