Professional Documents
Culture Documents
There Are Different Types of Servers, For Example:: Prepared by MR: Hussain K
Uploaded by
hussain korirOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
There Are Different Types of Servers, For Example:: Prepared by MR: Hussain K
Uploaded by
hussain korirCopyright:
Available Formats
NETWORK
A computer network consists of two or more computers and peripherals that are linked together.
These links can be made with cables. A wireless network uses radio waves, in the same way as televisions, radios
and mobile phones, to make the links. A wireless network following a common protocol is called Wi-Fi.
Wireless networks are also made available in places such as hotels, libraries and airports for general use. They
are known as Wi-Fi hotspots .
Most networks are controlled by the use of servers.
There are different types of servers, for example:
Different servers may be used to manage different tasks.
A file server is a computer that acts like a disk-drive, storing the programs and data files shared by client
computers.
A print server controls one or more printers and stores the print-image output from all computers on the system.
Web servers contain Web pages that can be viewed using a browser.
Mail servers manage e-mail
Computers connected to a network is called Client computer
An independent computer that is not connected to a network is called Stand alone computer.
Prepared By Mr: Hussain K
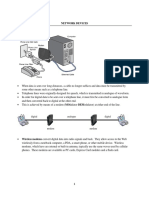
Network Devices
Data packets : It is a small amount of data sent over a network, such as a LAN or the Internet.
A typical packet includes two sections, a header and payload.
Packets of data header contains:
The sender’s IP address
The receiver’s IP address
The sequence/identity number of the packet (this is to ensure that all the packets can
be reassembled into the correct order once they reach the destination)
The packet size (this is to ensure the receiving station can check if all of the packets
have arrived intact)
How many data packets make up the whole message.
Prepared By Mr: Hussain K
Network Devices
The Hub
Network hubs are hardware devices that can have a number
of devices/computers connected to them.
Its main task is to take any data received via one of the ports
and then send out this data from all of the ports. Each
computer/device will receive the data, whether it is relevant
or not.
They are used primarily to connect devices together to form a
local area network (LAN),
Hubs are not very secure because every device will receive
every data packet there will be unnecessary traffic on the
network, which results in reduced bandwidth.
Prepared By Mr: Hussain K
The Switches
Switches are ‘intelligent’ versions of hubs.
As with hubs, they connect a number of devices together to
form a LAN.
However, unlike a hub, a switch stores the MAC addresses of
all devices on the network. Each port on the switch connected to
a device will have a matching MAC address.
This means that the network traffic only goes to where it is
needed and so a switch is more efficient than a hub, especially
when the network is very busy.
In summary:
» Both a hub and a switch are used to connect devices in a LAN
» Both hubs and switches use data packets
» Hubs send data packets to every device on the network; whereas
switches send data packets to a specific device only
» Security is lower with hubs than with switches
» A switch uses a look-up table to determine the destination device
» Switches use MAC addresses to locate the destination device.
Prepared By Mr: Hussain K
The Bridge
Bridges are devices that connect one LAN
to another LAN that uses the same
protocol (communication rules).
They are often used to connect together
different parts of a LAN so that they can
function as a single LAN.
Unlike routers, bridges cannot
communicate with other external
networks, such as the internet.
Prepared By Mr: Hussain K
The Router
Routers are devices used to route data packets from one
network to another network, based on IP addresses.
It can do this because each router has its own IP
address. Routers are used to join a LAN to the internet.
Routers do not store the MAC addresses of devices
(only IP addresses of all computers and devices are
stored).
Many modern broadband ‘routers’ actually combine the
functions of a router and a switch – this means that they
store MAC addresses and IP addresses to enable data
packets to be sent to the correct network and then to the
correct device on the network.
Prepared By Mr: Hussain K
The Modem
Modem means modulator demodulator and is a device which converts a
computer’s digital signal (i.e. modulates it) into an analogue signal for
transmission over an existing telephone line.
It also does the reverse process, in that it converts analogue signals from a
telephone line into digital signals (demodulates) to enable the computer to
process the data.
Modems are used to allow computers to connect to networks
Prepared By Mr: Hussain K
Network interface card (NIC)
A network interface card (NIC) is needed to allow a device to
connect to a
network. An NIC turns binary data into an electrical signal that
allows access to
a network.
The NIC is usually integrated into the motherboard on most
modern computers.
Each NIC is given a unique hardwired (or hard-coded) media
access control (MAC) address at the manufacturing stage.
When installed in a device, this uniquely identifies that device.
Wireless network interface cards (WNICs) are the same as
NICs in that they are used to connect devices to the internet or
other networks. However, they use
wireless connectivity, utilizing an antenna to communicate
with networks via
microwaves. They would normally plug into the USB port or
be part of an internal
integrated circuit.
Prepared By Mr: Hussain K
Media access control (MAC) address
The media access control (MAC) address is a number which uniquely identifies a device when it is connected to a network. The MAC address is made
up of 48 bits which are shown as six groups of hexadecimal digits with the general format:
NN – NN – NN – DD – DD – DD
manufacturer’s code device serial number
For example, 00 – 1C – B3 – 4F – 25 – FF , where the first six hex digits identify a device made by Apple and the second set of six hex digits are the
unique serial number of the device itself.
If the NIC card is replaced, the MAC address will also change. The MAC address is sometimes referred to as the physical address because it uniquely
identifies a device. MAC addresses are useful when trying to identify network faults because they never change, which makes it a more reliable method
of identifying data senders and data receivers on a network.
Internet protocol (IP) addresses
Whenever a computer connects to the internet it is given an internet protocol (IP) address. This is usually assigned to the computer by the internet
service provider (ISP). Because the operation of the internet is based on a set of protocols (rules), it is necessary to supply an IP address. Internet
protocols define the rules that must be agreed by senders and receivers of data
communicating through the internet. An IP address essentially identifies the
location of a device on a network.
This means that if you are using your laptop at home, it will have been given an IP address when it connected to the internet. If you now take your
laptop to a coffee shop, and log into the internet again, it will be assigned a new IP address.
Unlike the MAC address which remains constant, the IP address changes each time you log in at different locations.
There are two versions of IP: IPv4 and IPv6. IPv4 is based on 32 bits and the address is written as four groups of eight bits (shown in denary format); for
example:254.25.28.77
Because there are now so many devices connected to the internet, and this number is growing, in the future 32 bits will no longer be enough to give each
of them a unique address. Therefore, a newer version called IPv6 is now being used.
This uses a 128-bit address, which take the form of eight groups of hex digits; for
example:
A8FB:7A88:FFF0:0FFF:3D21:2085:66FB:F0FA
Prepared By Mr: Hussain K
Wi-Fi and Bluetooth
Both Wi-Fi and Bluetooth offer wireless communication between devices. They both use electromagnetic radiation as the carrier of data
transmission.
Bluetooth sends and receives radio waves in a band of 79 different frequencies (known as channels). These are all centered on a frequency of
2.45 GHz.
Devices using Bluetooth automatically detect and connect to each other, but they do not interfere with other devices because each
communicating pair uses a different channel (from the 79 options).
When a device wants to communicate, it picks one of the 79 channels at random to pair with another device. If the channel is already being
used, it randomly picks another channel. Once paired, to minimize the risks of interference with other devices, the devices constantly change
the channels they are using (several times a second).
This is known as spread-spectrum frequency hopping. Bluetooth uses key encryption to create a secure wireless personal area network
(WPAN).
Bluetooth is useful:
» when transferring data between two or more devices which are very close together (less than 30 meters distance)
» when the speed of data transmission is not critical
» for low-bandwidth applications (for example, when sending music files from a mobile phone to a headset).
Wi-Fi is a wireless networking technology makes it possible to connect devices with a wireless connection to a network or to a single
computer .
• Reduced cost of cabling/Safer – won’t trip over wires
• Easier to connect other devices to the network
• Makes the computer portable as long as it’s within range of the wireless access point
Prepared By Mr: Hussain K
The purposes of network include:
Sharing of data – Networking enables several computer users to share data. Thus individual users can work on the same
data at the same time. Depending on the configuration of the network, users work on real time updated data.
Sharing of peripheral devices – Networking enables several computer users to share laser printers, scanners, modems etc.
Typically, several computer users in the same office are served by a single printer. This is cost effective for organizations
with many computer users.
Sharing of programs – Networking enables several computer users to share the same programs. In most organizations,
people make use of the same software. Rather than purchasing individual software packages for each computer user,
organizations purchase network versions of the program.
Efficient communication – Networking enables efficient exchange messages and documents between several computer
users. Networking eliminates the typical delays encountered with standard inter-office mail delivery or telephone calls.
