Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Face Presentation: Asheber Gaym M.D. January 2009
Uploaded by
Israel WoseneOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Face Presentation: Asheber Gaym M.D. January 2009
Uploaded by
Israel WoseneCopyright:
Available Formats
Face Presentation
Asheber Gaym M.D.
January 2009
Outline
• Definition of a face presentation
• Discuss the mechanisms of labor in face
presentation
• Describe the diagnosis of face presentation
• Outline the management of a face
presentation
Asheber Gaym, 2009 2
Definitions in Face Presentation
• Boundaries of the face- supra orbital ridges and the root of the
nose superiorly; chins and the mentum inferiorly
• Presenting diameters in face:
– Biparietal diameter – 9.5 cms in a term fetus
– Sub-mento bregmatic diameter- 9 cms in a term fetus
– Denominator in face presentation – the mentum
– Possible positions – 8 – e.g. mento anterior, left mento transverse etc
• Face presentation occurs in fetuses with hyper extension of the
fetal head
• In addition to possible etiologies of all malpresentations, fetal
goiter and excessive nuchal cords are also possible causes of face
presentations
• In prolonged labor with facial edema, face presentation becomes a
differential diagnosis of breech presentation on vaginal exam
Asheber Gaym, 2009 3
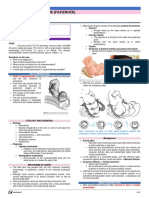
Diagnosis of a Face Presentation
Diagnostic approach Description
Leopold’s palpations Third maneuver- occipital prominence is on the same side of
the back indicating a hyper extended cephalic presentation
Vaginal exam •The supra orbital ridges; the fetal nose; eyes; mouth
openings and gums are felt on gentle vaginal exam. The
forehead is partially felt.
•Differentiation from breech presentation- Opening in breech
( anus ) is on the same line as the two eminences ( ischial
tuberosities) , while the mouth is at right angles to the two
prominences ( chick bones); opening has a tone in breech
presentations while none in face presentation but rather feel
the gums; mechonium is more prominent in breech
presentations and not much in face unless distressed; if not
too edematous the eyes and nose can be felt in the face
•Always assess pelvic capacity carefully in face presentation
Sonography Assess fetal size, anomalies, goiter
Asheber Gaym, 2009 4
Mechanisms of labor in Face Presentation
• Descent with further extension
• Engagement
• Internal rotation at mid pelvis- two possibilities
– Long rotation – upto 135 degrees to the mento anterior position OR
– Short rotation – less than 45 degrees to the mento posterior
position
• In mento anterior positions, delivery follows by flexion of the
head towards the symphysis pubis (face to pubes)
• Persistent mento posterior positions cannot be delivered
vaginally as the head cannot extend further
• The remainder of the mechanisms after delivery of the head
is the same as the vertex
Asheber Gaym, 2009 5
Outline of Management of Face Presentation
• Assess fetal size, pelvic adequacy and the presence of
anomalies at initial diagnosis and intervene with abdominal
delivery if cephalo pelvic disproportion or a contracted pelvis
is diagnosed
• Follow labor progress and ascertain internal rotation to
mento anterior position
• If internal rotation is to the mento posterior position and it
persists, deliver by caesarean section
• Augmentation of labor and application of forceps in delayed
second stage is controversial and if applied should be on an
individualized basis
