Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Steam Condensers and Cooling Towers
Uploaded by
ذال شراحبئيل0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
6 views22 pagesOriginal Title
Condenser Lect
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
6 views22 pagesSteam Condensers and Cooling Towers
Uploaded by
ذال شراحبئيلCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 22
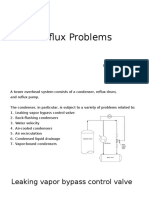
STEAM CONDENSERS AND COOLING TOWERS
Evaluate condenser performance
and select for proper application.
DALTONS LAW OF PARTIAL PRESSURE
• “Thetotal pressure exerted by mixture
of gases or a mixture of gas and vapors
(which have no chemical action on each
other) is equal to the sum of the partial
pressures of the constituents of the
mixture, if it occupies the volume of
mixture at temperature of mixture”.
DALTONS LAW OF PARTIAL PRESSURE
• The total pressure in the condenser is the
sum of the partial pressure of steam and air.
• Pressure of mixture= partial pressure of
steam + partial pressure of air
• So according to Daltons law total pressure
in the condenser is, Pc = Ps + Pa
Where , Pc= total pressure in condenser
Ps= partial pressure of steam
Pa= partial pressure of air.
DALTONS LAW OF PARTIAL PRESSURE
Pc Ps Pa
Steam + air steam Air
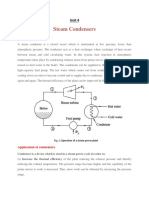
Steam condenser
• A steam condenser is a closed vessel in to which
the steam is exhausted, and condensed after
doing work in an engine cylinder or turbine.
• A steam condenser has the following two object:
• 1) the primary object is to maintain a low
pressure (below atmospheric pressure) so as to
obtain maximum possible energy from steam
and thus to secure high efficiency.
• 2) the secondary object is to supply pure feed
water to the hot well, from where it is pumped
back to boiler.
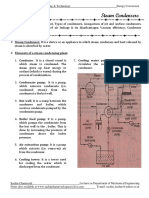
Classification of steam condenser
• The steam condensers may be broadly classified in to the
following two types, depending upon the way in which the
steam is condensed.
• 1) jet condensers or mixing type condensers
a) Parallel flow jet condenser
b) Counter flow jet condenser
c) Barometric or high level jet condenser
d) Ejector condenser.
• 2) surface condensers or non mixing type condensers.
A) Down flow surface condenser
B) Central flow surface condenser
C) Regenerative surface condenser
D)Evaporative condenser
Surface condenser
• A surface condenser has a great advantages over the jet
condenser, as the condensate does not mix up with
cooling water.
• As a result of this whole condensate can be reused in
the boiler.
• This type of condenser is essential in ships which can
carry only a limited quantity of fresh water for the
boilers.
• Fig . Shows a longitudinal section of a two pass surface
condenser.
Surface condenser
Surface condenser
• It consist of a horizontal cast iron cylindrical
vessel packed with tubes, through which the
cooling water flows.
• The end of the condensers are cut off by
vertical perforated types of plates into which
water tubes are fixed.
• This is done in such a manner that the leakage
of water into the centre condensing space is
prevented.
• The water tubes pass horizontally through the
main condensing space for the steam.
Surface condenser
• The steam enters at the top and is forced to
flow down words over the tubes due to the
suction of the extraction pump at the
bottom.
• The cooling water flows in one direction
through the lower half of the tubes and
returns in opposite direction through the
upper half.
Source of air leakage
• The following are main sources through which the
air may enter the condenser:
• The dissolved air in the feed water enters into the
boiler, which in turn enters into the condenser with
exhaust steam.
• The air leaks into the condenser, through various
joint, due to high vacuum pressure in the condenser.
• In case of jet condensers , dissolved air with the
injection water enters into the condenser.
Effect of air leakage
1) It reduces vacuum pressure in the
condenser.
2) Since air is poor heat conductor, particularly
at low densities, it reduces the rate of heat
transmission.
3) It requires a larger air pump. Moreover, an
increased power is required power is
required to drive the pump.
Condenser efficiency
• The condenser efficiency may be defined as the ratio
of temperature rise of cooling water to the vacuum
temperature minus inlet cooling water temperature.
• ᶯc = temperature rise of cooling water/(vacuum
temperature- inlet cooling water temperature)
• ᶯc = (to – ti ) / (tv-ti)
• Where, to= outlet temperature of cooling water.
• ti= inlet temperature of cooling water.
• tv= vacuum temperature
Vacuum efficiency
• The minimum absolute pressure (also called as ideal
pressure) at the steam inlet of a condenser is the pressure
corresponding to the temperature of the condensed
steam.
• The corresponding vacuum (called ideal vacuum) is the
maximum vacuum that can be obtained in a condensing
plant, with no air present at that temperature.
• The pressure in the actual condenser is greater than the
ideal pressure by an amount equal to the pressure of air
present in the condenser.
• The ratio of the actual vacuum to the ideal vacuum is
known as vacuum efficiency.
Vacuum efficiency
• ᶯv= actual vacuum /ideal vacuum
• Actual vacuum= barometric pressure- actual
pressure
• Ideal vacuum = barometric pressure- ideal
pressure
Cooling tower
• The main application are in power plants and
refrigeration plants.
• Its function is to cool the hot water from the
condenser by exposing it to the atmospheric air, so
that the cold water may be used again for circulation.
• The cooling towers are used in steam power plants
where there is a limited supply of cooling water.
• It is placed at a certain height (at about 9 meters
from the ground level).
Cooling tower
• The hot water falls in radial sprays from a
height and the atmospheric air enters from
the base of tower.
• The partial evaporation of water takes
place which reduces the temperature of
circulating water.
• This cooled water is collected in the pond
at the base of the tower and pumped in to
the condenser.
Types of cooling tower
1) Natural draught cooling tower
The circulation of air is produced by the
pressure difference of air inside and outside
the cooling tower.
2) Forced draught cooling tower
The circulation of air is produced by means of
fans placed at the base of tower.
3) Induced draught cooling tower
The circulation of air is provided by means of
fan placed at top of tower.
Natural draught cooling tower
Forced water cooling tower
Induced draught cooling tower
You might also like
- Understanding Process Equipment for Operators and EngineersFrom EverandUnderstanding Process Equipment for Operators and EngineersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (3)
- Techcombank Tower Project Team StrategiesDocument5 pagesTechcombank Tower Project Team StrategiesNguyên Trịnh CaoNo ratings yet
- Training On Steam CondensersDocument33 pagesTraining On Steam CondensersMayank GuptaNo ratings yet
- 5 Studyguide KeyDocument3 pages5 Studyguide KeyAnonymous PersonNo ratings yet
- Evaluate condenser performance and select applicationsDocument22 pagesEvaluate condenser performance and select applicationsVera WidyaNo ratings yet
- Condenser Cooling Towers 216Document28 pagesCondenser Cooling Towers 216rajushamla9927No ratings yet
- Steam CondenserDocument26 pagesSteam CondenserPushkar Pandit100% (1)
- Condensers and Cooling TowerDocument27 pagesCondensers and Cooling TowerVenkateswarlu VelisalaNo ratings yet
- CondensersDocument34 pagesCondensersShreyash VihirghareNo ratings yet
- Daltons Law of Partial PressureDocument14 pagesDaltons Law of Partial PressureDev PatelNo ratings yet
- 9 Condenser-1Document50 pages9 Condenser-1as2899142No ratings yet
- Presentation By: 3 Year Mech-D 17985A077 17985A078 17985A079 17985A083 17985A084 17985A088 17985A092 17985A095 17985A098Document15 pagesPresentation By: 3 Year Mech-D 17985A077 17985A078 17985A079 17985A083 17985A084 17985A088 17985A092 17985A095 17985A098pranavNo ratings yet
