Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Review of Present Tenses
Uploaded by
JOSE EDUARDO CRUZ PADRONCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Review of Present Tenses
Uploaded by
JOSE EDUARDO CRUZ PADRONCopyright:
Available Formats
Present Tense vs Progressive Tense Present Progressive Tense
Simple Present Tense
We use the simple present tense: We use the present progressive tense:
1. For facts 1. When somebody is doing something at this moment.
● Whales live in the ocean. ● Sarah is changing her clothes right now.
● Aconcagua is the highest mountain in Latin America. ● Her boyfriend is waiting for her.
● The flight from Chile to Australia is thirteen hours. ● We are learning the progressive tense in English.
2. For repeated or regular actions 2. When something is happening at this moment. When the
● Flights to Buenos Aires leave every hour. action has started but hasn't finished.
● I eat breakfast at the table. ● It is snowing at the moment.
● We work every day of the week. ● The economy is growing at an exponential rate.
3. For habits ● The children are sleeping, so please be quiet.
● I brush my teeth three times a day. 3. To talk about something that is happening around the time
● He only drinks Martinis. of speaking but not necessarily at that exact moment.
● We celebrate Christmas on the twenty-fifth of December. ● Alfredo is studying a lot for his exam.
4. For things that are generally true in the present time ● I'm reading a great book. (not necessary right at this
period: moment)
● Boca Juniors is the best team in Argentina at the ● We are planning a trip to Jamaica.
moment.
● She is my girlfriend.
● We study English.
Present vs. Progressive Tense
A significant difference between these two tenses is we use the simple present tense for things that are permanent or are in general and the
present progressive tense for things that may change or are temporary.
Compare:
Permanent Temporary
Simon lives in Birmingham. Simon is living with his friends for now.
James smokes. James is smoking in the kitchen.
We walk to work. We're walking in the park.
I speak English. I am speaking English right now.
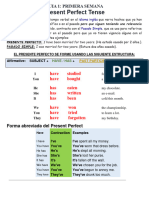
Present Perfect Tense
Contractions
The Present Perfect Tense is formed using the following structure: The contracted form of the perfect tense is quite common:
Affirmative: Subject + Have / Has + Past Participle
Negative: Subject + Haven't / Hasn't + Past Participle Have Contraction Examples
Question: Have / Has + Subject + Past Participle
I have I've I've spent all my
Subject Have Past Rest of the money.
Sentence You have You've You've worn that
Participle dress before.
I have studied for the exam. He has He's He's slept all
morning.
You have bought a new computer. She has She's She's lost her
purse.
He has eaten my chocolate. It has It's It's fallen off the
wall.
She has written an e-mail. We have We've We've chosen you
for the job.
It has been cold this month.
You have You've You've begun to
annoy me.
We have won the championship.
They have They've They've drunk too
You have tried to learn a lot. much.
They have forgotten my birthday.
Negative Sentences Questions
The contraction of the perfect tense in negative form is: Have Subject Past Rest of the
Have not = Haven't Participle Sentence
Has not = Hasn't
Have I been chosen for the
Subject Have Past Rest of the team?
Participle Sentence
Have you bought a new car?
I haven't studied for the exam.
You haven't bought a new Has he eaten my sandwich?
computer.
He hasn't eaten my chocolate.
Has she written the letter?
She hasn't written an e-mail.
Has it started on time?
It hasn't been cold this
month. Have we won a trophy?
We haven't won the
championship.
Have you kept my secret?
You haven't tried to learn a lot.
They haven't forgotten my birthday. Have they driven there?
When do we use the Present Perfect Tense? 4. Events that recently occurred (just)
● Do you want to go to a restaurant with me?
1. Unspecified point in the past
● No, thanks. I've just eaten lunch. (I recently ate lunch.)
● I have been to Spain three times.
5. Events that have occurred up to now (yet)
● (At some unspecified time in the past, I went to Spain).
● Are Carlos and Rodrigo here? No, they haven't arrived
Compare with the simple past:
yet. (they're still not here now)
● I went to Spain three times in 2005.
6. Events that occurred before you expected (already)
● (specified time in the past - the year 2005)
● I've already graduated from University. (I expected to
2. An action that occurred in the past, but has a result in
graduate at a later date.)
the present (now)
7. Events that began in the past and haven't changed (for,
● We can't find our luggage. Have you seen it?
since)
● (The luggage was lost in the past, do you know where it
● Mike has worked at Woodward for 3 years.
is now?)
● (Mike started working at Woodward 3 years ago and he
3. Talking about general experiences (ever, never)
still works there now.)
It usually refers to an event happening at some moment in your
● Julie has worked at Woodward since September last
life.
year.
● Has she ever tried Chilean wine before? (in her life)
● (Julie began working at Woodward in September of last
● I've never eaten monkey brains before. (in my life)
year, and that hasn't changed - she still works here now.)
You might also like
- The Present Perfect TenseDocument3 pagesThe Present Perfect TenseAlexander SanchezNo ratings yet
- Present Simple PDFDocument19 pagesPresent Simple PDFyorvin joel ordoñez huamanNo ratings yet
- Present Perfect TenseDocument10 pagesPresent Perfect TenseRHINEETHA KARUPPEIAHNo ratings yet
- Mari Present PerfectDocument10 pagesMari Present Perfectdavomartinez1408No ratings yet
- Rules of the Present Perfect TenseDocument3 pagesRules of the Present Perfect TenseCnorazimah OmarNo ratings yet
- Present Perfect TenseDocument3 pagesPresent Perfect TensebenjamindomadorxNo ratings yet
- Guia 1 Semana Present PerfectDocument5 pagesGuia 1 Semana Present Perfectmanuelcarvajal0109No ratings yet
- Intermediate & Advanced Level Study Guide on the Present Perfect TenseDocument3 pagesIntermediate & Advanced Level Study Guide on the Present Perfect TenseyeimiNo ratings yet
- Copia de Present PerfectDocument2 pagesCopia de Present PerfectKeyra BenzantNo ratings yet
- Ingilizce Proje Ahmet Kerem Safak 10E 211Document28 pagesIngilizce Proje Ahmet Kerem Safak 10E 211krmahm07No ratings yet
- Achievements and SuccessesDocument39 pagesAchievements and SuccessesKelly GuerreroNo ratings yet
- Present PerfectDocument5 pagesPresent PerfectMariam KobakhidzeNo ratings yet
- PRESENTnPERFECTnn 5865334bb68e3afDocument20 pagesPRESENTnPERFECTnn 5865334bb68e3afJuan OrtegaNo ratings yet
- Present Tense For English Grammar 1 PDFDocument7 pagesPresent Tense For English Grammar 1 PDFThamil M Thamil MNo ratings yet
- Present Perfect 1Document4 pagesPresent Perfect 1Alpha dookNo ratings yet
- General ReviewDocument6 pagesGeneral ReviewØptímí ŠtãNo ratings yet
- Simple Past X Present Perfect Grammar Guides 124605Document13 pagesSimple Past X Present Perfect Grammar Guides 124605Ruben MatthewsNo ratings yet
- Gold Exp Grammar PPT A1 U5Document8 pagesGold Exp Grammar PPT A1 U5jeffersongq1No ratings yet
- Present Continuous.: How Do We Make The Present Continuous Tense?Document11 pagesPresent Continuous.: How Do We Make The Present Continuous Tense?RANDY NAYID PADILLA BELENONo ratings yet
- Gold - Exp - Grammar - PPT - Present ContinuousDocument8 pagesGold - Exp - Grammar - PPT - Present ContinuousnguerreroNo ratings yet
- Present Cont - Grammar ReviewDocument8 pagesPresent Cont - Grammar ReviewYamile AbdalaNo ratings yet
- Present Continuous ExplanationDocument6 pagesPresent Continuous ExplanationLauraNo ratings yet
- Tenses Review - Differenes Between TensesDocument10 pagesTenses Review - Differenes Between TensesVirginia AlpaNo ratings yet
- PDF Present Perfect TenseDocument10 pagesPDF Present Perfect TenseellysanmayNo ratings yet
- Present TensesDocument4 pagesPresent TensesZorica ArnaudovaNo ratings yet
- Present Perfect: Yet, Just, AlreadyDocument2 pagesPresent Perfect: Yet, Just, AlreadyASLY CAMILA SOLARTE DELGADONo ratings yet
- Present ContinuousDocument23 pagesPresent ContinuousbandankapavlyshynNo ratings yet
- English TensesDocument19 pagesEnglish TensesPS DigitalEraNo ratings yet
- Present Perfect Simple and Continuous WorksheetDocument4 pagesPresent Perfect Simple and Continuous WorksheetMiguel RodriguesNo ratings yet
- Reglas - Present PerfectDocument1 pageReglas - Present Perfectkeyko vera ruizNo ratings yet
- Pontificia Universidad Católica Del Ecuador English A2.2: Who What Which Where When WhyDocument26 pagesPontificia Universidad Católica Del Ecuador English A2.2: Who What Which Where When WhyEralda HushNo ratings yet
- PPP PR Perfect GPPT 1Document33 pagesPPP PR Perfect GPPT 1Amira OsmankićNo ratings yet
- 12 Tenses by AkiDocument8 pages12 Tenses by AkiKaung Myat Thu AkihikoNo ratings yet
- Gold Exp GrammarDocument8 pagesGold Exp GrammarElder CuencaNo ratings yet
- Present ContinuousDocument8 pagesPresent ContinuousVirginiaNo ratings yet
- Grammar A1 - 5 Present ContinuousDocument8 pagesGrammar A1 - 5 Present ContinuousЮлия ДемьяноваNo ratings yet
- Semana2 Inglés2Document4 pagesSemana2 Inglés2Angelica LimasNo ratings yet
- Perfect TenseDocument22 pagesPerfect Tensejulfika100% (2)
- Gold Experience b1 2nd Edition SBDocument171 pagesGold Experience b1 2nd Edition SBCarolina Semilla100% (1)
- Past Tense For Real Life Conversations-1Document6 pagesPast Tense For Real Life Conversations-1Alberto OlveraNo ratings yet
- MAKALAH BAHASA INGGRIS PAST TENSEDocument71 pagesMAKALAH BAHASA INGGRIS PAST TENSEMahawan Ma'alyNo ratings yet
- Adobe Scan 28 Jun 2022Document1 pageAdobe Scan 28 Jun 2022IsnatainiNo ratings yet
- Present Perfect Continuous - ProgressiveDocument4 pagesPresent Perfect Continuous - ProgressiveIONESCU ADRIANANo ratings yet
- Gramar TensesDocument33 pagesGramar TensesSehrishNo ratings yet
- PAST PERFECT VS PAST SIMPLE ResueltoDocument9 pagesPAST PERFECT VS PAST SIMPLE ResueltoCortock GzNo ratings yet
- GREX3 U2RTG Chart2.1-2.7Document7 pagesGREX3 U2RTG Chart2.1-2.7alice barnesNo ratings yet
- Adobe Scan 25 Jun 2022Document1 pageAdobe Scan 25 Jun 2022IsnatainiNo ratings yet
- GRAMMAR For Speaking The Present PerfectDocument1 pageGRAMMAR For Speaking The Present Perfectkim bíchNo ratings yet
- Intermediate - Unit 2 (Present Perfect Progressive)Document16 pagesIntermediate - Unit 2 (Present Perfect Progressive)DanielNo ratings yet
- Present PerfectDocument18 pagesPresent PerfectPopescu DanielaNo ratings yet
- Was and WereDocument2 pagesWas and WereMaylin AguilarNo ratings yet
- Was Was Were: Instituto Internacional de Idiomas Facultad Seccional Chiquinquira Topic: Past of Be. Week: 2 Time: 1 WeekDocument4 pagesWas Was Were: Instituto Internacional de Idiomas Facultad Seccional Chiquinquira Topic: Past of Be. Week: 2 Time: 1 WeekDayana SanchezNo ratings yet
- Present PerfectDocument4 pagesPresent PerfectDessire FernandezNo ratings yet
- Present Perfect Tense GuideDocument13 pagesPresent Perfect Tense Guideshirley wongNo ratings yet
- Present Perfect Continuous Tenses ExplainedDocument10 pagesPresent Perfect Continuous Tenses ExplainedPetra StefanescuNo ratings yet
- T e N S e SDocument13 pagesT e N S e Snestani shiukashviliNo ratings yet
- Present Perfect Tense GuideDocument11 pagesPresent Perfect Tense GuideZahid Hussain BrohiNo ratings yet
- BookDocument27 pagesBookAnisa AragsanNo ratings yet
- Agreeing & DisagreeingDocument8 pagesAgreeing & DisagreeingJOSE EDUARDO CRUZ PADRONNo ratings yet
- Too, So, and EnoughDocument4 pagesToo, So, and EnoughJOSE EDUARDO CRUZ PADRONNo ratings yet
- How To Write A Complaint LetterDocument14 pagesHow To Write A Complaint LetterJOSE EDUARDO CRUZ PADRONNo ratings yet
- Cleft SentencesDocument22 pagesCleft SentencesJOSE EDUARDO CRUZ PADRONNo ratings yet
- Placement TestDocument14 pagesPlacement Testioana.airineiNo ratings yet
- PRESENT PERFECT Vs PRESENT PERFECT CONTINUOUSDocument8 pagesPRESENT PERFECT Vs PRESENT PERFECT CONTINUOUSPedro Mujica100% (1)
- Further Discussion Questions ENT1225Document5 pagesFurther Discussion Questions ENT1225Le Nguyen Ngoc Han (FPL HCM)No ratings yet
- ARTICLE MASTERYDocument3 pagesARTICLE MASTERYlinhNo ratings yet
- Report Attachment Sarova ZippyfinalDocument24 pagesReport Attachment Sarova Zippyfinaljohn mwangi50% (6)
- International Gcse English As A Second Language 4es1 Sam Paper 1 ReadingDocument20 pagesInternational Gcse English As A Second Language 4es1 Sam Paper 1 ReadingClover100% (1)
- Focus Unit 1Document6 pagesFocus Unit 1Elene ChkhaidzeNo ratings yet
- Welcome To: Qatar's Most Iconic ResortDocument18 pagesWelcome To: Qatar's Most Iconic ResortMohammed AadilNo ratings yet
- Assessing-Domalanta, Ashley Jade V. (12-Charity)Document4 pagesAssessing-Domalanta, Ashley Jade V. (12-Charity)Ashley Jade DomalantaNo ratings yet
- Technology and Home Economics (Cookery) : Generate A Business Idea That Relates With Career Choice in CookeryDocument21 pagesTechnology and Home Economics (Cookery) : Generate A Business Idea That Relates With Career Choice in Cookerykenneth sison100% (7)
- Semana Del 09.03.2020 Al 15.03.2020Document40 pagesSemana Del 09.03.2020 Al 15.03.2020Administracion TonyGasNo ratings yet
- Come to my house directionsDocument3 pagesCome to my house directionsKarim Villa RedkenNo ratings yet
- Germany Culture & EtiquetteDocument6 pagesGermany Culture & EtiquetteKartika OktavianiNo ratings yet
- I'm Gone 10Document1 pageI'm Gone 10aschleezamoraNo ratings yet
- Peta 1Document2 pagesPeta 1Mailyn G. ElacreNo ratings yet
- Sushi KingDocument4 pagesSushi Kingamber_river1119No ratings yet
- I. Put The Verbs Into The Correct Tense (Present Simple OR Present Continuous)Document4 pagesI. Put The Verbs Into The Correct Tense (Present Simple OR Present Continuous)Leah ClovisNo ratings yet
- January 25, 1979: Spell It Backward and Emanon Has No Name... Just JazzDocument1 pageJanuary 25, 1979: Spell It Backward and Emanon Has No Name... Just JazzrussellNo ratings yet
- 5-1 Future #1Document7 pages5-1 Future #1cesar antonio arriaga carrizalesNo ratings yet
- The Hilton Colon QuitoDocument3 pagesThe Hilton Colon QuitoSaida Calero RequelmeNo ratings yet
- Jo's Chicken Milagrina Restaurant ReviewDocument8 pagesJo's Chicken Milagrina Restaurant ReviewCamille PanerNo ratings yet
- Odyssey Restaurant - Google SearchDocument1 pageOdyssey Restaurant - Google SearchEliana Andrea GriffonettiNo ratings yet
- Proper Waiting & Table ServiceDocument2 pagesProper Waiting & Table ServiceJasmine BalbinNo ratings yet
- Case Study: Mcdonald'S "Seniors" RestaurantDocument2 pagesCase Study: Mcdonald'S "Seniors" RestaurantShubham PawarNo ratings yet
- At Home: Lingua House Lingua HouseDocument3 pagesAt Home: Lingua House Lingua HouseKovacs AlinaNo ratings yet
- In Partial Fulfilment of The Requirements in Quality Service Management in Tourism & Hospitality THC 123Document8 pagesIn Partial Fulfilment of The Requirements in Quality Service Management in Tourism & Hospitality THC 123ERICA VILLAGRACIANo ratings yet
- Curriculum Vitae: Personal DetailsDocument4 pagesCurriculum Vitae: Personal DetailsElawarasi NadarajanNo ratings yet
- Core1 Lo1 Info Sheet 1.1-4Document6 pagesCore1 Lo1 Info Sheet 1.1-4Anne MorenoNo ratings yet
- Food Chain Magnate Cards ListDocument1 pageFood Chain Magnate Cards ListBella HollóNo ratings yet
- Materi 7 - New - Market - Leader - Elementary - Course - Book-44-51 - CH 5Document8 pagesMateri 7 - New - Market - Leader - Elementary - Course - Book-44-51 - CH 5Immanuel PaternuNo ratings yet