Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Lecture 6-7
Uploaded by
Hamza Asif0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
6 views26 pagesThe document discusses unit linked insurance plans (ULIPs), which separate the protection and savings components of traditional life insurance policies. ULIPs allow policyholders to choose their investment funds and bear the investment risk, while insurers deduct transparent charges. Premiums are invested in funds of the policyholder's choice. The value of the policy fluctuates based on the underlying investments. The document provides examples of how ULIPs work, including typical charges, terms, formulae and calculations for premium allocation and fund growth over time.
Original Description:
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document discusses unit linked insurance plans (ULIPs), which separate the protection and savings components of traditional life insurance policies. ULIPs allow policyholders to choose their investment funds and bear the investment risk, while insurers deduct transparent charges. Premiums are invested in funds of the policyholder's choice. The value of the policy fluctuates based on the underlying investments. The document provides examples of how ULIPs work, including typical charges, terms, formulae and calculations for premium allocation and fund growth over time.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
6 views26 pagesLecture 6-7
Uploaded by
Hamza AsifThe document discusses unit linked insurance plans (ULIPs), which separate the protection and savings components of traditional life insurance policies. ULIPs allow policyholders to choose their investment funds and bear the investment risk, while insurers deduct transparent charges. Premiums are invested in funds of the policyholder's choice. The value of the policy fluctuates based on the underlying investments. The document provides examples of how ULIPs work, including typical charges, terms, formulae and calculations for premium allocation and fund growth over time.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 26
Non-traditional Life Insurance
Products/Unit Linked Products
(ULIP’s)
Chapter 4
Marked pages 61-78
Concentrate more on Examples in Presentation
(compared to coursepack)
Unit Linked Insurance Plan (ULIP)
Life Insurance products have significant
“Savings” component
In traditional products (WLP, Endowment) not
possible to gauge return on investment
Also no control on investment avenues
Pressure started to build up over time to
separate protection and savings components
for greater transparency
Unbundled (ULIP) version started in 50’s but
more popular in 80’s & 90
In Pakistan, private sector mainly ULIP’s
Main Characteristics of ULIP’s
1. All fees/charges known to policyholders
2. All premiums net of all charges invested in
funds of policyholder’s choice
3. Value of policy fluctuates with underlying
investments (investment risk borne by
policyholder)
4. Generally offers variety of investment choices
5. Generally does not work well for small
premium amounts
Working of ULIP
Policyholder deposits premium
Company deducts charges in a transparent manner
to meet expenses
Company also deducts mortality charge to pay
death benefits
Remaining premium paid into 1 or more “Unit
Fund(s)” and Units purchased a prevailing unit
price
Investment management charge deducted from
Fund (generally implicitly through unit price)
Savings component operates like investment in
mutual fund
Working of ULIP
Value of these units generally increases with
time
Fund Value + agreed amount (or higher of 2)
paid out at death (2 options)
Fund Value paid on maturity
Fund Value less Surrender Charges paid on
early withdrawal
Typical flow of ULIP
Initial No. Initial Fund Premium
of Units Value
+
-
Expenses Updated
Charges
-
Fund Value
Cost of
Insurance
Final Fund Purchase Total Units = Initial
Value No. of New Units + New Units
Units Purchased
Terms and Formulae related to Unit
Linked Insurance Plans
1. Sum Assured (SA) or Death Benefit – benefit
payable on death
2. Level SA – uniform benefit payable on death
regardless of timing
3. Increasing SA – Level SA plus Policy Value
(explained below)
Comment : In this case, SA will generally increase due
to increase in Policy Value over time.
4. Policy Value (PV) or Fund Value– Amount of
money in the investment account (or
accumulated savings + returns)
Terms and Formulae related to Unit
Linked Insurance Plans
5. Surrender charge (SC) - Charge that insurer levies
(generally in first 1-2 years) to recover initial
expenses if policy lapses early.
