Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Light
Uploaded by
Analiza Toledo0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
12 views17 pagesCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
12 views17 pagesLight
Uploaded by
Analiza ToledoCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 17
Isaac Newton
He believed that light behaves like a
particle.
Christian Huygens
He believed that light behaves like a
wave.
Max Planck
He came up with what is known as the
Dual-Nature of Light.
James Clark Maxwell
He proposed the Electromagnetic
Theory of Light.
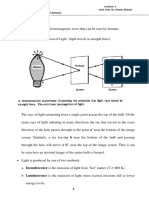
Transmission of Light
Transparent
-> matter that transmits most of the light
->transparent materials allow light
to pass through so you can clearly
see objects through them.
Translucent
-> other materials like frosted
glass allow some light to pass
through but you cannot
clearly see objects through
them
Opaque
-> matter that reflects or absorbs
but does not transmit light
Most solids are opaque. You
cannot see through them.
Speed of Light
Light travels with a speed of about 300
millions m/s in a vacuum.
At this amazing speed, light from the sun
takes only 8 minutes to travel to Earth.
Intensity of Light
The brightness of light depends on the source
and the distance from the source.
Brightness is qualitative and is dependent
of the person’s perception.
Brightness can be expresses as luminous
intensity with a unit known as candela.
One candle can approximately represent
the amount of visible radiation emitted
by a candle flame.
The quantity that measures the amount
of light illuminating a surface is called
intensity.
The Electromagnetic
Spectrum
Light waves are produced by the vibrations of
electric and magnetic fields.
Light is therefore a form of
electromagnetic radiation.
It is the complete range of electromagnetic
waves placed in order of increasing frequency.
The electromagnetic spectrum is made
up of radio waves, microwaves, infrared
rays, visible light, ultraviolet rays, x-rays
and gamma rays.
Visible Light
The visible part of which is known as white
light. Our eyes perceive different wavelengths
of light as the rainbow hues of color.
This narrow band of visible light is known as
ROYGBV.
Colors of Object
When all colors of light combine, you see
white light.
White light from the sun can be separated by a
prism into colors of visible spectrum.
The process of separation is called dispersion.
Dispersion is a phenomenon in which a prism
separates into white light into its component
colors.
When white light enters a prism and travels
slower in speed than in vacuum, color
separation is observed due to variation in the
frequency and wavelength of color lights.
You might also like
- For PhotographyDocument15 pagesFor Photographyrochelle posadasNo ratings yet
- LightDocument12 pagesLightapi-3703711100% (1)
- Chapter 5 Notes ShortXDocument46 pagesChapter 5 Notes ShortXdsckln/cmakNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetic Spectrum and Visible LightDocument14 pagesElectromagnetic Spectrum and Visible LightDreian Calaoagan PalalayNo ratings yet
- Phy 104 Atomic SpectraDocument24 pagesPhy 104 Atomic SpectraAisha abba HabibNo ratings yet
- Chapter 10 Light WavesDocument27 pagesChapter 10 Light WavesDom Christian LastNo ratings yet
- Module 2 in Forensic Photography Chapter 2Document9 pagesModule 2 in Forensic Photography Chapter 2escasinasjeralyn42No ratings yet
- The Nature of Light: Does It Behave? These Questions May Seem Simple To You, But They Have PresentedDocument5 pagesThe Nature of Light: Does It Behave? These Questions May Seem Simple To You, But They Have PresentedAbdul QuadirNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Investigatory Project: Name: Yogesh Singh Class: Xii B Submitted To: Ms - Sharaddha NarwariyaDocument36 pagesChemistry Investigatory Project: Name: Yogesh Singh Class: Xii B Submitted To: Ms - Sharaddha NarwariyaSinghnarwariyaNo ratings yet
- ProjectDocument11 pagesProjectMehak Parvez HamdaniNo ratings yet
- Light WavesDocument12 pagesLight WavesMpforgeNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetic WavesDocument10 pagesElectromagnetic WavesJelia fei MadarangNo ratings yet
- Definition of Light WavesDocument9 pagesDefinition of Light WavesJF BatucalNo ratings yet
- Light - WikipediaDocument89 pagesLight - WikipediaRaj ThakurNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetic SpectrumDocument17 pagesElectromagnetic SpectrumAviation/Space History Library100% (4)
