Professional Documents
Culture Documents
G10 Image Formation W2
Uploaded by
Antoinette0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
6 views32 pagesThis document discusses the concepts of reflection, mirrors, and lenses. It defines reflection as light bouncing off a surface, and describes specular and diffuse reflection. The law of reflection states that the angle of incidence equals the angle of reflection. Ray diagrams are used to determine the location, size, orientation, and type of image formed by a mirror. Key terms like center of curvature, principal axis, and focus are defined. Two example problems are given about determining the image location of objects placed in front of mirrors.
Original Description:
science ppt
Original Title
G10-IMAGE-FORMATION-W2-Copy (1)
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document discusses the concepts of reflection, mirrors, and lenses. It defines reflection as light bouncing off a surface, and describes specular and diffuse reflection. The law of reflection states that the angle of incidence equals the angle of reflection. Ray diagrams are used to determine the location, size, orientation, and type of image formed by a mirror. Key terms like center of curvature, principal axis, and focus are defined. Two example problems are given about determining the image location of objects placed in front of mirrors.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
6 views32 pagesG10 Image Formation W2
Uploaded by
AntoinetteThis document discusses the concepts of reflection, mirrors, and lenses. It defines reflection as light bouncing off a surface, and describes specular and diffuse reflection. The law of reflection states that the angle of incidence equals the angle of reflection. Ray diagrams are used to determine the location, size, orientation, and type of image formed by a mirror. Key terms like center of curvature, principal axis, and focus are defined. Two example problems are given about determining the image location of objects placed in front of mirrors.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 32
GOOD
GRADE 10 - OUR LADY OF CANDELARIA
AFTERNOON
REVIE
W
ACTIVITY 1:
Mirror, mirror on the
Image
formation on
Mirror and
Lenses
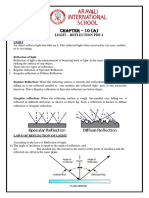
REFLECTION
Is the bouncing of light rays when it hits a surface.
(plane mirrors)
The reflection of light can be roughly
categorized into two types of reflection:
Specular reflection is defined as light reflected
from a smooth surface at a definite angle.
Diffuse reflection, which is produced by rough
surfaces that tend to reflect light in all
directions. (under the tree, buildings, rocks)
Law of
Reflection
States that the angle of incidence is equal to the angle of
reflection.
DEFINITION OF
TERMS
RAY DIAGRAMMING –
The goal of a ray diagram is to determine the location,
size, orientation, and type of image that is formed by
the concave mirror. Typically, this requires determining
where the image of the upper and lower extreme of the
object is located and then tracing the entire image.
The centre of curvature is the centre of the sphere of which
the spherical mirror is a part. It is denoted by 'C’.
The principal axis of a spherical mirror is the line passing
through the center of the mirror that is exactly perpendicular
to the surface of the mirror.
Focus the point on the axis of a lens or mirror to which
parallel rays of light converge or from which they appear to
diverge after refraction or reflection. a central point of
attention or interest.
Problem 1:
A bottle is placed 15 cm from the vertex of a
concave mirror that has a focal length of 12
cm.
Problem 2:
A Chess piece 1.2 cm high is standing 4.0
cm from a converging mirror having a focal
length of 20 cm.
You might also like
- Light Mirrors and LensesDocument28 pagesLight Mirrors and LensesJohn Malig100% (1)
- Light Reflection and Refraction Class 10 Notes Sci+Document19 pagesLight Reflection and Refraction Class 10 Notes Sci+Sahil GuptaNo ratings yet
- Reflection and Refraction - CBSE - XDocument7 pagesReflection and Refraction - CBSE - Xvidyamane23100% (1)
- Reflection of LightDocument11 pagesReflection of Lightlohitha charyNo ratings yet
- Science 10 Quarter 2 Module 4Document6 pagesScience 10 Quarter 2 Module 4Jess Anthony Efondo100% (4)
- Class 10 Science Chapter 10 Revision NotesDocument51 pagesClass 10 Science Chapter 10 Revision Notesved bhaskerNo ratings yet
- Chapter 10 - Light Reflection and Refraction Revision NotesDocument35 pagesChapter 10 - Light Reflection and Refraction Revision Notesprateeksahu1111No ratings yet
- XJHNZDMZ NHD Ahw AYag 3 RDocument38 pagesXJHNZDMZ NHD Ahw AYag 3 RVenu GopalNo ratings yet
- Physics - Light Reflection N Refraction Class 10Document11 pagesPhysics - Light Reflection N Refraction Class 10M S SHANKARNo ratings yet
- Light Mirrors and LensesDocument35 pagesLight Mirrors and LensesdeguzmanjannellegNo ratings yet
- Science Notes6Document37 pagesScience Notes6abhyudai.edwardsNo ratings yet
- Light Reflection and Refraction Images by Convex Concave R ExplainedDocument11 pagesLight Reflection and Refraction Images by Convex Concave R ExplainedSeetha SenthilNo ratings yet
- Reflection of Light 1Document28 pagesReflection of Light 1Anne MalobagoNo ratings yet
- Chapter Three:: Anatomy of A Curved MirrorDocument23 pagesChapter Three:: Anatomy of A Curved MirrorKay LagunaNo ratings yet
- Light (Mirrors and Lenses)Document19 pagesLight (Mirrors and Lenses)allijah gwyneth dalesNo ratings yet
- Reflection and Refraction of Light Chapter 10 NOTESDocument4 pagesReflection and Refraction of Light Chapter 10 NOTESTechnical AyushNo ratings yet
- Chapter 10 Light Reflection and Refraction NoteDocument10 pagesChapter 10 Light Reflection and Refraction NoteJay Maki100% (1)
- Class 10 LightDocument23 pagesClass 10 LightMathew AbrahamNo ratings yet
- Light MirrorsDocument57 pagesLight MirrorsPhylicia RamosNo ratings yet
- Reflection Mirrors 2022 2023Document92 pagesReflection Mirrors 2022 2023Jeon ManobanNo ratings yet
- Spherical MirrorsDocument8 pagesSpherical MirrorsJunaid HussainNo ratings yet
- Grade 10 Subject-Science CHAPTER - 10 Light - Reflection and Refraction NotesDocument9 pagesGrade 10 Subject-Science CHAPTER - 10 Light - Reflection and Refraction Notesluv manotNo ratings yet
- Reflection and MirrorsDocument30 pagesReflection and MirrorsDavidis DotaroNo ratings yet
- GRADE 10 - SCIENCE Notes 3 (2nd Quarter)Document3 pagesGRADE 10 - SCIENCE Notes 3 (2nd Quarter)gwenn enaje100% (1)
- Quarter 2-Lesson - Light and MirrorsDocument72 pagesQuarter 2-Lesson - Light and MirrorsTrendi Printing ServicesNo ratings yet
- DocumentDocument1 pageDocumentNica OmpocNo ratings yet
- Chapter 10 - LightDocument35 pagesChapter 10 - LightMadhanNo ratings yet
- Spherical MirrorsDocument5 pagesSpherical MirrorsAshir GillNo ratings yet
- Plane and Spherical MirrorsDocument9 pagesPlane and Spherical Mirrorschinkayaby16No ratings yet
- Optics 10-PhysicsDocument6 pagesOptics 10-PhysicsTapas BanerjeeNo ratings yet
- Class 10 SCIENCE - PhysicsDocument59 pagesClass 10 SCIENCE - PhysicsRamya L NNo ratings yet
- Mirror vs. LensDocument5 pagesMirror vs. LensEhr WinNo ratings yet
- Additional Notes - LightDocument10 pagesAdditional Notes - LightsidharthNo ratings yet
- CH 1 PhysicsDocument18 pagesCH 1 Physicsraj chopdaNo ratings yet
- Reflection of LightDocument17 pagesReflection of LightNishant SinghNo ratings yet
- Chapter - 10 (A) Light and ReflectionDocument12 pagesChapter - 10 (A) Light and ReflectionSuhani GosainNo ratings yet
- PhysicsX PDFDocument124 pagesPhysicsX PDFcitsNo ratings yet
- Chapter 9 - Light - Reflection and RefractionDocument48 pagesChapter 9 - Light - Reflection and Refractionsekhsayan0102No ratings yet
- 2 Navneeta Kunwar Public School Varanasi-1Document12 pages2 Navneeta Kunwar Public School Varanasi-1shashwatraipro1No ratings yet
- The Learners Demonstrate An Understanding of The Images Formed by The Different Types of Mirrors and LensesDocument78 pagesThe Learners Demonstrate An Understanding of The Images Formed by The Different Types of Mirrors and LensesWarren Dela CernaNo ratings yet
- Chapter-10 Light Final - Ejrm4pw4gjcvtmnndtktDocument17 pagesChapter-10 Light Final - Ejrm4pw4gjcvtmnndtktSarveshyaNo ratings yet
- What Is Visible Light Science Presentation in Light Blue Black Hand Drawn StyleDocument21 pagesWhat Is Visible Light Science Presentation in Light Blue Black Hand Drawn StyleJuliusNo ratings yet
- E111 - AgustinDocument20 pagesE111 - AgustinSeth Jarl G. AgustinNo ratings yet
- Light ReflectionDocument13 pagesLight ReflectionDivya PriolkarNo ratings yet
- Lecture On LightDocument4 pagesLecture On LightAshly DeniseNo ratings yet
- Refraction of LightDocument27 pagesRefraction of LighttejassidhpuraNo ratings yet
- Grade 6 Chapter 6 NoteDocument4 pagesGrade 6 Chapter 6 NotesiyaNo ratings yet
- Formation of ImagesDocument32 pagesFormation of ImagesBlueaux roseNo ratings yet
- Formation of Image LDocument24 pagesFormation of Image LTel BiscochoNo ratings yet
- Optics 1Document8 pagesOptics 1Stephson Micayee Da LastbornNo ratings yet
- PhysicsDocument5 pagesPhysicsLightning OfiicialNo ratings yet
- Light PDFDocument5 pagesLight PDFAninda RoyNo ratings yet
- Kendriya Vidyalaya Moradabad: Science ProjectDocument103 pagesKendriya Vidyalaya Moradabad: Science ProjectRishi Bhatia100% (1)
- Mirrors and Lenses ReviewerDocument9 pagesMirrors and Lenses ReviewerVannie MonderoNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class 7 Science Chapter 15 Light Revision NotesDocument28 pagesCBSE Class 7 Science Chapter 15 Light Revision NotesPRATUL SINGHNo ratings yet
- Mirror NotesDocument6 pagesMirror Notesmarife gupaal100% (1)
- Reflection: Light - Reflection and RefractionDocument11 pagesReflection: Light - Reflection and RefractionmathclubNo ratings yet
- Image Formation in Lenses AaliyaDocument15 pagesImage Formation in Lenses AaliyaAaliya PatelNo ratings yet
- I Can See Planets and Stars from My Room! How The Telescope Works - Physics Book 4th Grade | Children's Physics BooksFrom EverandI Can See Planets and Stars from My Room! How The Telescope Works - Physics Book 4th Grade | Children's Physics BooksNo ratings yet
- Group 4 TLE Lesson 2Document33 pagesGroup 4 TLE Lesson 2AntoinetteNo ratings yet
- PP4 Comparing and ContrastingDocument92 pagesPP4 Comparing and ContrastingAntoinetteNo ratings yet
- Kaliwa Dam CompleteDocument4 pagesKaliwa Dam CompleteAntoinette0% (1)
- Legalization of Abortion in The PhilippinesDocument3 pagesLegalization of Abortion in The PhilippinesAntoinetteNo ratings yet