6. Surrender Value (SV) or Cash Surrender Value (CSV)
= Policy Value less Surrender Charge
7. Sum At Risk (SAR) for Level SA= SA – Policy Value
before cost of insurance (subject to min SAR of Zero)
8. SAR for Increasing SA = Level SA
9. Cost of Insurance = SAR x Mortality rate at that age
Terms and Formulae related to
Unit Linked Insurance Plans
10. Unit Price (Investment Fund)=
11. Offer Price – Price at which units can be bought from
the investment fund (same as Unit Price)
12. Bid Price – Price at which Units can be redeemed
(sold) to the investment fund
13. Bid/Offer Spread – Percentage difference between
buying & selling price of units
or Bid/Offer Spread = x 100
Terms and Formulae related to
Unit Linked Insurance Plans
14. For a Level Death benefit structure, the Policy
Value increases at a faster rate than Increasing
Death benefit structure (as Cost of Insurance is lower
for Level Death benefit).
15. Cover Multiple = at start of policy.
Typical Charges of ULIP
A. Insurance Related charges
i. Percentage of premium charge
ii. Policy Fee / Initial charges
iii. Admin / Maintenance fee
B. Investment Related charges
i. Bid/offer spread
ii. Fund management fee
iii. Fund switching charge
iv. Surrender charge
C. Cost of Insurance (COI) or Mortality Charge
Flow of typical ULIP
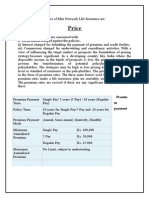
Typical ULIP example
Product Feature Assumptions
i. % of Premium charge 20%
ii. Policy Administration Fee 20 per annum
iii. Cost of Insurance Deducted on Sum at Risk
Other Assumptions
iv. Age of policyholder 40 years
v. Annual Premium beginning of year 1,000
vi. Sum Assured 15,000
vii. Mortality rate at age 40 2 per thousand age 40
viii.Offer Price of Unit Fund at beginning of 10 per unit
year
vi. Timing of deduction of charges beginning of year
vii. Beginning Fund Value Nil
Flow of typical ULIP
Working of typical ULIP Premium
1. Initial No. of Units = Nil
2. Initial Fund Value = 0
3. Premium = 1,000
4. Percentage of premium = (200)
Charge (0.2 x Premium)
5. Policy Admin fee = (20)
6. Premium after Expense Charges = 780
(Premium – Percentage of
Premium Charges – Policy Fee)
7. Updated Fund Value = 780
(Beginning Fund Value +
Premium - Expense charges)
Working of typical ULIP
8. Amount at risk = 14,220
(SA/DB less Updated Fund Value)
9. Cost of Insurance = 28.44
(Mortality Rate x Sum At Risk)
10. Net Premium after expense & mortality = 751.56
charges (Premium – Expense Charges –
Cost of Insurance)
11. No. of units purchased with net cash = 75.16
flow at beginning of year
(Net Premium / Offer Price)
Regular Premium Unit linked
Policy (Level Death Benefit)
Features of Policy
1. Annual Premium 50,000 uniform throughout
2. Percentage of premium 30% in Year 1, 10% in Year 2 and Nil
charge thereafter
3. Policy Fee 1,000 in Year 1 and 500 in Year 2 & onwards
4. Sum assured / Death Benefit 500,000 (cover multiple of 10)
5. Mortality Rate 2 per thousand in Year 1 &
3 per thousand in Year 2 & onwards
6. Surrender charge 3% of Fund value (or Policy Value) in year
1 and Nil thereafter
Regular Premium Unit linked
Policy (Level Death Benefit)
Other assumptions
1. Offer Price 100 in Year 1, 110 in Year 2 and 121 in
(beginning of year) Year 3
2. Bid Price 95 in Year 1, 104.5 in Year 2 and 114.95
(beginning of year) in Year 3
3. Beginning Fund / Nil
Policy Value
4. All charges are deducted at beginning of year
Implied from above
1. Rate of return per year 10%
2. Bid/Offer spread 5.26% ( x 100)
Regular Premium Unit linked
Policy (Level Death Benefit)
Year 1
1. Starting No. of Units Nil
2. Starting Fund/Policy Value Nil
3. Premium 50,000
4. Percentage of Premium 15,000
charge (.3 x 50,000)
5. Policy Fee 1,000
6. Fund Value after expense charges 34,000
(2. + 3. -4. -5.)
7. Sum at Risk 466,000
(500,000 – 6.)
8. Cost of Insurance 932
(7. x .002)
9. Net amount available for investment 33,068
(6. – 8.)
Regular Premium Unit linked
Policy (Level Death Benefit)
10. No. of Units purchased at beginning of year 330.68
(9. / 100)
11. Policy Value at beginning of year 31,414.6
(10. x 95)
12. Policy Value at end of year 34,556.06
(10. x 104.5)
13. Cash Surender Value of end of year 33,519.38
(12. x .97)
14. Death Benefit / Sum Assured 500,000
during the year
Regular Premium Unit linked
Policy (Level Death Benefit)
Year 2
1. Starting Fund/Policy Value at beginning of year 34,556.06
2. Premium 50,000
3. Percentage of Premium 5,000
charge (.1 x 50,000)
4. Policy Fee 500
5. Fund Value after expense charges 79,056.06
(1. + 2. -3. -4.)
6. Sum at Risk 420,943.94
(500,000 – 5.)
7. Cost of Insurance 1,262.83
(6. x .003)
8. Amount available for investment 43,237.17
From cash flows during the year
(2. – 3. -4. -7.)
Regular Premium Unit linked
Policy (Level Death Benefit)
9. New units purchased beginning of the year 393.07
(8. / 110)
10. Units at beginning of year 330.68
11. Total units at end of year 723.75
(9. + 10.)
12. Policy Value at beginning of year 34,556.06
13. Policy Value at end of year 83,195.06
(11. x 114.95)
14. Cash Surrender Value at end of year (13. x 1) 83,195.06
15. Death Benefit / (Sum Assured) during the year 500,000
Regular Premium ULIP
Increasing Death Benefit
Same as earlier example except death benefit increases
each year.
Increasing Death Benefit = Sum Assured (level) + Policy
Value
Sum at Risk (Generally) = Sum Assured – Policy Value
Therefore Sum at Risk
(for increasing death benefit) = Sum Assured (Level)
Works in exactly the same way except Sum at Risk
remains the same (50,000 in previous example)
Cost of Insurance in this case is higher
As such, policy value is lower than level death benefit
structure
Working of typical ULIP
Investment amount will generally increase
with time
Sum at risk will generally decrease (for level
SA)
Fund value (FV) will increase with new
premiums and investment income
On death, higher of SA or FV is payable
On maturity, FV is payable
On withdrawal, FV less any surrender charge
is payable
Pros of ULIP
Transparency
Flexibility
SA
Investment option
Top up premium facility
Disadvantages of ULIP
Difficult to gauge clear value of policy
although better than traditional products
Generally complicated design
Illustrations difficult to understand and
generally misleading (important to understand
various columns/rows)
Investment risk fully borne by policyholder
Risks to Company and Policyholders
Risks to Policyholder
Misunderstanding of Product
Potential Misunderstanding of Value
Investment risk
Risks to Company
Greater expense risk than conventional
products
Greater mortality risk
Reputation risk (bancassurance)
Summary
Transparent version
Has its pros & cons
Very prevalent in most markets
Main advantages of transparency and
investment options
Main disadvantages of bearing full investment
risk and having complicated design
You might also like
- Test Card CreditDocument32 pagesTest Card CreditHerard Gravi100% (4)
- Bodie Essentials Ch. 10 SolutionsDocument18 pagesBodie Essentials Ch. 10 SolutionsJPM190067% (6)
- EAS 545 Study SheetDocument4 pagesEAS 545 Study Sheettli04100% (2)
- Ift Study Notes Vol 3 PDFDocument243 pagesIft Study Notes Vol 3 PDFKarlNo ratings yet
- 06 A Mortality ProfitDocument6 pages06 A Mortality ProfitKimondo King100% (1)
- Clients' Guide To Private Placement Internationally Regulated Project Funding ProgramsDocument50 pagesClients' Guide To Private Placement Internationally Regulated Project Funding ProgramspashazahariNo ratings yet
- LIC S Market Plus - 512L238V01Document9 pagesLIC S Market Plus - 512L238V01Sharath KotaNo ratings yet
- ENDOWMENT PLAN - (Table No. 14) Benefit Illustration: Guaranteed Surrender ValueDocument3 pagesENDOWMENT PLAN - (Table No. 14) Benefit Illustration: Guaranteed Surrender ValueGBKNo ratings yet
- Ab Market Ke Utaar-Chadhaav Ki No Tension: Reliance Life Insurance Highest NAV Advantage PlanDocument28 pagesAb Market Ke Utaar-Chadhaav Ki No Tension: Reliance Life Insurance Highest NAV Advantage PlanDeepak SinghNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1Document70 pagesLecture 1rajabushabani321No ratings yet
- PDS Boost ProtectActiveDocument4 pagesPDS Boost ProtectActiveAizat HermanNo ratings yet
- Unit Linked Insurance Polices (Ulips) : Frequently Asked Questions (Faqs)Document6 pagesUnit Linked Insurance Polices (Ulips) : Frequently Asked Questions (Faqs)afzallodhi736No ratings yet
- What Is A ULIP?Document6 pagesWhat Is A ULIP?nirajvasavaNo ratings yet
- Special SunFlexi 250k F NS 25Document4 pagesSpecial SunFlexi 250k F NS 25Judy DetangcoNo ratings yet
- EFU Better Life Savings PlanDocument14 pagesEFU Better Life Savings PlanqasimhkNo ratings yet
- Wealth GainDocument9 pagesWealth GainSandeep Varma SagiNo ratings yet
- Ulips 221007Document6 pagesUlips 221007pushpendra_25No ratings yet
- KFD U39Document3 pagesKFD U39mniarunNo ratings yet
- Variable Life BrieferDocument18 pagesVariable Life BrieferSally AlvaredaNo ratings yet
- Gist of LIC's Samridhi Plus (Plan No 804)Document6 pagesGist of LIC's Samridhi Plus (Plan No 804)Avinash KolugadeNo ratings yet
- Smart Wealth Assure - BrochureDocument16 pagesSmart Wealth Assure - BrochureIswarya SelvarajNo ratings yet
- Life Insurance Linked With InvestmentDocument14 pagesLife Insurance Linked With InvestmentWyatt HurleyNo ratings yet
- Lic Pension PlusDocument10 pagesLic Pension PlustsrajanNo ratings yet
- Unit Linked Insurance PlanDocument5 pagesUnit Linked Insurance Planagarwal13No ratings yet
- Guaranteed Maturity Insurance Plan - Aug12Document16 pagesGuaranteed Maturity Insurance Plan - Aug12Diptesh SahaNo ratings yet
- FWAP LeafletDocument16 pagesFWAP LeafletsatishbhattNo ratings yet
- Fortune Builder NewDocument9 pagesFortune Builder NewVinoth NatarajanNo ratings yet
- Tata Aig Invest Assure ApexDocument7 pagesTata Aig Invest Assure ApexKrupa Karia ThakkarNo ratings yet
- Product Key Facts Statement: SwisssmartDocument40 pagesProduct Key Facts Statement: SwisssmartlucigenlionNo ratings yet
- Introduction To ULIP: Unit Link Insurance Plan ULIPDocument31 pagesIntroduction To ULIP: Unit Link Insurance Plan ULIPcreators_5No ratings yet
- Risk Chapter 5Document29 pagesRisk Chapter 5Wonde BiruNo ratings yet
- MPU 3353 Personal Financial Planning in Malaysia: Investment Basics: Understanding Risk and ReturnDocument33 pagesMPU 3353 Personal Financial Planning in Malaysia: Investment Basics: Understanding Risk and ReturnherueuxNo ratings yet