- 64359b020fd8f800181c4e8b - ## - Light - Reflection and Refraction 01: Class Notes - (Udaan 2024)Document14 pages64359b020fd8f800181c4e8b - ## - Light - Reflection and Refraction 01: Class Notes - (Udaan 2024)Lal BhaiNo ratings yet
- Light PropertiesDocument12 pagesLight PropertiessampreethpNo ratings yet
- Spectroscopy Intro PDFDocument35 pagesSpectroscopy Intro PDFonyxNo ratings yet
- Unidad 3 - Espectro Electromagnético (Inglés)Document32 pagesUnidad 3 - Espectro Electromagnético (Inglés)bemdasNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Investigatory Project 12 BDocument20 pagesChemistry Investigatory Project 12 Banitta0% (1)
- Review of LiteratureDocument5 pagesReview of LiteratureAllen HabibovicNo ratings yet
- Dispersion of LightDocument2 pagesDispersion of LightEmman Revilla100% (1)
- LightDocument14 pagesLightmarinellearbisNo ratings yet
- CBSE XII Chemistry Project Spectroscopy and Its ApplicationsDocument21 pagesCBSE XII Chemistry Project Spectroscopy and Its ApplicationsRichie SinghNo ratings yet
- Spectroscopy and Its ApplicationsDocument21 pagesSpectroscopy and Its Applicationspkkalai112No ratings yet
- Color Fundamentals (Study Material 1)Document13 pagesColor Fundamentals (Study Material 1)Harsh VermaNo ratings yet
- Focus: Light and Geometric Optics: Part I - Content UpdateDocument21 pagesFocus: Light and Geometric Optics: Part I - Content UpdateApril Joyce Ricamora NarcisoNo ratings yet
- LAS LightDocument2 pagesLAS LightMaricel ValenNo ratings yet
- The Nature of LightDocument27 pagesThe Nature of LightvlsiprabhuNo ratings yet
- Behavior of LightDocument19 pagesBehavior of LightCris MauleonNo ratings yet
- Behavior of LightDocument19 pagesBehavior of LightCris MauleonNo ratings yet
- Q2 Week 3Document58 pagesQ2 Week 3Zayra Melgar AtreroNo ratings yet
- Energy of LightDocument2 pagesEnergy of LightMarvin MelisNo ratings yet
- SCH 100 Notes 2013-2014 ALLDocument42 pagesSCH 100 Notes 2013-2014 ALLErick Wangila WanyonyiNo ratings yet
- The Physics of LightDocument6 pagesThe Physics of LightprashantsheetalNo ratings yet
- 1-Visual Testing FinalDocument68 pages1-Visual Testing FinalmohammedNo ratings yet
- Lecture Notes LightsDocument3 pagesLecture Notes LightsRhonoelle Reevenujlah100% (1)
- SpectrosDocument21 pagesSpectrosAman Rathore100% (1)
- Source of ColorDocument6 pagesSource of ColoryemiNo ratings yet
- What Is Light - An Overview of The Properties of LightDocument3 pagesWhat Is Light - An Overview of The Properties of LightLeo CerenoNo ratings yet
- Theory of Light and ColorDocument50 pagesTheory of Light and Colorelijah jirah binadayNo ratings yet
- Optics 1Document5 pagesOptics 1asopNo ratings yet
- Science G7 Q3 WK7.2 - LightDocument85 pagesScience G7 Q3 WK7.2 - Light• S h ı m m y •No ratings yet
- How Light Acts As A Wave and A ParticleDocument50 pagesHow Light Acts As A Wave and A ParticleNorhaima Tacoranga50% (2)
- Scii 1Document6 pagesScii 1ReignNo ratings yet
- OPTICSDocument49 pagesOPTICSKristine Cris VenusNo ratings yet
- Astronomy Upenn Survey of The Univer Astr001 - Chapter 5 NotesDocument12 pagesAstronomy Upenn Survey of The Univer Astr001 - Chapter 5 NotesTushar ShahaniNo ratings yet
- CBSE XII Chemistry/Physics Project Spectroscopy and Its ApplicationsDocument21 pagesCBSE XII Chemistry/Physics Project Spectroscopy and Its ApplicationsshantanurNo ratings yet
- ChemDocument15 pagesChemSachin RaiNo ratings yet
- LIGHTDocument37 pagesLIGHTalexymersNo ratings yet
- Fors211 Photo Lesson 3 (Light)Document34 pagesFors211 Photo Lesson 3 (Light)Almar MamarintaNo ratings yet
- Forensic PhotographyDocument20 pagesForensic PhotographyPrincess Trina Galapon RamosNo ratings yet
- Lesson 5 LightDocument75 pagesLesson 5 LightErica QuirobNo ratings yet
- Light Notes 1Document31 pagesLight Notes 1api-233194737No ratings yet
- Waves, Light & Electromagnetism: Prepared By: Group 3Document34 pagesWaves, Light & Electromagnetism: Prepared By: Group 3Alyssa MirandaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4: Lights and AtomsDocument32 pagesChapter 4: Lights and AtomsBainaot Abdul SumaelNo ratings yet
- Light and Sources of LightDocument12 pagesLight and Sources of LightPraneetha DumsapurNo ratings yet
- Ophthalmic Dispensing Revision Guide: First Year Part OneFrom EverandOphthalmic Dispensing Revision Guide: First Year Part OneRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (3)