• Manual rotation to mento anterior position is an outdated
management
Asheber Gaym, 2009 6
You might also like
- Brow PresentationDocument6 pagesBrow PresentationIsrael WoseneNo ratings yet
- Abnormal Fetus Presentations: D.R Thomas MutanikwaDocument40 pagesAbnormal Fetus Presentations: D.R Thomas Mutanikwaguidance100% (1)
- Malpresentation and Malposition of the FetusDocument41 pagesMalpresentation and Malposition of the FetusJonielyn LagunaNo ratings yet
- The Fetal Skull: Asheber Gaym M.D. January 2009Document8 pagesThe Fetal Skull: Asheber Gaym M.D. January 2009Israel WoseneNo ratings yet
- Bien Powerpoint Demo PresentationDocument58 pagesBien Powerpoint Demo PresentationbienNo ratings yet
- Abnormal Labour: Risks and Treatments for MalpositionsDocument92 pagesAbnormal Labour: Risks and Treatments for Malpositionsmohammed farajiNo ratings yet
- O&G CompendiumDocument676 pagesO&G Compendiumwalefamous100% (1)
- Face and Brow Presentation Summary PageDocument2 pagesFace and Brow Presentation Summary PageCyrelle Jen TorresNo ratings yet
- OppDocument41 pagesOppKiprotich Titus NgetichNo ratings yet
- Normal and Abnormal Present IonDocument31 pagesNormal and Abnormal Present IondeemNo ratings yet
- 5th Yr Gynec ExamDocument151 pages5th Yr Gynec ExamHIMANSHU GUPTANo ratings yet
- Shoulder Face PresentationDocument37 pagesShoulder Face PresentationOmar mohamedNo ratings yet
- MK Fetal Lie and Presentation (OBGY)Document9 pagesMK Fetal Lie and Presentation (OBGY)Moses Jr KazevuNo ratings yet
- Obstetric Physical ExaminationDocument17 pagesObstetric Physical ExaminationYusnida Rahmawati100% (1)
- Malpresentation and MalpositionDocument33 pagesMalpresentation and MalpositionPeprah Ondiba100% (1)
- Vo - Pob - Ab Labor (Passenger)Document5 pagesVo - Pob - Ab Labor (Passenger)hk5vnxp2x5No ratings yet
- CHAPTER 2 High Risk Labor and DeliveryDocument26 pagesCHAPTER 2 High Risk Labor and Deliveryjacobprince0016No ratings yet
- Many Types:: Definition of Malpresentation: Any Presentation Other Than Vertex PresentationDocument5 pagesMany Types:: Definition of Malpresentation: Any Presentation Other Than Vertex PresentationMelissa Aina Mohd YusofNo ratings yet
- Labor and Delivery CMCC NotesDocument12 pagesLabor and Delivery CMCC Notesrcestabillo6949100% (1)
- Feto Pelvic DisproportionDocument10 pagesFeto Pelvic DisproportionIsrael WoseneNo ratings yet
- Cephalopelvic Disproportion and Obstructed LabourDocument40 pagesCephalopelvic Disproportion and Obstructed Labournighat khanNo ratings yet
- The Birth Process - StudentDocument327 pagesThe Birth Process - StudentMio RuikoNo ratings yet
- Differentiate Between With AnswersDocument14 pagesDifferentiate Between With AnswersStephy SojanNo ratings yet
- DR Banacu Mihai - Fetal SkullDocument32 pagesDR Banacu Mihai - Fetal SkullSimRasuNo ratings yet
- Managing Mal-Positions and Mal-PresentationsDocument229 pagesManaging Mal-Positions and Mal-PresentationsPriscilla Sarah PayneNo ratings yet
- Fetal MalpresentationDocument83 pagesFetal MalpresentationArianJubaneNo ratings yet
- Malposition AND Malpresentat ION: Regala, Bianca Ysabelle M. BSN Ii - B Rle Group IiiDocument57 pagesMalposition AND Malpresentat ION: Regala, Bianca Ysabelle M. BSN Ii - B Rle Group IiiBiway RegalaNo ratings yet
- Abnormal Labor Lec 2Document40 pagesAbnormal Labor Lec 2Zahraa HasanNo ratings yet
- CPDDocument45 pagesCPDVijith.V.kumar100% (1)
- Abnormal Fetal Positions and Presentations ExplainedDocument14 pagesAbnormal Fetal Positions and Presentations ExplainedAsteway MesfinNo ratings yet
- Fetal SkullDocument32 pagesFetal Skullmoamen.nlNo ratings yet
- Abnormal Lie and PresentationsDocument31 pagesAbnormal Lie and PresentationsNattasha StephenNo ratings yet
- Abdominal Palpation For Fetal PositionDocument22 pagesAbdominal Palpation For Fetal PositionSandra Jane AcostaNo ratings yet
- Abdominal Palpation For Fetal PositionDocument22 pagesAbdominal Palpation For Fetal PositionFerreze AnnNo ratings yet
- 3 Problems With The Passenger and Powers of LaborDocument105 pages3 Problems With The Passenger and Powers of LaborRaquel M. MendozaNo ratings yet
- 4 P's of Labor and Birth: Presented By: Ana Laurice R. Nastor & Nerissa N. Natata RLE II-7.2Document56 pages4 P's of Labor and Birth: Presented By: Ana Laurice R. Nastor & Nerissa N. Natata RLE II-7.2steffiNo ratings yet
- Leopold Maneuvers1 1Document22 pagesLeopold Maneuvers1 1Gladys OdibuNo ratings yet
- Notes Processes of Labour and Birth (2)Document70 pagesNotes Processes of Labour and Birth (2)nsedighpoorNo ratings yet
- Malpositions and MalpresentationsDocument30 pagesMalpositions and Malpresentationsiqra HassanNo ratings yet
- Lecture Leopolds-ManeuverDocument32 pagesLecture Leopolds-ManeuverkrischaniNo ratings yet
- Determine Fetal Position and PresentationDocument22 pagesDetermine Fetal Position and PresentationCharlaine Gripal SudlaNo ratings yet
- The Fetus:Fetal Skull and Its Significance in Labour: Mihai BanacuDocument32 pagesThe Fetus:Fetal Skull and Its Significance in Labour: Mihai BanacuAlex DinuNo ratings yet
- Normal Labor and DeliveryDocument10 pagesNormal Labor and Deliverymendato marcabanNo ratings yet
- Complications With The Passenger 2Document77 pagesComplications With The Passenger 2JudyNo ratings yet
- The Nursing Role in LaborDocument56 pagesThe Nursing Role in LaborQuolette ConstanteNo ratings yet
- Gynecology Tickets All 1Document34 pagesGynecology Tickets All 1moamen.nlNo ratings yet
- Compound Presentation: Asheber Gaym M.D. January 2009Document6 pagesCompound Presentation: Asheber Gaym M.D. January 2009Israel WoseneNo ratings yet
- Maternal and Child Health Nursing - LaborDocument12 pagesMaternal and Child Health Nursing - LaborkimmybapkiddingNo ratings yet
- 40 Normal Labor and DystociaDocument47 pages40 Normal Labor and DystociaCitra Wulandari SofyanNo ratings yet
- NCM 107.1 NotesDocument7 pagesNCM 107.1 NoteskrischaniNo ratings yet
- Abnormal Labour: Perceptor: Dr. Nurul Islamy, M. Kes., Sp. OGDocument54 pagesAbnormal Labour: Perceptor: Dr. Nurul Islamy, M. Kes., Sp. OGramadhiena destia100% (1)
- Dystocia Fetal Malposition and Malpresentation DescriptionDocument7 pagesDystocia Fetal Malposition and Malpresentation Descriptionemi readNo ratings yet
- Shoulder PresentationsDocument5 pagesShoulder PresentationsIsrael WoseneNo ratings yet
- BREECH 2nijnjinijnuihiuhDocument7 pagesBREECH 2nijnjinijnuihiuhChethranNo ratings yet
- Management Normal Labor 2021 SBOGDocument118 pagesManagement Normal Labor 2021 SBOGAHMED .KNo ratings yet
- Final Modified Obsgyn Orals-1Document129 pagesFinal Modified Obsgyn Orals-1Ahmed Adel HassanNo ratings yet
- Malposition & Malpresentation: Ahmad MakhloufDocument72 pagesMalposition & Malpresentation: Ahmad Makhloufjssamc prasootitantraNo ratings yet
- ACFrOgBEGtOKqayqBNgWl7cRDozoAC7IIFrbJTuLoEqpdwn0pt Y4EGdcsgvfe9-0aZjQwd7EmTj3i3ibCKP1RvPW p1mB7cX Ubs8y 3Y1pfDKGb7HyWcIAqo5tJB62FaTOkEsx8QBbZg7u3b-CDocument27 pagesACFrOgBEGtOKqayqBNgWl7cRDozoAC7IIFrbJTuLoEqpdwn0pt Y4EGdcsgvfe9-0aZjQwd7EmTj3i3ibCKP1RvPW p1mB7cX Ubs8y 3Y1pfDKGb7HyWcIAqo5tJB62FaTOkEsx8QBbZg7u3b-CDustin Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Leopolds-Maneuver StudentsDocument40 pagesLeopolds-Maneuver StudentsCarlo GacadNo ratings yet
- Twelve Lessons on Breathing and Breath Control - For Singers, Speakers, and TeachersFrom EverandTwelve Lessons on Breathing and Breath Control - For Singers, Speakers, and TeachersRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Shoulder PresentationsDocument5 pagesShoulder PresentationsIsrael WoseneNo ratings yet
- Compound Presentation: Asheber Gaym M.D. January 2009Document6 pagesCompound Presentation: Asheber Gaym M.D. January 2009Israel WoseneNo ratings yet
- Malpresentations/Malpositions: Asheber Gaym M.D. January 2009Document7 pagesMalpresentations/Malpositions: Asheber Gaym M.D. January 2009Israel WoseneNo ratings yet
- Cord Presentation and ProlapseDocument7 pagesCord Presentation and ProlapseIsrael WoseneNo ratings yet
- Breech PresentationDocument13 pagesBreech PresentationIsrael WoseneNo ratings yet
- Obstructed Labor: Asheber Gaym M.D. January 2009Document10 pagesObstructed Labor: Asheber Gaym M.D. January 2009Israel WoseneNo ratings yet
- Preterm Labor and PrematurityDocument8 pagesPreterm Labor and PrematurityIsrael WoseneNo ratings yet
- Fetal Macrosomia: Asheber Gaym M.D. January 2009Document6 pagesFetal Macrosomia: Asheber Gaym M.D. January 2009Israel WoseneNo ratings yet
- Neonatal Resuscitation: Asheber Gaym M.D. January 2009Document6 pagesNeonatal Resuscitation: Asheber Gaym M.D. January 2009Israel WoseneNo ratings yet
- Uterine Rupture: Asheber Gaym M.D. January 2009Document9 pagesUterine Rupture: Asheber Gaym M.D. January 2009Israel Wosene100% (1)
- Perinatal Asphyxia: Asheber Gaym M.D. January 2009Document8 pagesPerinatal Asphyxia: Asheber Gaym M.D. January 2009Israel WoseneNo ratings yet
- Diabetes and PregnancyDocument1 pageDiabetes and PregnancyIsrael WoseneNo ratings yet
- Feto Pelvic DisproportionDocument10 pagesFeto Pelvic DisproportionIsrael WoseneNo ratings yet
- Pregestational DiabetesDocument1 pagePregestational DiabetesIsrael WoseneNo ratings yet
- The Umbilical Cord and Its AbnormalitiesDocument4 pagesThe Umbilical Cord and Its AbnormalitiesIsrael WoseneNo ratings yet
- Antepartum Fetal Well Being AssessmentDocument14 pagesAntepartum Fetal Well Being AssessmentIsrael WoseneNo ratings yet
- Abnormal Labor (Dystocia)Document14 pagesAbnormal Labor (Dystocia)Israel WoseneNo ratings yet
- The Puerperium: Asheber Gaym M.D. January 2009Document9 pagesThe Puerperium: Asheber Gaym M.D. January 2009Israel WoseneNo ratings yet
- Anemia in PregnancyDocument10 pagesAnemia in PregnancyIsrael WoseneNo ratings yet
- Assessment of Gestational AgeDocument12 pagesAssessment of Gestational AgeIsrael WoseneNo ratings yet
- Physiology of PregnancyDocument12 pagesPhysiology of PregnancyIsrael WoseneNo ratings yet
- Physiology of LaborDocument13 pagesPhysiology of LaborIsrael WoseneNo ratings yet
- Cardiology Handbook Gondar University Hospital: Management GuidelinesDocument42 pagesCardiology Handbook Gondar University Hospital: Management Guidelinessky nutsNo ratings yet
- Diagnosis of PregnancyDocument4 pagesDiagnosis of PregnancyIsrael WoseneNo ratings yet
- Prenatal Diagnosis: Asheber Gaym M.D. January 2009Document7 pagesPrenatal Diagnosis: Asheber Gaym M.D. January 2009Israel WoseneNo ratings yet
- Antenatal Care: Asheber Gaym M.D. January 2009Document13 pagesAntenatal Care: Asheber Gaym M.D. January 2009SehaRizaNo ratings yet
