Professional Documents
Culture Documents
On Light: Science Holiday Homework Made By-Aish Mishra Class-8 Diamond Roll No.-6
Uploaded by
Ansh Mishra0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
10 views9 pagesOriginal Title
Ppt on light
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
10 views9 pagesOn Light: Science Holiday Homework Made By-Aish Mishra Class-8 Diamond Roll No.-6
Uploaded by
Ansh MishraCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 9
Ppt on light
Science holiday homework
Made by-aish Mishra
Class-8 diamond
Roll no.-6
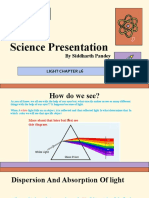
What is light ?
• Light is a form of energy that
enables us to see various things
present in our surroundings
• Light is an electromagnetic wave
that can travel through a medium
(any substance including air,
water, and glass) and vacuum. The
only natural source of light is
sunlight
• Light gets reflected off surfaces.
Any surface that is really well
polished or shiny acts as a mirror.
The phenomenon of light
bouncing off surfaces is called
reflection
• In an image formed by a
mirror the left of the
object appears on the
right and the right appears
Lateral inversion on the left. This is known
as lateral inversion.
L AW S O F
REFLECTION
• First law of reflection: According to the first
law, the incident ray, reflected ray, and normal
ray, all lie in the same plane.
• Second law of reflection: According to the
second law, the angle of reflection is always
equal to the angle of incidence. (∠i = ∠r)
Regular and
irregular reflection
• The kind of reflection in which
all reflected rays are parallel to
each other and it occurs
through a smooth surface is
called regular reflection
• When all the parallel rays
reflected from a rough or
irregular surface are not parallel,
the reflection is known as
diffused or irregular reflection
kaleidoscope
Image that is
seen through
• A kaleidoscope is an optical kaleidoscope
instrument with two or more reflecting
surfaces (or mirrors) tilted to each
other at an angle
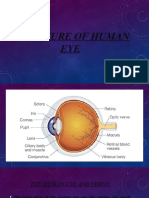
Human eye
• Light enters the eye through a thin membrane that
forms a transparent bulge on the front of the eye,
called the cornea.
• Iris is a dark muscular diaphragm that controls
the size of the pupil.
• The pupil is the small opening in the centre of the
iris.
• The lens which is behind the pupil helps to adjust
the focal length required to clearly focus on
objects at various distances.
• The retina is the screen where the images get
formed. It is a delicate membrane with a large
number of photosensitive cells called rods and
cones.
• Cones are sensitive to bright light and rods are
sensitive to dim light.
• The optic nerve transmits the electrical signals
from the eye to the brain
Persistence of human eye & defects of eye
•COMMON REFRACTIVE DEFECTS OF VISION.
• The impression (or sensation) of the • myopia or near-sightedness
object remains on the retina for • A person with myopia can see nearby
about (1/16)th of a second, even objects clearly but cannot see distant
after the object is removed from the objects distinctly.
sight. This continuance of the • hypermetropia or far – sightedness
sensation of eye is called the • A person with hypermetropia can see distant
persistence of vision. objects clearly but cannot see nearby objects
distinctly
• Presbyopia
• For most people, the near point gradually
recedes away. They find it difficult to see
nearby objects comfortably and distinctly
without corrective eye-glasses. This defect is
called Presbyopia
Care of eye
Too little or too much light is bad
It is necessary that you take
for eyes. Insufficient light causes
proper care of your eyes. If there
If advised, use suitable eyestrain and headaches. Too
is any problem you should go to
spectacles. much light, like that of the sun, a
an eye specialist. Have a regular
powerful lamp or a laser torch
checku
can injure the retina.
Never rub your eyes. If particles
of dust go into your eyes, wash Always read at the normal
Do not look at the sun or a your eyes with clean water. If distance for vision. Do not read
powerful light directly. there is no improvement go to a by bringing the book too close to
doctor. l Wash your eyes your eyes or keeping it too far.
frequently with clean water.
