Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Tenses (Autosaved)
Uploaded by
m manish kumar0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
12 views10 pagesOriginal Title
Tenses [Autosaved]
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
12 views10 pagesTenses (Autosaved)
Uploaded by
m manish kumarCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 10
Tense
A tense is used to refer to time- past, present and future. It
tells us whether the time of action is past, present or
future.
Tense can also be defined as the form of a verb which
shows the time and the state of an action or event.
We divide it in three parts:-
1. Present Tense
2. Past Tense
3. Future Tense.
Present Tense Singular Plural
1st Person I like We like
2nd Person You like You like
3rd Person He likes They like
Past Tense Singular Plural
1st Person I liked We liked
2nd Person You liked You liked
3rd Person He liked They liked
Future Tense Singular Plural
1st Person I shall like We shall like
2nd Person You will like You will like
3rd Person He will like They will like
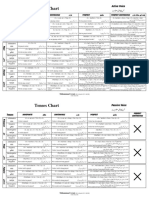
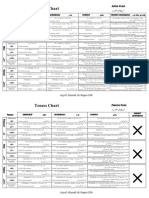
Each Tense can be sub- divided into four forms as is shown in the following table.
Simple Continuous Perfect Perfect Continuous
Present I play cricket
He plays cricket
I am playing cricket
He is playing cricket
I have played cricket
He has played cricket
I have been playing cricket for
two hours.
We play cricket We are playing cricket We have played cricket. He has been playing cricket since
You play cricket You are playing cricket You have played cricket morning.
We have been playing cricket
since morning.
You have been playing cricket for
two hours
Past I played cricket.
He played cricket.
I was playing cricket
He was playing cricket.
I had played cricket
He had played cricket.
I had been playing cricket for two
hours.
We played cricket. We were playing cricket. We had played cricket. He had been playing cricket since
You played cricket. You were playing cricket. You had played cricket. morning
We had been playing cricket since
morning.
You had been playing cricket
since morning
Future I will play cricket
He will play cricket.
I will be playing cricket.
He will be playing cricket.
I will have played cricket
He will have played cricket.
I will have been playing cricket for
two hours.
We will play cricket We will be playing cricket We will have played cricket. He will have been playing cricket
You will play cricket. You will be playing cricket You will have played cricket. since morning
We will have been playing cricket
since morning.
You will have been playing cricket
for two hours
Interrogative sentences
Simple Continuous Perfect Perfect Continuous
Present Do I play cricket?
Does he/she play?
Am I playing cricket?
Is he/she playing cricket?
Have I played cricket?
Has he/she played cricket?
Have I been playing cricket?
Has he been playing cricket?
cricket? Are we playing cricket? Have we played cricket? Have we been playing cricket?
Do we play cricket? Are you playing cricket? Have you played cricket? Have you been playing cricket?
Do you play cricket?
Past Did I play cricket?
Did he/she play
Was I playing cricket?
Was he/she playing cricket?
Had I played cricket?
Had he/she played cricket?
Had I been playing cricket for two
hours
cricket? Were we playing cricket? Had we played cricket? Had he/she been playing cricket?
Did we play cricket? Were you playing cricket? Had you played cricket? Had we been playing cricket?
Did You play cricket? Had you been playing cricket?
Future Will I play cricket?
Will he/she play
Will I be playing cricket?
Will he/she be playing
Will I have played cricket?
Will he/she have played
Will I have been playing cricket?
Will he/she have been playing
cricket? cricket. cricket. cricket?
Will we play cricket? Will we be playing cricket? Will we have played cricket? Will we have been playing
Will you play Will you be playing cricket? Will you have played cricket? cricket?
cricket? Will you have been playing
cricket?
Negative sentence structure
Simple Continuous Perfect Perfect Continuous
Present I do not play cricket.
He/she does not
I am not playing cricket
He/she is not playing cricket
I have not played cricket.
He/she has not played
I have not been playing cricket
since morning.
play cricket. We are not playing cricket cricket. He/she has not been playing
We do not play You are not playing cricket We have not played cricket. cricket for two hours
cricket. You have not played cricket. We have not been playing cricket.
You do not play You have not been playing cricket
cricket. since morning
Past I did not play cricket.
He/she did not play
I was not playing cricket.
He/she was not playing
I had not played cricket
He/she had not played
I had not been playing cricket for
two hours
cricket. cricket. cricket. He/she had not been playing
We did not play We were not playing We had not played cricket. cricket since morning
cricket. cricket. You had not played cricket. We had not been playing cricket
You did not play You were not playing since morning
cricket. cricket. You had not been playing cricket
since morning.
Future I will not play cricket
He/she will not play
I will not be playing cricket.
He/she will not be playing
I will not have played cricket
He/she will not have played
I will not have been playing
cricket for two hours
cricket. cricket. cricket. He/she will not have been playing
We will not play We will not be playing We will not have played cricket since morning
cricket cricket cricket. We will not have been playing
You will not play You will not be playing You will not have played cricket for two hours
cricket. cricket cricket. You will not have been playing
cricket since morning
The uses of the Tenses
Simple Present Tense:- (subj. + 1st form of the verb + obj.)
1. To indicate an action or event that take place at present.
e.g., He writes a book.
2. To express a habitual action.
e.g., Lalita drinks tea everyday.
3. To express general truths.
e.g., The sun sets in the West.
4. In exclamatory sentences beginning with here and there to express what is
actually taking place in the present.
e.g., Here comes the train!
5. To indicate a future event that is part of a plan or arrangement.
e.g., They go to Mumbai next week.
6. To introduce quotations.
e.g., Brevity is the soul of wit.
7. It is used instead of the Simple Future Tense, in clauses of time and of condition.
e.g., I shall bring a watch if I go to Delhi.
Present Continuous Tense: (Subj. + is/am/are + 1st form of verb+ing)
1. For an action going on at the time of speaking.
e.g., Sunita is singing a song.
2. For a temporary action which may not be actually happening at the time of
speaking.
e.g., Ram is reading ‘Oliver Twist’.
3. For an action that is planned or arranged to take place in the near future.
e.g., We are leaving for Delhi tonight.
4. The following verbs of preception , e.g. see, hear, smell, notice, recognize
Verb of appearing, e.g. appear, look,seem.
Verb of emotion, e.g. want, wish, desire, feel, like, love, hate, hope, refuse
Verb of thinking, e.g. think, suppose, believe, agree, consider, trust, remember,
forget, know, understand, imagine,
Possessive verb own, possess, belong to, contain, consist of.etc. are not used in
present continuous tense.
These verbs are generally used in the Simple Present.
Present Perfect Tense (sub+has/have+3rd form of verb)
1. To indicate completed activities in the immediate past.
e.g., Ram has just gone out.
2. To express past action whose time is not given and not definite.
e.g., Have you read The Fairy Tales?
3. To describe past events when we think more of their effect in the present than of tha
action itself
e.g., Ram has eaten all the apples It means he has left nothing.
4. To denote an action beginning at some time in the past and continuing up to the
present moment
e.g., we have known her for a long time.
5. The following adverb can be used with the Present Perfect Tense:- just, often, never,
ever, so far, till, now, yet, already etc.
Present Perfect Continuous (subj. + has/have + been + 1 st form of verb+ing)
2. The Present Perfect Continuous is used for an action which began at some time in
the past and is still continuing
e.g., Ram has been sleeping for five hours (and is still sleeping).
2. We sometimes use this tense for an action already finished. In such cases the
continuity of the activity is emphasized as an explanation of something
e.g., Why are you so tired?- I have been working hard for the last four days.
Simple Past Tense (subj + 2nd form of the verb+ object)
1. We use the Simple Past to indicate an action completed in the past. It often occurs
with adverbs or adverb phrases of past time.
e.g., We went to the market yesterday.
2. This tense can be used without an adverb of time. In such cases the time may be
either implied or indicated by the context.
e.g., My father learnt German in Germany.
3. The Simple Past can also be used for past habits.
e.g., We played many hours every day.
Past Continuous Tense (Subj.+ was/were+1st form of verb+ing)
2. The past continuous is used to denote an action going on at some time in the past.
The time of the action may or may not be indicated
e.g., We were reading when the light went out.
Past Perfect Tense( Subj. + had + 3rd form of the verb)
3. The Past Perfect Tense describes an action completed before certain moment in the
past
e.g., We had not seen him for the last five years.
2. When there are two past actions, the past perfect tense is used to indicate the earlier
action
e.g., We we reached the station the train had left.
Past perfect Continuous Tense( subj. + had been + 1 st form of verb + ing)
The Past Perfect Continuous can be used for an action that began before a certain point in
the past and continued up to that time
e.g., At that time Rita Had been painting a portrait for two week.
Simple Future Tense (subj. + will/shall + 1st form of the verb)
1. The Simple Future can be used for an action that is still to take place
e.g., We shall see you tomorrow.
Future Continuous Tense (subj. + will/shall be +1st form of verb + ing)
The Future Continuous Tense represents an action as going on at sometime in future
e.g., We shall be reading the magazines then.
This tense can also be used for future events that are planned
e.g., She will be staying here till Monday
Future Perfect Tense (Subj.+ will/shall + have + 3rd form of verb)
This tense is used to indicate the completion of an action by a certain future time.
e.g., We shall have written our articles by that time.
Future Perfect Continuous Tens ( subj. + will/shall +have + been + 1 st form of verb +ing)
The Future Perfect Continuous indicates an action represented as being in progress over a
period of time that will end in the future
e.g., By next month, we shall have been living here for two years.
You might also like
- Lesson 16 LullonDocument2 pagesLesson 16 LullonharpreetNo ratings yet
- All Tenses in One PageDocument2 pagesAll Tenses in One Pagekashiflashari674No ratings yet
- All Tenses in One PageDocument2 pagesAll Tenses in One PageMuneer AhmadNo ratings yet
- All Tenses by AqeelDocument2 pagesAll Tenses by AqeelAqeel AhmadNo ratings yet
- Czasy OdmianaDocument2 pagesCzasy OdmianaKrolewskaNo ratings yet
- Safari - 05-Nov-2017 at 1:46 PMDocument1 pageSafari - 05-Nov-2017 at 1:46 PMRobert RubensNo ratings yet
- Ashwin - Morgan Fight - 'Am I A Disgrace Like Eoin Morgan Said I Was - ' - R Ashwin Clears The Air On Altercation With KKR Skipper - Cricket NewsDocument4 pagesAshwin - Morgan Fight - 'Am I A Disgrace Like Eoin Morgan Said I Was - ' - R Ashwin Clears The Air On Altercation With KKR Skipper - Cricket Newsyusuf shaikhNo ratings yet
- Day Monday Tuesday Wednesday Thursday Friday Saturday SundayDocument1 pageDay Monday Tuesday Wednesday Thursday Friday Saturday SundayChloe OberlinNo ratings yet
- контрольна 6 класDocument2 pagesконтрольна 6 класЮлия ВознюкNo ratings yet
- Adverb Clause of Contrast/ ConcessionDocument4 pagesAdverb Clause of Contrast/ ConcessionMinh ThiNo ratings yet
- Year 4 Literacy Figurative Language 3 Levels With AnswersDocument10 pagesYear 4 Literacy Figurative Language 3 Levels With AnswersmanuNo ratings yet
