100% found this document useful (2 votes)
1K views23 pagesScience 6 - Q2 - L3 - Parts and Function of Digestive System
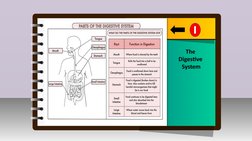
The document describes the major organs that make up the human digestive system and their functions. It begins with the mouth, which contains teeth for chewing food, and the tongue. It then discusses the esophagus, stomach, small intestine, large intestine, and anus. The small intestine, which is about seven meters long, absorbs nutrients with the help of villi. The large intestine or colon is attached to the end of the small intestine and is about 1.5 meters long. It discusses the roles and parts of each organ in digesting and breaking down food.
Uploaded by
Sonny MatiasCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
100% found this document useful (2 votes)
1K views23 pagesScience 6 - Q2 - L3 - Parts and Function of Digestive System
The document describes the major organs that make up the human digestive system and their functions. It begins with the mouth, which contains teeth for chewing food, and the tongue. It then discusses the esophagus, stomach, small intestine, large intestine, and anus. The small intestine, which is about seven meters long, absorbs nutrients with the help of villi. The large intestine or colon is attached to the end of the small intestine and is about 1.5 meters long. It discusses the roles and parts of each organ in digesting and breaking down food.
Uploaded by
Sonny MatiasCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd