Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Superiorvenacava DPT 1
Uploaded by
Super Ali0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
6 views12 pagesThe superior vena cava receives deoxygenated blood from the upper body and delivers it to the right atrium. It is formed by the merging of the brachiocephalic veins and travels through the thoracic region until draining into the superior portion of the right atrium. The superior vena cava has tributaries such as the brachiocephalic veins and azygos vein that deliver blood from the upper body to the superior vena cava.
Original Description:
Original Title
Superiorvenacava Dpt 1
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe superior vena cava receives deoxygenated blood from the upper body and delivers it to the right atrium. It is formed by the merging of the brachiocephalic veins and travels through the thoracic region until draining into the superior portion of the right atrium. The superior vena cava has tributaries such as the brachiocephalic veins and azygos vein that deliver blood from the upper body to the superior vena cava.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
6 views12 pagesSuperiorvenacava DPT 1
Uploaded by
Super AliThe superior vena cava receives deoxygenated blood from the upper body and delivers it to the right atrium. It is formed by the merging of the brachiocephalic veins and travels through the thoracic region until draining into the superior portion of the right atrium. The superior vena cava has tributaries such as the brachiocephalic veins and azygos vein that deliver blood from the upper body to the superior vena cava.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 12
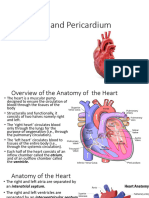
Superior vena cava
Superior Vena Cava
• The superior vena cava receives deoxygenated blood
from the upper body (superior to the diaphragm,
excluding the lungs and heart), delivering it to the right
atrium.
• It is formed by merging of the brachiocephalic veins,
travelling inferiorly through the thoracic region until
draining into the superior portion of the right atrium at
the level of the 3rd rib.
• .
Superior Vena Cava
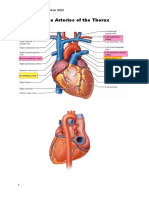
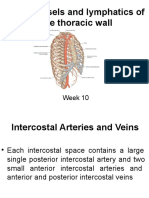
• The following tributaries of the superior vena cava
are located within the superior mediastinum:
– Brachiocephalic veins – draining blood from the upper
body.
– Left superior intercostal vein – collects blood from the
left 2nd and 3rd intercostal vein. It drains into the left
brachiocephalic vein.
– Supreme intercostal vein – drains the vein from first
intercostal space directly into the brachiocephalic veins.
– Azygos vein – receiving blood from the right posterior
intercostal veins. The left intercostal veins drain first into
the hemiazygos and accessory hemiazygos veins before
joining the azygos vein around T7-T9.
Superior Vena Cava
Important lenghts to remember (1,2,3
inches)
• The right brachiocephalic vein:
………about 1 inch long.
• The Superior Vena Cava:
………about 2 inches long
• The left brachiocephalic vein:
………about 3 inch long.
Superior Vena Cava
• Superior Vena Cava is about 7 cm long and 1.25 cm
in diameter.
• Its location is in the superior and middle
mediastina.
• The extrapericardial part is located in the
superior mediastinum and intrapericardial part is
located in the middle mediastinum.
Superior Vena Cava
• The superior vena cava is composed at the lower
border of the right 1st costal cartilage by the union
of left and right brachiocephalic (innominate) veins.
• It enters vertically downwards behind the right
border of the sternum and pierces
the pericardium in the level of the right 2nd costal
cartilage
Base of the heart. Diaphragmatic surface of the heart.
Superior Vena Cava
ANTERIOR: A. Right internal thoracic vessels.
B. Margin of right lung and pleura.
C. Chest wall.
POSTERIOR: A. Trachea (posteromedial).
B. Right pulmonary artery and right bronchus.
TO THE LEFT: A. Ascending aorta (anteromedial).
B. Brachiocephalic artery.
TO THE RIGHT: A.Right phrenic nerve and pericardiophrenic
vessels.
B. Right lung and pleura.
Superior Vena Cava
• SUBDIVISIONS
• The superior vena cava is subdivided into the following 2
parts:
• A. Extrapericardial part
–(in superior mediastinum).
• B. Intrapericardial part
–(in middle mediastinum).
Superior Vena Cava
• TRIBUTARIES
• A. Left and right brachiocephalic veins.
• B. Azygos vein, which arches over the root of the right lung
and opens into SVC just before it pierces fibrous
pericardium.
• C. Mediastinal and pericardial veins.
You might also like
- Anatomy Quizbook PDFDocument92 pagesAnatomy Quizbook PDFLipid Berger67% (3)
- Anatomy 2nd-U-1 CVSDocument121 pagesAnatomy 2nd-U-1 CVSsinte beyuNo ratings yet
- Embryology of The Heart and The Great VesselsDocument66 pagesEmbryology of The Heart and The Great VesselsNavya HegdeNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of Heart: Mr. Binu Babu MBA, M.Sc. (N) Asst. Professor Mrs. Jincy Ealias M.Sc. (N) LecturerDocument71 pagesAnatomy of Heart: Mr. Binu Babu MBA, M.Sc. (N) Asst. Professor Mrs. Jincy Ealias M.Sc. (N) Lecturerjyoti kunduNo ratings yet
- Anatomy - PDF Plab ResourcesDocument12 pagesAnatomy - PDF Plab ResourcesYoumna ShaabanNo ratings yet
- Anatomy & Physiology Cardiac SystemDocument1 pageAnatomy & Physiology Cardiac SystemTori RolandNo ratings yet
- Blood Supply of HeartDocument51 pagesBlood Supply of HeartHema Malani MurthiNo ratings yet
- (Principles of Cardiovascular Imaging) Stuart J. Hutchison - Principles of Cardiovascular Radiology (2011, Saunders)Document461 pages(Principles of Cardiovascular Imaging) Stuart J. Hutchison - Principles of Cardiovascular Radiology (2011, Saunders)Adeel LakhiarNo ratings yet
- Anatomy Quiz 2Document45 pagesAnatomy Quiz 2Upscaled100% (1)
- Stephen Hobbs - Thoracic Imaging - A Core Review-Lippincott Williams & Wilkins (2015)Document564 pagesStephen Hobbs - Thoracic Imaging - A Core Review-Lippincott Williams & Wilkins (2015)hüseyin vururNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of The Thorax MCQDocument7 pagesAnatomy of The Thorax MCQInnocent Clifford Marandu93% (14)
- Anatomy of HeartDocument63 pagesAnatomy of HeartClement NjingiNo ratings yet
- Revisiting The Vertebral Venous Plexus BatsonDocument15 pagesRevisiting The Vertebral Venous Plexus BatsonMorteza Mazloom Farsi BafNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of CT PDFDocument415 pagesFundamentals of CT PDFAl Marchese100% (1)
- Anatomi JantungDocument54 pagesAnatomi JantungsaifudinNo ratings yet
- Eat Vessels of The ThoraxDocument36 pagesEat Vessels of The ThoraxIshimwe TheotimeNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of CVS: 3. Blood Vessels of The ThoraxDocument20 pagesAnatomy of CVS: 3. Blood Vessels of The Thoraxsultan khabeebNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of Thoracic Vessels .Document13 pagesAnatomy of Thoracic Vessels .Luminita A-LumyNo ratings yet
- Blood Supply of ThoraxDocument22 pagesBlood Supply of ThoraxZahidKhanNo ratings yet
- 3.01 Aorta and Blood Supply 3rd YearDocument12 pages3.01 Aorta and Blood Supply 3rd YearJedoNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular System Part 2 PDFDocument46 pagesCardiovascular System Part 2 PDFVizhiNo ratings yet
- HeartDocument28 pagesHeartZahidKhanNo ratings yet
- Blood Supply To The HeartDocument28 pagesBlood Supply To The Heartmarkmuiruri581No ratings yet
- Lecture ChestDocument467 pagesLecture ChestMai IbrahimNo ratings yet
- MediastinumDocument41 pagesMediastinumwashma SoomroNo ratings yet
- Sheet 3 CVS PDFDocument14 pagesSheet 3 CVS PDFSabah SolimanNo ratings yet
- Null 1Document37 pagesNull 1Esdras DountioNo ratings yet