- Steam Condensers and Cooling Towers ExplainedDocument43 pagesSteam Condensers and Cooling Towers ExplainedrrhoshackNo ratings yet
- ME 310a Steam Turbines: Cooling TowersDocument33 pagesME 310a Steam Turbines: Cooling Towersshivkumar shindeNo ratings yet
- Steam Condenser - Lecture SlideDocument43 pagesSteam Condenser - Lecture SlideKing KNo ratings yet
- CondenserDocument8 pagesCondenserManish MauryaNo ratings yet
- Reflux Problems: CH Venkatesh 13021A2536Document14 pagesReflux Problems: CH Venkatesh 13021A2536Venkatesh ChNo ratings yet
- Steam CondenserDocument16 pagesSteam CondenserAtharv MarneNo ratings yet
- Heat ExchangersDocument29 pagesHeat ExchangerscooLkiD1412No ratings yet
- STEAM CONDENSERS: KEY COMPONENTS AND TYPESDocument32 pagesSTEAM CONDENSERS: KEY COMPONENTS AND TYPESaadhithyarajasekaranNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 Steam CondenserDocument40 pagesChapter 5 Steam CondenserHabtamu Tkubet EbuyNo ratings yet
- Thermal Engineering-CondenserDocument17 pagesThermal Engineering-CondenserJayNo ratings yet
- Condenser Efficiency EngineeringDocument9 pagesCondenser Efficiency Engineeringโอม ปามาติกะ100% (2)
- Steam CondensersDocument59 pagesSteam CondensersBLACK GAMINGNo ratings yet
- KIET Group of Institutions, GhaziabadDocument8 pagesKIET Group of Institutions, GhaziabadSandeep ChhabraNo ratings yet
- Steam Surface Condenser OperationDocument10 pagesSteam Surface Condenser OperationJohn Noel TalandronNo ratings yet
- Steam Condenser: Me 420 - Me Laboratory 2Document74 pagesSteam Condenser: Me 420 - Me Laboratory 2daanNo ratings yet
- Vacuum SystemDocument28 pagesVacuum SystemDalveer SinghNo ratings yet
- Vacuum SystemDocument28 pagesVacuum SystemSam100% (1)
- Condenser8 5 2020Document3 pagesCondenser8 5 2020anupnaskar naskarNo ratings yet
- Cooling tower evaporative technologyDocument22 pagesCooling tower evaporative technologyFatin AnisahNo ratings yet
- Condenser in Power PlantDocument20 pagesCondenser in Power PlantPrabir Kumar PatiNo ratings yet
- PP Ws CondenserDocument14 pagesPP Ws CondenserBhaskar AnupamNo ratings yet
- Steam Condensers: 3/28/2015 1 Footer TextDocument23 pagesSteam Condensers: 3/28/2015 1 Footer TextKumari YehwaNo ratings yet
- Chapter One: CondenserDocument10 pagesChapter One: Condenserشاكر العاقل100% (1)
- Vacuum SystemDocument49 pagesVacuum Systemssmith2007100% (3)
- Turbine TestsDocument30 pagesTurbine TestsReeyan Dave DagandanNo ratings yet
- Forced Draft Cooling TowersDocument21 pagesForced Draft Cooling TowersJustin SibonghanoyNo ratings yet
- Steam Turbine Auxiliaries Question & AnswersDocument10 pagesSteam Turbine Auxiliaries Question & AnswersLaxman Veerepalli100% (1)
- Cooling Tower DriveDocument32 pagesCooling Tower DriveHassan KhanNo ratings yet
- CondensersDocument25 pagesCondensersARSAL HASHMINo ratings yet
- Condensate SystemDocument35 pagesCondensate SystemSam100% (6)
- Condensor and Cooling TowerDocument25 pagesCondensor and Cooling TowerYASH ACHARYANo ratings yet
- Condensers PDFDocument29 pagesCondensers PDFsandhya100% (1)
- Thermal Power PlantDocument29 pagesThermal Power Plantshamna AbdullaNo ratings yet
- pptPPE (15&17)Document22 pagespptPPE (15&17)HarshitNo ratings yet
- Condenser PDFDocument14 pagesCondenser PDFnirmalk1222No ratings yet
- CONDENSER PERFORMANCE: Factors Affecting Heat Transfer & VacuumDocument26 pagesCONDENSER PERFORMANCE: Factors Affecting Heat Transfer & VacuumFranz MonsantoNo ratings yet