You might also like
- The Human Eye and The Colourful World: Anchli Singh, Class XADocument17 pagesThe Human Eye and The Colourful World: Anchli Singh, Class XAshashank100% (1)
- 8th Grade: Science PresentationDocument16 pages8th Grade: Science PresentationSaroj PandeyNo ratings yet
- Topic-The Human Eye: Submitted To. Submitted BYDocument10 pagesTopic-The Human Eye: Submitted To. Submitted BYsanju kumarNo ratings yet
- Class 8 Light PDFDocument5 pagesClass 8 Light PDFMamta JoshiNo ratings yet
- Class 8 Light Notes: Laws of ReflectionDocument4 pagesClass 8 Light Notes: Laws of ReflectionHagua MakuaNo ratings yet
- Light - 2Document42 pagesLight - 2Sarika AhujaNo ratings yet
- Anatomy Eye ReportDocument1 pageAnatomy Eye ReportbrylleNo ratings yet
- D.A.V Senior Secondary School: Biology Investigatory ProjectDocument22 pagesD.A.V Senior Secondary School: Biology Investigatory ProjecthashimNo ratings yet
- HSB Form 5 The EyeDocument9 pagesHSB Form 5 The Eyekevin maheshNo ratings yet
- Notes of 10th Cbse Human EyeDocument7 pagesNotes of 10th Cbse Human EyeAvichal TatuNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7: Light at Work: Lesson 7.1: The Human EyeDocument25 pagesChapter 7: Light at Work: Lesson 7.1: The Human EyeMar SelaNo ratings yet
- Reffractive ErrorsDocument13 pagesReffractive ErrorsSagiraju SrinuNo ratings yet
- Light Class 8 NotesDocument6 pagesLight Class 8 Notesthecakebox2007No ratings yet
- Human EyeDocument9 pagesHuman EyeNimish MalhotraNo ratings yet
- The Human Eye - StructureDocument8 pagesThe Human Eye - Structuremarealyn.hermida.camachoNo ratings yet
- Structure of Human Eye DipiyDocument10 pagesStructure of Human Eye Dipiyvineet_knwrNo ratings yet
- S - 8 - CH 16 - Ho 16.3 - LightDocument3 pagesS - 8 - CH 16 - Ho 16.3 - LightVector HuntNo ratings yet
- Coursebook: Track Your ProgressDocument5 pagesCoursebook: Track Your ProgressKrishaNo ratings yet
- The Human Eye: OpticsDocument43 pagesThe Human Eye: OpticsMichael BeltranNo ratings yet
- Refractiveerror 200625072525Document18 pagesRefractiveerror 200625072525Akshay BadoreNo ratings yet
- Physics CH 10Document12 pagesPhysics CH 10Zeel GajeraNo ratings yet
- 2nd Q Reviewer Science 10Document2 pages2nd Q Reviewer Science 10kingarthur012802No ratings yet
- CH 11Document30 pagesCH 11piyushNo ratings yet
- Human Eye NotesDocument10 pagesHuman Eye NotesBhavesh KalkhandaNo ratings yet
- Decoding Light: Siva PrasadDocument30 pagesDecoding Light: Siva PrasadAWS DEVELOPERNo ratings yet
- Sense of VisionDocument34 pagesSense of VisionqqqqqNo ratings yet
- Ch-11-Human Eye and The Colouful World 285-307 Physics Sem-1Document22 pagesCh-11-Human Eye and The Colouful World 285-307 Physics Sem-1MAYUR DESAI II BeingMD in PHYSICS IINo ratings yet
- 187 RefractionDocument5 pages187 RefractionShabir KhanNo ratings yet
- CL X Physics Ch-11 The Human EyeDocument12 pagesCL X Physics Ch-11 The Human EyeDeepanshu BindalNo ratings yet
- Class 8 Light and Vision Study MaterialDocument12 pagesClass 8 Light and Vision Study Materialasmit.cgrNo ratings yet
- Physics U2Document6 pagesPhysics U2Alima IqbalNo ratings yet
- What Are Refractive Errors?Document20 pagesWhat Are Refractive Errors?Eduardo Niepes Jr.No ratings yet
- Introduction To Light (Notes)Document7 pagesIntroduction To Light (Notes)Shivang GuptaNo ratings yet
- EyeDocument43 pagesEyeMichael BeltranNo ratings yet
- Human Eye and The Colorful World PDFDocument12 pagesHuman Eye and The Colorful World PDFJyothi DeepakNo ratings yet
- PresbiopiDocument4 pagesPresbiopiapriyani ramahliaNo ratings yet
- Optics and Refraction For 5 Year Medical Students Mutaz Gharaibeh, MDDocument52 pagesOptics and Refraction For 5 Year Medical Students Mutaz Gharaibeh, MDShahar ShababNo ratings yet
- Notes Human EyeDocument9 pagesNotes Human EyeGeetanshi OberoiNo ratings yet
- HypermetropiaDocument5 pagesHypermetropiaAnne Marian Anak JOSEPHNo ratings yet
- Presbyopia: What Is Presbyopia? What Is Refraction?Document2 pagesPresbyopia: What Is Presbyopia? What Is Refraction?UlfNo ratings yet
- Optics and Refraction For 5 Year Medical Students Mutaz Gharaibeh, MDDocument52 pagesOptics and Refraction For 5 Year Medical Students Mutaz Gharaibeh, MDHidayadNo ratings yet
- Light Sensitivity FactsheetDocument9 pagesLight Sensitivity FactsheetJuan DevotoNo ratings yet
- NCERT Books For Class 10 Science Chapter 11 Human Eye and Colorful WorldDocument18 pagesNCERT Books For Class 10 Science Chapter 11 Human Eye and Colorful WorldVanitha raoNo ratings yet
- Jesc111 MinDocument12 pagesJesc111 Min2021abhikchowdhuryNo ratings yet
- Light Human Eye 1Document53 pagesLight Human Eye 1Devika ManiNo ratings yet
- Lens and The EyeDocument58 pagesLens and The EyeEisle Keith Rivera TapiaNo ratings yet
- Physiology of VisionDocument49 pagesPhysiology of VisionPrakash PanthiNo ratings yet
- The Human EyeDocument38 pagesThe Human EyeDarlo HernandezNo ratings yet
- 5793565-Class 10 - Science - Phy - Human Eye and The Colourful World - Handouts - Shyni & VipinaDocument9 pages5793565-Class 10 - Science - Phy - Human Eye and The Colourful World - Handouts - Shyni & VipinaUrmila GNo ratings yet
- 3.2 Sense OrganDocument8 pages3.2 Sense OrganMod HollNo ratings yet
- CATARACTS and GLAUCOMADocument11 pagesCATARACTS and GLAUCOMAAmoroso, Marian Corneth D.No ratings yet
- Defects in Human EyeDocument10 pagesDefects in Human Eyechayan sarbadhikariNo ratings yet
- Eye Diseases: An Investigatory Project by Shrikanth Pillai XII BDocument11 pagesEye Diseases: An Investigatory Project by Shrikanth Pillai XII BCR7STUDIO 7100% (1)
- Physics of The EyeDocument59 pagesPhysics of The EyePrincess Dianna SulitNo ratings yet
- 11 Human Eye and Colorful World NotesDocument9 pages11 Human Eye and Colorful World NotesvenkatNo ratings yet
- Eent DisordersDocument12 pagesEent DisordersCarelle Faith Serrano AsuncionNo ratings yet
- Ch-10 Human Eye Notes FinalDocument27 pagesCh-10 Human Eye Notes Finalkilemas494No ratings yet
- Dr. - Montecalvo Prescribing PrismDocument187 pagesDr. - Montecalvo Prescribing PrismVan KochkarianNo ratings yet
- Refractive Errors (Najla) - 1Document74 pagesRefractive Errors (Najla) - 1Muhammad LukmanNo ratings yet
- 02 - Functional EquationsDocument2 pages02 - Functional EquationsGopinath PaikNo ratings yet
- Whats NewDocument30 pagesWhats NewCastro BagalanonNo ratings yet
- Class VIII Maths Question Bank For 2017 18 PDFDocument140 pagesClass VIII Maths Question Bank For 2017 18 PDFSujay BharadhwajNo ratings yet
- Ioqm by FiitjeeDocument94 pagesIoqm by FiitjeeAnsh MishraNo ratings yet
- RarDocument42 pagesRarntc7035No ratings yet
- Read MeDocument1 pageRead MeSourav SharmaNo ratings yet
- LicenseDocument3 pagesLicenseSourav SharmaNo ratings yet
- LICENSEDocument12 pagesLICENSEArafat AnamNo ratings yet
- RarDocument42 pagesRarntc7035No ratings yet
- H XXXXXXXXXXDocument1 pageH XXXXXXXXXXAnsh MishraNo ratings yet
- NewsDocument509 pagesNewsHWX10149No ratings yet
- EeDocument1 pageEeAnsh MishraNo ratings yet
- FFDocument2 pagesFFAnsh MishraNo ratings yet
- GGDocument1 pageGGAnsh MishraNo ratings yet
- DDDocument1 pageDDAnsh MishraNo ratings yet
- LicenseDocument3 pagesLicenseSourav SharmaNo ratings yet
- Read MeDocument1 pageRead MeSourav SharmaNo ratings yet
- RarDocument42 pagesRarntc7035No ratings yet
- YyDocument2 pagesYyAnsh MishraNo ratings yet
- Whats NewDocument30 pagesWhats NewCastro BagalanonNo ratings yet
- Architecture and Its Close Relationship With PhysicsDocument7 pagesArchitecture and Its Close Relationship With PhysicsMarco AponteNo ratings yet
