0% found this document useful (0 votes)
247 views19 pagesChapter 1 Pneumatic System
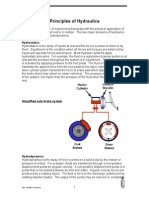
The document introduces pneumatic systems, which use compressed air to transmit power or motion, and describes their applications in areas like pressing, clamping, and packaging machines. It explains the basic components of a pneumatic system like compressors, cylinders, valves, and actuators. Finally, it covers the advantages and disadvantages of pneumatic systems compared to other technologies.
Uploaded by
divien rajCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
247 views19 pagesChapter 1 Pneumatic System
The document introduces pneumatic systems, which use compressed air to transmit power or motion, and describes their applications in areas like pressing, clamping, and packaging machines. It explains the basic components of a pneumatic system like compressors, cylinders, valves, and actuators. Finally, it covers the advantages and disadvantages of pneumatic systems compared to other technologies.
Uploaded by
divien rajCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd