Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Case Study: Plastic Bottles: References
Case Study: Plastic Bottles: References
Uploaded by
E0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
12 views1 pagePlastic bottles were first mass produced in 1947 but became popular in the 1960s with the introduction of high-density polyethylene. Plastic bottles are commonly used to store liquids like water, soft drinks, oils, and cleaners. The main types of plastic used for bottles are polyethylene terephthalate (PET), high-density polyethylene (HDPE), and polyvinyl chloride (PVC). Each has advantages like being lightweight, low-cost, and resistant to breakage but also disadvantages like toxicity if made from certain materials and pollution if not recycled properly.
Original Description:
comparison of all plastic qualities
Original Title
Plastic Bottles
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentPlastic bottles were first mass produced in 1947 but became popular in the 1960s with the introduction of high-density polyethylene. Plastic bottles are commonly used to store liquids like water, soft drinks, oils, and cleaners. The main types of plastic used for bottles are polyethylene terephthalate (PET), high-density polyethylene (HDPE), and polyvinyl chloride (PVC). Each has advantages like being lightweight, low-cost, and resistant to breakage but also disadvantages like toxicity if made from certain materials and pollution if not recycled properly.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
12 views1 pageCase Study: Plastic Bottles: References
Case Study: Plastic Bottles: References
Uploaded by
EPlastic bottles were first mass produced in 1947 but became popular in the 1960s with the introduction of high-density polyethylene. Plastic bottles are commonly used to store liquids like water, soft drinks, oils, and cleaners. The main types of plastic used for bottles are polyethylene terephthalate (PET), high-density polyethylene (HDPE), and polyvinyl chloride (PVC). Each has advantages like being lightweight, low-cost, and resistant to breakage but also disadvantages like toxicity if made from certain materials and pollution if not recycled properly.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 1
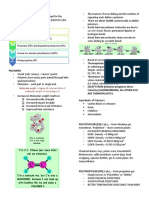
Bottles were first commercially produced in 1947 but became quickly popular in 1960s with the introduction of high-density
polyethylene. They are typically used to store liquids, such as
water, soft drinks, motor oil, cooking oil, medicine, shampoo, milk, and ink.
Case Study: Advantages
Disadvantages
Lightweight nature
Plastic Bottles Relatively low production and transportation costs (compared to glass bottles)
Toxicity problems for some qualities
Pollution if not discarded properly
Superior resistance to breakage in both production and transportation
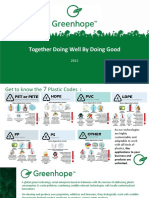
Polyet hyle ne Terephthalate ( PET, PET E or polyester )
o Very good alcohol & essential oil barrier Recycling:
Common usage: o Safe for one-time use - repeated use poses risk
properties
o Bottles for water, cooking oil, peanut of leaching & bacterial growth.
o Good chemical resistance (although
butter, soda, carbonated beverage . o Recycled material is of lower quality than the
acetones & ketones will attack PET).
o High degree of impact resistance and original PET, until it can no longer be recycled
Qualities: and becomes landfill waste.
tensile strength. o 29% is recycled into: polyester fiber for fleece
o Maximum temperature applications 93 °C o Thin, clear
clothing, fabric, carpet or plastic lumber.
Hi g h De nsi ty Polyet hyl ene (H D PE )
o Economic Common usage: Recycling:
o Impact resistant o Milk and water jugs o 29% recycled into bottles for non-food items
o Good moisture barrier compatible with a wide o Juice bottles like shampoo, laundry detergent, motor oil;
o Containers for detergent, shampoo plastic lumber and furniture, piping, recycling
range of products (including acids and caustics , bins, fencing etc.
but not solvents). and motor oil o Post Consumer Resin (PCR) is a blend of HDPE
o Naturally translucent and flexible (primarily from milk and water containers) and
o FDA-approved food grade Qualities: virgin resin.
o Application temperature <71 °C o Thick, opaque
Poly vinyl Chlor i de
(PVC) o Naturally clear Common usage: Recycling:
o Extremely good resistance to oils, very low o Few types of food, detergent o Very low recycling rate -it contaminates the
oxygen transmission, excellent barrier to containers, mattress covers and recycling stream
most gases. commercial-grade plastic wrap o Recycled PVC can become packaging, binders,
o Very good drop impact resistance, chemically decking, paneling, insulation, mud flaps, film
resistant but vulnerable to some solvents. Qualities: and sheet, flooring, garden hoses.
o Poor resistance to high temperatures >71 °C. o May be rigid or flexible (may contain o manufacture of PVC creates dioxin, a potent
phthalates to soften it) carcinogen that contaminates environment.
