Professional Documents
Culture Documents
What Is Translation Biology Class 12th
Uploaded by
Naman0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
39 views6 pagesTranslation is the process by which ribosomes in the cytoplasm synthesize proteins using mRNA produced from DNA transcription in the cell's nucleus. It involves three main steps - initiation, where the ribosome binds to the start codon on mRNA; elongation, where amino acids are sequentially added to form a polypeptide as the ribosome moves along mRNA; and termination, where a release factor binds to the stop codon and releases the complete polypeptide.
Original Description:
Original Title
What is Translation Biology class 12th
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentTranslation is the process by which ribosomes in the cytoplasm synthesize proteins using mRNA produced from DNA transcription in the cell's nucleus. It involves three main steps - initiation, where the ribosome binds to the start codon on mRNA; elongation, where amino acids are sequentially added to form a polypeptide as the ribosome moves along mRNA; and termination, where a release factor binds to the stop codon and releases the complete polypeptide.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
39 views6 pagesWhat Is Translation Biology Class 12th
Uploaded by
NamanTranslation is the process by which ribosomes in the cytoplasm synthesize proteins using mRNA produced from DNA transcription in the cell's nucleus. It involves three main steps - initiation, where the ribosome binds to the start codon on mRNA; elongation, where amino acids are sequentially added to form a polypeptide as the ribosome moves along mRNA; and termination, where a release factor binds to the stop codon and releases the complete polypeptide.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 6
Translation
by- Naman Rajpura
What is Translation ?
• Translation refers to the process of polymerization of amino acids to form a polypeptide.
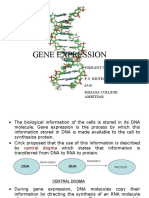
• In molecular biology and genetics, translation is the process in which ribosomes in the
cytoplasm or endoplasmic reticulum synthesize proteins after the process of transcription of DNA
to RNA in the cell's nucleus. The entire process is called gene expression.
• translation starts with its three steps-
1. Initiation
2. Elongation
3. Termination
Let’s discuss the steps in detail:
• Initiation - For initiation, the ribosome binds to the mRNA at the start codon (AUG)
that is recognised only by the initiator tRNA.
•Elongation-
1. The ribosome proceeds to the elongation phase of protein synthesis.
2. During elongation stage, complexes composed of an amino acid linked to tRNA, sequentially
bind to the appropriate codon in mRNA by forming complementary base pairs with the tRNA
anticodon.
3. The ribosome moves from codon to codon along the mRNA.
4.Amino acids are added one by one, translated into Polypeptide sequences dictated by DNA and
represented by mRNA.
•Termination - At the end, a release factor binds to the stop codon, terminating
translation and releasing the complete polypeptide from the ribosome.
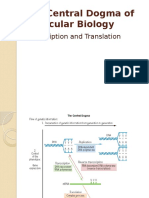
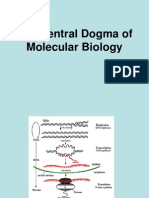
Translation diagram
Thank You
You might also like
- Microbial PhysiologyFrom EverandMicrobial PhysiologyAlbert G. MoatNo ratings yet
- Protein SynthesisDocument60 pagesProtein Synthesislucky mbaselaNo ratings yet
- Transciption and TranslationDocument31 pagesTransciption and TranslationDuduetsang MosalakataneNo ratings yet
- Nucleic Acid Metabolism TAUDocument38 pagesNucleic Acid Metabolism TAUFaatimah EssaNo ratings yet
- 22 - Protein BiosynthesisDocument34 pages22 - Protein Biosynthesisمحمد صالح ابراهيم محمدNo ratings yet
- Studying BiologyDocument62 pagesStudying BiologyNicolas AliasNo ratings yet
- Science FairDocument41 pagesScience FairSafanaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2Document33 pagesLecture 2SUNDAS FATIMANo ratings yet
- Transcription and RegulationDocument40 pagesTranscription and RegulationRUDRANSH PUJARINo ratings yet
- Protein SynthesisDocument7 pagesProtein SynthesisCreznin YapNo ratings yet
- Central Dogma of BiologyDocument28 pagesCentral Dogma of BiologyJabin Sta. TeresaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 Protein SynthesisDocument26 pagesChapter 5 Protein SynthesisT MokshithaNo ratings yet
- Transcriptiontranslation 170210171328Document34 pagesTranscriptiontranslation 170210171328Farah B. BtoushNo ratings yet
- L3 MLB 110 PROTEIN SYNTHESIS ATU CorectDocument18 pagesL3 MLB 110 PROTEIN SYNTHESIS ATU Corectmaxwell amponsahNo ratings yet
- Transcription and Translation 2Document21 pagesTranscription and Translation 2editing visualsNo ratings yet