- Signed-Off Science8 q1 Mod3 PotentialAndKineticEnergy Axaxv2Document23 pagesSigned-Off Science8 q1 Mod3 PotentialAndKineticEnergy Axaxv2sei gosa100% (4)
- Unit 4 Laser and Advances in MetrologyDocument74 pagesUnit 4 Laser and Advances in MetrologyS. SARGUNA THAMIZHAN MECHNo ratings yet
- Torsion in Circular ShaftDocument51 pagesTorsion in Circular ShaftHitesh MudgilNo ratings yet
- Iit RPR Ma201Document2 pagesIit RPR Ma201atggregNo ratings yet
- MITRES 6 008S11 Sol04 PDFDocument9 pagesMITRES 6 008S11 Sol04 PDFsowNo ratings yet
- Tes Master List of IMTE 2019 Back UpDocument120 pagesTes Master List of IMTE 2019 Back UprommyfebriNo ratings yet
- Lecture 07Document18 pagesLecture 07zaidNo ratings yet
- Fast Electrochemical Impedance Spectroscopy As A Statistical Condition Monitoring ToolDocument90 pagesFast Electrochemical Impedance Spectroscopy As A Statistical Condition Monitoring ToolrenatojrNo ratings yet
- ITR HV CablesDocument2 pagesITR HV CablesYulianti Rahmi PurnamawatiNo ratings yet
- Data Sheet 6ES7297-0AX30-0XA0: General InformationDocument2 pagesData Sheet 6ES7297-0AX30-0XA0: General InformationsebouelletNo ratings yet
- Design of Experiments - Week 1, 2Document50 pagesDesign of Experiments - Week 1, 2Akram KhanNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1 Math 311Document5 pagesLesson 1 Math 311mc604011No ratings yet
- Prodi Teknik Pertambangan, Fakultas Teknik, Universitas Islam Bandung, Jl. Tamansari No.1 Bandung 40116 EmailDocument12 pagesProdi Teknik Pertambangan, Fakultas Teknik, Universitas Islam Bandung, Jl. Tamansari No.1 Bandung 40116 EmailFajar ShodikNo ratings yet
- University of Bahrain Department of Mechanical Engineering MENG 263 TUTORIAL # 5 (Chapter 5)Document4 pagesUniversity of Bahrain Department of Mechanical Engineering MENG 263 TUTORIAL # 5 (Chapter 5)Vivin MathewNo ratings yet
- Nuclear and Particle Physics QuestionsDocument41 pagesNuclear and Particle Physics QuestionsSid KNo ratings yet
- DRD Rescue: Double Rope Descender With Two Jamming PositionsDocument3 pagesDRD Rescue: Double Rope Descender With Two Jamming PositionsferreiraNo ratings yet
- Failure Theories..Document93 pagesFailure Theories..adnanmominNo ratings yet
- Assignment n1Document1 pageAssignment n1Afzaal FiazNo ratings yet
- Air Dynamic Analysis of Wind and Dynamic Optimization of Solar PVDocument17 pagesAir Dynamic Analysis of Wind and Dynamic Optimization of Solar PValawi747594No ratings yet
- JP 32 91 260Document5 pagesJP 32 91 260MonikaNo ratings yet
- Class 6 Physics: (Lesson Details For Final Exams) : Syllabus: Chapter 2.07, 2.08 and 2.10Document2 pagesClass 6 Physics: (Lesson Details For Final Exams) : Syllabus: Chapter 2.07, 2.08 and 2.10tasnimNo ratings yet
- Newton, Isaac - The Correspondence of Isaac Newton (1959)Document517 pagesNewton, Isaac - The Correspondence of Isaac Newton (1959)Albus DumbledoreNo ratings yet
- Wright - Cosmology in AntiquityDocument206 pagesWright - Cosmology in AntiquityCuca Beludo100% (1)
- Material Test and Different Mix DesignDocument118 pagesMaterial Test and Different Mix DesignBekele MekonenNo ratings yet
- Example PDFDocument280 pagesExample PDFivoryhornNo ratings yet
- Kami Export - Ashton Gopaul - FL - 8.P - 8.4 - ClassifyingMatter - INTERVENTION - IndependentPracticeDocument2 pagesKami Export - Ashton Gopaul - FL - 8.P - 8.4 - ClassifyingMatter - INTERVENTION - IndependentPracticeAshton GopaulNo ratings yet
- Solid Mensuration 1Document16 pagesSolid Mensuration 1Franc Luiz VertudesNo ratings yet
- Power Factor Sizing GuideDocument6 pagesPower Factor Sizing GuideMatt SmithNo ratings yet
- Collision of Two Balls in A GrooveDocument8 pagesCollision of Two Balls in A GrooveHanif Daffa BramantyoNo ratings yet