Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Data Flow Diagram of ARM: 1 39v10 The ARM Architecture
Uploaded by
Mohnish0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
35 views7 pagesMicroprocessor
Original Title
FALLSEM2021-22_EEE4001_ETH_VL2021220100842_Reference_Material_I_03-Dec-2021_arm_registers
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentMicroprocessor
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
35 views7 pagesData Flow Diagram of ARM: 1 39v10 The ARM Architecture
Uploaded by
MohnishMicroprocessor
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 7
Data Flow Diagram of ARM
39v10 The ARM Architecture TM
1 1
The Registers
ARM has 37 registers all of which are 32-bits long.
1 dedicated program counter
1 dedicated current program status register
5 dedicated saved program status registers
30 general purpose registers
The current processor mode governs which of several banks is
accessible. Each mode can access
a particular set of r0-r12 registers
a particular r13 (the stack pointer, sp) and r14 (the link register, lr)
the program counter, r15 (pc)
the current program status register, cpsr
Privileged modes (except System) can also access
a particular spsr (saved program status register)
39v10 The ARM Architecture TM
2 2
Data Sizes and Instruction Sets
The ARM is a 32-bit architecture.
When used in relation to the ARM:
Byte means 8 bits
Halfword means 16 bits (two bytes)
Word means 32 bits (four bytes)
Most ARM’s implement two instruction sets
32-bit ARM Instruction Set
16-bit Thumb Instruction Set
Jazelle cores can also execute Java bytecode
39v10 The ARM Architecture TM
3 3
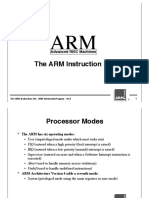
Processor Modes
The ARM has seven basic operating modes:
User : unprivileged mode under which most tasks run
FIQ : entered when a high priority (fast) interrupt is raised
IRQ : entered when a low priority (normal) interrupt is raised
Supervisor : entered on reset and when a Software Interrupt
instruction is executed
Abort : used to handle memory access violations
Undef : used to handle undefined instructions
System : privileged mode using the same registers as user mode
39v10 The ARM Architecture TM
4 4
The ARM Register Set
Current Visible Registers
r0
Abort
Undef
SVC
IRQ
FIQ
User Mode
Mode
Mode
Mode
Mode
r1
r2
r3 Banked out Registers
r4
r5
r6 User FIQ IRQ SVC Undef Abort
r7
r8 r8 r8
r9 r9 r9
r10 r10 r10
r11 r11 r11
r12 r12 r12
r13 (sp) r13 (sp) r13 (sp) r13 (sp) r13 (sp) r13 (sp) r13 (sp)
r14 (lr) r14 (lr) r14 (lr) r14 (lr) r14 (lr) r14 (lr) r14 (lr)
r15 (pc)
cpsr
spsr spsr spsr spsr spsr spsr
39v10 The ARM Architecture TM
5 5
The ARM Register Set
Current Visible Registers
r0
Abort
Undef
SVC
IRQ
FIQ
User Mode
Mode
Mode
Mode
Mode
r1
r2
r3 Banked out Registers
r4
r5
r6 User FIQ IRQ SVC Undef Abort
r7
r8 r8 r8
r9 r9 r9
r10 r10 r10
r11 r11 r11
r12 r12 r12
r13 (sp) r13 (sp) r13 (sp) r13 (sp) r13 (sp) r13 (sp) r13 (sp)
r14 (lr) r14 (lr) r14 (lr) r14 (lr) r14 (lr) r14 (lr) r14 (lr)
r15 (pc)
cpsr
spsr spsr spsr spsr spsr spsr
39v10 The ARM Architecture TM
6 6
Register Organization Summary
User FIQ IRQ SVC Undef Abort
r0
r1
User
r2 mode
r3 r0-r7,
r4 r15, User User User User
and mode mode mode mode Thumb state
r5
cpsr r0-r12, r0-r12, r0-r12, r0-r12, Low registers
r6
r15, r15, r15, r15,
r7 and and and and
r8 r8 cpsr cpsr cpsr cpsr
r9 r9
r10 r10 Thumb state
r11 r11 High registers
r12 r12
r13 (sp) r13 (sp) r13 (sp) r13 (sp) r13 (sp) r13 (sp)