- Kuliah 9 Gene Expression THB 2022Document28 pagesKuliah 9 Gene Expression THB 2022Dea puspita DewiNo ratings yet
- Ch. 14 - Gene Expression - From Gene To ProteinDocument9 pagesCh. 14 - Gene Expression - From Gene To ProteinMeera RaoNo ratings yet
- Eukaryote Translation PDFDocument21 pagesEukaryote Translation PDFChandra Mohan Meena100% (1)
- RNA and Protein Synthesis Notes - HONORS-Website PDFDocument30 pagesRNA and Protein Synthesis Notes - HONORS-Website PDFSphumelele AndiswaNo ratings yet
- Gene ExpressionDocument64 pagesGene ExpressiondesyNo ratings yet
- Grade 10 ReviewerDocument2 pagesGrade 10 ReviewerLanie De la TorreNo ratings yet
- Kuliah 8. Transcription (Oke)Document43 pagesKuliah 8. Transcription (Oke)Sinta DosiNo ratings yet
- Gene ExpressionDocument21 pagesGene ExpressionShowmiya NNo ratings yet
- Central Dogma (Module)Document63 pagesCentral Dogma (Module)Raab ReyesNo ratings yet
- Transcription and TranslationDocument43 pagesTranscription and TranslationSaqlain Ali ShahNo ratings yet
- RNA - Cell Physiology...Document13 pagesRNA - Cell Physiology...siddhi meenaNo ratings yet
- Regulation of Gene Expression in Eukaryotes: Presented by Quratulain (19-Arid-1403) Asadullah (19-Arid-1379)Document32 pagesRegulation of Gene Expression in Eukaryotes: Presented by Quratulain (19-Arid-1403) Asadullah (19-Arid-1379)Beauty LiciousNo ratings yet
- Physio Protein SynthesisDocument3 pagesPhysio Protein SynthesisM.TAYYAB KHANNo ratings yet
- Protein-Synthesis Online 1st ClassDocument43 pagesProtein-Synthesis Online 1st ClassAkasha khanNo ratings yet
- Introduction To ScienceDocument16 pagesIntroduction To SciencevergelglazaroNo ratings yet
- Microbial GeneticsDocument72 pagesMicrobial GeneticsKhánh Trà QuốcNo ratings yet
- CH 15Document26 pagesCH 15Mohammad RameezNo ratings yet
- TranscriptionDocument4 pagesTranscriptionkaiaNo ratings yet
- Central-Dogma 2Document22 pagesCentral-Dogma 2Milena De CresentNo ratings yet
- TDNº3 Part2Document3 pagesTDNº3 Part2selmi bouzidNo ratings yet
- Ekspresi GenDocument63 pagesEkspresi GenIndraPramanaIdaBagusNo ratings yet
- Protein Synthesis NotesDocument17 pagesProtein Synthesis Notesapi-655732711100% (1)
- 11b. Protein Synthesis - 2Document24 pages11b. Protein Synthesis - 2Arisha razaNo ratings yet
- Transcription Kezia Joice BautistaDocument43 pagesTranscription Kezia Joice BautistaKeziajoicee Bautista0% (1)
- Protein Synthesis: Teresia OkarinaDocument13 pagesProtein Synthesis: Teresia OkarinaTere CantikkNo ratings yet
- Translation: By: Racquel F. BaiganDocument23 pagesTranslation: By: Racquel F. BaiganJezTian ExplorerNo ratings yet
- Unit 4Document5 pagesUnit 4Jehitha CNo ratings yet
- Principles of Microbiology 1 (Summary)Document8 pagesPrinciples of Microbiology 1 (Summary)Mabelle DucusinNo ratings yet
- Gene Expression and Regulation-TRFDocument6 pagesGene Expression and Regulation-TRFAnanya PriyadarsineeNo ratings yet
- K3 - Central DogmaDocument41 pagesK3 - Central DogmaAditya MuchayatsyahNo ratings yet
- Unit 6. Proteins SynthesisDocument57 pagesUnit 6. Proteins Synthesismunyanezaolivier422No ratings yet
- Bio ToulouseDocument15 pagesBio ToulouseMohamed AlaeddinNo ratings yet
- 106 Ceng w10Document62 pages106 Ceng w10mertNo ratings yet
- Food Bioengineering: LIFS324Document96 pagesFood Bioengineering: LIFS324Dania LyewNo ratings yet
- Transcription and Translation.: Protein SynthesisDocument2 pagesTranscription and Translation.: Protein SynthesisShivani SriramNo ratings yet
- Gene Expression, RNA, Transcription and Translation: Higher Human BiologyDocument58 pagesGene Expression, RNA, Transcription and Translation: Higher Human BiologyShruthiNo ratings yet
- Gene Expression: Vikrant Joshi F.Y. Biotechnology 6519 Khalsa College AmritsarDocument31 pagesGene Expression: Vikrant Joshi F.Y. Biotechnology 6519 Khalsa College Amritsarvikrant4018No ratings yet
- 6 Lecture-TranslationDocument25 pages6 Lecture-Translationmoazzanrana678No ratings yet
- Translation of mRNA (Protein Synthesis)Document80 pagesTranslation of mRNA (Protein Synthesis)Cok AnggaNo ratings yet
- DNA, RNA and ProteinsDocument47 pagesDNA, RNA and ProteinsShanice RhuleNo ratings yet
- The Central Dogma of Molecular Biology: Transcription and TranslationDocument37 pagesThe Central Dogma of Molecular Biology: Transcription and TranslationfangirltonNo ratings yet
- Translation Process (Protein Biosynthesis) & The Genetic CodeDocument70 pagesTranslation Process (Protein Biosynthesis) & The Genetic CodeAlexandro Ivan CahyadiNo ratings yet
- From Gene To ProteinDocument18 pagesFrom Gene To Proteinakramtiti0% (1)
- Central DogmaDocument15 pagesCentral DogmaJean Rene100% (1)