- SYBBIDocument13 pagesSYBBIshekhar landageNo ratings yet
- One-Pager - Future ProtectDocument1 pageOne-Pager - Future ProtectVivek BnNo ratings yet
- Unit Linked Insurance PlanDocument11 pagesUnit Linked Insurance Planjainmohit23No ratings yet
- Aapki Zaroorat - Wealth AccumulationDocument13 pagesAapki Zaroorat - Wealth AccumulationRohitNo ratings yet
- SWG Joint Life BrochureDocument19 pagesSWG Joint Life BrochureHardik BajajNo ratings yet
- Premium Calculation: Juhi Sharma Rajat Gupta Deepak SinghDocument23 pagesPremium Calculation: Juhi Sharma Rajat Gupta Deepak SinghDeepak SinghNo ratings yet
- SWG Child Wealth BrochureDocument22 pagesSWG Child Wealth BrochureBalajiNo ratings yet
- LIC S SIIP Brochure 9 Inch X 8 Inch Eng SingleDocument20 pagesLIC S SIIP Brochure 9 Inch X 8 Inch Eng SingleRajaramNo ratings yet
- CM1Document28 pagesCM1Chhavi KhandujaNo ratings yet
- Heading DescriptionDocument4 pagesHeading DescriptionSri Ram SahooNo ratings yet
- Benefits of ULIPsDocument5 pagesBenefits of ULIPsanand98809880No ratings yet
- Unit 1 - Investment SettingDocument9 pagesUnit 1 - Investment SettingDa-lex WattNo ratings yet
- QT Nil P 0281201503151442615Document51 pagesQT Nil P 0281201503151442615Dinesh MuruganNo ratings yet
- Written Report in M103Document7 pagesWritten Report in M103Katrina EreseNo ratings yet
- FWAP ULIP Leaflet RevisedDocument16 pagesFWAP ULIP Leaflet Revisedmantoo kumarNo ratings yet
- Computation of Premium of Life Insurance PlansDocument9 pagesComputation of Premium of Life Insurance PlansAbhishek Singh PariharNo ratings yet
- EXAM 2-NoteDocument1 pageEXAM 2-NoteStevatoNo ratings yet
- EdelweissTokioLife WealthAccumulation AcceleratedCover WAAC UIN147L003V02Document12 pagesEdelweissTokioLife WealthAccumulation AcceleratedCover WAAC UIN147L003V02avisekgNo ratings yet
- Giluano B Mlprime 18052022172755Document23 pagesGiluano B Mlprime 18052022172755Gerome Eugenio100% (1)
- The Certificate Examination in Investment-Linked Life Insurance (CEILI) Summary Slides (English)Document118 pagesThe Certificate Examination in Investment-Linked Life Insurance (CEILI) Summary Slides (English)JunHong ChenNo ratings yet
- Valuation of Bonds and SharesDocument30 pagesValuation of Bonds and SharesJohn TomNo ratings yet
- Smart Scholar Brochure BRDocument21 pagesSmart Scholar Brochure BRshabeer123No ratings yet
- SmartSampoornaRaksha BrochureDocument16 pagesSmartSampoornaRaksha BrochureSuraj DubeyNo ratings yet
- Yield To Maturity Yield To CallDocument14 pagesYield To Maturity Yield To CallAdamNo ratings yet
- ULIP's SATHYADocument9 pagesULIP's SATHYAsantoduNo ratings yet
- MM AssignmentDocument16 pagesMM AssignmentRahul ParasharNo ratings yet
- Edelweiss Tokio Life: Group Employee Benefit PlanDocument8 pagesEdelweiss Tokio Life: Group Employee Benefit Plan松田 文貴No ratings yet
- Lectures 12 14Document30 pagesLectures 12 14Hamza AsifNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3-4 17.01.22Document39 pagesLecture 3-4 17.01.22Hamza AsifNo ratings yet
- Lectures 13 15Document40 pagesLectures 13 15Hamza AsifNo ratings yet
- Question 1 (25 Minutes - 16 Points)Document2 pagesQuestion 1 (25 Minutes - 16 Points)Hamza AsifNo ratings yet
