Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Vaksinasi Covid 19 Bumil IDI
Uploaded by
Budy Nugraha SolehudinOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Vaksinasi Covid 19 Bumil IDI
Uploaded by
Budy Nugraha SolehudinCopyright:
Available Formats
Covid 19 Vaccination in Pregnancy
Budi Wiweko
Perkumpulan Obstetri Ginekologi Indonesia
Membangun kesehatan reproduksi Indonesia
Recent reports, however, are more consistent with initial expectations. A systematic multi-
national review of 60 studies on SARSCoV - 2 in pregnancy reported that severe illness occurred
in up to 18% of pregnant patients and critical disease complicated up to 5% of cases, comparable
to rates in the general population
Membangun kesehatan reproduksi Indonesia
Membangun kesehatan reproduksi Indonesia
Membangun kesehatan reproduksi Indonesia
Membangun kesehatan reproduksi Indonesia
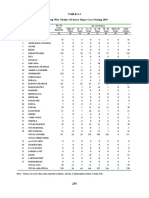
Penyebab Kematian Ibu Januari – Juni 2021
Penyebab Kematian Ibu
Kode Wilayah Jumlah Kematian Ibu
Perdarahan Hipertensi Infeksi Abortus Gangguan Darah Gangguan Metabolik Jantung COVID-19 Lain2
11 ACEH 80 30 7 1 1 2 0 3 6 30
12 SUMATERA UTARA 110 25 21 4 0 1 3 5 9 42
13 SUMATERA BARAT 95 28 14 2 0 0 3 4 10 34
14 RIAU 8 2 0 0 0 1 0 0 5 0
15 JAMBI 17 3 9 0 0 1 0 1 0 3
16 SUMATERA SELATAN 28 6 16 1 0 0 0 0 0 5
17 BENGKULU 14 3 5 0 0 0 0 0 2 4
18 LAMPUNG 49 12 12 2 0 1 0 3 4 15
19 KEPULAUAN BANGKA BELITUNG 12 2 5 0 0 0 0 1 1 3
21 KEPULAUAN RIAU 18 5 4 0 1 0 0 0 0 8
31 DKI JAKARTA 76 19 12 0 0 3 7 2 15 18
32 JAWA BARAT 536 114 111 19 3 4 9 44 168 64
33 JAWA TENGAH 106 21 18 1 0 0 0 3 43 20
34 DI YOGYAKARTA 26 5 5 1 0 0 0 3 4 8
35 JAWA TIMUR 339 47 55 18 0 1 3 19 130 66
36 BANTEN 101 19 13 4 0 2 1 11 10 41
51 BALI 35 5 1 0 0 0 0 4 15 10
52 NUSA TENGGARA BARAT 80 25 19 7 0 0 0 5 11 13
53 NUSA TENGGARA TIMUR 152 42 16 14 0 1 11 8 0 60
61 KALIMANTAN BARAT 65 17 19 3 0 1 0 4 9 12
62 KALIMANTAN TENGAH 39 18 9 1 0 0 0 0 3 8
63 KALIMANTAN SELATAN 67 13 19 1 0 2 6 3 13 10
64 KALIMANTAN TIMUR 37 3 15 0 0 1 0 9 1 8
65 KALIMANTAN UTARA 10 0 2 0 0 0 0 0 5 3
71 SULAWESI UTARA 9 2 0 1 0 0 0 3 0 3
72 SULAWESI TENGAH 54 15 10 5 1 1 0 1 4 17
73 SULAWESI SELATAN 75 23 20 1 0 0 0 1 4 26
74 SULAWESI TENGGARA 37 4 11 1 0 0 3 0 2 16
75 GORONTALO 13 2 1 1 0 0 2 0 0 7
76 SULAWESI BARAT 29 13 3 2 0 0 0 1 1 9
81 MALUKU 18 8 3 0 0 0 0 1 0 6
82 MALUKU UTARA 2 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1
91 PAPUA BARAT 19 14 2 2 0 0 0 0 0 1
94 PAPUA 17 4 3 2 0 0 1 0 4 3
TOTAL 2373 550 460 94 6 22 49 139 479 574
Membangun kesehatan reproduksi Indonesia
Research agenda
Ensure that pregnant women are afforded the
same autonomy as other adults to participate
in clinical trials of vaccines and therapies for
emerging pathogens
1. Vaccination in pregnancy for the primary prevention of communicable diseases has proved one of the most effective public health
interventions in recent decades, leading to significant reductions in maternal and perinatal morbidity and mortality
2. The influenza pandemics of history have highlighted the value of international surveillance systems for critical illness in pregnant women,
the importance of including pregnant women in clinical trials of vaccine efficacy and the imperative for community engagement to optimize
vaccine uptake
3. The rubella epidemics of the 1960s have highlighted the need for birth defect surveillance systems to identify teratogenic links with viral
pathogens, and the importance of understanding disease epidemiology to optimize vaccination uptake and efficacy
4. The benefits of passive immunity for tetanus and pertussis have resulted in significant reduction in infant mortality and morbidity due to
optimal timing and dosing during pregnancy
Membangun kesehatan reproduksi Indonesia
To enable the inclusion of pregnant and lactating women in the development of COVID-19
vaccines, three key questions need to be answered:
1. What is the short term and long-term burden of COVID-19 in pregnant women, the foetus,
and infants (in all populations and ethnic groups);
2. Do pregnant women wish to be vaccinated against COVID-19 and participate in such trials;
3. Which of the candidate COVID-19 vaccines are suitable for pregnant women and should be
the focus of early clinical trials
Membangun kesehatan reproduksi Indonesia
Pregnant persons were excluded from the initial phase 3 clinical trials of COVID-19 vaccines,
limited data are available on their efficacy and safety during pregnancy.
After developmental and reproductive toxicology studies are completed, some companies are
expected to conduct clinical trials in pregnant persons. Until then, pregnant persons and their
obstetricians will need to use available data to weigh the benefits and risks of COVID-19 vaccines.
Membangun kesehatan reproduksi Indonesia
Membangun kesehatan reproduksi Indonesia
Membangun kesehatan reproduksi Indonesia
Considerations for Counselling Pregnant Persons Regarding Coronavirus Disease
2019 (COVID-19) Vaccination
1. Data from animal studies (once developmental and reproductive toxicology studies become
available)
2. Lack of data on pregnancies during vaccine clinical trials
3. Risks of vaccine reactogenicity, including fever; treatment with antipyretic medications (eg,
acetaminophen) might reduce this risk
4. Timing of planned vaccination during pregnancy
5. Extensive evidence for safety of other vaccines during pregnancy
6. Risk of COVID-19 complications due to pregnancy (increased risk to pregnant person of severe
disease and death)
7. Risk of COVID-19 complications due to underlying conditions (eg, diabetes, obesity, heart
disease)
8. Risk of COVID-19 to foetus or new-born (intrauterine transmission is rare, but preterm birth
appears to be increased)
9. Risk of exposure to SARS-CoV-2 and potential for mitigation with working
Membangun kesehatan reproduksi Indonesia
Membangun kesehatan reproduksi Indonesia
• Most states in the United States (36 of 51; 71%) encompassing 71% of the population in the
United States do not include pregnant individuals among their priority populations.
• Only 6 of 13 states that mentioned pregnancy as a priority indication for COVID-19 vaccination
and none of the 36 states not including pregnancy in priority groups linked back to the Centers for
Disease Control and Prevention definition of pregnancy as an increased risk of severe illness.
Membangun kesehatan reproduksi Indonesia
Membangun kesehatan reproduksi Indonesia
Membangun kesehatan reproduksi Indonesia
METHODS
From December 14, 2020, to February 28, 2021, we used data from the “v-safe after vaccination
health checker” surveillance system, the v-safe pregnancy registry, and the Vaccine Adverse
Event Reporting System (VAERS) to characterize the initial safety of mRNA Covid-19 vaccines in
pregnant persons.
• Monitoring Systems and Covered Populations
V-safe Surveillance System and Pregnancy Registry
• V-safe is a new CDC smartphone-based active- surveillance system developed for the
Covid-19 vaccination program; enrollment is voluntary
Membangun kesehatan reproduksi Indonesia
Outcomes
• V-safe outcomes included participant-reported local and systemic reactogenicity to the
BNT162b2 (Pfizer–BioNTech) vaccine and the mRNA-1273 (Moderna) vaccine on the day after
vaccination among all pregnant persons 16 to 54 years of age and among nonpregnant
women 16 to 54 years of age as a comparator.
• For analysis of pregnancy outcomes in the v-safe pregnancy registry, data were restricted to
completed pregnancies (i.e., live-born infant, spontaneous abortion, induced abortion, or
stillbirth).
• Participant-reported pregnancy outcomes included pregnancy loss (spontaneous abortion
and stillbirth) and neonatal outcomes (preterm birth, congenital anomalies, small size for
gestational age, and neonatal death
Membangun kesehatan reproduksi Indonesia
Membangun kesehatan reproduksi Indonesia
Membangun kesehatan reproduksi Indonesia
Membangun kesehatan reproduksi Indonesia
Membangun kesehatan reproduksi Indonesia
Membangun kesehatan reproduksi Indonesia
1. Early data from the v-safe surveillance system, the v-safe pregnancy registry, and
the VAERS do not indicate any obvious safety signals with respect to pregnancy or
neonatal outcomes associated with Covid-19 vaccination in the third trimester of
pregnancy.
2. Continued monitoring is needed to further assess maternal, pregnancy, neonatal,
and childhood outcomes associated with maternal Covid-19 vaccination, including
in earlier stages of pregnancy and during the preconception period.
3. Meanwhile, the present data can help inform decision making about vaccination by
pregnant persons and their health
Membangun kesehatan reproduksi Indonesia
Membangun kesehatan reproduksi Indonesia
Membangun kesehatan reproduksi Indonesia
Membangun kesehatan reproduksi Indonesia
Membangun kesehatan reproduksi Indonesia
TERIMA KASIH
Membangun kesehatan reproduksi Indonesia
You might also like
- #Sno Panchayat Total No. of Households Others SC ST MinorityDocument2 pages#Sno Panchayat Total No. of Households Others SC ST MinorityKailash KumarNo ratings yet
- Capaian Iva 2020-2022 (BLN Juni)Document2 pagesCapaian Iva 2020-2022 (BLN Juni)Dita LutfiNo ratings yet
- Member Comparison by Gold Medal11111Document1 pageMember Comparison by Gold Medal11111Heri AfitriansyahNo ratings yet
- Lampiran 1: Tabel 3.1 Input DataDocument1 pageLampiran 1: Tabel 3.1 Input DataAken Andha RuniawanNo ratings yet
- Rekap Stats Gizi Bulan NovemberDocument2 pagesRekap Stats Gizi Bulan NovemberEva suryaniNo ratings yet
- Oci Geriatri AgustDocument37 pagesOci Geriatri AgustRanap LilyNo ratings yet
- Rekapan Pendataan Dan Intervensi Pis PK Bulan Mei S/D Juni Tahun 2020 Puskesmas: MarauwDocument1 pageRekapan Pendataan Dan Intervensi Pis PK Bulan Mei S/D Juni Tahun 2020 Puskesmas: MarauwMansar SiburNo ratings yet
- Rekap Progres Perekaman KTP El Oktober 2023Document2 pagesRekap Progres Perekaman KTP El Oktober 2023HARDANI MUTAKIMNo ratings yet
- Laporan Bulanan Bulan Juli 2023-1Document3 pagesLaporan Bulanan Bulan Juli 2023-1Indra Wati 2020No ratings yet
- Form Q1 Q2 GradesDocument10 pagesForm Q1 Q2 GradesMARLO ALVAREZNo ratings yet
- Coimbatore 50 VEH OPERATION PDFDocument12 pagesCoimbatore 50 VEH OPERATION PDFAravindh RNo ratings yet
- q4 Qra Form 5 Gr.1 10 ModifiedDocument159 pagesq4 Qra Form 5 Gr.1 10 ModifiedMarilyn BrigoliNo ratings yet
- Data Backlog Fighting Posyandu Kelurahan RobanDocument2 pagesData Backlog Fighting Posyandu Kelurahan RobanEda WandiNo ratings yet
- Laporan Harga Bulanan Logistik Farmasi Ugd 1 - 31 DESEMBER 2012Document130 pagesLaporan Harga Bulanan Logistik Farmasi Ugd 1 - 31 DESEMBER 2012Co DiovanNo ratings yet