Prepared By Mr: Hussain K
Cloud Computing
Cloud computing is a method of data storage where data is stored on remote servers – there may be thousands of
servers in many different locations.
The same data is stored on more than one server in case of maintenance or repair, allowing clients to access data at
any time. This is known as data redundancy. The physical environment of the cloud servers is owned and
managed by a hosting company.
There are three common cloud storage systems:
» Public cloud – this is a storage environment where the customer/client and cloud storage provider are different
companies.
» Private cloud – this is storage provided by a dedicated environment behind a company firewall; customer/client
and cloud storage provider are integrated and operate as a single entity.
» Hybrid cloud – this is a combination of the two previous environments; some data resides in the private cloud
and less sensitive/less-commercial data can be accessed from a public cloud storage provider.
>>Instead of, or in addition to, saving data on a local hard disk or other storage device, a user can save their data ‘in the
cloud’.
Prepared By Mr: Hussain K
Advantages of cloud computing (storage)
» Customer/client files stored in the cloud can be accessed at any time, from any device, anywhere in the world, as
long as internet access is available.
» There is no need for a customer/client to carry an external storage device with them, or even use the same
computer, to store and retrieve information.
» The cloud provides the user with remote backup of data, with obvious advantages in the event of data
loss/disaster recovery on their own computer.
» If a customer/client has a failure of their hard disk or backup device, cloud storage will allow recovery of their
data.
» The cloud system offers almost unlimited storage capacity (at a price!).
Prepared By Mr: Hussain K
Disadvantages of cloud computing (storage)
» Security aspects of storing data in the cloud (see comments later on).
» If the customer/client has a slow or unstable internet connection, they could have many problems accessing or
downloading their data/files.84
» Costs can be high if a large storage capacity or high download/upload data transfer is required.
» The potential failure of the cloud storage company is always possible – this poses a risk of loss of all backup data.
Prepared By Mr: Hussain K
You might also like
- Computer Networking: An introductory guide for complete beginners: Computer Networking, #1From EverandComputer Networking: An introductory guide for complete beginners: Computer Networking, #1Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (2)
- Sun Cluster 3.2 Student GuideDocument602 pagesSun Cluster 3.2 Student GuideLiew Kok HowNo ratings yet
- Computer Network Notes Class 12Document13 pagesComputer Network Notes Class 12om100% (1)
- Basic Computer Network PDFDocument35 pagesBasic Computer Network PDFTep TepNo ratings yet
- Unix Commands For Oracle AppsDocument13 pagesUnix Commands For Oracle AppsRabindra P.SinghNo ratings yet
- Computer Networking NotesDocument28 pagesComputer Networking NotesAnujNo ratings yet
- Networking Concepts: by Mrudula Marathe Grade 8 Ekam Roll No: 14Document11 pagesNetworking Concepts: by Mrudula Marathe Grade 8 Ekam Roll No: 14Mrudula Marathe [Borivali]No ratings yet
- 9 IG - Chapter 4 - SummaryDocument53 pages9 IG - Chapter 4 - SummaryMohab MqattashNo ratings yet
- Networks Summary ICTDocument7 pagesNetworks Summary ICTTomás BORRASASNo ratings yet
- G11 2nd Term ICT Notes - Week 1Document7 pagesG11 2nd Term ICT Notes - Week 1fatima manuel AzarateNo ratings yet
- Computer NetworkDocument18 pagesComputer NetworkRaju LalNo ratings yet
- Computer Network Notes Class 12Document14 pagesComputer Network Notes Class 12Mohit HoodaNo ratings yet
- 4.1. NetworksDocument26 pages4.1. NetworksSara Ali100% (1)
- Hardware Componenets of NetworkDocument13 pagesHardware Componenets of NetworkZain AlyNo ratings yet
- The Common Network DevicesDocument14 pagesThe Common Network DevicesNylevonNo ratings yet
- What Is A Computer Network - Lecture - 5aDocument6 pagesWhat Is A Computer Network - Lecture - 5atantos557No ratings yet
- Hardware Componenets of NetworkDocument13 pagesHardware Componenets of NetworkZain AlyNo ratings yet
- W-10 Introduction To Network1Document28 pagesW-10 Introduction To Network1aminurrahman333No ratings yet
- Computer Networks IGCSE 2022 New SyllabusDocument124 pagesComputer Networks IGCSE 2022 New SyllabusitzmeayinibNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of NetworkDocument52 pagesFundamentals of Networkumurita37No ratings yet
- Study of Networking Devices: Network Interface CardsDocument17 pagesStudy of Networking Devices: Network Interface CardsvikashNo ratings yet
- What Is A Network?Document9 pagesWhat Is A Network?amrit singhaniaNo ratings yet
- Network DevicesDocument15 pagesNetwork DevicesShilpa PutanikarNo ratings yet
- Unit 4 - Networks and The Effects of Using ThemDocument12 pagesUnit 4 - Networks and The Effects of Using ThemEdwardNo ratings yet
- Components of Computer NetworksDocument7 pagesComponents of Computer NetworksLaurNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 Chapter 7Document7 pagesUnit 2 Chapter 7deshmukhkushal094No ratings yet
- Networking Lecture Summary 1Document8 pagesNetworking Lecture Summary 1Reaper XNo ratings yet
- Data Communication and Computer NetworksDocument151 pagesData Communication and Computer NetworksmandviNo ratings yet
- Lanwan Network DevicesDocument3 pagesLanwan Network DevicesVIKALP KULSHRESTHANo ratings yet
- Computer NetworkDocument32 pagesComputer Networkcapt shivakumarNo ratings yet
- Network Devices: Digital Digital AnalogueDocument6 pagesNetwork Devices: Digital Digital AnalogueAbygayle IveyNo ratings yet
- W-10 Introduction To InternetDocument44 pagesW-10 Introduction To InternetUmair AhmadNo ratings yet
- Activity 5 CNDocument15 pagesActivity 5 CNshifa dafedarNo ratings yet
- ST Anselm.'S SR Sec School, AjmerDocument9 pagesST Anselm.'S SR Sec School, Ajmermaanvendra singh rajawatNo ratings yet
- CHPT 4Document23 pagesCHPT 4eimoncho173No ratings yet
- CH 1 Basics of NetworkingDocument32 pagesCH 1 Basics of NetworkingRanganath KrishnaNo ratings yet
- XII Cs Summary Notes 23 24Document12 pagesXII Cs Summary Notes 23 24Piyush MishraNo ratings yet
- Assignment From Server Room-Esther EzekielDocument3 pagesAssignment From Server Room-Esther EzekielEsther EzekielNo ratings yet
- U3 Communication Technology A LevelDocument59 pagesU3 Communication Technology A LevelsurnewardsNo ratings yet
- U3 Communication Technology Network A LevelDocument42 pagesU3 Communication Technology Network A LevelsurnewardsNo ratings yet
- U3 Communication Technology NetworkDocument62 pagesU3 Communication Technology NetworksurnewardsNo ratings yet
- Network Hardware: LO 2:-Install and Configure Internet and ServicesDocument2 pagesNetwork Hardware: LO 2:-Install and Configure Internet and ServicesIsrael KifleNo ratings yet
- 12 - Network Devices or ComponentsDocument3 pages12 - Network Devices or ComponentsOmer107100% (1)
- Introduction To Computer Network: by Ajay Singh Meena Class: Xii-E Roll No.: 04Document30 pagesIntroduction To Computer Network: by Ajay Singh Meena Class: Xii-E Roll No.: 04Ajay Singh MeenaNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Computer Network: by Ajay Singh Meena Class: Xii-E Roll No.: 04Document30 pagesIntroduction To Computer Network: by Ajay Singh Meena Class: Xii-E Roll No.: 04Ajay Singh MeenaNo ratings yet
- Computer NetworkDocument9 pagesComputer NetworkNirmanyu SoodNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1 - Introduction To NetworkingDocument37 pagesLecture 1 - Introduction To NetworkingAdam MuizNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1. Introduction: Basic of NetworkingDocument28 pagesChapter 1. Introduction: Basic of NetworkingAmanNo ratings yet
- Networks and The Effects of Using ThemDocument23 pagesNetworks and The Effects of Using ThemSeif MahmoudNo ratings yet
- Chapter4-Networking - Term2Document12 pagesChapter4-Networking - Term2Mohammad MoosaNo ratings yet
- Final Network Fdsklajf Dsafjlk Dsafjsdajf Sajksdjaf Jsldajdjfj JFJFJFJFJ FJFJFJFJF Jslafjlk Sdjalfkj Dsafjlkjlsad J Lasjlkjlj LJSD FaDocument5 pagesFinal Network Fdsklajf Dsafjlk Dsafjsdajf Sajksdjaf Jsldajdjfj JFJFJFJFJ FJFJFJFJF Jslafjlk Sdjalfkj Dsafjlkjlsad J Lasjlkjlj LJSD FaJether Pactol TeroNo ratings yet
- Network Tools and Testing DevicesDocument9 pagesNetwork Tools and Testing DevicesCamilleNo ratings yet
- Management Information System Unit - 1: Network and Its ComponentsDocument6 pagesManagement Information System Unit - 1: Network and Its ComponentsSourav DasNo ratings yet
- ICT Study Docs Term 1: TopicsDocument25 pagesICT Study Docs Term 1: Topicshaneefa yusufNo ratings yet
- Computer NetworkingDocument15 pagesComputer NetworkingkentNo ratings yet
- NETWORKDocument13 pagesNETWORKmanav dodaniNo ratings yet
- Files 1 2018 June NotesHubDocument 1528361608Document10 pagesFiles 1 2018 June NotesHubDocument 1528361608sumit kumarNo ratings yet
- C4e580a2 1635313557264Document20 pagesC4e580a2 1635313557264AdipNo ratings yet
- Ln.5 - Computer NetworkingDocument16 pagesLn.5 - Computer NetworkingKrittika 55No ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Lesson 1Document57 pagesChapter 2 Lesson 1casseyareolaNo ratings yet
- Grade 5Document1 pageGrade 5hussain korirNo ratings yet
- Primary Time Block Time TableDocument1 pagePrimary Time Block Time Tablehussain korirNo ratings yet
- School Pupilage Record 2022-2023 by 26TH Sept 2022Document5 pagesSchool Pupilage Record 2022-2023 by 26TH Sept 2022hussain korirNo ratings yet
- LabelsDocument4 pagesLabelshussain korirNo ratings yet
- Grade SevenDocument1 pageGrade Sevenhussain korirNo ratings yet
- Primary BlankDocument1 pagePrimary Blankhussain korirNo ratings yet
- Grade FourDocument1 pageGrade Fourhussain korirNo ratings yet
- Grade SixDocument1 pageGrade Sixhussain korirNo ratings yet
- Schemes Geography Year 6 2022Document3 pagesSchemes Geography Year 6 2022hussain korirNo ratings yet
- ROBOTICS Yr9Document10 pagesROBOTICS Yr9hussain korirNo ratings yet
- Yasser HussainDocument1 pageYasser Hussainhussain korirNo ratings yet
- Samara MariaDocument1 pageSamara Mariahussain korirNo ratings yet
- TermsDocument19 pagesTermshussain korirNo ratings yet
- Rivers Year SixDocument16 pagesRivers Year Sixhussain korirNo ratings yet
- Junior TelaDocument1 pageJunior Telahussain korirNo ratings yet
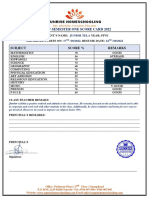
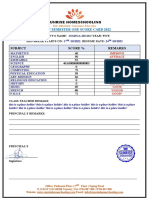
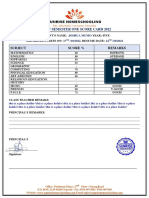
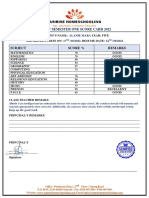
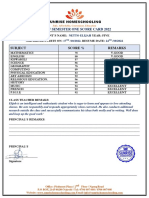
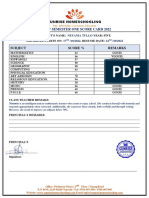
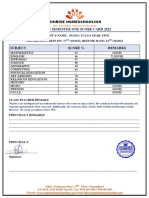
- Score Card TemplateDocument1 pageScore Card Templatehussain korirNo ratings yet