- Q 1-Diagnostic TestDocument4 pagesQ 1-Diagnostic TestJane PanhayNo ratings yet
- Revision Past Simple 3ac Mars 2020Document2 pagesRevision Past Simple 3ac Mars 2020Melek AltunNo ratings yet
- Future Perfect Tense: What Will The Future Bring and When?Document6 pagesFuture Perfect Tense: What Will The Future Bring and When?Jose Jacob Ortiz MoralesNo ratings yet
- Dictionary of Idioms and Their OriginsDocument224 pagesDictionary of Idioms and Their OriginsJosé Carlos Medina Alejo75% (4)
- Rubric For Assessment in Oral Communication Performance TaskDocument3 pagesRubric For Assessment in Oral Communication Performance TaskSnow BollNo ratings yet
- 5B GRAMMAR Superlatives (+ Ever + Present Perfect) : Write The Opposite SuperlativesDocument1 page5B GRAMMAR Superlatives (+ Ever + Present Perfect) : Write The Opposite SuperlativesB McNo ratings yet
- Virtual Tour Guiding Rubric: Total Score For The Above Presentation /100Document1 pageVirtual Tour Guiding Rubric: Total Score For The Above Presentation /100Michelle AsneNo ratings yet
- Hard Math For Middle SchoolDocument184 pagesHard Math For Middle SchoolJani TandaNo ratings yet
- Old English Period: Main Phonetic ChangesDocument13 pagesOld English Period: Main Phonetic ChangesKamillaJuhászNo ratings yet
- Reading Buddhist Sanskrit Texts An Elementary Grammatical Guide (Dhammajoti, Kuala Lumpur)Document442 pagesReading Buddhist Sanskrit Texts An Elementary Grammatical Guide (Dhammajoti, Kuala Lumpur)liu chingNo ratings yet
- Preview Activity 1: The Evolution of Ancient Egypt's Pyramids (C1)Document6 pagesPreview Activity 1: The Evolution of Ancient Egypt's Pyramids (C1)Dajana SamardzicNo ratings yet
- Subject-Verb AgreementDocument35 pagesSubject-Verb AgreementNandy DacoycoyNo ratings yet
- EulogyDocument24 pagesEulogymarinel de claroNo ratings yet
- LITERACY HOUR LESSON Plan WRITINGDocument5 pagesLITERACY HOUR LESSON Plan WRITINGLeesha St. ClaireNo ratings yet
- Mfantse KasasuaDocument74 pagesMfantse KasasuaCharlesNo ratings yet
- Plano de Estudo B1Document29 pagesPlano de Estudo B1Lyzandra FigueiredoNo ratings yet
- Ipsoot FAQDocument4 pagesIpsoot FAQMahi SinghNo ratings yet
- The Origin of Haplogroup I1-M253 in Eastern Europe Alexander ShtrunovDocument11 pagesThe Origin of Haplogroup I1-M253 in Eastern Europe Alexander ShtrunovАлександр Штрунов100% (2)
- Invitation To LinguisticsDocument196 pagesInvitation To LinguisticsZara NurNo ratings yet
- Embedded QuestionsDocument20 pagesEmbedded QuestionsNghé XùNo ratings yet
- Learning Guide Eng 9 Week 3-4Document6 pagesLearning Guide Eng 9 Week 3-4Juvelyn Abugan LifanaNo ratings yet
- Simple Future TenseDocument6 pagesSimple Future TenseNurul NurhayatiNo ratings yet
- Nekopara ED - Hidamari No KaoriDocument6 pagesNekopara ED - Hidamari No KaoriМаксимNo ratings yet
- Problems of Lexicology and LexicographyDocument9 pagesProblems of Lexicology and LexicographyIsianya JoelNo ratings yet
- The Four Main Linguistic Schools of ThoughtDocument1 pageThe Four Main Linguistic Schools of ThoughtHelena LópezNo ratings yet
- Latihan BHS InggrisDocument19 pagesLatihan BHS InggrisFatiah Andhara IsyaNo ratings yet
- English Language and Literature (184) Set 2 3 2 Class X Marking Scheme 2020Document10 pagesEnglish Language and Literature (184) Set 2 3 2 Class X Marking Scheme 2020KishiNo ratings yet
- Lexicology IndividualDocument12 pagesLexicology IndividualShahin İbrahimNo ratings yet