Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Histology
Uploaded by
Jescyl Jane Egomes0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
11 views39 pagesCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
11 views39 pagesHistology
Uploaded by
Jescyl Jane EgomesCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 39
Histology
The study of Tissues
Four Types of Tissues
Types of Tissues
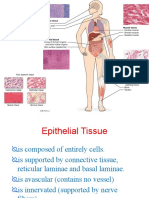
1. Epithelial Tissues:
it covers or lines something
• Absorb- lining of the small intestines
• Transport – kidney tubules
• Excrete – sweat and endocrine glands
• Protect- the skin
• Contain nerve cells for sensory reception- the taste
buds in the tongue
Classification of Epithelial
Tissues
According to layers:
1. simple epithelial – consist only one layer of cells
2. Stratified epithelial- consist of two or more layers of
cells.
3. Pseudostratified- false layered cells
According to shape:
1. Squamous epithelium- flat, platelike cells
2. Cuboidal epithelium- shaped like a cube
3. Columnar epithelium- columnlike cells
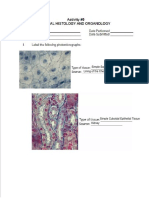
Squamous Epithelium
Simple Cuboidal Epithelial Tissue
Simple Cuboidal
Simple Columnar Epithelial Tissue
Ciliated Pseudostratified Columar Epithelial Tissue
Stratified Squamous Epithelial Tissue
Transitional epithelium
(also known as urothelium) is a type of
tissue consisting of multiple layers of
epithelial cells which can contract and
expand. These cells, part of the epithelium,
are found in the urinary bladder, in the
ureters, and in the superior urethra and
gland ducts of the prostate.
Transitional epithelium
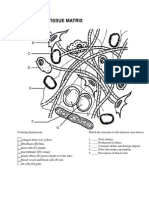
Connective Tissues
Connections and Support
Two types of fiber arrangements
1. Loose Connective tissue- strong, flexible fibers of
the protein collagen are interwoven with fine, elastic,
and reticular fibers, giving loose connective tissue its
elastic consistency and making it an excellent binding
tissue.
2. Fibrous connective Tissue- collagen fibers are
densely packed and may lie parallel to one another,
creating very strong cords, such as tendons and
ligaments.
Examples of Loose Connective tissue (Adipose tissue located around
kidneys, under skin, in bones, within abdomen, in breast.) Provide reserve fuel,
insulates against heat loss, support and protects organs.
Areolar Connective tissue, found beneath the skin
Hyaline Cartilage
(nose, trachea, larynx and ends of long bones)
Elastic cartilage (external ear, epiglottis,)
Fibrocartilage (intervertebral disc, pubic symphysis, knee joint)
Fibrous connective Tissue (Tendons)
connects muscles to bone
Ligaments (connects bone to bone)
Bone Tissue (support protect, provide leverage for muscles
to act on, stores calcium and fat and forms blood cells)
Blood Tissue located within blood vessels, transport oxygen,
carbon dioxide, nutrients, water, hormones, minerals, vits. Etc.
Muscular Tissue
Skeletal Muscles ( Voluntary movements, attached to the bones,
Straited muscles)
Cardiac muscles (involuntary control, straited, found wall of the heart)
Smooth Involuntary Muscles (moves subtances or objects, like
foodstuff and urine along internal passageways; involuntary control, non
straited)
Nervous Tissue ( Brain, spinal cord, and nerves), transmit electrical signals .
Sensory cells
( found in sense
organs)
Sensory nerves - carries information from the sense
organ to the Brain and Spinal cord.
Motor neuron- nerves that carries information
from the brain and spinal cord to the body (muscles and
glands)
Brain and Spinal Cord- integrates or interprets
information
You might also like
- Animal Tissues Levels of Organization: TissueDocument15 pagesAnimal Tissues Levels of Organization: TissueDiane Fontanilla100% (1)
- Animal TissuesDocument15 pagesAnimal TissuesLitaMeilinaNo ratings yet
- Tissues, Organs and Organ SystemsDocument17 pagesTissues, Organs and Organ SystemsDestinee Sullivan100% (1)
- Chapter 7 Structural Organisation in AnimalsDocument25 pagesChapter 7 Structural Organisation in Animalsamit lakraNo ratings yet
- Animal TissuesDocument11 pagesAnimal TissuesEduard LaudeNo ratings yet
- Animal Tissue TypesDocument17 pagesAnimal Tissue TypesMuskan Shree100% (1)
- Animal TissuesDocument44 pagesAnimal TissuesMary Sutingco100% (1)
- Anatomy LectureDocument76 pagesAnatomy LectureLagnajit Behera100% (1)
- Tissue Membranes GuideDocument4 pagesTissue Membranes GuideElleNo ratings yet
- BIOL223-Lab 9Document53 pagesBIOL223-Lab 9chicken fries100% (1)
- Anatomy - TissuesDocument43 pagesAnatomy - TissuesGleceree Filomeno100% (1)
- Zoology Notes: 007 Chapter 4Document4 pagesZoology Notes: 007 Chapter 4humanupgradeNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 - Tissues Glands and MembranesDocument49 pagesChapter 4 - Tissues Glands and MembranesNess G. Mamasabulod100% (1)
- Animal TissuesDocument24 pagesAnimal TissuesPrecy Ann ReyesNo ratings yet
- HISTOLOGY Is The Study of Tissues.: 4 MAJOR TISSUE TYPES: Epithelial (Covering)Document5 pagesHISTOLOGY Is The Study of Tissues.: 4 MAJOR TISSUE TYPES: Epithelial (Covering)Katie RodriguezNo ratings yet
- TissuesDocument70 pagesTissuesayssNo ratings yet
- Animal TissueDocument6 pagesAnimal TissueAhmad NadeemNo ratings yet
- Animal TissuesDocument7 pagesAnimal TissuesBeaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7 Points To RememberDocument7 pagesChapter 7 Points To RememberNANDA KISHORE S X A AD : 1 0 6 4 4100% (1)
- Tissue Anatomy and Physiology: The Four Main Tissue TypesDocument35 pagesTissue Anatomy and Physiology: The Four Main Tissue Typessnp88100% (1)
- Structures and Functions of Animal Tissues and Cell ModificationDocument105 pagesStructures and Functions of Animal Tissues and Cell ModificationArvie Jay Castillo100% (1)
- Human Body OrganizationDocument6 pagesHuman Body OrganizationWolverineInZenNo ratings yet
- Animal Tissues: Structures and Functions in 40 CharactersDocument41 pagesAnimal Tissues: Structures and Functions in 40 Charactersenkidani100% (1)
- Embryonic Germ Layers Determine Vertebrate StructureDocument5 pagesEmbryonic Germ Layers Determine Vertebrate StructureYannaNo ratings yet
- Types of TissuesDocument7 pagesTypes of TissuesKaren Mae AlcantaraNo ratings yet
- Cells and Tissues: TissueDocument4 pagesCells and Tissues: Tissueقى قىNo ratings yet
- Animal TissueDocument6 pagesAnimal TissueSarveshrau MagentharauNo ratings yet
- Epithelial TissuesDocument14 pagesEpithelial TissuesJhunelyn100% (2)
- Body Tissues-AnatomyDocument10 pagesBody Tissues-AnatomyJhulianne MarieNo ratings yet
