0% found this document useful (0 votes)
250 views31 pagesImportance of Electrical Engineering
Electrical engineering is an important field because electricity powers and controls many aspects of modern life and technology. Some key points covered in the document include:
- Electricity is used for communication technologies like phones, wireless devices, and data transmission.
- Electrical engineers develop problem solving skills through circuit problems that require reasoning rather than just formulas.
- There is a growing need to develop renewable and sustainable energy alternatives due to issues with non-renewable resources like oil and coal.
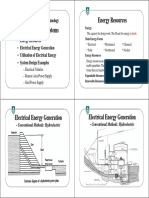
- Electricity is generated mostly from coal in the US, with natural gas and nuclear also contributing significantly. It is distributed through high voltage power lines and transformers before reaching homes and businesses.
Uploaded by
syed42210Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
250 views31 pagesImportance of Electrical Engineering
Electrical engineering is an important field because electricity powers and controls many aspects of modern life and technology. Some key points covered in the document include:
- Electricity is used for communication technologies like phones, wireless devices, and data transmission.
- Electrical engineers develop problem solving skills through circuit problems that require reasoning rather than just formulas.
- There is a growing need to develop renewable and sustainable energy alternatives due to issues with non-renewable resources like oil and coal.
- Electricity is generated mostly from coal in the US, with natural gas and nuclear also contributing significantly. It is distributed through high voltage power lines and transformers before reaching homes and businesses.
Uploaded by
syed42210Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd