Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Maintenance of Machinery and Installation (Meng5311) : Adama Science and Technology University
Uploaded by
Abel MeketaOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Maintenance of Machinery and Installation (Meng5311) : Adama Science and Technology University
Uploaded by
Abel MeketaCopyright:
Available Formats
Maintenance of Machinery and
Installation (MEng5311)
Adama Science and Technology University
School of Mechanical, Chemical and Materials Engineering
Department of Mechanical Engineering
03/06/2022 Prepared by Biftu H. and Kuba D.
Chapter 1
Introduction
1. Background of Maintenance
2. Objectives of Maintenance and Maintenance Engineering
3. Maintenance Functions
4. Classification Of Maintenance
03/06/2022 Prepared by Biftu H. and Kuba D.
CHAPTER OBJECTIVES
At the end of this chapter the student will be able to:
Define maintenance
Explain the needs of maintenance
Identify the terms of maintenance
Describe the main objective of
maintenance
Discuss about maintenance function
03/06/2022 Prepared by Biftu H. and Kuba D.
Background
Maintenance of equipment is still a challenge due to factors such as size,
cost, complexity, and competition
Effective asset management and maintenance practices that will
positively influence critical success factors such as safety, product
quality, speed of innovation, price, profitability, and reliable delivery.
Each year billions of dollars are spent on equipment maintenance around
the world
Maintenance engineering is a discipline that assists in acquisition of
resources needed for maintenance, and provides policies and plans for
the use of resources in performing or accomplishing maintenance
03/06/2022 Prepared by Biftu H. and Kuba D.
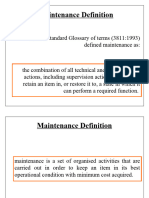
Definition of Maintenance
• Maintenance engineering and maintenance have the same end
objective or goal (ready equipment/item at minimum cost)
• Maintenance:
– All actions appropriate for retaining an item/part/equipment
in, or restoring it to, a given condition.
• Maintenance engineering:
– The activity of equipment/item maintenance that develops
concepts, criteria, and technical requirements in conception
and acquisition phases to be used and maintained in a
current status during the operating phase to assure effective
maintenance support of equipment.
– is an analytical function as well as it is deliberate and
methodical
03/06/2022 Prepared by Biftu H. and Kuba D.
Maintenance Facts and Figures
Each year U. S spent over $300 billion for maintenance,
Approximately 80% of this is spent to correct the chronic failure
of machines, systems, and people.
Maintenance cost the United Kingdom (UK) was approximately
£3000 million annually.
The typical size of a plant maintenance group in a manufacturing
organization varied from 5 to 10% of the total operating force.
The operation and maintenance budget request of the U.S.
Department of Defense for fiscal year 1997 was on the order of
$79 billion.
03/06/2022 Prepared by Biftu H. and Kuba D.
cont ..
Annually, the U.S. Department of Defense spends around $12 billion for depot
maintenance of weapon systems and equipment: Navy (59%), Air Force (27%),
Army (13%), and others (1%).
In 1968, it was estimated that better maintenance practices in the U.K. could have
saved approximately £300 million annually of lost production due to equipment
unavailability.
03/06/2022 Prepared by Biftu H. and Kuba D.
Maintenance management is the process of overseeing
maintenance resources so that the organization does not
experience downtime from broken equipment or waste money on
inefficient maintenance procedures.
Maintenance management software (MMS) programs can assist
with the process.
The primary objectives of maintenance management are to
schedule work efficiently, control costs and ensure regulatory
compliance.
03/06/2022 Prepared by Biftu H. and Kuba D.
Terms and definitions used in engineering maintenance
Maintenance:- All appropriate actions for retaining an
item/equipment in, or restoring it to, a given condition.
Maintenance engineering: The activity of equipment/item
maintenance that develops concepts, criteria, and technical
requirements in conceptional and acquisition/gaining phases to be
used and maintained in a current status during the operating phase to
assure effective maintenance support of equipment.
Preventive maintenance: All actions carried out on a planned,
periodic, and specific schedule to keep an` item/equipment in stated
working condition through the process of checking and
reconditioning.
03/06/2022 Prepared by Biftu H. and Kuba D.
Cont, …
Corrective maintenance: The unscheduled maintenance or repair to
return items/equipment to a defined state and carried out because
maintenance persons or users perceived deficiencies or failures
Predictive maintenance: The use of modern measurement and signal-
processing methods to accurately diagnose item/equipment condition
during operation.
Maintenance concept: A statement of the overall concept of the
item/product specification or policy that controls the type of maintenance
action to be employed for the item under consideration.
Maintenance plan: A document that outlines the management and
technical procedure to be employed to maintain an item; usually describes
facilities, tools, schedules, and resources.