- 1 2022 Immunization Services - Child, Maternal & Senior CitizenDocument204 pages1 2022 Immunization Services - Child, Maternal & Senior CitizenKenneth SantosNo ratings yet
- Mei 2019-PneumonieDocument10 pagesMei 2019-PneumonieAnnisa Caul HasanahNo ratings yet
- Puskesmas: Pasarmatangor Provinsi: Sumatera Utara Tahun: 2019Document2 pagesPuskesmas: Pasarmatangor Provinsi: Sumatera Utara Tahun: 2019Nurjannah HasibuanNo ratings yet
- PWS KB Nurussalam 2022Document52 pagesPWS KB Nurussalam 2022Nadya SaviraNo ratings yet
- Rekap F2 2013Document57 pagesRekap F2 2013restu wahyuNo ratings yet
- Resultado GeralDocument1 pageResultado GeraloswaldovbNo ratings yet
- Final Result SC by WS20 29-05 PDFDocument1 pageFinal Result SC by WS20 29-05 PDFAdi PermanaNo ratings yet
- Lap Dikses Labsus 2016Document27 pagesLap Dikses Labsus 2016puskesmas katobengkeNo ratings yet
- Pasca SalinDocument4 pagesPasca SalinDpp-KB MUNANo ratings yet
- THE BEST OF THE BEST 2011 - 1 EtapaDocument15 pagesTHE BEST OF THE BEST 2011 - 1 EtapaoswaldovbNo ratings yet
- Cooperativas Activas Al 30 de Abril de 2021Document1 pageCooperativas Activas Al 30 de Abril de 2021Efraín VenturaNo ratings yet
- Target Dan Capaian Program HivDocument3 pagesTarget Dan Capaian Program Hivmaya febrina UtamiNo ratings yet
- Gizi 2018Document66 pagesGizi 2018Revan Otto GobelNo ratings yet
- ESTADUAL 2010 - ResultadosDocument19 pagesESTADUAL 2010 - ResultadososwaldovbNo ratings yet
- Book1 Pencapaian Jan - Sept 2016Document4 pagesBook1 Pencapaian Jan - Sept 2016Enal JhiNo ratings yet
- English 10 Proficiency Level 2022-2023Document2 pagesEnglish 10 Proficiency Level 2022-2023Ehdz B Visperas-TarangcoNo ratings yet
- Cooperativas Activas A Julio 2021Document1 pageCooperativas Activas A Julio 2021Victor Erasmo Mejicano AriasNo ratings yet
- GOLKARDocument14 pagesGOLKARGilang Putra MuhammadNo ratings yet
- 1-ESED KP Vacant Posts SSTs (BPS-16) (Male) - REVISED 17-12-21 (MANSEHRA UPDATED) - REVISEDDocument1 page1-ESED KP Vacant Posts SSTs (BPS-16) (Male) - REVISED 17-12-21 (MANSEHRA UPDATED) - REVISEDChcjcjciNo ratings yet
- Formulir Pemantauan Garam Beryodium Di Masyarakat Tingkat Masyarakat Di Jawa Timur Th. 2019 Desa PuskesmasDocument6 pagesFormulir Pemantauan Garam Beryodium Di Masyarakat Tingkat Masyarakat Di Jawa Timur Th. 2019 Desa PuskesmasmayaNo ratings yet
- Laporan TelingaDocument1,438 pagesLaporan TelingaSyilvia Rosyita DewiNo ratings yet
- Pmjjby Pmsby 22112022 0645PMDocument2 pagesPmjjby Pmsby 22112022 0645PMRavindran RajaNo ratings yet
- Form - Lansia 2018 Panca - MaretDocument12 pagesForm - Lansia 2018 Panca - Marettoni_nagrakNo ratings yet
- Laporan Puskesmas Rawat Inap 2022Document157 pagesLaporan Puskesmas Rawat Inap 2022pkmsilo1No ratings yet
- Assalamualaikum WarrahmatullahiwabarakatuDocument13 pagesAssalamualaikum WarrahmatullahiwabarakatuPuskesmas ParianganNo ratings yet
- Ritase CG Pertanggal 27 November 2022Document2 pagesRitase CG Pertanggal 27 November 2022Vici KharismaNo ratings yet
- TABLE-5.3 Age-Group-Wise Victims of Incest (Rape) Cases During 2005Document6 pagesTABLE-5.3 Age-Group-Wise Victims of Incest (Rape) Cases During 2005Govind DabralNo ratings yet
- IvarcomDocument446 pagesIvarcomZoldyck KilluaNo ratings yet
- Cooperativas Activas Al 30 de Junio de 2023Document1 pageCooperativas Activas Al 30 de Junio de 2023Beatriz SánchezNo ratings yet
- Rekapitulasi Registrasi PasienDocument2 pagesRekapitulasi Registrasi PasienyanikNo ratings yet
- 1-31 Januari CL2.CL4Document10 pages1-31 Januari CL2.CL4M Siri BaharongNo ratings yet
- SepptDocument3 pagesSepptsatria ibrahim sambayangNo ratings yet
- Report 220321Document7 pagesReport 220321Sandip BanerjeeNo ratings yet
- Summary Scoreboard 24.2.24-1Document1 pageSummary Scoreboard 24.2.24-1noorazianie92No ratings yet
- Data Stunting Kec BatiknauDocument8 pagesData Stunting Kec BatiknauPuskesmas BatiknauNo ratings yet
- Sasaran Bias 2021Document2 pagesSasaran Bias 2021khofifahNo ratings yet
- Promkes - Data Kegiatan Pemberdayaan Masyarakat 2019Document19 pagesPromkes - Data Kegiatan Pemberdayaan Masyarakat 2019Tyas HapsariNo ratings yet
- Data Pegawai Kab. Bengkayang - DapodikdasmenDocument3 pagesData Pegawai Kab. Bengkayang - DapodikdasmenFreddy LantuNo ratings yet
- Laporan Puskesmas Binanga Bulan MaretDocument45 pagesLaporan Puskesmas Binanga Bulan MaretNency EllizaNo ratings yet
- Total Number of Collection 2023Document16 pagesTotal Number of Collection 2023CarlNo ratings yet
- Lap KB Januari 2022Document11 pagesLap KB Januari 2022Eyang GhaulNo ratings yet
- Data Per 25 OktDocument13 pagesData Per 25 OktAtikNo ratings yet
- Stunting 2022Document2 pagesStunting 2022HASTA MUNANo ratings yet
- New Microsoft Excel WorksheetDocument36 pagesNew Microsoft Excel WorksheetNency EllizaNo ratings yet
- Technical Tables for Schools and Colleges: The Commonwealth and International Library Mathematics DivisionFrom EverandTechnical Tables for Schools and Colleges: The Commonwealth and International Library Mathematics DivisionNo ratings yet
- Evaluation in Science EducationDocument27 pagesEvaluation in Science EducationBudy Nugraha SolehudinNo ratings yet
- Dosen Dan Kualitas Perguruan Tinggi: 8 Februari 2010Document22 pagesDosen Dan Kualitas Perguruan Tinggi: 8 Februari 2010Budy Nugraha SolehudinNo ratings yet
- Jadwal Pelaksanaan Bias DT/TD Kelas 1, 2, 3 SD/ Mi SD/ Mi Wilayah Kerja Uptd Puskesmas DTP Bungursari TAHUN 2013Document1 pageJadwal Pelaksanaan Bias DT/TD Kelas 1, 2, 3 SD/ Mi SD/ Mi Wilayah Kerja Uptd Puskesmas DTP Bungursari TAHUN 2013Budy Nugraha SolehudinNo ratings yet
- Sdnegeri Indihiang Indihiang TasikmalayaDocument1 pageSdnegeri Indihiang Indihiang TasikmalayaBudy Nugraha SolehudinNo ratings yet
- Spider Silk in Goat MilkDocument4 pagesSpider Silk in Goat MilkInfinity_plus_oneNo ratings yet
- DapusDocument3 pagesDapusNur Zahratul JannahNo ratings yet
- Parts Structure Function(s) : Cedar Girls Secondary School Biology Notes Chapter 2: CellsDocument3 pagesParts Structure Function(s) : Cedar Girls Secondary School Biology Notes Chapter 2: CellsVinodini RaviNo ratings yet
- Purification of ProteinsDocument28 pagesPurification of ProteinsaasthaNo ratings yet
- Biology 5 Biology 5 Cell Biology and Gen PDFDocument144 pagesBiology 5 Biology 5 Cell Biology and Gen PDFJazmin AVNo ratings yet
- CARDOSO Et Al 2010 - Propolis Staphylo e Malassezia - Otite CaninaDocument3 pagesCARDOSO Et Al 2010 - Propolis Staphylo e Malassezia - Otite CaninaDébora SakiyamaNo ratings yet