- Economics Unit 1 - 6 Review QuestionsDocument26 pagesEconomics Unit 1 - 6 Review QuestionsEfa WedajoNo ratings yet
- Tremors in Primary CareDocument67 pagesTremors in Primary CareAmir MahmoudNo ratings yet
- Essay 2 Second DraftDocument4 pagesEssay 2 Second Draftapi-644369411No ratings yet
- Health Talk HTNDocument10 pagesHealth Talk HTNSimran KaurNo ratings yet
- Thesis 01Document14 pagesThesis 01Vladimere Censon Reyes100% (1)
- Intestinal Nematodes: Hookworms and Strongyloides ComparisonDocument81 pagesIntestinal Nematodes: Hookworms and Strongyloides ComparisonBituin Amor ParachaNo ratings yet
- CT For PE Breathing Technique PRESENTATIONDocument17 pagesCT For PE Breathing Technique PRESENTATIONEka JuliantaraNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument2 pagesDrug StudymatthewchadNo ratings yet
- MaternityDocument91 pagesMaternityAnonymous D8KswoNo ratings yet
- RCTs in Child and Adolescent Health in Developing Countries 2021-2022Document129 pagesRCTs in Child and Adolescent Health in Developing Countries 2021-2022Sowdatu Abdullah-SandyNo ratings yet
- Antiinflammatory and Antimicrobial Activity of Hexane Extract of Seed of Psoralea Corylifolia LinnDocument9 pagesAntiinflammatory and Antimicrobial Activity of Hexane Extract of Seed of Psoralea Corylifolia Linnvani srcmNo ratings yet
- Mathur 2015Document7 pagesMathur 2015Maximiliano OliveraNo ratings yet
- Badhkummed Indane Gramin Vitark-21-22Document9 pagesBadhkummed Indane Gramin Vitark-21-22gera 0734No ratings yet
- Clear Cell Acanthoma of The Mammary Region: A Case: Laporan Kasus Divisi TBKDocument12 pagesClear Cell Acanthoma of The Mammary Region: A Case: Laporan Kasus Divisi TBKJulian LeeNo ratings yet
- Sumy KrokDocument0 pagesSumy KrokfaithfavourNo ratings yet
- Vet Pathol 2011 2011 ACVP Annual Meeting E1 E51Document52 pagesVet Pathol 2011 2011 ACVP Annual Meeting E1 E51Haroon RashidNo ratings yet
- Techno - Obstetric miniOSCEDocument153 pagesTechno - Obstetric miniOSCEIssa JbourNo ratings yet
- Case Study Pneumonia)Document20 pagesCase Study Pneumonia)Jai - Ho83% (6)
- Brachial Plexus Most ImportantDocument2 pagesBrachial Plexus Most ImportantFlowerNo ratings yet
- Nursing English I Course OutlineDocument5 pagesNursing English I Course OutlineUmmu AL KiramNo ratings yet
- The Beer Geek Handbook - Living A Life Ruled by Beer (2016)Document58 pagesThe Beer Geek Handbook - Living A Life Ruled by Beer (2016)zaratustra21No ratings yet
- Breast ExaminationDocument3 pagesBreast ExaminationShum Wing Hei JoanneNo ratings yet
- DOH Memo For Local Health Departments 12.3.21Document5 pagesDOH Memo For Local Health Departments 12.3.21News10NBCNo ratings yet
- Myasthenia Gravis in The Elderly: NeurologyDocument4 pagesMyasthenia Gravis in The Elderly: NeurologyAirin QueNo ratings yet
- Word ScoutDocument104 pagesWord ScoutMobina RadNo ratings yet
- Vestibular NeuritisDocument2 pagesVestibular NeuritisElsa Nabila YumezaNo ratings yet
- Understand Earthing by Q&ADocument22 pagesUnderstand Earthing by Q&AMohamed ElfekyNo ratings yet
- Evaluation and Management of Autonomic Nervous System DisordersDocument10 pagesEvaluation and Management of Autonomic Nervous System DisordersbpppbbNo ratings yet
- Original PDF Physiology of The Gastrointestinal Tract 6th Edition PDFDocument41 pagesOriginal PDF Physiology of The Gastrointestinal Tract 6th Edition PDFnoe.simons469100% (34)
- Case Study AppendectomyDocument39 pagesCase Study AppendectomyHomework Ping100% (1)
- IVF Drug StudyDocument5 pagesIVF Drug StudyHannah Angelu CabadingNo ratings yet