Reliability:
03/06/2022
The probabilityPrepared
that byan item will perform its stated function
Biftu H. and Kuba D.
Cont, …
Maintainability: The probability that a failed item will be restored to
adequately working condition.
Active repair time: The component of downtime when repair persons
are active to effect a repair.
Mean time to repair (MTTR): A figure of merit depending on item
maintainability equal to the mean item repair time. In the case of
exponentially distributed times to repair, MTTR is the reciprocal of the
repair rate.
Overhaul: A comprehensive/complete inspection and restoration of an
item or a piece of equipment to an acceptable level at a durability time or
usage limit.
03/06/2022 Prepared by Biftu H. and Kuba D.
Cont, …
Quality: The degree to which an item, function, or process
satisfies requirements of customer and user.
Maintenance person: An individual who conducts
preventive maintenance and responds to a user’s service call
to a repair facility, and performs corrective maintenance on
an item. Also called custom engineer, service person,
technician, field engineer, mechanic, repair person, etc.
Inspection: The qualitative observation of an item’s
performance or condition.
03/06/2022 Prepared by Biftu H. and Kuba D.
Objectives of Maintenance
Improve maintenance operations,
Reduce the amount and frequency of maintenance,
Reduce the effect of complexity,
Reduce the maintenance skills required,
Reduce the amount of supply support,
Establish optimum frequency and extent of preventive maintenance
to be carried out,
Improve and ensure maximum utilization of maintenance facilities,
and improve the maintenance organization.
03/06/2022 Prepared by Biftu H. and Kuba D.
All over the world, industries have various ways to organize
maintenance activities, namely;
planned,
unplanned,
preventive,
corrective, or
predictive maintenance.
The primary objective is arrived at achieving maximum plant
availability at minimum cost, that is: To prevent breakdown of
equipment,
03/06/2022 Prepared by Biftu H. and Kuba D.
Cont, …
To prolong the life span of equipment,
To restore equipment to acceptable condition with minimum
delay after an eventual breakdown.
03/06/2022 Prepared by Biftu H. and Kuba D.
Generally, the objectives of maintenance should be
consistent with and subordinate to production goals.
The relation between maintenance objectives and
production goals is reflected in the action of
keeping production machines and facilities in the best
possible condition.
Maximising production or increasing facilities
availability at the lowest cost and at the highest quality
and safety standards.
Reducing breakdowns and emergency shutdowns.
Optimising resources utilisation.
Prepared by Biftu H. and Kuba D. 03/06/2022
Reducing downtime.
Improving spares stock control.
Improving equipment efficiency and reducing scrap
rate.
Minimising energy usage.
Optimising the useful life of equipment.
Providing reliable cost and budgetary control.
Identifying and implementing cost reductions.
Prepared by Biftu H. and Kuba D. 03/06/2022
PLANT
M Reducing Breakdowns
Maximising Production
A
I
Reducing Downtime
Minimising Energy Usage N
T
Optimising Useful Life of E Improving Equipment Efficiency
Equipment N
A
Providing Budgetary Control N Improving Inventory Control
C
Optimising Resource Utilisation E Implementing Cost Reduction
Figure 1: Objectives of Maintenance
Prepared by Biftu H. and Kuba D. 03/06/2022
Types of Maintenance
Run to Failure Maintenance (RTF)
Preventive Maintenance (PM)
Corrective Maintenance (CM)
Improvement Maintenance (IM)
Predictive Maintenance (PdM)
Reliability Cantered Maintenance (RCM)
Total Productive Maintenance (TPM)
Prepared by Biftu H. and Kuba D. 03/06/2022
MAINTENANCE
PLANNED UNPLANNED
MAINTENANCE MAINTENANCE
(PROACTIVE) (REACTIVE)
EMERGENCY BREAKDOWN
PREDECTIVE PREVENTIVE IMPROVEMENT CORRECTIVE
MAINTENANCE MAINTENANCE MAINTENANCE MAINTENANCE
STATISTICAL - CONDITION - DEFERRED REMEDIAL
ENGINEERING DESIGN - OUT
BASED BASED
SERVICES
Shutdown Maintenance
WINDOW RUNNING ROUTINE OPPORTU- SHUTDOWN SHUTDOWN SHUTDOWN
NITY PREVENTIVE IMPROVEMENT CORRECTIVE
Figure 2: Types of Maintenance
Prepared by Biftu H. and Kuba D. 03/06/2022
Run to Failure Maintenance (RTF)
• It is the oldest type of maintenance.
• The required repair, replacement, or restore action
performed on a machine or a facility after the
occurrence of a failure in order to bring this machine
or facility to at least its minimum acceptable
condition.
Prepared by Biftu H. and Kuba D. 03/06/2022
Cont, …
• It is subdivided into two types:
– Emergency maintenance: it is carried out as fast
as possible in order to bring a failed machine or
facility to a safe and operationally efficient
condition.
– Breakdown maintenance: it is performed after
the occurrence of an advanced considered failure
for which advanced provision has been made in
the form of repair method, spares, materials,
labour and equipment.
Prepared by Biftu H. and Kuba D. 03/06/2022
Cont, …
• Disadvantages:
1. Its activities are expensive in terms of both direct and
indirect cost.
2. Using this type of maintenance, the occurrence of a failure
in a component can cause failures in other components in
the same equipment, which leads to low production
availability.
3. Its activities are very difficult to plan and schedule in
advance.
Prepared by Biftu H. and Kuba D. 03/06/2022
Cont, …
• This type of maintenance is useful in the following
situations:
1. The failure of a component in a system is unpredictable.
2. The cost of performing run to failure maintenance activities
is lower than performing other activities of other types of
maintenance.
3. The equipment failure priority is too low in order to include
the activities of preventing it within the planned
maintenance budget.
Prepared by Biftu H. and Kuba D. 03/06/2022
Preventive Maintenance (PM)
It is a set of activities that are performed on plant
equipment, machinery, and systems before the
occurrence of a failure in order to protect them and to
prevent or eliminate any degradation in their operating
conditions.
The maintenance carried out at predetermined intervals
or according to prescribed criteria and intended to
reduce the probability of failure or the degradation of
the functioning and the effects limited.
• The advantage of applying preventive maintenance
activities is to satisfy most of maintenance objectives.
Prepared by Biftu H. and Kuba D. 03/06/2022
Cont, …
The factors that affect the efficiency of this type of maintenance:
1. The need for an adequate number of staff in the maintenance
department in order to perform this type of maintenance.
2. The right choice of production equipment and machinery that
is suitable for the working environment and that can tolerate
the workload of this environment.
3. The required staff qualifications and skills, which can be
gained through training.
4. The support and commitment from executive management to
the PM programme.
5. The proper planning and scheduling of PM programme.
6. The ability to properly apply the PM programme.
Prepared by Biftu H. and Kuba D. 03/06/2022
Cont, …
It is good for those machines and facilities which
their failure would cause serious production losses.
Its aim is to maintain machines and facilities in such a
condition that breakdowns and emergency repairs are
minimised.
Its activities include replacements, adjustments,
major overhauls, inspections and lubrications.
Prepared by Biftu H. and Kuba D. 03/06/2022
Cont, …
Researchers subdivided preventive maintenance into different kinds
according to the nature of its activities:
Routine maintenance which includes those maintenance activities
that are repetitive and periodic in nature such as lubrication,
cleaning, and small adjustment.
Running maintenance which includes those maintenance activities
that are carried out while the machine or equipment is running and
they represent those activities that are performed before the actual
preventive maintenance activities take place.
Opportunity maintenance which is a set of maintenance activities
that are performed on a machine or a facility when an unplanned
opportunity exists during the period of performing planned
maintenance activities to other machines or facilities.
Window maintenance which is a set of activities that are carried out
when a machine or equipment is not required for a definite period
of time.
Shutdown preventive maintenance, which is a set of preventive
maintenance activities that are carried out when the production line
is in total stoppage situation. 03/06/2022
Prepared by Biftu H. and Kuba D.
Corrective Maintenance (CM)
• In this type, actions such as repair, replacement, or
restore will be carried out after the occurrence of a
failure in order to eliminate the source of this
failure or reduce the frequency of its occurrence.
In the British Standard 3811:1993 Glossary of terms,
corrective maintenance is defined as
The maintenance carried out after recognition and intended
to put an item into a state in which it can perform a required
function.
Prepared by Biftu H. and Kuba D. 03/06/2022
Cont, …
This type of maintenance is subdivided into three types:
1. Remedial maintenance, which is a set of activities that
are performed to eliminate the source of failure without
interrupting the continuity of the production process.
The way to carry out this type of corrective maintenance is by
taking the item to be corrected out of the production line and
replacing it with reconditioned item or transferring its workload
to its redundancy.
Prepared by Biftu H. and Kuba D. 03/06/2022
Cont, …
2. Deferred maintenance, which is a set of corrective
maintenance activities that are not immediately
initiated after the occurrence of a failure but are
delayed in such a way that will not affect the
production process.
3. Shutdown corrective maintenance, which is a set of
corrective maintenance activities that are performed
when the production line is in total stoppage situation.
Prepared by Biftu H. and Kuba D. 03/06/2022
Cont, …
• The main objectives of corrective maintenance are the
maximisation of the effectiveness of all critical plant
systems, the elimination of breakdowns, the elimination of
unnecessary repair, and the reduction of the deviations from
optimum operating conditions.
• The difference between corrective maintenance and
preventive maintenance is that for the corrective
maintenance, the failure should occur before any corrective
action is taken.
• Corrective maintenance is different from run to failure
maintenance in that its activities are planned and regularly
taken out to keep plant’s machines and equipment in
optimum operating condition.
Prepared by Biftu H. and Kuba D. 03/06/2022
Cont, …
• The way to perform corrective maintenance activities is by
conducting four important steps:
1. Fault detection.
2. Fault isolation.
3. Fault elimination.
4. Verification of fault elimination.
In the fault elimination step several actions could be taken
such as adjusting, aligning, calibrating, reworking,
removing, replacing or renovation.
Prepared by Biftu H. and Kuba D. 03/06/2022
Cont, …
• Corrective maintenance has several prerequisites in
order to be carried out effectively:
1. Accurate identification of incipient problems.
2. Effective planning which depends on the skills of the
planners, the availability of well developed maintenance
database about standard time to repair, a complete repair
procedures, and the required labour skills, specific tools,
parts and equipment.
3. Proper repair procedures.
4. Adequate time to repair.
5. Verification of repair.
Prepared by Biftu H. and Kuba D. 03/06/2022
Improvement Maintenance (IM)
• It aims at reducing or eliminating entirely the need for
maintenance.
• This type of maintenance is subdivided into three types as
follows:
1. Design-out maintenance which is a set of activities that
are used to eliminate the cause of maintenance, simplify
maintenance tasks, or raise machine performance from the
maintenance point of view by redesigning those machines
and facilities which are vulnerable to frequent occurrence of
failure and their long term repair or replacement cost is very
expensive.
Prepared by Biftu H. and Kuba D. 03/06/2022
Cont, …
2. Engineering services which includes construction and
construction modification, removal and installation, and
rearrangement of facilities.
3. Shutdown improvement maintenance, which is a set of
improvement maintenance activities that are performed
while the production line is in a complete stoppage situation.
Prepared by Biftu H. and Kuba D. 03/06/2022
Predictive Maintenance (PDM)
Predictive maintenance is a set of activities that detect changes
in the physical condition of equipment (signs of failure) in
order to carry out the appropriate maintenance work for
maximising the service life of equipment without increasing
the risk of failure.
It is classified into two kinds according to the methods of
detecting the signs of failure:
Condition-based predictive maintenance
Statistical-based predictive maintenance
Prepared by Biftu H. and Kuba D. 03/06/2022
Cont, …
Condition-based predictive maintenance depends on
continuous or periodic condition monitoring equipment to
detect the signs of failure.
Statistical-based predictive maintenance depends on
statistical data from the meticulous recording of the stoppages
of the in-plant items and components in order to develop
models for predicting failures.
Prepared by Biftu H. and Kuba D. 03/06/2022
Cont, …
The drawback of predictive maintenance is that it depends
heavily on information and the correct interpretation of the
information.
Some researchers classified predictive maintenance as a type
of preventive maintenance.
The main difference between preventive maintenance and
predictive maintenance is that predictive maintenance uses
monitoring the condition of machines or equipment to
determine the actual mean time to failure whereas preventive
maintenance depends on industrial average life statistics.
Prepared by Biftu H. and Kuba D. 03/06/2022
Reliability centered maintenance (RCM)
Reliability centered maintenance (RCM) is a process to ensure
that systems continue to do what their users require in their
present operating context.
It is generally used to achieve improvements in fields such as the
establishment of safe minimum levels of maintenance.
Successful implementation of RCM will lead to increase in cost
effectiveness, reliability, machine uptime, and a greater
understanding of the level of risk that the organization is
managing.
Reliability centered maintenance is an engineering framework
that enables the definition of a complete maintenance regimen.
It regards maintenance as the means to maintain the functions a
user may require of machinery in a defined operating context.
Prepared by Biftu H. and Kuba D. 03/06/2022
Cont, …
As a discipline it enables machinery stakeholders to monitor,
assess, predict and generally understand the working of their
physical assets.
This is embodied in the initial part of the RCM process
which is to identify the operating context of the machinery,
and write a Failure Mode Effects and Criticality Analysis
(FMECA).
The second part of the analysis is to apply the "RCM logic",
which helps determine the appropriate maintenance tasks for
the identified failure modes in the FMECA.
Once the logic is complete for all elements in the FMECA,
the resulting list of maintenance is "packaged", so that the
periodicities of the tasks are rationalized to be called up in
work packages; it is important not to destroy the applicability
of maintenance in this phase.
Prepared by Biftu H. and Kuba D. 03/06/2022
Cont, …
Lastly, RCM is kept live throughout the "in-service" life of
machinery, where the effectiveness of the maintenance is
kept under constant review and adjusted in light of the
experience gained.
RCM can be used to create a cost-effective maintenance
strategy to address dominant causes of equipment failure. It
is a systematic approach to defining a routine maintenance
program composed of cost-effective tasks that preserve
important functions.
Prepared by Biftu H. and Kuba D. 03/06/2022
Cont, …
The important functions (of a piece of equipment) to preserve with
routine maintenance are identified, their dominant failure modes and
causes determined and the consequences of failure ascertained.
Levels of criticality are assigned to the consequences of failure. Some
functions are not critical and are left to "run to failure" while other
functions must be preserved at all cost.
Maintenance tasks are selected that address the dominant failure causes.
This process directly addresses maintenance preventable failures.
Failures caused by unlikely events, non-predictable acts of nature, etc
will usually receive no action provided their risk (combination of severity
and frequency) is trivial (or at least tolerable).When the risk of such
failures is very high, RCM encourages (and sometimes mandates) the
user to consider changing something which will reduce the risk to a
tolerable level.
Prepared by Biftu H. and Kuba D. 03/06/2022
Cont, …
The result is a maintenance program that focuses scarce
economic resources on those items that would cause the
most disruption if they were to fail.
RCM emphasizes the use of Predictive Maintenance
(PdM) techniques in addition to traditional preventive
measures.
Prepared by Biftu H. and Kuba D. 03/06/2022
Total productive maintenance (TPM)
Total productive maintenance (TPM) is a system of maintaining
and improving the integrity of production and quality systems
through the machines, equipment, processes, and employees that
add business value to an organization.
TPM focuses on keeping all equipment in top working condition to
avoid breakdowns and delays in manufacturing processes.
TPM also focuses on the total Participation of individuals from
top management to shop floor (lower employees).
Prepared by Biftu H. and Kuba D. 03/06/2022
Cont, …
One of the main objectives of TPM is to increase the
productivity of plant and equipment with a modest investment in
maintenance.
Total quality management (TQM) and
total productive maintenance (TPM) are considered as the key
operational activities of the quality management system.
In order for TPM to be effective, the full support of the total
workforce is required.
This should result in accomplishing the goal of TPM: "Enhance
the volume of the production, employee morale and job
satisfaction."
Prepared by Biftu H. and Kuba D. 03/06/2022
Cont, …
The main objective of TPM is to increase the
Overall Equipment Effectiveness (OEE) of plant equipment.
TPM addresses the causes for accelerated deterioration while creating
the correct environment between operators and equipment to create
ownership.
OEE has three factors which are multiplied to give one measure called
OEE:
OEE = Performance * Availability * Quality
Each factor has two associated losses making 6 in total, these 6 losses
are as follows:
Performance = (1) running at reduced speed - (2) Minor Stops
Availability = (3) Breakdowns - (4) Product changeover
Quality = (5) Startup rejects - (6) Running rejects
The objective finally is to identify then prioritize and eliminate the
causes of the losses. This is done by self-managing teams that problem
solve. Employing consultants to create this culture is common practice.
Prepared by Biftu H. and Kuba D. 03/06/2022
The eight pillars of TPM are mostly focused on proactive and
preventative techniques for improving equipment reliability:
1. PROCESS AND MACHINE Improvement
2. Autonomous maintenance
3. Preventive/Planned Maintenance
4. Process Quality maintenance
5. Cost Deployment/ administrative work
6. Early Management of new Equipment
7. Training and Education
8. Safety sustain success and Health Environment
Prepared by Biftu H. and Kuba D. 03/06/2022
Figure 3: Pillars of TPM
Prepared by Biftu H. and Kuba D. 03/06/2022
You might also like
- Maintenance and Operational Reliability: 24 Essential Building BlocksFrom EverandMaintenance and Operational Reliability: 24 Essential Building BlocksNo ratings yet
- Professional DevelopmentDocument1 pageProfessional Developmentapi-488745276No ratings yet
- (Nikolaj Wolfson, Alexander Lerner, Leonid Roshal (B-Ok - CC)Document589 pages(Nikolaj Wolfson, Alexander Lerner, Leonid Roshal (B-Ok - CC)Andi sutandi100% (1)
- PFI Freediver ManualDocument69 pagesPFI Freediver ManualLuca MariniNo ratings yet
- Maintenance of Machinery and Installation (Meng5311) : Adama Science and Technology UniversityDocument16 pagesMaintenance of Machinery and Installation (Meng5311) : Adama Science and Technology UniversityAbel MeketaNo ratings yet
- Maintenance Engineering (CH: 2,0) : Instructors: Dr. M. Zeeshan Zahir Engr. Adnan RasheedDocument13 pagesMaintenance Engineering (CH: 2,0) : Instructors: Dr. M. Zeeshan Zahir Engr. Adnan RasheedMinhaj UllahNo ratings yet
- 0 MaintenanceDocument35 pages0 MaintenanceMohamed Al-OdatNo ratings yet
- Chapter Five - TEED 2106 - Maintenance Engineering NotesDocument23 pagesChapter Five - TEED 2106 - Maintenance Engineering Notesodeke aronNo ratings yet
- TX427 01 PDFDocument8 pagesTX427 01 PDFEdivaldo VisqueNo ratings yet
- Topic 1. Maintenance EngineeringDocument4 pagesTopic 1. Maintenance EngineeringJamil MenciasNo ratings yet
- Test 1 Dec 2014Document6 pagesTest 1 Dec 2014honshin1230% (1)
- Maintanance Engg MaterialDocument58 pagesMaintanance Engg MaterialSiva KrishnanNo ratings yet
- MaintenanceDocument35 pagesMaintenanceDINO FANNo ratings yet
- Building Maintenance Notes Part 1Document10 pagesBuilding Maintenance Notes Part 1Masagege100% (1)
- Mechanical Maintenance of Machines: V.NAVEEN KUMAR (09611A0351)Document58 pagesMechanical Maintenance of Machines: V.NAVEEN KUMAR (09611A0351)Suresh YadavNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 - Preventive and Predictive MaintenanceDocument61 pagesChapter 4 - Preventive and Predictive Maintenance000No ratings yet
- Introduction To Maintenance: Environment Maintenance and Safety 6 Semester Spring 2020Document50 pagesIntroduction To Maintenance: Environment Maintenance and Safety 6 Semester Spring 2020Jawad Ahmad Bin KhanNo ratings yet
- Construction EquipmentsDocument94 pagesConstruction EquipmentsArok A100% (2)
- Chapter 4 - Preventive and Predictive MaintenanceDocument61 pagesChapter 4 - Preventive and Predictive MaintenanceAzimZakwanNo ratings yet
- Planned Maintenance Vs Unplanned Maintenance and FDocument10 pagesPlanned Maintenance Vs Unplanned Maintenance and FNo NameNo ratings yet
- Financial JustificationDocument5 pagesFinancial JustificationDilippndtNo ratings yet
- Maintenance 1Document40 pagesMaintenance 1Muhammad BilalNo ratings yet
- Basic 9 Basic Tech 3RD Term E-NotesDocument17 pagesBasic 9 Basic Tech 3RD Term E-NotesAkinyemi OdunayoNo ratings yet
- Chapter (2) 2.0 Maintenance Management System: November 2017Document28 pagesChapter (2) 2.0 Maintenance Management System: November 2017Eslam MansourNo ratings yet
- Maintenance Engineering (CH: 2,0) : Instructors: Dr. M. Zeeshan Zahir Engr. Adnan RasheedDocument13 pagesMaintenance Engineering (CH: 2,0) : Instructors: Dr. M. Zeeshan Zahir Engr. Adnan RasheedAltamash MunirNo ratings yet
- BLD 304Document41 pagesBLD 304DavidNo ratings yet
- Advanced Maintenance Management: Jose K Puthur RCBSDocument178 pagesAdvanced Maintenance Management: Jose K Puthur RCBSSharath PanickerNo ratings yet
- Maintenence BasicsDocument51 pagesMaintenence BasicsKarim Magdy100% (1)
- Maintenance QualificationDocument10 pagesMaintenance Qualificationprashant parmarNo ratings yet
- Building Maintenance StrategyDocument8 pagesBuilding Maintenance StrategyNeels Ram100% (3)
- Preventive Maintenance Part IDocument21 pagesPreventive Maintenance Part IKABADDI RISINGNo ratings yet
- Makalah PMDocument28 pagesMakalah PMdarealzNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3A MaintenanceDocument43 pagesLecture 3A Maintenancemoyo josephNo ratings yet