- Mesenchymal Stem Cell in Veterinary Sciences: Mudasir Bashir Gugjoo Amar Pal EditorsDocument347 pagesMesenchymal Stem Cell in Veterinary Sciences: Mudasir Bashir Gugjoo Amar Pal EditorsHilmi CeylanNo ratings yet
- Presentation1 171022084035Document16 pagesPresentation1 171022084035Akkipero123No ratings yet
- Biotechnology and New Drug Development: Duhok Polytechnic University Duhok Technical Institute Pharmacy DepartmentDocument19 pagesBiotechnology and New Drug Development: Duhok Polytechnic University Duhok Technical Institute Pharmacy DepartmentTurkiya Shammo AliNo ratings yet
- B.SC (CBCS) Botany-I Year Semester-II - Paper-II Bryophytes, Pteridophytes, Gymnosperms and Paleobotany DSC-1B (4 Hrs./week) Theory Syllabus Credits - 4 (60 Hours) Unit-IDocument5 pagesB.SC (CBCS) Botany-I Year Semester-II - Paper-II Bryophytes, Pteridophytes, Gymnosperms and Paleobotany DSC-1B (4 Hrs./week) Theory Syllabus Credits - 4 (60 Hours) Unit-INAVEEN0% (1)
- Mendel LawDocument4 pagesMendel Lawleon08jayNo ratings yet
- C Science 10 Quarter 3 Module 3 (Week 4)Document14 pagesC Science 10 Quarter 3 Module 3 (Week 4)Daisy Soriano Prestoza100% (1)
- Supplementary Learning Material in Earth and Life SciencesDocument20 pagesSupplementary Learning Material in Earth and Life SciencesOtrebor OmalaNo ratings yet
- IFPMA Position Paper On Redundant TestingDocument8 pagesIFPMA Position Paper On Redundant TestingRhiey BallovarNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Cornell NotesDocument3 pagesChapter 1 Cornell NotesgNo ratings yet
- Laboratory 5 CellsDocument3 pagesLaboratory 5 CellsKuna KunavathiNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1 - Gene Regulation - Edpuzzle Video With QuestionsDocument3 pagesAssignment 1 - Gene Regulation - Edpuzzle Video With QuestionsThuy DinhNo ratings yet
- Principles of Genetics 6th Edition Snustad Test BankDocument15 pagesPrinciples of Genetics 6th Edition Snustad Test BankMelissaLeetioyq100% (18)
- Chapter 22 GENERAL BIOLOGYDocument89 pagesChapter 22 GENERAL BIOLOGYKatelyn ValeraNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1 - Database - Feb 2022Document2 pagesAssignment 1 - Database - Feb 2022Ngọc VânNo ratings yet
- Aertics On Cell OrganelleDocument3 pagesAertics On Cell OrganelleMahak JandwaniNo ratings yet
- Experiment 3 Nucleic AcidsDocument5 pagesExperiment 3 Nucleic AcidsLloyd Patrick D. Gilig83% (6)
- Population GeneticDocument30 pagesPopulation GeneticGuggs Lert-itthipornNo ratings yet
- Gene Therapy PDFDocument3 pagesGene Therapy PDFhmak2002No ratings yet
- ClustalwDocument9 pagesClustalwLoquendorksNo ratings yet
- 3415 1488 1 PB PDFDocument12 pages3415 1488 1 PB PDFAyi Yurike Tri YantiNo ratings yet
- CK-12 Biology Chapter 6 WorksheetsDocument17 pagesCK-12 Biology Chapter 6 WorksheetsNuria TaranconNo ratings yet
- Illustration Showing The Steps in DNA FingerprintingDocument3 pagesIllustration Showing The Steps in DNA FingerprintingCHEE HONG CHANNo ratings yet
- Veer Narmad South Gujarat UniversityDocument5 pagesVeer Narmad South Gujarat UniversityArun PatelNo ratings yet
- Industries PharmaDocument23 pagesIndustries PharmaThanhhai NguyenNo ratings yet