- Steam Condensers: Unit 4Document12 pagesSteam Condensers: Unit 4sameer jainNo ratings yet
- Condenser S and Cooling Towers: By, Prof. M.B. GohilDocument55 pagesCondenser S and Cooling Towers: By, Prof. M.B. Gohilanilm130484meNo ratings yet
- Requirements of Steam Condensing PlantDocument9 pagesRequirements of Steam Condensing PlantHung NguyenNo ratings yet
- COOLING TOWER THEORY AND TYPESDocument28 pagesCOOLING TOWER THEORY AND TYPESPriyank kanjariyaNo ratings yet
- Ppe Steam CondenserDocument27 pagesPpe Steam CondenserNilesh SinghNo ratings yet
- Module 5-Multi-Stage Air CompressorDocument26 pagesModule 5-Multi-Stage Air Compressoramit3184No ratings yet
- Steam Condensers and Evaporators ExplainedDocument32 pagesSteam Condensers and Evaporators Explainedvipul sharma100% (1)
- CondenserDocument37 pagesCondenserGaurav SrivastavaNo ratings yet
- Steam CondensorDocument12 pagesSteam CondensorTiwari MadanjitNo ratings yet
- Jgl710 30 CondenserDocument37 pagesJgl710 30 CondenserVaibhav SarinNo ratings yet
- Condensing Cooling System-27042020Document21 pagesCondensing Cooling System-27042020Ashmit TaliyanNo ratings yet
- Unit 6 Steam CondenserDocument7 pagesUnit 6 Steam CondenserSamrat KumarNo ratings yet
- Mechanics of the Household: A Course of Study Devoted to Domestic Machinery and Household Mechanical AppliancesFrom EverandMechanics of the Household: A Course of Study Devoted to Domestic Machinery and Household Mechanical AppliancesNo ratings yet
- Performance of Steam Turbine With Feedwater HeatersDocument42 pagesPerformance of Steam Turbine With Feedwater Heatersذال شراحبئيلNo ratings yet
- Disadvantages and Essentials of Steam Power PlantsDocument120 pagesDisadvantages and Essentials of Steam Power Plantsذال شراحبئيلNo ratings yet
- CO-GENERATION SYSTEMS EXPLAINEDDocument47 pagesCO-GENERATION SYSTEMS EXPLAINEDDeshdeepak Sharma D DNo ratings yet
- Code For Rankine With 3 FHWsDocument10 pagesCode For Rankine With 3 FHWsذال شراحبئيلNo ratings yet
- Homework 6: Advantages and Disadvantages of Solving Problems As A Team andDocument1 pageHomework 6: Advantages and Disadvantages of Solving Problems As A Team andذال شراحبئيلNo ratings yet
- Academic advising key to successDocument1 pageAcademic advising key to successذال شراحبئيلNo ratings yet
- Homework 1Document1 pageHomework 1ذال شراحبئيلNo ratings yet
- Homework: in Teams of 10, Find The Meanings of The Following WordsDocument1 pageHomework: in Teams of 10, Find The Meanings of The Following Wordsذال شراحبئيلNo ratings yet
- Homework 2: 1-What Have You Learned About Succeeding at The College?Document1 pageHomework 2: 1-What Have You Learned About Succeeding at The College?ذال شراحبئيلNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class 11 Chemistry Notes - Chemical Bonding and Molecular Structure - AglaSem SchoolsDocument14 pagesCBSE Class 11 Chemistry Notes - Chemical Bonding and Molecular Structure - AglaSem SchoolsAswar ShaileshNo ratings yet
- Conservation Biology - 2005 - AGOSTINHO - Conservation of The Biodiversity of Brazil S Inland WatersDocument7 pagesConservation Biology - 2005 - AGOSTINHO - Conservation of The Biodiversity of Brazil S Inland WatersStefani CamposNo ratings yet
- Midterm Exam (NSCI 111 - People & The Earth's Ecosystem)Document10 pagesMidterm Exam (NSCI 111 - People & The Earth's Ecosystem)Jov Soyom100% (1)
- Opportunities and Challenges in CO2 UtilizationDocument23 pagesOpportunities and Challenges in CO2 UtilizationDaraNo ratings yet
- Quantum PhysicsDocument21 pagesQuantum PhysicsMartin DelgadoNo ratings yet
- Cambridge International School Syllabus Plan Term 1 EVMDocument3 pagesCambridge International School Syllabus Plan Term 1 EVMHabiba ElwaselyNo ratings yet
- GB Pyrolysis an-ARTIMDocument12 pagesGB Pyrolysis an-ARTIMsentoneNo ratings yet
- Conceptual Design For Tidal Energy Power Plant: A Supplementary Power Generation Plant For Residential Use in Neighboring Areas of Sarangani BayDocument18 pagesConceptual Design For Tidal Energy Power Plant: A Supplementary Power Generation Plant For Residential Use in Neighboring Areas of Sarangani BayVanne Jo PajoNo ratings yet
- Class 3 Science Exam QuestionsDocument3 pagesClass 3 Science Exam QuestionsPrasenjit NandiNo ratings yet
- Disc 15 SolutionDocument4 pagesDisc 15 Solutionmmounir79No ratings yet
- Types of Exhaust Gas Boiler (EGB) Fires and Ways To Prevent ThemDocument4 pagesTypes of Exhaust Gas Boiler (EGB) Fires and Ways To Prevent ThemGiorgi KandelakiNo ratings yet
- RenewableDocument222 pagesRenewableTaimur AkhtarNo ratings yet
- Hall TheArrlAntennaBook TextDocument338 pagesHall TheArrlAntennaBook TextWilfredo Rafael Perez Gutierrez100% (3)
- RAC Experimental Water Cooler Storage TypeDocument7 pagesRAC Experimental Water Cooler Storage TypeShashi Bhushan PatelNo ratings yet
- Noise Reduction Coefficient of Recycled Textile and Waste Paper Composite As Compared To Rigid Polyurethane FoamDocument6 pagesNoise Reduction Coefficient of Recycled Textile and Waste Paper Composite As Compared To Rigid Polyurethane FoamJohn Mark TicarNo ratings yet
- Distribution of Juice Heater Surface For Optimum Performance ofDocument10 pagesDistribution of Juice Heater Surface For Optimum Performance ofjuanNo ratings yet
- MIDTERM EXAM: CEE 460: Groundwater Hydraulics August 23, 2020 Time: 1 HR 20 Mins Answer The Following Questions. (6 X 10 60)Document2 pagesMIDTERM EXAM: CEE 460: Groundwater Hydraulics August 23, 2020 Time: 1 HR 20 Mins Answer The Following Questions. (6 X 10 60)Avijit SahaNo ratings yet
- Anna University Chennai B.E Aerodynamics Question PapersDocument3 pagesAnna University Chennai B.E Aerodynamics Question Papersabhishek_mahadevanNo ratings yet
- Quiz #1 on the Rise of Industrial PollutionDocument21 pagesQuiz #1 on the Rise of Industrial PollutionGautam SauravNo ratings yet
- Eep-Internal Arc Testing of MV Switchgear IEC 62271200 Part OneDocument2 pagesEep-Internal Arc Testing of MV Switchgear IEC 62271200 Part Oneabdulyunus_amirNo ratings yet
- Efficient CombustionDocument1 pageEfficient CombustionDilhara PinnaduwageNo ratings yet
- Research Progressonthe Extractive Metallurgyof Titaniumand Its AlloysDocument19 pagesResearch Progressonthe Extractive Metallurgyof Titaniumand Its Alloysleonel00000No ratings yet
- Study of The Adsorption and Desorption of Multiple Adsorbates in A Fixed BedDocument17 pagesStudy of The Adsorption and Desorption of Multiple Adsorbates in A Fixed BedJesús Miguel Jacinto NavaNo ratings yet
- Pemodelan Oksigen Terlarut (Dissolved Oxygen/DO) Di Perairan Teluk BenoaDocument11 pagesPemodelan Oksigen Terlarut (Dissolved Oxygen/DO) Di Perairan Teluk BenoaIbnu Khusnuz ZainNo ratings yet
- Meghalaya H.E. Project Progress ReportDocument13 pagesMeghalaya H.E. Project Progress ReportmadhueeNo ratings yet
- Early Life. The Cambrian PeriodDocument225 pagesEarly Life. The Cambrian Periodmisheyfoo92% (13)
- 17 References PDFDocument6 pages17 References PDFVedhas WalimbeNo ratings yet
- Global warming outlineDocument1 pageGlobal warming outlineItzKenMC INo ratings yet