- MEM AssignmentDocument17 pagesMEM AssignmentDibyanshu GuruNo ratings yet
- Maintenance Engineering (Che-405) : DR Sikander Rafiq Assoc. ProfessorDocument37 pagesMaintenance Engineering (Che-405) : DR Sikander Rafiq Assoc. ProfessorHajra AamirNo ratings yet
- ME2037 Maintenance EngineeringDocument46 pagesME2037 Maintenance Engineeringrp0212100% (2)
- LEC1 Maintenance DefinitionDocument35 pagesLEC1 Maintenance DefinitionabdulNo ratings yet
- Preventive Maintenance Part IDocument20 pagesPreventive Maintenance Part Ismodi20No ratings yet
- Maintenance of Medical EquipmentDocument33 pagesMaintenance of Medical EquipmentAbe CyberCrewPlusDotmy100% (1)
- Akif 2Document41 pagesAkif 2tazeem_akifNo ratings yet
- X IPMVP M - V Issues Statutory ReviewDocument53 pagesX IPMVP M - V Issues Statutory ReviewIvánArizaNo ratings yet
- Maintenance Engineering (ME6012)Document68 pagesMaintenance Engineering (ME6012)ElementifyItNo ratings yet
- Maintenance DefinitionDocument35 pagesMaintenance DefinitionVaraGoudNo ratings yet
- ME2037 Maintenance EngineeringDocument51 pagesME2037 Maintenance EngineeringVicky Vignesh100% (1)
- Operations Management: (Shashank Tilak)Document7 pagesOperations Management: (Shashank Tilak)Vijay Singh ThakurNo ratings yet
- Chap. OneDocument26 pagesChap. OnesitoawNo ratings yet
- SECOND SCHEDULE-energy Management Audit GuidelinesDocument5 pagesSECOND SCHEDULE-energy Management Audit GuidelinesClaris muthoniNo ratings yet
- Group 4Document19 pagesGroup 4Byamukama AsaphNo ratings yet
- LEC1-Maintenance DefinitionDocument35 pagesLEC1-Maintenance DefinitionMilin SutharNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Mee 506Document9 pagesIntroduction To Mee 506Akunwa GideonNo ratings yet
- Part 04 Preventive MaintenanceDocument26 pagesPart 04 Preventive MaintenancejayferjohnNo ratings yet
- Me6012 - Maintenance EngineeringDocument13 pagesMe6012 - Maintenance EngineeringIyswaryaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2 - COST CONCEPTS AND BEHAVIOURDocument41 pagesLecture 2 - COST CONCEPTS AND BEHAVIOUROkello PaulNo ratings yet
- Deputy Manager (Electrical) / Electrical Engineer: RequirementDocument4 pagesDeputy Manager (Electrical) / Electrical Engineer: RequirementSwarup NayakNo ratings yet
- Subject: Production and Operations Management Unit 5: Maintenance and Waste ManagementDocument19 pagesSubject: Production and Operations Management Unit 5: Maintenance and Waste ManagementAnonymous yL88Jj100% (1)
- Moving From Preventive To Predictive Maintenance To Enhance EfficiencyDocument44 pagesMoving From Preventive To Predictive Maintenance To Enhance EfficiencySteven CookeNo ratings yet
- CH 4Document63 pagesCH 4girma workuNo ratings yet
- Guidelines for Wind Resource Assessment: Best Practices for Countries Initiating Wind DevelopmentFrom EverandGuidelines for Wind Resource Assessment: Best Practices for Countries Initiating Wind DevelopmentNo ratings yet
- Economic Analysis of Climate-Proofing Investment ProjectsFrom EverandEconomic Analysis of Climate-Proofing Investment ProjectsNo ratings yet
- Energy Storage in Grids with High Penetration of Variable GenerationFrom EverandEnergy Storage in Grids with High Penetration of Variable GenerationNo ratings yet
- Guide for Asset Integrity Managers: A Comprehensive Guide to Strategies, Practices and BenchmarkingFrom EverandGuide for Asset Integrity Managers: A Comprehensive Guide to Strategies, Practices and BenchmarkingNo ratings yet
- Handbook for Developing Joint Crediting Mechanism ProjectsFrom EverandHandbook for Developing Joint Crediting Mechanism ProjectsNo ratings yet
- Worksheet OneDocument3 pagesWorksheet OneAbel MeketaNo ratings yet
- PPC Individual AssignmentDocument1 pagePPC Individual AssignmentAbel MeketaNo ratings yet
- Table of ContentsDocument7 pagesTable of ContentsAbel MeketaNo ratings yet
- Trouble Shooting and Diagnosis of Machine Component MaintenanceDocument23 pagesTrouble Shooting and Diagnosis of Machine Component MaintenanceAbel MeketaNo ratings yet
- Coca-Cola Vending MachineDocument27 pagesCoca-Cola Vending MachineAbel MeketaNo ratings yet
- Fuel Supply System1Document96 pagesFuel Supply System1Abel MeketaNo ratings yet