r14 (lr) r14 (lr) r14 (lr) r14 (lr) r14 (lr) r14 (lr)
r15 (pc)
cpsr
spsr spsr spsr spsr spsr
Note: System mode uses the User mode register set
39v10 The ARM Architecture TM
7 7
You might also like
- ESD Reference PDFDocument81 pagesESD Reference PDFswap14327No ratings yet
- HP Troubleshooting AssessmentDocument5 pagesHP Troubleshooting AssessmentDayner Rizo SeguraNo ratings yet
- Beginning FPGA Programming - Partie57Document5 pagesBeginning FPGA Programming - Partie57ali alilouNo ratings yet
- ARM Introduction & Instruction Set ArchitectureDocument71 pagesARM Introduction & Instruction Set ArchitecturebalaNo ratings yet
- Organisation Key Person Designation Email Phone SL NoDocument8 pagesOrganisation Key Person Designation Email Phone SL NojaisuryabanerjeeNo ratings yet
- QTHi1-Technical Document PDFDocument50 pagesQTHi1-Technical Document PDFtarunkumar soniNo ratings yet
- ArmDocument44 pagesArmSiva SankaranNo ratings yet
- Arm7 ArchitectureDocument20 pagesArm7 ArchitectureCharitha CherryNo ratings yet
- Odi2-065r17m18jj02-Gq V1 PDFDocument3 pagesOdi2-065r17m18jj02-Gq V1 PDFJuan Manuel RojasNo ratings yet
- Arm BriefDocument29 pagesArm BriefJoginder YadavNo ratings yet
- ARM Founded in November 1990: Advanced RISC MachinesDocument27 pagesARM Founded in November 1990: Advanced RISC MachinesArkajyoti SahaNo ratings yet
- The ARM Architecture The ARM ArchitectureDocument26 pagesThe ARM Architecture The ARM ArchitecturesudhirNo ratings yet
- C Sec Eiot Unit3Document23 pagesC Sec Eiot Unit3209X1A0467 KOTLA ANUSHANo ratings yet
- ARM Architecture GuideDocument25 pagesARM Architecture GuideRohith ThurlapatiNo ratings yet
- ARM Architecture GuideDocument25 pagesARM Architecture GuideRohith ThurlapatiNo ratings yet
- ARM Basic HelpDocument48 pagesARM Basic HelpKOMAL SONINo ratings yet
- arm proseccorDocument198 pagesarm proseccorshreyansh.saurav21No ratings yet
- 3 ARM ProcessorDocument33 pages3 ARM ProcessorRandell cookNo ratings yet
- ARM - Advanced RISC Machines: RISC-Reduce Instruction Set ComputersDocument60 pagesARM - Advanced RISC Machines: RISC-Reduce Instruction Set Computershitesh bonamNo ratings yet
- Arm ProcessorDocument92 pagesArm ProcessorReddappa ReddyNo ratings yet
- ARM ArchitectureDocument85 pagesARM ArchitectureGurram KishoreNo ratings yet
- ARM Instruction Set OverviewDocument60 pagesARM Instruction Set OverviewDevid gakharNo ratings yet
- ARM Instruction SetDocument58 pagesARM Instruction SetECE TheivanayakiNo ratings yet
- ARM Embedded Hardware Design Lecture on Processor Models and RegistersDocument42 pagesARM Embedded Hardware Design Lecture on Processor Models and RegistersD StarNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3Document88 pagesLecture 3Praveen RathnamNo ratings yet
- Embedded Systems ProgrammingDocument28 pagesEmbedded Systems ProgrammingAbdallah AdelNo ratings yet
- Arm Exploitation PDFDocument57 pagesArm Exploitation PDFjokllNo ratings yet
- ARM Instruction Set IntroductionDocument32 pagesARM Instruction Set IntroductionRiver AbodNo ratings yet
- ARM ProcessorDocument88 pagesARM ProcessorAyan AcharyaNo ratings yet
- Esdl4 PPSXDocument71 pagesEsdl4 PPSXPrasad JadhavNo ratings yet
- ARMInst - UNIT 4Document64 pagesARMInst - UNIT 4MarupakaNo ratings yet
- 1.evolution and Improvement of ARM ArchitectDocument35 pages1.evolution and Improvement of ARM ArchitectRohini0% (1)
- ARMInst (1)Document58 pagesARMInst (1)Priti DhekneNo ratings yet
- ARM7,9,11 ProcessorDocument34 pagesARM7,9,11 Processorharshad lokhandeNo ratings yet
- ARM Architecture OverviewDocument44 pagesARM Architecture Overviewpraneeth chinthireddyNo ratings yet
- The ARM Architecture: AgendaDocument14 pagesThe ARM Architecture: AgendaLala Prieto RiverosNo ratings yet
- Arm FundamentalsDocument32 pagesArm FundamentalsSatyanarayana SankuNo ratings yet
- Lec Arm PDFDocument25 pagesLec Arm PDFspaulsNo ratings yet
- Module 4Document82 pagesModule 4Rakesh LodhiNo ratings yet
- The ARM Instruction SetDocument58 pagesThe ARM Instruction SetAggelos KouroumalosNo ratings yet
- The First EncounterDocument44 pagesThe First EncounterRANJITHANo ratings yet
- Transitioning From ARM v7 To ARM v8 - All The Basics Your Must KnowDocument18 pagesTransitioning From ARM v7 To ARM v8 - All The Basics Your Must KnowTuyen DinhNo ratings yet
- Arm PPTDocument25 pagesArm PPTsudarsanareddyNo ratings yet
- ARMDocument40 pagesARMhifazat aliNo ratings yet
- The ARM Instruction Set: Advanced RISC MachinesDocument11 pagesThe ARM Instruction Set: Advanced RISC MachinesGilberto VirgilioNo ratings yet
- Assembly Arm 7Document75 pagesAssembly Arm 7Thanh NguyenNo ratings yet
- ARM - An Understanding and MoreDocument87 pagesARM - An Understanding and MoreSivasini Netra S ANo ratings yet
- ARM Founded in November 1990: Advanced RISC MachinesDocument45 pagesARM Founded in November 1990: Advanced RISC MachinesaesyopNo ratings yet
- Arm AssemblyDocument76 pagesArm AssemblyQuan DehatNo ratings yet
- ARM KDocument32 pagesARM KARPAN KUMAR BHANDARINo ratings yet
- Arm Instruction ProgramDocument121 pagesArm Instruction ProgramErmin KatardzicNo ratings yet
- ARM Has 7 Operating Modes ARM Has 7 Operating Modes: - Fa F Fa FDocument18 pagesARM Has 7 Operating Modes ARM Has 7 Operating Modes: - Fa F Fa FSampathhhhh Sai TadepalliNo ratings yet
- ARM Instruction Sets and Program: Jin-Fu Li Department of Electrical Engineering National Central UniversityDocument116 pagesARM Instruction Sets and Program: Jin-Fu Li Department of Electrical Engineering National Central UniversityRANJITHANo ratings yet
- ARM Instr Set PDFDocument116 pagesARM Instr Set PDFnaveenNo ratings yet
- Stack Examples: r5 r4 r3 r1 r0 SP r5 r4 r3 r1 r0 SPDocument2 pagesStack Examples: r5 r4 r3 r1 r0 SP r5 r4 r3 r1 r0 SPGilberto VirgilioNo ratings yet
- Week 10 PDFDocument83 pagesWeek 10 PDFPoison RemarkNo ratings yet
- The ARM Instruction Set: Advanced RISC MachinesDocument58 pagesThe ARM Instruction Set: Advanced RISC MachinesarthicseNo ratings yet
- Arm Intro l01Document47 pagesArm Intro l01Tanishq GuptaNo ratings yet
- Thumb InstructionsDocument43 pagesThumb InstructionsJyothi B.R.No ratings yet
- Freescale Cortex.m0.code - DensityDocument66 pagesFreescale Cortex.m0.code - DensitycatgadhaNo ratings yet
- ROUTING INFORMATION PROTOCOL: RIP DYNAMIC ROUTING LAB CONFIGURATIONFrom EverandROUTING INFORMATION PROTOCOL: RIP DYNAMIC ROUTING LAB CONFIGURATIONNo ratings yet
- FALLSEM2021-22 EEE4001 ETH VL2021220100842 Reference Material I 26-Nov-2021 PipeliningDocument14 pagesFALLSEM2021-22 EEE4001 ETH VL2021220100842 Reference Material I 26-Nov-2021 PipeliningMohnishNo ratings yet
- FALLSEM2021-22 EEE4001 ETH VL2021220100842 Reference Material I 10-Dec-2021 Instrution ARM NewDocument10 pagesFALLSEM2021-22 EEE4001 ETH VL2021220100842 Reference Material I 10-Dec-2021 Instrution ARM NewMohnishNo ratings yet
