Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Lecture 3
Uploaded by
Syed Muneeb0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
14 views20 pagesToday's document discusses different types of computers classified according to their capabilities and applications. It describes supercomputers, mainframes, servers/mini computers, desktop computers, and portable computers. Supercomputers are the most powerful and expensive, used for complex tasks like weather prediction. Mainframes are for large businesses, servers are for small/medium businesses, desktops are for individual use, and portables allow mobile computing. The document provides details about the hardware, usage, and costs of each type.
Original Description:
Original Title
lecture 3
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentToday's document discusses different types of computers classified according to their capabilities and applications. It describes supercomputers, mainframes, servers/mini computers, desktop computers, and portable computers. Supercomputers are the most powerful and expensive, used for complex tasks like weather prediction. Mainframes are for large businesses, servers are for small/medium businesses, desktops are for individual use, and portables allow mobile computing. The document provides details about the hardware, usage, and costs of each type.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
14 views20 pagesLecture 3
Uploaded by
Syed MuneebToday's document discusses different types of computers classified according to their capabilities and applications. It describes supercomputers, mainframes, servers/mini computers, desktop computers, and portable computers. Supercomputers are the most powerful and expensive, used for complex tasks like weather prediction. Mainframes are for large businesses, servers are for small/medium businesses, desktops are for individual use, and portables allow mobile computing. The document provides details about the hardware, usage, and costs of each type.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 20
Today’s Goal
• To learn to classify computers according to
their capability and targeted applications
• To find out about the essential building
blocks that make up a modern computer
Computer Types
• Super Computers
• Mainframes Computers
• Servers or Mini Computers
• Desktop Computers
• Portable Computers
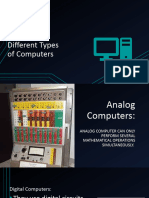
Super Computers
• State-of-the-art machines designed to perform
calculations as fast as the current technology
allows
• Supercomputers are ideal for handling large
and highly complex problems that require
extreme calculating power.
Super Computers
Super Computers
• Used for weather prediction, Simulation of
atomic explosion, Movie animations and
aircraft design
• Costs tens of millions of dollars
• Designed to focus all the resources and
capabilities on single task at a time
• Early super computers used only single or few
processors
Super Computers
• These processors were custom built that’s why
they were very expensive
• Modern Supercomputers use same processors
that are used n desktop PC’s.
ASCI White
• Most powerful computer as of February 2002
• Capable of 12.3 trillions of calculations/sec
74000 times faster than Cray 1
1000 times faster than Deep Blue
• Designed for complex 3-D simulations
required for testing nuclear weapons
• 6 TB of memory; 160 TB of storage capacity
Mainframe Computers
• Also called “Enterprise Servers”
• Designed for performing multiple, intensive tasks for
multiple users simultaneously
• Used by large businesses (e.g. banks, e-commerce
sites), military, and industrial organizations
• Can be serviced/upgraded while in operation
• Generally consist of multiple processors, GB’s of
memory, and TB’s of storage
Mainframe Computers
Servers/Minicomputers
• The name minicomputers used to define the
class of computers that lies between personal
computers and mainframes
• Then very high-end desktop computers called
low-end or mid-range servers took over the
role that was previously played by
minicomputers
Servers/Minicomputers
• Low-end and mid-range servers are used by
small businesses and organizations as file-
stores, to run e-mail systems and Web sites
• Generally are more reliable than desktops, but
not as solid as the mainframes
• Generally consist of 2 or more processors,
GB’s of memory, and TB’s of storage
• Costs in hundreds of thousands of dollars
Servers
A server , or network server , is a central
computer that holds collections of data
(databases) and programs for connecting or
supplying services to PCs, workstations, and
other devices, which are called clients. These
clients are linked by a wired or wireless network.
The entire network is called a client/server
network.