- Animal TissuesDocument13 pagesAnimal TissuesYudatami TiaraNo ratings yet
- Ch. 4 TissuesDocument55 pagesCh. 4 TissuesBora YaNo ratings yet
- Handout-Animal-Tissues-2023-2024Document4 pagesHandout-Animal-Tissues-2023-2024reece sayamNo ratings yet
- TissuesDocument33 pagesTissuesAnonymous imF0MCd9UNo ratings yet
- Anaphy TissuesDocument4 pagesAnaphy TissuesYo1No ratings yet
- Plant Tissue TypesDocument6 pagesPlant Tissue TypesBhoomika GoyalNo ratings yet
- TissuesDocument91 pagesTissuesSon Ezekiel Gabriel I. BenitezNo ratings yet
- Classification of Tissue: Suman Kumar Mekap Asst. Professor (Pharmacology) CUTM, BhubaneswarDocument20 pagesClassification of Tissue: Suman Kumar Mekap Asst. Professor (Pharmacology) CUTM, BhubaneswarSaad Zafar AwanNo ratings yet
- Tissues PPT SummaryDocument16 pagesTissues PPT SummarySamarjeet BaliyanNo ratings yet
- BIO122 - CHAPTER 7 Part 1Document53 pagesBIO122 - CHAPTER 7 Part 1lili100% (1)
- ch-6 PPT 1Document17 pagesch-6 PPT 1UtkarshNo ratings yet
- Tissues and Glands Histology LectureDocument7 pagesTissues and Glands Histology LectureMaddie HallNo ratings yet
- 01 Animal TissueDocument8 pages01 Animal TissueRohit SharmaNo ratings yet
- M 1 PPT-PDF XI Bio CH 7 Structural Organisation in AnimalsDocument39 pagesM 1 PPT-PDF XI Bio CH 7 Structural Organisation in Animalsamarendrar87No ratings yet
- Chapter 4: The Tissue Level of OrganizationDocument42 pagesChapter 4: The Tissue Level of OrganizationMichael Lester100% (1)
- Yy Yyy Y Yy Y YYYDocument64 pagesYy Yyy Y Yy Y YYYsreedam100% (1)
- Animal Structure and FunctionDocument9 pagesAnimal Structure and FunctionkpenalesNo ratings yet
- Animal TissueDocument32 pagesAnimal TissueIan Kerby Sollano100% (1)
- Chapter 4 Tissues, Glands, Membranes OverviewDocument3 pagesChapter 4 Tissues, Glands, Membranes OverviewKate MontenegroNo ratings yet
- Body TissuesDocument10 pagesBody TissuesNaanmatha PuspanathanNo ratings yet
- Histology Notes: Epithelial TissueDocument4 pagesHistology Notes: Epithelial TissueSteph AsideNo ratings yet
- Cell OrganizationDocument8 pagesCell OrganizationKiele Nicole Calansingin100% (1)
- Animal Tissues 2023Document70 pagesAnimal Tissues 2023yxcz.rzNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1: Animals' Specialized StructuresDocument58 pagesLesson 1: Animals' Specialized StructuresPhoenixNo ratings yet
- Secret MineralizeDocument2 pagesSecret MineralizeMaricris CosmeNo ratings yet
- Cell DiversityDocument3 pagesCell DiversityMrGilmartinNo ratings yet
- Deciphering nCoV19, Quest for Cure, Prophylaxis, and VaccineFrom EverandDeciphering nCoV19, Quest for Cure, Prophylaxis, and VaccineNo ratings yet
- Advanced farriery knowledge: A study guide and AWCF theory course companionFrom EverandAdvanced farriery knowledge: A study guide and AWCF theory course companionNo ratings yet
- Connective TissueDocument26 pagesConnective TissueooiszehuiNo ratings yet
- Human TissuesDocument7 pagesHuman Tissuesapi-277771710No ratings yet
- Bio100 - Le3 ReviewerDocument20 pagesBio100 - Le3 ReviewerMariel De Leon GinesNo ratings yet
- Test Bank For Principles of Human Physiology 5th Edition Cindy L StanfieldDocument24 pagesTest Bank For Principles of Human Physiology 5th Edition Cindy L StanfieldKevinHarrisonnkrqm100% (37)
- Meat & Meat Products Technology Including Poultry Products TechnDocument151 pagesMeat & Meat Products Technology Including Poultry Products TechnVoll EntertainmentNo ratings yet
- Anaphy Notes, I - Cells, Cell Division and TissueDocument14 pagesAnaphy Notes, I - Cells, Cell Division and TissueLindley PareñoNo ratings yet
- CH14 L1Document5 pagesCH14 L1Henry TalackoNo ratings yet
- Histological Study On Sinus Lift Grafting by Fisiograft and Bio-OssDocument6 pagesHistological Study On Sinus Lift Grafting by Fisiograft and Bio-OssmaxNo ratings yet
- Cells and TissuesDocument88 pagesCells and TissuesJeanie UyNo ratings yet
- LAPORAN LENGKAP Jaringan IkatDocument19 pagesLAPORAN LENGKAP Jaringan Ikatjeon niaNo ratings yet
- TLE-10-COOKERY-Q4-MODULE-1Document11 pagesTLE-10-COOKERY-Q4-MODULE-1Danica DaniotNo ratings yet
- Luchau Til Ed Advanced Myofascial Techniques Vol 1 ShoulderDocument451 pagesLuchau Til Ed Advanced Myofascial Techniques Vol 1 ShoulderВовочка Дудакин100% (1)
- Simple Squamous Epithelial Tissue & Connective Tissue FunctionsDocument10 pagesSimple Squamous Epithelial Tissue & Connective Tissue FunctionsRose CostaNo ratings yet
- Terminologia HistologicaDocument2 pagesTerminologia HistologicaLute CastroNo ratings yet
- Quiz MusculoskeletalDocument117 pagesQuiz MusculoskeletalMedShare89% (9)
- Connective Tissue Guide: Cells, Fibers & FunctionsDocument54 pagesConnective Tissue Guide: Cells, Fibers & FunctionsSaaraAlleyahAlAnaziNo ratings yet
- 29105-Medical Terminology WorkbookDocument344 pages29105-Medical Terminology WorkbookLee Hing Wah100% (2)
- Anaphy and Physiology - Review MaterialDocument7 pagesAnaphy and Physiology - Review MaterialKennethNo ratings yet
- Picmonic Step 1 Study Plan V2Document32 pagesPicmonic Step 1 Study Plan V2Smiti ChhabraNo ratings yet
- Connective Tissue NotesDocument6 pagesConnective Tissue NotesNand PrakashNo ratings yet
- CBLM Cookery Uc 6Document187 pagesCBLM Cookery Uc 6mary ann coperNo ratings yet
- Stevens&Lowes Human Histology 4 EDocument452 pagesStevens&Lowes Human Histology 4 Eusuario desconocido100% (1)
- Wa0000.Document22 pagesWa0000.thesatyamjha09No ratings yet
- Genbio1 - Mod2 - Cell-Types and Cell ModificationsDocument20 pagesGenbio1 - Mod2 - Cell-Types and Cell ModificationsAndevie Balili IguanaNo ratings yet
- True/False: Indicate Whether The Statement Is True or FalseDocument5 pagesTrue/False: Indicate Whether The Statement Is True or FalseNuk MooreNo ratings yet
- Connective Tissue MatrixDocument2 pagesConnective Tissue MatrixCherr Noll0% (1)
- Connective TissuesDocument10 pagesConnective Tissuesbenishgulzar50No ratings yet
- Detailed Tissues Class 9 Notes (NCERT Book Chapter 6)Document12 pagesDetailed Tissues Class 9 Notes (NCERT Book Chapter 6)suman_das1983100% (7)
- Tabalba 1-Y1-2 Lab Exercise 3Document4 pagesTabalba 1-Y1-2 Lab Exercise 3Shane V. TabalbaNo ratings yet
- Histology Students AtlasDocument101 pagesHistology Students AtlasXerox med75% (4)