- Von-Neumann Architecture Harvard ArchitectureDocument8 pagesVon-Neumann Architecture Harvard ArchitectureMohnishNo ratings yet
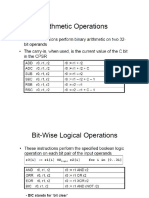
- CPSR Has Four Fields Flag Status Extension Control: 1 39v10 The ARM ArchitectureDocument3 pagesCPSR Has Four Fields Flag Status Extension Control: 1 39v10 The ARM ArchitectureMohnishNo ratings yet
- 16 by 2 LCDDocument5 pages16 by 2 LCDgouttNo ratings yet
- Wyg2Gma Converter - Quickstart Guide: 1. Export CSV From WysiwygDocument4 pagesWyg2Gma Converter - Quickstart Guide: 1. Export CSV From WysiwygJavier ParraNo ratings yet
- ACS730LLC Datasheet PDFDocument24 pagesACS730LLC Datasheet PDFRicardo UrioNo ratings yet
- Console PinoutDocument11 pagesConsole Pinouta_giri1No ratings yet
- OS ReviewerDocument4 pagesOS ReviewerNickNo ratings yet
- Diode Laser Firmware Design SpecificationDocument42 pagesDiode Laser Firmware Design SpecificationJoel Allbert PimentelNo ratings yet
- Department of Education: Learning Activity Sheet For Learning Strand 6 Digital CitizenshipDocument3 pagesDepartment of Education: Learning Activity Sheet For Learning Strand 6 Digital CitizenshipMarkee Joyce GalanNo ratings yet
- Lenovo Legion T7 34IAZ7: PsrefDocument2 pagesLenovo Legion T7 34IAZ7: PsrefHhfugNo ratings yet
- ITC Assignment 3Document14 pagesITC Assignment 3Sheikh AamirNo ratings yet
- 8085 Instructions: Institute of Lifelong Learning, University of DelhiDocument21 pages8085 Instructions: Institute of Lifelong Learning, University of DelhiMonika SharmaNo ratings yet
- BUF16821 DC To DC IcDocument29 pagesBUF16821 DC To DC IcsachinNo ratings yet
- Mips Assembly Language Programming Using Qtspim: Ed Jorgensen November 2014Document165 pagesMips Assembly Language Programming Using Qtspim: Ed Jorgensen November 2014João AlvesNo ratings yet
- MN050009 - EN Easysoft Manual PDFDocument725 pagesMN050009 - EN Easysoft Manual PDFmisuci100% (1)
- IMG - 0093 MCQ Bank For Computer Fundamentals MRC 18Document1 pageIMG - 0093 MCQ Bank For Computer Fundamentals MRC 18Arwyn BermasNo ratings yet
- RJK5020DPK Mosfet N 500V 40amp 200W + - 30VDocument7 pagesRJK5020DPK Mosfet N 500V 40amp 200W + - 30VVictorManuelBernalBlancoNo ratings yet
- Lab 3 - Transistor FundamentalsDocument5 pagesLab 3 - Transistor FundamentalsWilliam ChruchillNo ratings yet
- Power Electronics Board Exam QuestionsDocument2 pagesPower Electronics Board Exam Questionsganesh shyamNo ratings yet
- Read and Write Action of RAM Using IC 7489Document5 pagesRead and Write Action of RAM Using IC 7489Deepak Kumbhar100% (1)
- CM8828Document23 pagesCM8828evasiveNo ratings yet
- MX-19.2 Users Manual: v. 20200801 Manual AT Mxlinux DOT OrgDocument199 pagesMX-19.2 Users Manual: v. 20200801 Manual AT Mxlinux DOT OrgHibozoNo ratings yet
- Hytera - Mission Critical Communications For The Private Security Industry - PDF PDFDocument24 pagesHytera - Mission Critical Communications For The Private Security Industry - PDF PDFVíctor CasadoNo ratings yet
- CITIZEN - CL-S700 - Tech MANUAL PDFDocument257 pagesCITIZEN - CL-S700 - Tech MANUAL PDFPiedmontNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 - IntroductionDocument34 pagesChapter 1 - IntroductionSohaib ChoudharyNo ratings yet
- Fallo MacDocument13 pagesFallo MacMiguel MartinezNo ratings yet
- 510607F3 Spec - Sheet Rev1 PDFDocument1 page510607F3 Spec - Sheet Rev1 PDFAlberto MillaNo ratings yet