• Only 10% of the cost of bottled water goes
to the actual water -90% goes to the
Low Dens i ty Polyet hyle ne ( LD PE ) packaging, transportation and marketing
Common usage: Recycling:
o Similar to HDPE in composition, but o Squeezable bottles (and grocery store o Low recycling rate-Difficult to recycle.
less rigid, less chemically resistant but o Can be made into compost bins, paneling, • At least 40% of bottled water is tap water
bags, plastic wrap for household use,
more translucent.
garbage bags) plastic lumber.
o Primarily used for squeeze • 66% of energy is saved when producing
applications. new plastic products from recycled materials
o Significantly more expensive than Qualities: instead of raw (virgin) materials.
HDPE. o Soft, flexible
Pol ypropyl ene (PP)
o Stable at high temperatures, up to Common usage:
Recycling:
104 °C o Syrup bottles, ice cream and yogurt o Low recycling rate (often pigmented or mixed
o Autoclavable, potential for steam containers, drinking straws, salad bar with other resins)
sterilization, containers and diapers
o Excellent chemical resistance
o Poor resistance in cold temperatures. Qualities:
o Hard but flexible
Pol ystyrene (PS)
o Offers excellent clarity and stiffness at Common usage: Recycling:
an economical cost . o Styrofoam coffee cups and meat o Very low recycling rate, difficult process
o Used with dry products including trays; opaque plastic spoons and forks o PS can leach styrene, a known neurotoxin with
vitamins, petroleum jellies, and spices. other harmful health effects.
Qualities:
o Not good barrier properties, and poor o Rigid
impact resistance.
F luori ne Treated (H D PE ) Common usage:
o Bottles are exposed to fluorine gas in o Bottles for insecticides, pesticides, herbicides, photographic chemicals, agricultural chemicals,
a secondary operation. household and industrial cleaners, electronic chemicals, medical cleaners and solvents, citrus
o Similar in appearance to HDPE and products, d-limonene, flavors, fragrances, essential oils, surfactants, polishes, additives, graffiti
have exceptional barrier properties cleaning products, stone and tile care products, waxes, paint,
to hydrocarbons and aromatic gasoline, biodiesel, xylene, acetone, kerosene and more.
solvents.
Qualities:
o Thin, clear
Pol ycar bonate ( PC)
o Dangerous plastic in the food Common usage: Recycling:
production , releases BPA chemicals. o five-gallon water bottles, sports o Very low
bottles recycling rate
Qualities:
o May be rigid or flexible
References:
Bottled Water Facts, www.yorku.ca/sustainability
Peter Anderson, Message in a Bottle: The Impacts of PVC on Plastics Recycling, 2004.
Plastics – the Facts 2014/2015, An analysis of European plastics production, demand and waste data, Plastics Europe.
Facts on Plastic Bottles and Bottled Water -Sources: Environmental Working Group, National Resources Defense Council, Plastic Pollution Coalition, Project Aware, U.S. Department of Agriculture, U.S. National Oceanic & Atmospheric Administration, U.S. National Highway
Transportation Board
http://www.lifewithoutplastic.com/store/common_plastics_no_1_to_no_7#.V6yCntSLRkp
http://www.healthychild.org/know-your-plastics/
https://www.ebottles.com/resins.htm
http://www.greenerpackage.com/bottles/plastic_bottles_and_closures_market_trends_europe
You might also like
- Article 16 Magnetic Flux Leakage (MFL) ExaminationDocument5 pagesArticle 16 Magnetic Flux Leakage (MFL) ExaminationleonciomavarezNo ratings yet
- End-Of-Chapter ProblemsDocument9 pagesEnd-Of-Chapter ProblemsSheila CortezNo ratings yet
- Action Plan Learning Continuity PlanDocument7 pagesAction Plan Learning Continuity PlanLuzviminda Morallos Camarista100% (2)
- B2600 and Add-OnsDocument4 pagesB2600 and Add-OnsvishadkapadiaNo ratings yet
- Case Study: Plastic Bottles: ReferencesDocument1 pageCase Study: Plastic Bottles: ReferencesENo ratings yet
- Plastic Waste Age 12-18Document20 pagesPlastic Waste Age 12-18Wilhelmina MurrayNo ratings yet
- Recycled Plastic ClassificationDocument14 pagesRecycled Plastic Classificationiqbal anzifaNo ratings yet
- Chemours Capstone For Textiles K25183-1Document1 pageChemours Capstone For Textiles K25183-1Kushagradhi DebnathNo ratings yet
- Better by Recycling : 1 Tonne of Reformedplastics Material vs. 1 Tonne of Virgin PlasticDocument2 pagesBetter by Recycling : 1 Tonne of Reformedplastics Material vs. 1 Tonne of Virgin PlasticMichelle KanokangaNo ratings yet
- ATHENADocument3 pagesATHENAThé AltamuraNo ratings yet
- PlasticDocument3 pagesPlasticTsz Kei (Kate) LONo ratings yet
- PolyethyleneDocument31 pagesPolyethyleneHesham chemecology100% (1)
- CBD FiberFacts PolyesterDocument1 pageCBD FiberFacts PolyesterMaría ManzanoNo ratings yet
- Case 4 - Recommendation For A Green ProductDocument11 pagesCase 4 - Recommendation For A Green ProductMai Phạm HươngNo ratings yet
- Consumer Trend Canvas - Bio VaseDocument1 pageConsumer Trend Canvas - Bio VaseMohd HaafizNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Polymers NotesDocument3 pagesChemistry Polymers Noteskainaattufail111No ratings yet
- Section A - Fact Files - PlasticDocument5 pagesSection A - Fact Files - PlasticSafo NewmanNo ratings yet
- Life Cycle AssessmentDocument8 pagesLife Cycle AssessmentDaman Huri WibowoNo ratings yet
- Silicones For Coatings & InksDocument34 pagesSilicones For Coatings & Inksnano100% (1)
- Presentation Product KnowledgeDocument15 pagesPresentation Product KnowledgeMaulana MughirohNo ratings yet
- Polymers and Properties WorksheetDocument4 pagesPolymers and Properties WorksheetRaghav GanaNo ratings yet
- 1 150903121804 Lva1 App6891Document149 pages1 150903121804 Lva1 App6891veselieNo ratings yet
- Positives Negatives: High Density PolyethyleneDocument2 pagesPositives Negatives: High Density PolyethyleneaishaNo ratings yet
- Resin Identification CodeDocument21 pagesResin Identification CodepraveenNo ratings yet
- Antiskid Product Info PDFDocument11 pagesAntiskid Product Info PDFSachin KothariNo ratings yet
- Zero Plastics PosterDocument1 pageZero Plastics PosterKarafton IndiaNo ratings yet
- Polyethylene Product PDFDocument16 pagesPolyethylene Product PDFpolymeianNo ratings yet
- Keratech Eco FlowDocument1 pageKeratech Eco Flowzaid8182No ratings yet
- Cat Aqeco 4-2021 Ing NP 2105Document164 pagesCat Aqeco 4-2021 Ing NP 2105Ofertare InstalatiiNo ratings yet
- Literature Review: Using Recycled Plastics For Compounding and AdditivesDocument27 pagesLiterature Review: Using Recycled Plastics For Compounding and AdditivesFahad MohamedNo ratings yet
- Summary of Macromolecules MidtermDocument12 pagesSummary of Macromolecules MidtermBegad SalahNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Wax: Wax Types and PropertiesDocument4 pagesIntroduction To Wax: Wax Types and Propertiesسلوى سلمان داود سلمانNo ratings yet
- Práctica 1C4 MaterialesDocument7 pagesPráctica 1C4 Materialesxpstt576ztNo ratings yet
- 63108-Spec-Sheet-90040 Warranty PolikenDocument40 pages63108-Spec-Sheet-90040 Warranty PolikenPungkas Nisworo100% (1)
- Packaging Trends in Polyolefins - 2015Document26 pagesPackaging Trends in Polyolefins - 2015Hector AmarfilNo ratings yet
- 2021 Repel o Tex BrochureDocument6 pages2021 Repel o Tex BrochureEnrico MolinoNo ratings yet
- TDS DR Bio 7211 Compostable Filler FilmsDocument3 pagesTDS DR Bio 7211 Compostable Filler FilmsMukul SareenNo ratings yet
- POLYMER and GeotextileDocument6 pagesPOLYMER and GeotextileRCBacayNo ratings yet
- Abecote 384Document2 pagesAbecote 384engramir07No ratings yet
- R300 - FT Resina - enDocument1 pageR300 - FT Resina - ensoporte.etirapidNo ratings yet
- Product Type/ Year 1 2 3 4 5 Key PointsDocument1 pageProduct Type/ Year 1 2 3 4 5 Key PointsRiturajPaulNo ratings yet
- Materials - PlasticsDocument20 pagesMaterials - PlasticsHafizh PrashantyoNo ratings yet
- Liveable Cities Lab - Circular EconomyDocument38 pagesLiveable Cities Lab - Circular EconomyarmagnetoNo ratings yet
- Lecture 12 RecyclingDocument37 pagesLecture 12 RecyclingelmomonsteNo ratings yet
- Primer HT 03 eDocument2 pagesPrimer HT 03 eishaquesoomroNo ratings yet
- Plastics and PolymersDocument9 pagesPlastics and PolymersKharylle Ann IglesiasNo ratings yet
- Polymers in Flexible PackagingDocument9 pagesPolymers in Flexible PackagingGul' Love100% (2)
- SmolaDocument1 pageSmolatirrexNo ratings yet
- Men S & Women S Sneakers Core Item Updates A W 21 22Document7 pagesMen S & Women S Sneakers Core Item Updates A W 21 22Raquel MantovaniNo ratings yet
- Plastic Lumber ReportDocument6 pagesPlastic Lumber ReportsonakshiNo ratings yet
- Also Could Be Natural Milky White or Honey ColoredDocument2 pagesAlso Could Be Natural Milky White or Honey Coloredusebio64No ratings yet
- Zinc MTCDocument2 pagesZinc MTCMohd imranNo ratings yet
- Davco Fine Plaster ECO CatalogueDocument2 pagesDavco Fine Plaster ECO Cataloguepiakhong.cheongNo ratings yet
- Polymers in Flexible PackagingDocument9 pagesPolymers in Flexible PackagingMd Ali RazuNo ratings yet
- Procesos de Manufactura - T5 PPT Proyecto Final Fibra de Coco Con Resina de PoliésterDocument13 pagesProcesos de Manufactura - T5 PPT Proyecto Final Fibra de Coco Con Resina de PoliésterKenneth MosqueraNo ratings yet
- Unit 30 SolutionDocument13 pagesUnit 30 Solutionapi-3704862No ratings yet
- Accessories Footwear Materials Forecast A W 23 24 Leather Non LeatherDocument15 pagesAccessories Footwear Materials Forecast A W 23 24 Leather Non LeatherRajnish JackerNo ratings yet
- Polyester Vs PolypropyleneDocument2 pagesPolyester Vs PolypropyleneLuan NguyenNo ratings yet
- Abecote PU PDFDocument2 pagesAbecote PU PDFAshvin ParmessurNo ratings yet
- Recircle Final Pitch v2 - C4zRLRM3WDocument15 pagesRecircle Final Pitch v2 - C4zRLRM3WReCircle360 for FutureNo ratings yet
- Sustainable Post-Consumer Diaper Recycler: Designer: Bei-Ren Wu, Miley Tsai, Sz-Chwun John HwangDocument22 pagesSustainable Post-Consumer Diaper Recycler: Designer: Bei-Ren Wu, Miley Tsai, Sz-Chwun John HwangluisNo ratings yet
