Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Evaporative Cooling
Uploaded by
Pal MehtaOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Evaporative Cooling
Uploaded by
Pal MehtaCopyright:
Available Formats
EVAPORATIVE COOLING
•Evaporative cooling lowers indoor air temperature by evaporating water.
•It is effective in hot and dry climate where the atmospheric humidity is low.
•In evaporative cooling, the sensible heat of air is used to evaporate water, thereby
cooling the air, which, in turn, cools the living space of the building.
•Increase in contact between water and air increases the rate of evaporation.
•The presence of a water body such as a pond, lake, and sea near the building or a
fountain in a courtyard can provide a cooling effect.
•The most commonly used system
is a desert cooler, which comprises
water, evaporative pads, a fan, and
pump.
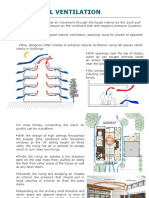
1. Ground cover
2. Water sprinkler
3. Insulated roof
4. Shading trees
5. Water trough
A TYPICAL SECTION SHOWING PASSIVE SOLAR FEATURES OF WALMI BUILDING,BHOPAL
PASSIVE DOWN DRAUGHT COOLING
•Evaporative cooling has been used for many
centuries in parts of the middle east, notably
Iran and turkey.
•In this system, wind catchers guide outside air
over water-filled pots, inducing evaporation and
causing a significant drop in temperature before
the air enters the interior.
•Such wind catchers become primary elements of
the architectural form also.
•Passive downdraught evaporative cooling is
particularly effective in hot and dry climates. It
has been used to effectively cool the Torrent
Research Centre in Ahmedabad.
DETAILS OF THE PASSIVE DOWN DRAUGHT COOLING INLETS
You might also like
- Unit Iii Passive CoolingDocument56 pagesUnit Iii Passive CoolingRaksha sivakumarNo ratings yet
- Solar - EnergtDocument11 pagesSolar - EnergtVignesh PanneerselvamNo ratings yet
- Week 10 - Passive Cooling Techniques - 2021Document31 pagesWeek 10 - Passive Cooling Techniques - 2021Ken Mendoza SencillaNo ratings yet
- Passive Cooling TechniquesDocument16 pagesPassive Cooling TechniquesSANDALI RATHORENo ratings yet
- Passive-Cooling-Techniques 220917Document16 pagesPassive-Cooling-Techniques 220917Cebo DharuNo ratings yet
- Igbc-Vcap Session 1Document81 pagesIgbc-Vcap Session 1Mahindra ChoudaryNo ratings yet
- Waterfs CoolingtowersDocument64 pagesWaterfs CoolingtowersLakshmiprasad KadariNo ratings yet
- Insulation Installation: - Provide Hot Air - Choose Windows With MaximumDocument20 pagesInsulation Installation: - Provide Hot Air - Choose Windows With MaximumNetraNo ratings yet
- Solar Passive TechniquesDocument13 pagesSolar Passive TechniquesAnkit Kashmiri GuptaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 19 Fundamentals of Climate Responsive Buildings - IIDocument16 pagesLecture 19 Fundamentals of Climate Responsive Buildings - IInikita chawlaNo ratings yet
- Ethos of Past, Viability in Present: Dissertation Report OnDocument16 pagesEthos of Past, Viability in Present: Dissertation Report Onnivetha jayaramanNo ratings yet
- Passive Cooling TechniquesDocument15 pagesPassive Cooling TechniquesmadhurimaroyNo ratings yet
- Roof Ponding and Sprinkled Roof: Bs-IiiDocument8 pagesRoof Ponding and Sprinkled Roof: Bs-IiiPriya UdamaleNo ratings yet
- GlossaryDocument2 pagesGlossaryankitfunNo ratings yet
- Condensers: Report By-Ashna Anamika Mugdha PratishthaDocument17 pagesCondensers: Report By-Ashna Anamika Mugdha PratishtharashmiNo ratings yet
- Roof Pond and SkythermDocument19 pagesRoof Pond and SkythermAbishaTeslinNo ratings yet
- Lecture On EvaporationDocument56 pagesLecture On EvaporationMuhammad Shuja ArshadNo ratings yet
- Unit - 03 - Passive CoolingDocument51 pagesUnit - 03 - Passive CoolingSuruthi ATKNo ratings yet
- Design AND Development OF A LOW Cost AIR Cooler: V. S. Shammy, Srinivasa, H. S. LohitDocument7 pagesDesign AND Development OF A LOW Cost AIR Cooler: V. S. Shammy, Srinivasa, H. S. LohitBhupendraNo ratings yet
- Green Buidling InfoDocument35 pagesGreen Buidling Infosaahasitha 14No ratings yet
- A Review of Porous Evaporative Cooling For The Preservation of Fruits and VegetablesDocument8 pagesA Review of Porous Evaporative Cooling For The Preservation of Fruits and VegetablesJessa SolisNo ratings yet
- Cooling Tower PresentationDocument90 pagesCooling Tower Presentationnermeen ahmedNo ratings yet
- Module 1 - Passive StrategiesDocument26 pagesModule 1 - Passive StrategiesDHEESHNA DILEEP 200545No ratings yet
- Ce122 - 6Document26 pagesCe122 - 6공명형No ratings yet
- Cooling WaterDocument61 pagesCooling WaterEmavwodia SolomonNo ratings yet
- Roof PondsDocument21 pagesRoof PondsBhavani U KulkarniNo ratings yet
- Condensor AKMDocument14 pagesCondensor AKMSharmin SumiNo ratings yet
- Geothermal Energy PDFDocument62 pagesGeothermal Energy PDFsapnaNo ratings yet
- TROP3Document33 pagesTROP3louiseNo ratings yet
- The Specific Objectives of This Lesson Are ToDocument11 pagesThe Specific Objectives of This Lesson Are TobellaNo ratings yet
- Wind, Ventilation & IaqDocument18 pagesWind, Ventilation & IaqUpashana DhakalNo ratings yet
- Passive Cooling TechniquesDocument16 pagesPassive Cooling TechniquesPrakhar JainNo ratings yet
- FinalDocument5 pagesFinalKaustubh KingeNo ratings yet
- Hydro Chapter 5 - EvaporationDocument4 pagesHydro Chapter 5 - EvaporationRoel SebastianNo ratings yet
- Unit 3 XX Passive CoolingDocument109 pagesUnit 3 XX Passive CoolingShamreen RoofinaNo ratings yet
- Industrial Plant Cooling EquipmentDocument15 pagesIndustrial Plant Cooling EquipmentkennnNo ratings yet
- Accu 210 Manual t08Document21 pagesAccu 210 Manual t08walter joseNo ratings yet
- Terrace Garden FinalDocument20 pagesTerrace Garden FinalAnonymous t65pTy3MLs86% (7)
- WindcatcherDocument5 pagesWindcatcherfilepzNo ratings yet
- HelloevaporateDocument2 pagesHelloevaporateVarun ZotaNo ratings yet
- Ncert Class11Document41 pagesNcert Class11Manoj SadanandamNo ratings yet
- Unit 3 XX Passive CoolingDocument114 pagesUnit 3 XX Passive CoolingtinabhuvanNo ratings yet
- Architecture For Hot & Humid ClimateDocument40 pagesArchitecture For Hot & Humid ClimateVAGEESHANo ratings yet
- Assignment 3Document5 pagesAssignment 3sejalNo ratings yet
- EvapotranspirationDocument3 pagesEvapotranspirationHAZEL SANDRONo ratings yet
- Passive TechniquesDocument22 pagesPassive TechniquesArnizya noushadNo ratings yet
- Passive CoolingDocument79 pagesPassive CoolingBirimumaso DavidNo ratings yet
- Irrigation Engineering: Evaporation & Infiltration: Presented By: Nicole Primavera Nicole AlicerDocument20 pagesIrrigation Engineering: Evaporation & Infiltration: Presented By: Nicole Primavera Nicole Alicermich cunananNo ratings yet
- Hydrology NotesDocument20 pagesHydrology NotesJennifer JavierNo ratings yet
- Cooling TowerDocument11 pagesCooling TowerDinesh BabuNo ratings yet
- Hot and Dry JaipurDocument20 pagesHot and Dry Jaipur2GI18AT026No ratings yet
- Ijett V23P254Document4 pagesIjett V23P254presly25No ratings yet
- Hydrology (Precipitation)Document12 pagesHydrology (Precipitation)Aj AguilarNo ratings yet
- Passive CoolingDocument27 pagesPassive CoolingAkriti GhildiyalNo ratings yet
- ABEN 70A - 4. Components of Hydrologic CycleDocument44 pagesABEN 70A - 4. Components of Hydrologic CycleJoel GuanzonNo ratings yet
- Climogroundcoolingppt 141103225308 Conversion Gate02Document14 pagesClimogroundcoolingppt 141103225308 Conversion Gate02priyankaNo ratings yet
- Cooling by Underground Earth Tubes PDFDocument4 pagesCooling by Underground Earth Tubes PDFtrola666910No ratings yet
- CT PresentationDocument22 pagesCT PresentationJithin DasNo ratings yet
- Fire Safety Requirements Of: Mercantile OccupancyDocument27 pagesFire Safety Requirements Of: Mercantile OccupancyPal MehtaNo ratings yet
- Vertical Transportation (Bs&e)Document12 pagesVertical Transportation (Bs&e)Pal MehtaNo ratings yet
- Gwalior FortDocument26 pagesGwalior FortPal MehtaNo ratings yet
- Wind Tower: Wind Tower in Jodhpur Hostel To Catch Favorable Cool Wind From South-West For Passive CoolingDocument2 pagesWind Tower: Wind Tower in Jodhpur Hostel To Catch Favorable Cool Wind From South-West For Passive CoolingPal MehtaNo ratings yet
- Natural VentDocument2 pagesNatural VentPal MehtaNo ratings yet
- Earth Air TunnelDocument2 pagesEarth Air TunnelPal MehtaNo ratings yet
- Real World Experience:: - Software RelatedDocument1 pageReal World Experience:: - Software RelatedPal MehtaNo ratings yet
- Manual For Selecting Literature StudiesDocument2 pagesManual For Selecting Literature StudiesPal MehtaNo ratings yet
- P Atel J AL AK: Nati Onal I TY: I NDI ANDocument1 pageP Atel J AL AK: Nati Onal I TY: I NDI ANPal MehtaNo ratings yet
- CoACOE BDossierDocument17 pagesCoACOE BDossierPal MehtaNo ratings yet
- To Do List of StudentsDocument2 pagesTo Do List of StudentsPal MehtaNo ratings yet
- Script For Convocation: RD ND STDocument2 pagesScript For Convocation: RD ND STPal MehtaNo ratings yet
- Ms For Securing Position in Bachelor of Architecture Year at Veer Narmad South Gujarat University, Surat in The Academic YearDocument2 pagesMs For Securing Position in Bachelor of Architecture Year at Veer Narmad South Gujarat University, Surat in The Academic YearPal MehtaNo ratings yet