Professional Documents
Culture Documents
NB-Thickness Design of Two Way Slabs-5
Uploaded by
Afzal Tunio0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
11 views5 pagesCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
11 views5 pagesNB-Thickness Design of Two Way Slabs-5
Uploaded by
Afzal TunioCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 5
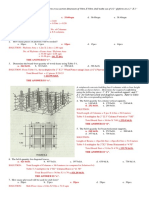
The floor system shown in Fig.
consists of solid slabs and beams in two directions
supported on 20-in. square columns. Determine the minimum slab thickness
required for an interior panel. Use f`c = 3 ksi and fy = 60 ksi.
Solution
Since slab is supported on beams, we determine its thickness. To apply the
equation of ACI we need to find out Ib and Is etc. Effective X-Sec of T beam is
Shown in fig. Assume h = 7 in .
Ib = Ig +a1h1˄2 (h1 = 8.2 – 3.50 = 4.7 in)
The moment of inertia of the slab in the long direction assuming slab thickness of 7
in
The moment of inertia of the slab in the short direction
Eq. 9.12
--------
Eq. 9.13
---------
Also, hmin = 3.5 in. Therefore, h = 6.27 in. controls. A slab
thickness of 6.5 in. or 7.0 in. may be adopted. Note that in
most practical cases, Eq. 17.2 controls.
A flat plate floor system with panels 24 by 20 ft is supported on
20 in. square columns. Determine the minimum slab thickness
required for the interior and corner panels.Use fc= 4 ksi and fy =
60 ksi.
1 . For corner panel No.1
Slab thickness, from table 9.5(c) ( fy = 60 ksi and no edge
beams)
ln
hmin
30
20 in. 1 ft.
ln 24 ft. 2 22.33 ft.
2 12 in.
12 in.
22.33 ft.
1 ft.
hmin 8.93 in. 9 in.
30
2 .For interior panel No. 3
Slab thickness, from table 9.5(c) (fy = 60 ksi
and no edge beams for a = am = 0 )
ln
hmin
33
12 in.
22.33 ft.
1 ft. 8.12 in. 8.5 in.
hmin
33
If a uniform slab thickness is used for all
panels , then h = 9.0 inch will be adopted.
You might also like
- Lecture 17Document27 pagesLecture 17jailan omarNo ratings yet
- ACI Coefficient Method Worked ExampleDocument4 pagesACI Coefficient Method Worked ExampleMuhammad Ahmed Farooq100% (1)
- SlabsDocument14 pagesSlabsابراهيم الربيعيNo ratings yet
- BT JOE Quiz 1a FormworksDocument2 pagesBT JOE Quiz 1a Formworkscorazon philNo ratings yet
- Two-Way Slabs: by Dr. Salah UddinDocument48 pagesTwo-Way Slabs: by Dr. Salah UddinZohaibShoukatBalochNo ratings yet
- Lecture 35 - Design of Two-Way Floor Slab System: April 23, 2003 CVEN 444Document52 pagesLecture 35 - Design of Two-Way Floor Slab System: April 23, 2003 CVEN 444Chen ManNo ratings yet
- Home Work - Cem605Document5 pagesHome Work - Cem605neelNo ratings yet
- Design of Two-Way Slabs - Design ExamplesDocument19 pagesDesign of Two-Way Slabs - Design ExamplesAhmad HussainNo ratings yet
- Chapter - 4Document25 pagesChapter - 4Wai Yann ZawNo ratings yet
- Waffle SlabsDocument9 pagesWaffle Slabsahsana2878% (9)
- Two Way Slab BestDocument25 pagesTwo Way Slab BestErnest Christian Nanola100% (1)
- Two Way Slab SystemsDocument264 pagesTwo Way Slab Systemsali hasanNo ratings yet
- Chapt 10Document22 pagesChapt 10yaori700% (1)
- 560.325 Homework Assignment 5: Two Problems Due Tuesday, October 25 at 5pm, Latrobe 212Document1 page560.325 Homework Assignment 5: Two Problems Due Tuesday, October 25 at 5pm, Latrobe 212BELAL ALSUBARINo ratings yet
- Design of A Spread FootingDocument10 pagesDesign of A Spread FootingkiranNo ratings yet
- Tugas 2 Rek - Pondasi Dalam - 2019Document4 pagesTugas 2 Rek - Pondasi Dalam - 2019Putri YusellaNo ratings yet
- Eigen Modes - PDF Timesaving-Torsiondesign-Ia PDFDocument32 pagesEigen Modes - PDF Timesaving-Torsiondesign-Ia PDFGeorge GeorgianNo ratings yet
- Lecture 8 Two Way Slab-1Document93 pagesLecture 8 Two Way Slab-1Syed Agha Shah AliNo ratings yet
- AE401 - Tee Spandrel and SlabsDocument13 pagesAE401 - Tee Spandrel and SlabsThomas MartinNo ratings yet
- SlabDocument60 pagesSlabAdigwe George ChimaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 35 - Design of Two-Way Floor Slab SystemDocument52 pagesLecture 35 - Design of Two-Way Floor Slab Systemsohaib_121No ratings yet
- Preliminary Sizing of Structural Members - Building Construction Principles, Materials, and SystemsDocument8 pagesPreliminary Sizing of Structural Members - Building Construction Principles, Materials, and SystemsaikalessNo ratings yet
- Design of A One-Way Reinforced Concrete Basement Retaining WallDocument7 pagesDesign of A One-Way Reinforced Concrete Basement Retaining WallSeifeldin Ali MarzoukNo ratings yet
