Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Ac Machines Pesentation: Prepared by
Uploaded by
SANJAY0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
19 views19 pagesSYNCHRONOUS MOTOR
Original Title
Voltage Regulation
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentSYNCHRONOUS MOTOR
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
19 views19 pagesAc Machines Pesentation: Prepared by
Uploaded by
SANJAYSYNCHRONOUS MOTOR
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 19
AC MACHINES PESENTATION
PREPARED BY :
Amey Nashikkar (130410109002)
Shrey Bhatt (130410109007)
Mihir Chauhan (130410109014)
GUIDED BY: PROF. Sanjay sir
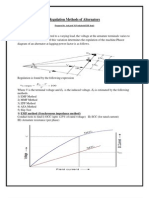
Voltage regulation of an alternator
by DIRECT METHOD
E-V
% Regulation = * 100
V
Where E is the no load terminal voltage
V is the full load terminal voltage
Voltage regulation of an alternator
Generally the alternator working at upf has 10% regulation
maximum and at lagging powerfactor has 30% regulation .
Voltage difference (E-V) depends an effective armature
resistance ( Reff) and synchronous reactance (Xs)
Less amount of % regulation indicates the good performance of
the alternator
% Regulation is +ve value for unity and lagging power factor
load
% Regulation is –ve value for leading power factor load.
Determination of Regulation
By Direct method :
In this method no load voltage of an alternator is taken as
induced emf ‘ E’ .
Then alternator is loaded step by step directly
Each load condition terminal voltage (V) is noted down
% Regulation = (E- V / V ) * 100
In this method power is wasted hence it is used for small
ratings .
INDIRECT Method of Regulation
EMF Method ( Synchronous –impedance method)
MMF Method ( Ampere turn method)
ZPF Method ( Zero power factor method ) or potier method
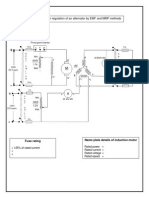
MMF METHOD
For an alternator , the field MMF required to produce
the normal voltage V on full load is the vector sum of
the following:
1) The field MMF required to produce rated terminal
voltage on no-load.
2) Field MMF required to neutralize the demagnetizing
effect of armature reaction on full load.
Steps:
1. By suitable tests plot OCC and SCC
2. From the OCC find the field current If1 to
produce rated voltage, V.
3. From SCC find the magnitude of field
current If2 to produce the required
armature current.
4. Draw If2 at angle (90+Φ) from If1, where
Φ is the phase angle of current from
voltage. If current is leading, take the
angle of If2 as (90-Φ).
5. Find the resultant field current, If and
mark its magnitude on the field current
axis.
6. From OCC. find the voltage
corresponding to If, which will be E0.
Steps:
1. By suitable tests plot OCC and SCC
2. Draw tangent to OCC (air gap line)
3. Conduct ZPF test at full load for rated
voltage and fix the point B.
4. Draw the line BH with length equal to
field current required to produce full load
current at short circuit.
5. Draw HD parallel to the air gap line so as
to touch the OCC.
6. Draw DE parallel to voltage axis. Now,
DE represents voltage drop IXL and BE
represents the field current required to
overcome the effect of armature reaction.
Triangle BDE is called Potier triangle
and XL is the Potier reactance
7. Find E from V, IXL and Φ. Consider Ra
also if required. The expression to use is
( cos )2 ( sin )2 a L E = V Φ + IR + V Φ + IX
8. Find field current corresponding to E.
9. Draw FG with magnitude equal to BE at
angle (90+Ψ) from field current axis,
where Ψ is the phase angle of current
from voltage vector E (internal phase
angle).
10. The resultant field current is given by
OG. Mark this length on field current
axis.
11. From OCC find the corresponding E0.
THANK YOU.
You might also like
- Jeffrey Epstein39s Little Black Book Unredacted PDFDocument95 pagesJeffrey Epstein39s Little Black Book Unredacted PDFasdasdasd75% (4)
- The Synchronous Generator: 2.1. Synchronizing A Generator To An AC SystemDocument10 pagesThe Synchronous Generator: 2.1. Synchronizing A Generator To An AC SystemsantoshkumarNo ratings yet
- Designing Learning Spaces For Children On The AutiDocument17 pagesDesigning Learning Spaces For Children On The AutilalecrimNo ratings yet
- Steam Turbine Buy OnkarDocument965 pagesSteam Turbine Buy OnkarSandip Kumar100% (5)
- Banking Management System 7030Document34 pagesBanking Management System 7030sanjaysingh meharaNo ratings yet
- Practical Troubleshooting of Electrical Equipment and Control CircuitsFrom EverandPractical Troubleshooting of Electrical Equipment and Control CircuitsRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5)
- Keller SME 12e PPT CH02Document22 pagesKeller SME 12e PPT CH02NAM SƠN VÕ TRẦNNo ratings yet
- Sultan Saed Al - Zahrani Est ProfileDocument60 pagesSultan Saed Al - Zahrani Est ProfileaayasirNo ratings yet
- RAM TheoryDocument15 pagesRAM Theorysiddhansh jainNo ratings yet
- Regulation of Alternators by M.venkateshDocument5 pagesRegulation of Alternators by M.venkateshPrakash ChavanNo ratings yet
- Regulation of Alternators by M.venkateshDocument6 pagesRegulation of Alternators by M.venkateshKrishnamoorthi DuraisamyNo ratings yet
- EEE II II EM IInotes PDFDocument9 pagesEEE II II EM IInotes PDFYamini KNo ratings yet
- 5.regultion of A Three Phase Alternator (MMF Method)Document7 pages5.regultion of A Three Phase Alternator (MMF Method)mandadi_saileshNo ratings yet
- Voltage Regulation of Three-Phase Alternator: No Load Full Load Full Load o T T o TDocument8 pagesVoltage Regulation of Three-Phase Alternator: No Load Full Load Full Load o T T o TethanNo ratings yet
- Voltage regulation of alternatorsDocument11 pagesVoltage regulation of alternatorsJagath ArchonNo ratings yet
- Voltage Regulation of Alternator by Zero Power Factor MethodDocument6 pagesVoltage Regulation of Alternator by Zero Power Factor MethodsumanktrNo ratings yet
- Emf & MMF MethodsDocument2 pagesEmf & MMF Methodsven_avv3382No ratings yet
- EM-3 Unit-3Document14 pagesEM-3 Unit-3Prathap Vuyyuru0% (1)
- EMF MethodDocument5 pagesEMF Methodpurushg62No ratings yet
- Vce 1Document7 pagesVce 1Uppili RajuNo ratings yet
- Ac 9Document39 pagesAc 9Ehmed BazNo ratings yet
- Regulation by Zero Power FactorDocument2 pagesRegulation by Zero Power FactorashishNo ratings yet
- DC MachinesDocument22 pagesDC MachinesMadhu TallapanenimadhuNo ratings yet
- Regulation of 3 Phase Alternator MethodsDocument12 pagesRegulation of 3 Phase Alternator Methodsvish5936No ratings yet
- Zero Power Factor Method or Potier MethodDocument1 pageZero Power Factor Method or Potier MethodMarkAlumbroTrangiaNo ratings yet
- 9 Level Cascaded Multilevel Inverter Reduces THDDocument4 pages9 Level Cascaded Multilevel Inverter Reduces THDRavinder RangaNo ratings yet
- Potier Reactance ExperimentDocument5 pagesPotier Reactance Experimentbt21eee122No ratings yet
- Single Phase TransformerDocument11 pagesSingle Phase TransformerArijeet MondalNo ratings yet
- Transformer Performance TestDocument6 pagesTransformer Performance TestVIJAY KUMARNo ratings yet
- Electrical Machines II: Ahmed Mortuza SalequeDocument14 pagesElectrical Machines II: Ahmed Mortuza SalequeAhsan Kabir NuhelNo ratings yet
- E M 1 Lab ManualDocument63 pagesE M 1 Lab ManualdsparanthamanNo ratings yet
- Suhasini Lohar - Voltege Regulation by Emf Method - EnglishDocument19 pagesSuhasini Lohar - Voltege Regulation by Emf Method - EnglishSuhasini Vilas LoharNo ratings yet
- Voltage Regulation by MMFDocument4 pagesVoltage Regulation by MMFKrushna PisalNo ratings yet
- Oc and SC TransDocument9 pagesOc and SC TransshonmlrNo ratings yet
- Statcom Static Synchronous Compensator: Theory, Modeling, ApplicationsDocument7 pagesStatcom Static Synchronous Compensator: Theory, Modeling, ApplicationsCesario GillasNo ratings yet
- Alternator at Various Loads, Armature Reaction & Voltage RegulationDocument3 pagesAlternator at Various Loads, Armature Reaction & Voltage RegulationYash BansalNo ratings yet
- Ac Machines Lab ManualDocument55 pagesAc Machines Lab ManualYakkali Kiran0% (1)
- Alternator Regulation (E.M.F. & M.M.F. Methods) : 1. ObjectDocument8 pagesAlternator Regulation (E.M.F. & M.M.F. Methods) : 1. Objectsajd abbasNo ratings yet
- Transmission Line Model AnalysisDocument19 pagesTransmission Line Model Analysissemuty92No ratings yet
- Inverter SheetDocument1 pageInverter SheetMahmoud A. AboulhasanNo ratings yet
- Voltage Regulation of 3-Phase Alternator by ZPF and ASA MethodsDocument6 pagesVoltage Regulation of 3-Phase Alternator by ZPF and ASA Methods61EEPrabhat Pal100% (1)
- Modeling and Testing a Single-Phase TransformerDocument13 pagesModeling and Testing a Single-Phase TransformerMuhammad ImadNo ratings yet
- Alternator NotesDocument24 pagesAlternator Notesarunima arunimaNo ratings yet
- Synchronizing Power in Synchronous MachinesDocument15 pagesSynchronizing Power in Synchronous Machinesgurunathan14No ratings yet
- Control System Lab ManualDocument62 pagesControl System Lab ManualVenkata Subramanian0% (1)
- Chapter 10 Sinusoidal Voltages and CurrentsDocument40 pagesChapter 10 Sinusoidal Voltages and CurrentsAeron James V. Basilio100% (1)
- Laboratory Session 3 Single-Phase Transformers: Milwaukee School of Engineering EE-340Document10 pagesLaboratory Session 3 Single-Phase Transformers: Milwaukee School of Engineering EE-340Isabell GonzalesNo ratings yet
- Chapter One: 1.1 Phasor RepresentationDocument57 pagesChapter One: 1.1 Phasor RepresentationMohamad AbdulghaniNo ratings yet
- EMFmethodDocument5 pagesEMFmethodaryan sarangNo ratings yet
- ELEG 310L Prelab 4Document3 pagesELEG 310L Prelab 4ghaliaNo ratings yet
- A New ISPWM Switching Technique For THD Reduction in Custom Power DevicesDocument7 pagesA New ISPWM Switching Technique For THD Reduction in Custom Power DevicesBharathkumars89No ratings yet
- AlternatorDocument13 pagesAlternatorPratikTiwari0% (1)
- AssignmentsDocument17 pagesAssignmentsKunal SakharkarNo ratings yet
- AssignmentsDocument22 pagesAssignmentsKunal SakharkarNo ratings yet
- 1.EMF and MMF MethodDocument12 pages1.EMF and MMF Methodbalaer05100% (1)
- EEE 224 Wien-bridge Oscillator Using OPAMPDocument3 pagesEEE 224 Wien-bridge Oscillator Using OPAMPJames Adrian Abalde SaboNo ratings yet
- Controlled Rectifier Single Phase Full WaveDocument7 pagesControlled Rectifier Single Phase Full WaveJesus BecerraNo ratings yet
- Aptitude Test-1Document7 pagesAptitude Test-1Bala SubramanianNo ratings yet
- Power ElectronicsDocument89 pagesPower Electronicsneelam sanjeev kumarNo ratings yet
- Notes Chapter 1Document90 pagesNotes Chapter 1yusoff_aishahNo ratings yet
- Interpret AC Voltages & CurrentsDocument46 pagesInterpret AC Voltages & CurrentsKelvin LooiNo ratings yet
- Influence of System Parameters Using Fuse Protection of Regenerative DC DrivesFrom EverandInfluence of System Parameters Using Fuse Protection of Regenerative DC DrivesNo ratings yet
- Electrical and Electronic Principles 3 Checkbook: The Checkbook SeriesFrom EverandElectrical and Electronic Principles 3 Checkbook: The Checkbook SeriesNo ratings yet
- Electric Utilities Fundamentals and FutureDocument35 pagesElectric Utilities Fundamentals and FutureSANJAYNo ratings yet
- Torque - Slip Characteristic of A Three - Phase Induction MachineDocument28 pagesTorque - Slip Characteristic of A Three - Phase Induction MachineAli AltahirNo ratings yet
- 3-Phase Induction Motor GuideDocument15 pages3-Phase Induction Motor GuideSANJAYNo ratings yet
- Sardar Vallabhbhai Patel Institute of Technology, Vasad: Equivalent Circuit of Induction Motor & Phasor DiagramDocument23 pagesSardar Vallabhbhai Patel Institute of Technology, Vasad: Equivalent Circuit of Induction Motor & Phasor DiagramSANJAYNo ratings yet
- Torque - Slip Characteristic of A Three - Phase Induction MachineDocument28 pagesTorque - Slip Characteristic of A Three - Phase Induction MachineAli AltahirNo ratings yet
- By:-Gaurav Patel & Alesh TalsaniaDocument18 pagesBy:-Gaurav Patel & Alesh TalsaniaSANJAYNo ratings yet
- 3-Phase Induction Motor GuideDocument15 pages3-Phase Induction Motor GuideSANJAYNo ratings yet
- Sardar Vallabhbhai Patel Institute of Technology, Vasad: Equivalent Circuit of Induction Motor & Phasor DiagramDocument23 pagesSardar Vallabhbhai Patel Institute of Technology, Vasad: Equivalent Circuit of Induction Motor & Phasor DiagramSANJAYNo ratings yet
- Design of SMDocument20 pagesDesign of SMSANJAYNo ratings yet
- Sardar Vallabhbhai Institute of Technology, VasadDocument15 pagesSardar Vallabhbhai Institute of Technology, VasadSANJAYNo ratings yet
- Output Equation - Selection of Specific LoadingDocument8 pagesOutput Equation - Selection of Specific LoadingSANJAYNo ratings yet
- Design of SMDocument20 pagesDesign of SMSANJAYNo ratings yet
- Types of Synchronous Machines: Subject:-ACMDDocument12 pagesTypes of Synchronous Machines: Subject:-ACMDSANJAYNo ratings yet
- Short Circuit Ratio & Effect of SCR On Machine PerformanceDocument8 pagesShort Circuit Ratio & Effect of SCR On Machine PerformanceSANJAYNo ratings yet
- Sardar Vallabhbhai Patel Institute of Technology, VasadDocument17 pagesSardar Vallabhbhai Patel Institute of Technology, VasadSANJAYNo ratings yet
- Design of SMDocument20 pagesDesign of SMSANJAYNo ratings yet
- Selection of Length of AirgapDocument15 pagesSelection of Length of AirgapSANJAYNo ratings yet
- Stator SlotsDocument12 pagesStator SlotsSANJAYNo ratings yet
- Design of End Rings in Induction Motor: Guided By: Prof. Sanjay PatelDocument8 pagesDesign of End Rings in Induction Motor: Guided By: Prof. Sanjay PatelSANJAYNo ratings yet
- Three Phase Induction Motor: Prepared by D.Sharmitha AP/EEE Kumaraguru College of TechnologyDocument29 pagesThree Phase Induction Motor: Prepared by D.Sharmitha AP/EEE Kumaraguru College of TechnologySANJAYNo ratings yet