Desktop Computers
• Also called microcomputers
• Low-end desktops are called PC’s and high-
end ones “Workstations”
• Generally consist of a single processor only,
some times 2, along with MB’s of memory,
and GB’s of storage
• PC’s are used for running productivity
applications, Web surfing, messaging
Desktop Computers
• Workstations for more demanding tasks like
low-end 3-D simulations and other
engineering & scientific apps
• Are not as reliable and fault-tolerant as
servers
• Workstations cost a few thousand dollars; PC
around a $1000
Mobile Computers
• Laptops, palmtops, and wearable computers are very
capable computers but are light-weight and consume
very little power
• Laptops (also called notebook computers) generally
weigh around 2kg, use special low-power processors,
typically have 256MB memory, 40GB of storage, can
work for more than 2 hours on battery
• Their usage is similar to that of PCs
• They cost in the range of $1500-2500
Mobile Computers
• Palmtops, also known as PDA’s - Personal Digital
Assistants
• Weigh less than a pound, have very low-power
processors, KB’s of memory, MB’s of storage capacity
• Can run for many hours on AA batteries
• Used as an electronic version of a pocket diary. Also
for Web surfing and e-mail or even as mobile
phones
• Palmtops cost $200-600
Mobile Computers
• Wearable's are small in size, carried in a pocket,
worn on the arm, waist, or head or elsewhere on
the body
• Capability similar to PDA’s, but more expensive
• They are always ON, and always accessible. That
is, the user can always enter and execute
commands, even while walking around or doing
other activities
• Each soldier of the future will be fitted with one
Ranking w.r.t. installed number
• PC’s
• PDA’s
• Workstations
• Servers
• Wearable's (will take the top spot in future)
• Mainframes
• Supercomputers
You might also like
- Classification of ComputersDocument17 pagesClassification of ComputersN AkilanNo ratings yet
- CS101 Introduction To ComputingDocument40 pagesCS101 Introduction To ComputingFahad NabeelNo ratings yet
- ITT04101-Types of ComputersDocument12 pagesITT04101-Types of ComputersGallant RockNo ratings yet
- Computers: Computer SystemsDocument34 pagesComputers: Computer SystemskasunNo ratings yet
- Lec1 ComputersDocument34 pagesLec1 ComputerskasunNo ratings yet
- A Computer Is A Programmable MachineDocument9 pagesA Computer Is A Programmable MachineSupreet KaurNo ratings yet
- Types of ComputerDocument41 pagesTypes of ComputerAngelita CapagalanNo ratings yet
- ICT-week 2Document36 pagesICT-week 2hafsaashraf4093No ratings yet
- ClasClassification of Computers According To Size and Purposesification of Computers According To Size and PurposeDocument5 pagesClasClassification of Computers According To Size and Purposesification of Computers According To Size and PurposeNicole SorianoNo ratings yet
- CS100 Lec 1 (Types of Computer)Document20 pagesCS100 Lec 1 (Types of Computer)Jamie WongNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2: The Shapes of Computers TodayDocument13 pagesLesson 2: The Shapes of Computers TodaySaumyata PandeyNo ratings yet
- Classification of ComputersDocument11 pagesClassification of ComputersrangarajantrNo ratings yet
- Chapter 03 - Classification of ComputersDocument27 pagesChapter 03 - Classification of Computersakila IndurangaNo ratings yet
- 03 Chapter 03 - Classification of ComputersDocument27 pages03 Chapter 03 - Classification of ComputersThe ShieldNo ratings yet
- Classification of ComputersDocument28 pagesClassification of ComputersSiddharth GuptaNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 PDFDocument59 pagesUnit 1 PDFsrinivasanNo ratings yet
- Lecture Notes 2: Categories & Types of ComputerDocument44 pagesLecture Notes 2: Categories & Types of ComputerMd Sakawat Hossain100% (1)
- What Is Computer?Document9 pagesWhat Is Computer?r10943700No ratings yet
- N4 Less 02Document10 pagesN4 Less 02Omkar ComputersNo ratings yet
- The Shapes of Computers Today: Prepared by Naveed Ali & MansoorDocument6 pagesThe Shapes of Computers Today: Prepared by Naveed Ali & MansoorALAMDAR HUSSAINNo ratings yet
- Categories of Computers: Sept 15, 2009Document33 pagesCategories of Computers: Sept 15, 2009isareamNo ratings yet
- Types of ComputersDocument15 pagesTypes of Computersbabita singhNo ratings yet
- Different Types of ComputersDocument17 pagesDifferent Types of ComputersRichie SalubreNo ratings yet
- Introduction & History of Computers, Their Applications: Sarhad University of Science & Information Technology PeshawarDocument26 pagesIntroduction & History of Computers, Their Applications: Sarhad University of Science & Information Technology PeshawarAvian DwijayaNo ratings yet
- Personal ComputerDocument23 pagesPersonal ComputerJERWIN HONRADONo ratings yet
- Introduction & History of Computers, Their Applications: Sarhad University of Science & Information Technology PeshawarDocument26 pagesIntroduction & History of Computers, Their Applications: Sarhad University of Science & Information Technology PeshawarAarav MishraNo ratings yet
- IT in BusinessDocument44 pagesIT in BusinessBOSS HASHMINo ratings yet
- Types of ComputerDocument28 pagesTypes of ComputerOtencianoNo ratings yet
- Tle Computer SizesDocument12 pagesTle Computer SizesChloeNo ratings yet
- Classification of ComputerDocument30 pagesClassification of ComputerGagan JosanNo ratings yet
- Typesofcomputer 200709121128Document21 pagesTypesofcomputer 200709121128Benjie F. AndrianoNo ratings yet
- 3 Classification Based On SizeDocument13 pages3 Classification Based On SizeAthul Raj SabuNo ratings yet
- Types of Computers and Computing: Presented by Ratnadeep B.Tech (Computer Science and Engineering)Document35 pagesTypes of Computers and Computing: Presented by Ratnadeep B.Tech (Computer Science and Engineering)ratnadeepNo ratings yet
- Classification of ComputersDocument11 pagesClassification of ComputersADITYA RAJNo ratings yet
- Computers Are Classified According To Their Data Processing SpeedDocument3 pagesComputers Are Classified According To Their Data Processing SpeedArchay Tehlan70% (10)
- Computer Superiority and Main TypesDocument30 pagesComputer Superiority and Main TypesDymond DanielNo ratings yet
- Classification of ComputersDocument2 pagesClassification of ComputersHarry GillNo ratings yet
- Lesson 4 - Types of ComputersDocument28 pagesLesson 4 - Types of ComputersAnthonyNo ratings yet
- Classification of ComputersDocument8 pagesClassification of ComputersNawszNo ratings yet
- Basic Elements of IT InfrastructureDocument11 pagesBasic Elements of IT Infrastructurekenneth avenidoNo ratings yet
- Classification of ComputersDocument108 pagesClassification of ComputersShashi BhandariNo ratings yet
- Unit-1: Mr. Anurag Pandey Assistant Professor PSIT College of EngineeringDocument40 pagesUnit-1: Mr. Anurag Pandey Assistant Professor PSIT College of EngineeringVaibhav GuptaNo ratings yet
- Introduction To ComputerDocument30 pagesIntroduction To Computerসায়েম মুহাম্মাদNo ratings yet
- 4-Introduction To Computing-Classification of ComputerDocument16 pages4-Introduction To Computing-Classification of ComputerMisbah Ul HassanNo ratings yet
- TLE 10 - CSS (Week 1 Day 1) ASSEMBLE COMPUTER HARDWAREDocument35 pagesTLE 10 - CSS (Week 1 Day 1) ASSEMBLE COMPUTER HARDWAREJohn King johnking.monderinNo ratings yet
- Module 1 Learning Unit 1: Microprocessors and Microcontrollers/Architecture of Microprocessors Lecture NotesDocument148 pagesModule 1 Learning Unit 1: Microprocessors and Microcontrollers/Architecture of Microprocessors Lecture NotesSushma BorkarNo ratings yet
- Classification of ComputersDocument23 pagesClassification of ComputersRona EA SyNo ratings yet
- Computer Notes MonthlyDocument3 pagesComputer Notes MonthlyJ-Mi AlejanoNo ratings yet
- Lecture 4Document14 pagesLecture 4Aasma KhalidNo ratings yet
- Types of ComputersDocument41 pagesTypes of Computerssubramani muthusamyNo ratings yet
- Classiffication of ComputerDocument15 pagesClassiffication of Computervenkat sai bharatNo ratings yet
- Information Technology & Business: Computer Based Information SystemsDocument79 pagesInformation Technology & Business: Computer Based Information SystemsRosedemaeBolongaitaNo ratings yet
- The Shapes of Computers Today: Introduction To ComputerDocument16 pagesThe Shapes of Computers Today: Introduction To Computersughra afzaliNo ratings yet
- g11 Types of Computer AutosavedDocument67 pagesg11 Types of Computer AutosavedJasper B CodoyNo ratings yet
- What Is The One of The Most BrilliantDocument44 pagesWhat Is The One of The Most BrilliantJelyn OkekeNo ratings yet
- Computer Concepts and HardwareDocument68 pagesComputer Concepts and HardwareRose Bella Lacanilao100% (1)
- Different Types of ComputersDocument12 pagesDifferent Types of ComputersLeah Pinili BlancoNo ratings yet
- ZakaatDocument6 pagesZakaatSyed MuneebNo ratings yet
- NamazDocument12 pagesNamazSyed MuneebNo ratings yet
- FastDocument9 pagesFastSyed MuneebNo ratings yet
- Lecture 8Document15 pagesLecture 8Syed MuneebNo ratings yet
- Lecture 9Document9 pagesLecture 9Syed MuneebNo ratings yet
- Lecture 15Document34 pagesLecture 15Syed MuneebNo ratings yet
- Lecture 4Document30 pagesLecture 4Syed MuneebNo ratings yet
- Lecture 14Document28 pagesLecture 14Syed MuneebNo ratings yet
- Lecture 12Document29 pagesLecture 12Syed MuneebNo ratings yet
- Lecture 7Document23 pagesLecture 7Syed MuneebNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2Document20 pagesLecture 2Syed MuneebNo ratings yet
- Comprehension SkillsDocument9 pagesComprehension SkillsSyed MuneebNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1Document15 pagesLecture 1Syed MuneebNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3 Hamming CodeDocument14 pagesLecture 3 Hamming Codegoutam sanyalNo ratings yet
- Stima CLS Windows Quick Setup GuideDocument16 pagesStima CLS Windows Quick Setup Guideestanis1su1rezNo ratings yet
- Cryptography & Network Security: Chester Rebeiro IIT MadrasDocument29 pagesCryptography & Network Security: Chester Rebeiro IIT MadrasNimeesha OrugundlaNo ratings yet
- Authorization To Alter Crash Recovery2Document1 pageAuthorization To Alter Crash Recovery2Kanishka MandalNo ratings yet
- L. D. College of Engineering Lab Manual: System Software (3160715)Document53 pagesL. D. College of Engineering Lab Manual: System Software (3160715)Suraj MulchandaniNo ratings yet
- Impact of ICT On IndividualsDocument2 pagesImpact of ICT On IndividualsJohanna Soyum100% (1)
- Fortinet - FortiGate Cookbook v4.0 MR3 PDFDocument394 pagesFortinet - FortiGate Cookbook v4.0 MR3 PDFsatcomerNo ratings yet
- Cybersecurity Framework Profile Ransomware Risk MG Beckman 1623394907Document22 pagesCybersecurity Framework Profile Ransomware Risk MG Beckman 1623394907Chandrashekar MNo ratings yet
- Quick Mikrotik / Freeradius HowtoDocument6 pagesQuick Mikrotik / Freeradius HowtoBarnabie Riddick OpiyoNo ratings yet
- LoaderDocument64 pagesLoaderAmanda DodsonNo ratings yet
- Long History of NetworkingDocument2 pagesLong History of NetworkingJosiah OduroNo ratings yet
- Adaptive Server Enterprise: Security Administration GuideDocument434 pagesAdaptive Server Enterprise: Security Administration GuideWeraNo ratings yet
- Fujitsu Server PRIMERGY RX4770 M6 Rack Server: Data SheetDocument11 pagesFujitsu Server PRIMERGY RX4770 M6 Rack Server: Data SheetAnonymous YLI2wFNo ratings yet
- 5 Best Free Classical Music Download SourcesDocument20 pages5 Best Free Classical Music Download Sourceshardman3107No ratings yet
- Claro Battery Soft-Lock ActivationDocument10 pagesClaro Battery Soft-Lock ActivationAntonio MilianNo ratings yet
- MINI PROJECT Sem 4Document16 pagesMINI PROJECT Sem 4ITB450RUTIKA SALUNKHENo ratings yet
- Taxonomy of Challenges For Digital ForensicsDocument28 pagesTaxonomy of Challenges For Digital ForensicsasdasdasdasdNo ratings yet
- Huawei HG8247 Huawei Router Default ConfigurationDocument3 pagesHuawei HG8247 Huawei Router Default ConfigurationElizabeth RichNo ratings yet
- Question & Answers: Certified in Cybersecurity (CC)Document6 pagesQuestion & Answers: Certified in Cybersecurity (CC)ArifNo ratings yet
- Exam MB 901 Microsoft Dynamics 365 Fundamentals Skills MeasuredDocument9 pagesExam MB 901 Microsoft Dynamics 365 Fundamentals Skills MeasuredMarcelo Plada IntNo ratings yet
- Agile Micro System Is Established During Late 1990s Primarily As Suppliers and Service Providers of ITDocument2 pagesAgile Micro System Is Established During Late 1990s Primarily As Suppliers and Service Providers of ITNipun CpNo ratings yet
- Week2 CM MDL CP1212Document13 pagesWeek2 CM MDL CP1212Kassandra GlorNo ratings yet
- Delinea Datasheet Server SuiteDocument2 pagesDelinea Datasheet Server SuitedfgdfsgNo ratings yet
- SaltStackEnterpriseHelp-V6 1 0 OctoberDocument238 pagesSaltStackEnterpriseHelp-V6 1 0 OctoberGaurav SwaroopNo ratings yet
- 4.4.2.3 Lab - Configuring A Wireless Router and Client - ILM PDFDocument17 pages4.4.2.3 Lab - Configuring A Wireless Router and Client - ILM PDFMaksim Korsakov50% (2)
- Network Design ProposalDocument14 pagesNetwork Design Proposalnice guyNo ratings yet
- Course: Network Service Administrator Code BCN3043 Topic Lab Module: 3 DURATION: 2 HoursDocument6 pagesCourse: Network Service Administrator Code BCN3043 Topic Lab Module: 3 DURATION: 2 HoursDenny ChanNo ratings yet
- Technical Support International: Module 8: Software UpdateDocument10 pagesTechnical Support International: Module 8: Software UpdateBrayan RamírezNo ratings yet
- 10 02 A Manual Erase E.V. I.I. Mod.#27 6K4023 030812Document12 pages10 02 A Manual Erase E.V. I.I. Mod.#27 6K4023 030812Iranildo Barbosa100% (1)
- App-4Sdd Data Acquisition Software Operation Manual: Technoap Co., LTDDocument37 pagesApp-4Sdd Data Acquisition Software Operation Manual: Technoap Co., LTDOmar SuarezNo ratings yet