- Full Beam Design Example: GivenDocument17 pagesFull Beam Design Example: Giventap ramosNo ratings yet
- Baffled Apron DropsDocument9 pagesBaffled Apron Dropsraghurmi100% (1)
- 16 Model Question 1 (Feb 2020) WoaDocument28 pages16 Model Question 1 (Feb 2020) WoakhaledNo ratings yet
- Ce364 CDocument4 pagesCe364 Cu19n6735No ratings yet
- Tutorial 5Document2 pagesTutorial 5Anonymous Vx9KTkM8n67% (3)
- 1Document9 pages1Harf Jucoy MirandaNo ratings yet
- Rectangular Footing Sample ProblemDocument11 pagesRectangular Footing Sample ProblemKhalil Furio100% (4)
- Maths Lit Worksheet - Estimating and MeasuringDocument3 pagesMaths Lit Worksheet - Estimating and MeasuringCape Town After-School TutorialsNo ratings yet
- Two Way Slab ExampleDocument16 pagesTwo Way Slab ExampleJason EdwardsNo ratings yet
- Foundation Engg Modal Question BDocument3 pagesFoundation Engg Modal Question Bmahil1234No ratings yet
- TIME SAVING DESIGN AIDS - Concrete WallsDocument6 pagesTIME SAVING DESIGN AIDS - Concrete WallsalshaijiNo ratings yet
- Beam Analogy DerivationDocument9 pagesBeam Analogy DerivationYassine Iferden TorssanovskiNo ratings yet
- CE363 Old Homework Solutions Part2Document21 pagesCE363 Old Homework Solutions Part2Irmak ÜnalNo ratings yet
- 3.2 University of Glasgow Geotechnical Exam Question ExamplesDocument5 pages3.2 University of Glasgow Geotechnical Exam Question ExamplesFırat PulatNo ratings yet
- Book of Nadeem Hussain - Chapter 9 One Way Joist SlabDocument19 pagesBook of Nadeem Hussain - Chapter 9 One Way Joist SlabahmadNo ratings yet
- CE404 Sarda Type II Fall ProblemDocument5 pagesCE404 Sarda Type II Fall ProblemAshish Satpute67% (6)
- Geotechnical Engineering ExamDocument4 pagesGeotechnical Engineering ExammikeengineeringNo ratings yet
- 560.325 Homework Assignment 2Document1 page560.325 Homework Assignment 2BELAL ALSUBARINo ratings yet
- Combined Footing On PilesDocument13 pagesCombined Footing On PilesJohn GuerielNo ratings yet
- Guidlines For Waffle Slab DesignDocument5 pagesGuidlines For Waffle Slab Designhafiz zain saeedNo ratings yet
- QuestionsDocument8 pagesQuestionsAhmad AlyNo ratings yet
- Two Way Slab Design PDFDocument12 pagesTwo Way Slab Design PDFAnand Kumar Pandiri100% (1)
- GabionDocument6 pagesGabionRalph Bantoi100% (1)
- Student Self-Led Activity Exercises On Supported Vertical Sided ExcavationsDocument1 pageStudent Self-Led Activity Exercises On Supported Vertical Sided ExcavationsZaid AlsarayrehNo ratings yet
- Design of Walls and Shear WallsDocument19 pagesDesign of Walls and Shear WallsMay100% (1)
- Previous Year UPTU End Sem Exam Papers - SOM / MOSDocument4 pagesPrevious Year UPTU End Sem Exam Papers - SOM / MOSnitin_johriNo ratings yet
- FINAL Shallow Foundation Design ReportDocument43 pagesFINAL Shallow Foundation Design Reportanabelle rosarioNo ratings yet
- Exercise On Lateral Earth PressureDocument4 pagesExercise On Lateral Earth PressureTing Wee KietNo ratings yet
- O level Physics Questions And Answer Practice Papers 2From EverandO level Physics Questions And Answer Practice Papers 2Rating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Comfort Crocheted Afghans: Three Heirloom Blankets for Home and FamilyFrom EverandComfort Crocheted Afghans: Three Heirloom Blankets for Home and FamilyRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (2)
- Pianos: Their Construction, Tuning, And Repair - With Numerous Engravings And DiagramsFrom EverandPianos: Their Construction, Tuning, And Repair - With Numerous Engravings And DiagramsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (2)
- ATI TEAS Calculation Workbook: 300 Questions to Prepare for the TEAS (2023 Edition)From EverandATI TEAS Calculation Workbook: 300 Questions to Prepare for the TEAS (2023 Edition)No ratings yet
- GWH - 04 (2-Hrs) - Determination of Aquifer ParametersDocument19 pagesGWH - 04 (2-Hrs) - Determination of Aquifer ParametersAfzal TunioNo ratings yet
- SWH-09 (2 Hors) - Methods of Water Measurement - Dr. SM KoriDocument51 pagesSWH-09 (2 Hors) - Methods of Water Measurement - Dr. SM KoriAfzal TunioNo ratings yet
- SWH-10 (2hrs) - Indus Water Treaty, Water Accord 1991, Indus River System Authority (IRSA)Document28 pagesSWH-10 (2hrs) - Indus Water Treaty, Water Accord 1991, Indus River System Authority (IRSA)Afzal TunioNo ratings yet
- NB-Flat Slab With Drops (Example)Document26 pagesNB-Flat Slab With Drops (Example)Afzal TunioNo ratings yet