- Output Equation - Selection of Specific LoadingDocument8 pagesOutput Equation - Selection of Specific LoadingSANJAYNo ratings yet
- Rotor Design Optimization for Induction MotorsDocument9 pagesRotor Design Optimization for Induction MotorsSANJAYNo ratings yet
- GA450Document2 pagesGA450timingtoolNo ratings yet
- Automated Planning For Tomorrow AIDocument7 pagesAutomated Planning For Tomorrow AIColin LewisNo ratings yet
- Aec-2348-01-1001 P&i DiagramDocument1 pageAec-2348-01-1001 P&i Diagramuma raneNo ratings yet
- Integrated Voice Evacuation System VM-3000 Series: Operating InstructionsDocument144 pagesIntegrated Voice Evacuation System VM-3000 Series: Operating InstructionsAbraham GamaNo ratings yet
- Chat group discusses joining details for new roleDocument106 pagesChat group discusses joining details for new rolejigarsampat0% (1)
- Rodenstock CV1000PDocument2 pagesRodenstock CV1000PemoboysliveNo ratings yet
- PRESENTATION ON HUMANOID ROBOTSDocument17 pagesPRESENTATION ON HUMANOID ROBOTSAGRIM GAURNo ratings yet
- PPU UNIT 1 Part-1Document23 pagesPPU UNIT 1 Part-1VeeturiVarunNo ratings yet
- Itu Survey On Radio Spectrum Management 17-01-07 FinalDocument280 pagesItu Survey On Radio Spectrum Management 17-01-07 FinalĐại Gia Nam ĐịnhNo ratings yet
- Customizing AOSP For Different Embedded Devices and Integration at Application Layer.Document11 pagesCustomizing AOSP For Different Embedded Devices and Integration at Application Layer.IJAFRCNo ratings yet
- Vodafone Case FinalDocument25 pagesVodafone Case FinalpavanbhatNo ratings yet
- Introducing ActifioDocument50 pagesIntroducing ActifiowiproycaNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan WoodworkDocument4 pagesLesson Plan Woodworkapi-223390716No ratings yet
- 2010-2011 CatalogDocument378 pages2010-2011 CatalogHouston Community College91% (43)
- L6 Software Tools For Plagiarism CheckingDocument13 pagesL6 Software Tools For Plagiarism Checkingrahulyadav.hbtiNo ratings yet
- rr321201 Multimedia and Web DesignDocument4 pagesrr321201 Multimedia and Web DesignSRINIVASA RAO GANTANo ratings yet
- Improve accuracy of specific heat experiment using crushed ice and control setupDocument6 pagesImprove accuracy of specific heat experiment using crushed ice and control setuprazanmk961214No ratings yet
- ASTM D3689 (Prueba de Carga en Traccion)Document11 pagesASTM D3689 (Prueba de Carga en Traccion)Josh ClaureNo ratings yet
- Acoustic sciences corp designs revolutionary soundproof roomDocument1 pageAcoustic sciences corp designs revolutionary soundproof roomAcoustics GlobalNo ratings yet
- BAVARIA Phoenix - Technical Spec - 2018Document2 pagesBAVARIA Phoenix - Technical Spec - 2018Kareem Abo SeifNo ratings yet
- RESUME2: Major MD Rakibul Hassan, Raqueeb HassanDocument8 pagesRESUME2: Major MD Rakibul Hassan, Raqueeb Hassanapi-19821641No ratings yet
- Digital Image Processing and Signal Processing PhD Research ProposalDocument1 pageDigital Image Processing and Signal Processing PhD Research ProposalKimberly MitchellNo ratings yet
- Vacon NXP Marine APFIFF09 Application Manual UD010Document214 pagesVacon NXP Marine APFIFF09 Application Manual UD010TanuTiganu0% (1)
- 1031 1192105956 13 202109 FGH F Torque Converter Erosion Jory For Cep - PDF 51376613 v1Document7 pages1031 1192105956 13 202109 FGH F Torque Converter Erosion Jory For Cep - PDF 51376613 v1Jesús SarriaNo ratings yet