- Tugas AbrahamDocument5 pagesTugas AbrahamHana MariaNo ratings yet
- Deep Dive Into IEV and Views From The Market: Sanket KawatkarDocument62 pagesDeep Dive Into IEV and Views From The Market: Sanket Kawatkarankur taunkNo ratings yet
- Ref - No. 11532934-16309213-3: Pintukumar Rameshbhai PatelDocument4 pagesRef - No. 11532934-16309213-3: Pintukumar Rameshbhai Patelpintukumar rameshbhaiNo ratings yet
- Class Work & Home Work Question of Final Account of Banking Conpany 22-23Document23 pagesClass Work & Home Work Question of Final Account of Banking Conpany 22-23DARK KING GamersNo ratings yet
- Diagnostic Exam Accounting 1.1 AKDocument14 pagesDiagnostic Exam Accounting 1.1 AKRobert CastilloNo ratings yet
- Financial Statement Analysis at Lanco InfratechDocument78 pagesFinancial Statement Analysis at Lanco Infratechnaveen100% (1)
- Print Challan Kapil VatsDocument1 pagePrint Challan Kapil VatsPankaj VatsaNo ratings yet
- BNI Taplus Muda - Group8 - Tourism CDocument27 pagesBNI Taplus Muda - Group8 - Tourism CsayudeviNo ratings yet
- IficDocument33 pagesIficRuhul Amin JaseemNo ratings yet
- Maramag Water District Bukidnon Executive Summary 2020Document6 pagesMaramag Water District Bukidnon Executive Summary 2020cpa126235No ratings yet
- FABM2-Chapter 2Document31 pagesFABM2-Chapter 2Marjon GarabelNo ratings yet
- PNB BankDocument87 pagesPNB Bankagrawalrohit_228384No ratings yet
- BD5 SM30Document2 pagesBD5 SM30ksgNo ratings yet
- Are You Ready To Go Paperless?: Crawfordtech Bank Statement SampleDocument2 pagesAre You Ready To Go Paperless?: Crawfordtech Bank Statement SampleITNo ratings yet
- Bahir Dar University College of Business & Economics Department of Accounting and Finance MSC Program T-Learning ProcessDocument7 pagesBahir Dar University College of Business & Economics Department of Accounting and Finance MSC Program T-Learning Processyohannes kindalem100% (1)
- Quiz 1 ProblemsDocument6 pagesQuiz 1 ProblemsRuthchell CiriacoNo ratings yet
- Zero ToleranceDocument16 pagesZero ToleranceABDUL BASITNo ratings yet
- Excel Professional Services, Inc.: Discussion QuestionsDocument4 pagesExcel Professional Services, Inc.: Discussion QuestionsSadAccountantNo ratings yet
- B071GTXBS3Document119 pagesB071GTXBS3Anonymous 94TBTBRks100% (2)
- Restated Earnings Largely Driven by Non-Cash Expenses: 2GO Group, IncDocument4 pagesRestated Earnings Largely Driven by Non-Cash Expenses: 2GO Group, IncJNo ratings yet
- Copy Cost Accting-1Document205 pagesCopy Cost Accting-1Kassawmar DesalegnNo ratings yet
- The Application and Disclosures of Iass & Ifrss by The Dse Listed Companies of BangladeshDocument20 pagesThe Application and Disclosures of Iass & Ifrss by The Dse Listed Companies of BangladeshAbdullah Hish ShafiNo ratings yet
- Hong Leong Bank Wise Credit Card Application (Malaysia) 2014Document5 pagesHong Leong Bank Wise Credit Card Application (Malaysia) 2014kamarulxNo ratings yet
- Estatement - 2022 05 19Document3 pagesEstatement - 2022 05 19tanjaNo ratings yet
- Cambridge IGCSE™: Accounting 0452/21Document19 pagesCambridge IGCSE™: Accounting 0452/21grengtaNo ratings yet
- Asian Paints Ltd. (India) : SourceDocument6 pagesAsian Paints Ltd. (India) : SourceDivyagarapatiNo ratings yet