- Plastic Injection Molding MachineDocument21 pagesPlastic Injection Molding MachineAbel MeketaNo ratings yet
- Adama Science and Technology University: School of Mechanical, Chemical & Materials EngineeringDocument12 pagesAdama Science and Technology University: School of Mechanical, Chemical & Materials EngineeringAbel MeketaNo ratings yet
- Machine Shop ReportDocument8 pagesMachine Shop ReportNazib Ul Islam Sazib78% (9)
- Ijeit1412201301 15Document4 pagesIjeit1412201301 15ennaguNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Welding Technology and SMFDocument14 pagesIntroduction To Welding Technology and SMFAbel Meketa100% (1)
- Machine Shop ReportDocument8 pagesMachine Shop ReportNazib Ul Islam Sazib78% (9)
- 3.3 Lathe Accessories & AttachmentsDocument8 pages3.3 Lathe Accessories & AttachmentsAbel MeketaNo ratings yet
- Recent Methods For Optimization of Plastic Injection Molding Process A Literature ReviewDocument8 pagesRecent Methods For Optimization of Plastic Injection Molding Process A Literature ReviewRakshith KNo ratings yet
- Research ProposalDocument3 pagesResearch ProposalAbel Meketa100% (1)
- Design Calculation & AnalysisDocument13 pagesDesign Calculation & AnalysisAbel Meketa100% (1)
- Finalllllll BPDocument46 pagesFinalllllll BPSheypia Agustin JacintoNo ratings yet
- CORONADocument25 pagesCORONAMohammedNo ratings yet
- FilterFlow Cartridge Installation GuideDocument8 pagesFilterFlow Cartridge Installation GuideSilver FoxNo ratings yet
- Memorandum - World Safety Day "2023''Document2 pagesMemorandum - World Safety Day "2023''attaullaNo ratings yet
- Anesthesiology GuideDocument4 pagesAnesthesiology GuideGeorge Wang100% (1)
- Mayank Yadav: Academic QualificationDocument2 pagesMayank Yadav: Academic QualificationJacob PruittNo ratings yet
- 6 Ijasrjun20196Document8 pages6 Ijasrjun20196TJPRC PublicationsNo ratings yet
- Varisco Solid Pumping SolutionsDocument12 pagesVarisco Solid Pumping SolutionsCatalin FrincuNo ratings yet
- Glare CompositeDocument10 pagesGlare Compositewsjouri2510No ratings yet
- RPLB NewDocument22 pagesRPLB NewMeta learnNo ratings yet
- SAVULESCU, Julian - A Simple Solution To The Puzzles of End of LifeDocument5 pagesSAVULESCU, Julian - A Simple Solution To The Puzzles of End of Lifediradosta_1992No ratings yet
- CoC VampireCharacterPrimerPDFDocument5 pagesCoC VampireCharacterPrimerPDFDavid Alexander TomblinNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 Marks: 15 Introduction To Micro System and Smart SystemsDocument9 pagesUnit 1 Marks: 15 Introduction To Micro System and Smart SystemsSudarsh KNo ratings yet
- NURS FPX 6410 Assessment 2 Executive Summary To AdministrationDocument7 pagesNURS FPX 6410 Assessment 2 Executive Summary To Administrationzadem5266No ratings yet
- WaveLab - BUC Datasheet - Ku Band 80W 100WDocument4 pagesWaveLab - BUC Datasheet - Ku Band 80W 100WLeonNo ratings yet
- Algerian Carob Tree Products PDFDocument10 pagesAlgerian Carob Tree Products PDFStîngă DanielaNo ratings yet
- SD502 (V22) 05.2021Document4 pagesSD502 (V22) 05.2021Beaulah HunidzariraNo ratings yet
- Princess Joy Placement and General Services vs. BinallaDocument2 pagesPrincess Joy Placement and General Services vs. Binallaapple_doctoleroNo ratings yet
- Benefits of Playing Badminton (An Essay)Document2 pagesBenefits of Playing Badminton (An Essay)Haryoung Sta CruzNo ratings yet
- Project PPT Spot WeldingDocument19 pagesProject PPT Spot WeldingMehul BariyaNo ratings yet
- Grandma StoriesDocument38 pagesGrandma StoriesSita Rani Devi DasiNo ratings yet
- Lab Manual For Series Parallel Rasonant CircuitDocument3 pagesLab Manual For Series Parallel Rasonant CircuitManoj PardhanNo ratings yet
- Buy Lizol Floor Cleaner 5000 ML Online - GeMDocument4 pagesBuy Lizol Floor Cleaner 5000 ML Online - GeMHimanshu ShuklaNo ratings yet
- Project DesertsDocument17 pagesProject Desertssuja_sriniNo ratings yet
- Connection DesignDocument33 pagesConnection Designjesus curielNo ratings yet
- Lab 2 - Capacitive ReactanceDocument4 pagesLab 2 - Capacitive Reactanceali basitNo ratings yet
- ASME Single Certification MarkDocument3 pagesASME Single Certification MarkahmadghasusNo ratings yet