- MMProject Moiez Sohail Muhammad Yasir (1) - 221230 - 145423Document12 pagesMMProject Moiez Sohail Muhammad Yasir (1) - 221230 - 145423azeem niaziNo ratings yet
- EC Tech Report High Performance Polyurethanes: PDFFrom EverandEC Tech Report High Performance Polyurethanes: PDFVincentz Network GmbH & Co. KGNo ratings yet
- Ec tech report architectural and decorative coatings: Water-based and sustainableFrom EverandEc tech report architectural and decorative coatings: Water-based and sustainableVincentz Network GmbH & Co KGNo ratings yet
- Information Science: Competency Levels of Nursing InformaticsDocument6 pagesInformation Science: Competency Levels of Nursing InformaticsCnette S. LumboNo ratings yet
- Agresso Webinar - Back-Office Best Practices 111209Document29 pagesAgresso Webinar - Back-Office Best Practices 111209Michael AlexisNo ratings yet
- Land MOU Phase-2Document22 pagesLand MOU Phase-2Uraj PatelNo ratings yet
- West Crame - Brgy Ordinance 03-2023 - Prescribing Rules and Regulation On Livelihood AreaDocument3 pagesWest Crame - Brgy Ordinance 03-2023 - Prescribing Rules and Regulation On Livelihood AreaMitch Fronteras100% (1)
- Inbound 4445609552032316026Document9 pagesInbound 4445609552032316026CyrishNo ratings yet
- Chapter 17Document26 pagesChapter 17ProfessorTextechNo ratings yet
- Easy JavaScript Notes ?Document32 pagesEasy JavaScript Notes ?VIS SHINo ratings yet
- CopyrightDocument31 pagesCopyrightAwol EbNo ratings yet
- Technology For Teaching and Learning-2-UNIT-1Document30 pagesTechnology For Teaching and Learning-2-UNIT-1Jude Vincent MacalosNo ratings yet
- Matching Propulsion Engine With PropulsorDocument9 pagesMatching Propulsion Engine With PropulsorAnonymous gxAd4liNo ratings yet
- SH 2016 FinalJuly252016byCJose&BOmbrogDocument117 pagesSH 2016 FinalJuly252016byCJose&BOmbrogMiyageEmplamadoAquinoNo ratings yet
- Steel Rule TopicsDocument4 pagesSteel Rule Topicsmohamed fayasNo ratings yet
- Continental Steel Vs Montano DigestedDocument3 pagesContinental Steel Vs Montano DigestedSCFNo ratings yet
- Caterpillar Part 2Document29 pagesCaterpillar Part 2lionkinghdNo ratings yet
- Complaint Affidavit Legal ResearchDocument8 pagesComplaint Affidavit Legal ResearchAlleoh AndresNo ratings yet
- Literature Review 3Document3 pagesLiterature Review 3m khurram riazNo ratings yet
- Microsoft Word 2007Document6 pagesMicrosoft Word 2007JoshLowensohn100% (32)
- Notes On Cash and Cash EquivalentsDocument1 pageNotes On Cash and Cash EquivalentsMariz Julian Pang-aoNo ratings yet
- ABC GROUP-Supplier-Quality-and-Development-Manual-2016-3Document43 pagesABC GROUP-Supplier-Quality-and-Development-Manual-2016-3Ajay Deshpande100% (1)
- Variable Rate Equipment-Technology For Weed ControlDocument4 pagesVariable Rate Equipment-Technology For Weed ControlRodrigo Nogueira MartinsNo ratings yet
- sSOP Production - (Company Name) : ScopeDocument3 pagessSOP Production - (Company Name) : ScopeAlfred Rangel100% (1)
- Business Account Statement: Account Summary For This PeriodDocument2 pagesBusiness Account Statement: Account Summary For This PeriodBrian TalentoNo ratings yet
- Air Force News Jan-Dec 1927Document431 pagesAir Force News Jan-Dec 1927CAP History LibraryNo ratings yet
- Tle-2-M5l1-Barruela, Angelica C. Beed3aDocument14 pagesTle-2-M5l1-Barruela, Angelica C. Beed3aangelica barruelaNo ratings yet
- Metrology 2Document99 pagesMetrology 2venkeekuNo ratings yet
- Global Timesheet GuidanceDocument3 pagesGlobal Timesheet GuidanceprakashNo ratings yet