- Ella KendiDocument1 pageElla Kendihussain korirNo ratings yet
- Joshua MumoDocument1 pageJoshua Mumohussain korirNo ratings yet
- Ariana MainaDocument1 pageAriana Mainahussain korirNo ratings yet
- ALLANIEDocument1 pageALLANIEhussain korirNo ratings yet
- Gibson WamaeDocument1 pageGibson Wamaehussain korirNo ratings yet
- Reyian RisaDocument1 pageReyian Risahussain korirNo ratings yet
- Netto ElijahDocument1 pageNetto Elijahhussain korirNo ratings yet
- Pola SakwaDocument1 pagePola Sakwahussain korirNo ratings yet
- Noni GathoniDocument1 pageNoni Gathonihussain korirNo ratings yet
- Netania TulloDocument1 pageNetania Tullohussain korirNo ratings yet
- Nessia TulloDocument1 pageNessia Tullohussain korirNo ratings yet
- 2019 Version 70-741 Dumps With VCE and PDFDocument91 pages2019 Version 70-741 Dumps With VCE and PDFwilvarelNo ratings yet
- R - How To Do Web Scraping of Key Stats From FinViz Tables Per Stock - Stack OverflowDocument3 pagesR - How To Do Web Scraping of Key Stats From FinViz Tables Per Stock - Stack OverflowdopiorototoNo ratings yet
- GC1000 GS Modbus 04 PDFDocument6 pagesGC1000 GS Modbus 04 PDFmhafizanNo ratings yet
- DS Argos FeaturesDocument4 pagesDS Argos FeaturesGaston ZamoranoNo ratings yet
- Exam Az 500 Microsoft Azure Security TechnologiesDocument7 pagesExam Az 500 Microsoft Azure Security TechnologiesAldo SENo ratings yet
- IMPRESS - Digital Presentation Class IX Unit 5: Multiple Choice QuestionsDocument6 pagesIMPRESS - Digital Presentation Class IX Unit 5: Multiple Choice QuestionsDeven Bari100% (1)
- Assignment PPSDocument27 pagesAssignment PPSAtharv DanaveNo ratings yet
- Access ch8Document6 pagesAccess ch8raj dosNo ratings yet
- Exception Handling in PL SQL Oracle PDFDocument2 pagesException Handling in PL SQL Oracle PDFJeffreyNo ratings yet
- Host Name Resolution RequirementsDocument1 pageHost Name Resolution RequirementsAvinash McaNo ratings yet
- ACX 780 781 8 Door Access Controller PDFDocument6 pagesACX 780 781 8 Door Access Controller PDFLesmes CarreroNo ratings yet
- COL331/COL633 Major Exam Operating Systems Sem II, 2016-17Document14 pagesCOL331/COL633 Major Exam Operating Systems Sem II, 2016-17Rohit JoshiNo ratings yet
- Seksion 1.1Document100 pagesSeksion 1.1zisngonoNo ratings yet
- Chap 09 MCDocument46 pagesChap 09 MCRituahNo ratings yet
- OODBMS&ORDBMSDocument43 pagesOODBMS&ORDBMSMohan KhedkarNo ratings yet
- HPDocument118 pagesHPjama99No ratings yet
- T Rec G.984.3 200402 S!!PDF eDocument116 pagesT Rec G.984.3 200402 S!!PDF eAnonymous GK9mHwnrNo ratings yet
- CodeDocument3 pagesCodeTranNguyenBaoKhangNo ratings yet
- CS9252Document2 pagesCS9252R Gandhimathi RajamaniNo ratings yet
- ELOprofessional 2011 Advanced Training - T2 - Komplett PDFDocument196 pagesELOprofessional 2011 Advanced Training - T2 - Komplett PDFpiciul2010No ratings yet
- GP1.Global Processing-R13Document38 pagesGP1.Global Processing-R13Gnana SambandamNo ratings yet
- BDII Tema02Document5 pagesBDII Tema02VanceaLoredanaNo ratings yet
- Database Course Outline INFO1101Document5 pagesDatabase Course Outline INFO1101Md Rubaiyat BhuiyanNo ratings yet
- 6.006 Introduction To Algorithms: Mit OpencoursewareDocument7 pages6.006 Introduction To Algorithms: Mit Opencoursewareraw.junkNo ratings yet
- A/d and D/a Convertor Digital TechnicsDocument6 pagesA/d and D/a Convertor Digital Technicskaran007_m100% (1)
- T Rec G.987.3 201010 S!!PDF eDocument134 pagesT Rec G.987.3 201010 S!!PDF eNghia DoNo ratings yet
- Ict 7 - Q1 ExamDocument3 pagesIct 7 - Q1 ExamdodongmakattigbasNo ratings yet
- Oracle Question BankDocument139 pagesOracle Question BankAlokdev MishraNo ratings yet