- Dr. Ariho. MediasternumDocument40 pagesDr. Ariho. MediasternumERIAS TENYWANo ratings yet
- Aims and Objectives: To Identify The Cross-Sectional Anatomy of The Following StructuresDocument23 pagesAims and Objectives: To Identify The Cross-Sectional Anatomy of The Following StructuresRoro91No ratings yet
- Kuliah The Heart, Pericardium, and Coronary VesselsDocument62 pagesKuliah The Heart, Pericardium, and Coronary VesselsRafianza AkbarNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of CVS: 2. The HeartDocument68 pagesAnatomy of CVS: 2. The Heartsultan khabeebNo ratings yet
- Heart, Mammary Glands.Document22 pagesHeart, Mammary Glands.Shimmering MoonNo ratings yet
- Anatomy5.heart and Large VesselesDocument73 pagesAnatomy5.heart and Large VesselesAhmadNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of The HeartDocument62 pagesAnatomy of The Heartgksah711No ratings yet
- Heart Anatomy For BSC NursingDocument57 pagesHeart Anatomy For BSC NursingVIJAYA KUMAR YNo ratings yet
- Lec 4 HeartDocument42 pagesLec 4 HeartEntesarNo ratings yet
- Bloodsupplytoheart 180518090422Document22 pagesBloodsupplytoheart 180518090422GodAlones GamingNo ratings yet
- 9 Superior MediastinumDocument20 pages9 Superior MediastinumtawandarukwavamadisonNo ratings yet
- AnatomyDocument8 pagesAnatomyOM BAWNENo ratings yet
- SDL - Thorax MediastinumDocument43 pagesSDL - Thorax MediastinumMatthew GiscombeNo ratings yet
- Posterior MediastinumDocument121 pagesPosterior MediastinumAuza Moses IbrahimNo ratings yet
- Cardio VasDocument99 pagesCardio VashellerkittyNo ratings yet
- المحاضرة الثانية عشر - مادة التشريح العام - المرحلة الاولىDocument10 pagesالمحاضرة الثانية عشر - مادة التشريح العام - المرحلة الاولىAbdullah TheNo ratings yet
- Aortic DissectionDocument24 pagesAortic Dissectionsameeha semiNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular System +Document14 pagesCardiovascular System +Yasin AbassNo ratings yet
- The Heart and PericardiumDocument40 pagesThe Heart and PericardiumMartha Orendu Oche AttahNo ratings yet
- Embryologi & Normal Structure of Cardiovascular System, Dr. Hasan NyambeDocument61 pagesEmbryologi & Normal Structure of Cardiovascular System, Dr. Hasan NyambeWahyunitadotokaNo ratings yet
- VASCULAR AnatomyDocument19 pagesVASCULAR AnatomyIA CREATIONSNo ratings yet
- Anatomy Pericardium & HeartDocument28 pagesAnatomy Pericardium & Heartprofvip_abotalebNo ratings yet
- Introduction of Angiology and HeartDocument58 pagesIntroduction of Angiology and Heart9999999999999-567421No ratings yet
- Thoracic Arteries, Aorta &veinsDocument42 pagesThoracic Arteries, Aorta &veinsmakondotakundaNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular System - The HeartDocument77 pagesCardiovascular System - The HeartZiraili VidalNo ratings yet
- Blood Flow Through HeartDocument7 pagesBlood Flow Through HeartMacoy LasqueNo ratings yet
- Heart AnatomyDocument7 pagesHeart AnatomyArjon BalaNo ratings yet
- Blood Supply of Whole BodyDocument60 pagesBlood Supply of Whole BodyProsanjit Majumder100% (1)
- Large Vessels of The Thorax 2022Document30 pagesLarge Vessels of The Thorax 2022Osama AbdelazizNo ratings yet
- Cardio Vascular SystemDocument56 pagesCardio Vascular SystemtazebNo ratings yet
- The Circulatory SystemDocument114 pagesThe Circulatory SystemKhant Si ThuNo ratings yet
- General Anatomy 5.thoracic Cavity (Intro To Cardivascular and Respiratory)Document49 pagesGeneral Anatomy 5.thoracic Cavity (Intro To Cardivascular and Respiratory)amrokhalefa21No ratings yet
- Lecture 4 - HeartDocument87 pagesLecture 4 - Heartsamabakr2003No ratings yet
- 38.anatomy of The HeartDocument21 pages38.anatomy of The HeartAbdul Samee AslamNo ratings yet
- Heart A Student WordDocument9 pagesHeart A Student Word46bwilsonNo ratings yet
- Mediastinum and Pericardium PDFDocument24 pagesMediastinum and Pericardium PDFMuhanad ShahinNo ratings yet
- Pathology of HEART - 1Document175 pagesPathology of HEART - 1Abdukadir AzamNo ratings yet
- Cardiac Anatomy, Physiology, and Cardiac Cycle: Ayu Puspita SariDocument42 pagesCardiac Anatomy, Physiology, and Cardiac Cycle: Ayu Puspita SariAyu PuspitaNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology,: Jantung OutlineDocument15 pagesAnatomy and Physiology,: Jantung OutlineChula Anak Bina IPGKRNo ratings yet
- Blood Supply of HeartDocument20 pagesBlood Supply of HeartPraneethaNo ratings yet
- Lec 3Document11 pagesLec 3Mhmead AbdNo ratings yet
- Glosario VenosoDocument207 pagesGlosario VenosoMary L CastroNo ratings yet
- 2nd Yr Syllabus BSMSDocument36 pages2nd Yr Syllabus BSMSmmmonmissionNo ratings yet
- ANA 202 WK 10Document22 pagesANA 202 WK 10TeeNo ratings yet
- Anomalous Pulmonary Venous Drainage: A Pictorial Essay With A CT FocusDocument13 pagesAnomalous Pulmonary Venous Drainage: A Pictorial Essay With A CT FocusIchel Silva FndzNo ratings yet
- Lucr - III Part 3Document130 pagesLucr - III Part 3Dan GaidauNo ratings yet
- Chest WallDocument26 pagesChest WallDeepti KakkarNo ratings yet
- M2F Cardiovascular SystemDocument8 pagesM2F Cardiovascular SystemMeteor 858No ratings yet
- Plaman Pleura Esofag Timus StadializariDocument32 pagesPlaman Pleura Esofag Timus StadializarikoxNo ratings yet
- Anatomy Practical Exam 2003Document7 pagesAnatomy Practical Exam 2003mohamedNo ratings yet
- Normal Chest RadiographDocument108 pagesNormal Chest RadiographVenu Madhav100% (1)
- Artery Supply Venous Drainage Nerve Supply Lymphatic DrainageDocument9 pagesArtery Supply Venous Drainage Nerve Supply Lymphatic DrainageTamim IshtiaqueNo ratings yet
- Anterior Posterior Lateral Superior Inferior: of 1 2 Vascular Biology LECTURE 1Document2 pagesAnterior Posterior Lateral Superior Inferior: of 1 2 Vascular Biology LECTURE 1Fazreena EleenaNo ratings yet
- INICET November 2021Document244 pagesINICET November 2021sonali bhakhoreeNo ratings yet
- Blood Supply of Whole BodyDocument60 pagesBlood Supply of Whole BodyProsanjit Majumder100% (1)
- SECTION 6: Spleen: and OverviewDocument38 pagesSECTION 6: Spleen: and Overviewtudoranluciana1No ratings yet
- ACD 15 - Pericardium & External HeartDocument8 pagesACD 15 - Pericardium & External Heartpranky neyneyNo ratings yet
- Gross30 - Mediastinum Handout - FagaldeDocument3 pagesGross30 - Mediastinum Handout - FagaldeAmar AlkhafajiNo ratings yet
- Azygos Venos System 2Document17 pagesAzygos Venos System 2Fazil Omar BelwaelNo ratings yet
- BRS Anatomy - Thorax Flashcards by Grace Caldwell - BrainscapeDocument45 pagesBRS Anatomy - Thorax Flashcards by Grace Caldwell - BrainscapeCarmela MarianoNo ratings yet
- Netter 7-1Document1 pageNetter 7-1MateiNo ratings yet
- Rabbit Vasculature Book Print August Final 2023Document35 pagesRabbit Vasculature Book Print August Final 2023Ana Katrina AguilaNo ratings yet