Professional Documents
Culture Documents
How Animals Survive (Circulation and Gas
Uploaded by
John Ted Bañez0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
12 views24 pagesCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
12 views24 pagesHow Animals Survive (Circulation and Gas
Uploaded by
John Ted BañezCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 24
How Animals Survive
(Circulation and Gas Exchange)
Content Standard
The learners demonstrate an
understanding of circulation in the
internal transport system, and gas
exchange with the environment.
Specific Learning Outcomes
At the end of the lesson, the learners
will be able to:
1. Know the structure function
relationship in the various organ
systems
2. Able to synthesize the various
functions of the organ systems
in the day-today activity of an
individual
Used their knowledge of
physiological processes to
understand the different diseases
associated with the organ
systems
QUESTION
Why do you think most
people consider the heart as
one of the busiest organ in
our body?
FACTS
Each day, your heart
pumps about 2,000
gallons of blood.
A woman’s average
heartbeat is faster than a
man’s by almost 8 beats a
minute
Eating dark chocolate every
day reduces the risk of heart
disease by one-third
Your heartbeat changes
and mimics the music you
listen to
Worldwide, 17.3 million people die
each year from heart disease or stroke,
which accounts for 31% of all deaths
Happiness and a strong sense
of emotional vitality helps
lower your risk of heart disease
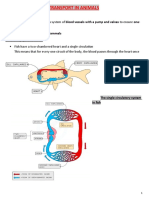
The Circulatory System
Animals have evolved structures which
carry substances (circulatory fluid, e.g.
blood), pipes (blood and lymph vessels) and
a pumping organ (heart). Animals with
these structures either have an open or
closed circulatory system
OPEN CIRCULATORY SYSTEM
In an open circulatory system, blood is not
fully enclosed in a vessel and is pumped
out of the system via an exit called an
ostium to a space which surrounds tissues
called a sinus.
THE CLOSED CIRCULATORY SYSTEM
Once the circulatory fluid has passed through
the capillaries, in order for diffusion to be
efficient, speed of movement of the circulatory
should decrease.
THE CLOSED CIRCULATORY SYSTEM
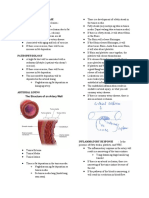
STRUCTURE
1. Atrium- receives blood
2. Ventricle- pumps blood
3. Artery- transports blood away from
the heart, muscular
STRUCTURE
4. Vein- transports blood back to the heart, has
valves and thinner in structure
5. Capillary- exchange of substances, has very thin
walls
6. Venule - small vein
7. Arteriole- small artery
a. The pulse is the wavelike force which is a
result of the pumping of blood through an
artery with decreasing diameter. As the
diameter of the artery decreases, the walls of
the artery stretch to accommodate the blood
that is passing through it.
The heart has the ability to produce
its own electrical signal to stimulate
the contraction of the heart muscles.
Systole- is the contraction phase of
the cardiac cycle
Diastole – is the relaxation phase of
the cardiac cycle
CORONARY ARTERY DISEASE - CAD
is the narrowing or blockage of
the coronary arteries, usually
caused by atherosclerosis.
You might also like
- The Circulatory SystemDocument2 pagesThe Circulatory Systemolivia majcherNo ratings yet
- EACVI Handbook of Cardiovascular CT 2023Document385 pagesEACVI Handbook of Cardiovascular CT 2023Munkhjin MNo ratings yet
- Circulatory System and Heart Biology Summarisation.Document5 pagesCirculatory System and Heart Biology Summarisation.Jumana ElkhateebNo ratings yet
- Circulatory System of MammalsDocument10 pagesCirculatory System of Mammalsben-jNo ratings yet
- KS3 Science Year 9 The Circulatory System-2Document15 pagesKS3 Science Year 9 The Circulatory System-2f72ktyd78nNo ratings yet
- CHP 05 (Blood and Circulation) DrRiyadAhmed PC 3Document69 pagesCHP 05 (Blood and Circulation) DrRiyadAhmed PC 3Kamrun NaherNo ratings yet
- STPM BIOLOGY TransportDocument18 pagesSTPM BIOLOGY Transportwkwhui100% (2)
- Cardiovascular System - Heart: AssignmentDocument14 pagesCardiovascular System - Heart: AssignmentKriss MisraNo ratings yet
- Cardiac Control CentreDocument8 pagesCardiac Control CentregeorgeloxdaleNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of HeartDocument35 pagesAnatomy of HeartIstaleih Puerto100% (1)
- Health Assessment BSN 1-Ruby: SUBMITTED TO: Miss Rossini Birad SUBMITTED BY: Shandy PansaDocument7 pagesHealth Assessment BSN 1-Ruby: SUBMITTED TO: Miss Rossini Birad SUBMITTED BY: Shandy PansaShan DyNo ratings yet
- Transport in Animals-Topic 9Document14 pagesTransport in Animals-Topic 9sukiiNo ratings yet
- Circulation NotesDocument2 pagesCirculation NotesBhkti MittalNo ratings yet
- Circulation and Cardiovascular SystemDocument12 pagesCirculation and Cardiovascular SystemSatria MandalaNo ratings yet
- القلبDocument11 pagesالقلبNajwa AbdualgaderNo ratings yet
- Transport in AnimalsDocument12 pagesTransport in AnimalsJedidiah DickNo ratings yet
- Anatomy Case StudyDocument15 pagesAnatomy Case StudyHazreen HazwanyNo ratings yet
- Seventh Grade Circulatory SystemDocument8 pagesSeventh Grade Circulatory SystemCarlo MakilingNo ratings yet
- Manuel Sills y Agustín Blanco Pinto TerminadoDocument4 pagesManuel Sills y Agustín Blanco Pinto TerminadoholaNo ratings yet
- Cardio Disease - Full Document - LightGBMDocument29 pagesCardio Disease - Full Document - LightGBMThe MindNo ratings yet
- Circulatory System: Cardiologist: Dr. Jennifer, Dr. William, Dr. Daniel, Dr. Jennifer M., Dr. Joshua, Dr. LourdesDocument8 pagesCirculatory System: Cardiologist: Dr. Jennifer, Dr. William, Dr. Daniel, Dr. Jennifer M., Dr. Joshua, Dr. Lourdesmsacosta7No ratings yet
- Biology Unit 1Document11 pagesBiology Unit 1Islam ElsayedNo ratings yet
- A Review of The Cardiovascular System and ECG Performance, Troubleshooting, and InterpretationDocument47 pagesA Review of The Cardiovascular System and ECG Performance, Troubleshooting, and InterpretationRetroPilotNo ratings yet
- Anaphy CardioDocument10 pagesAnaphy Cardiojonel lorenzoNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular System Lecture 1 2020 2021Document5 pagesCardiovascular System Lecture 1 2020 2021olawandeilo123No ratings yet
- Alwadi International School Grade 9 Biology 9. Transport in Animals NotesDocument62 pagesAlwadi International School Grade 9 Biology 9. Transport in Animals NotesMohammed HelmyNo ratings yet
- Circulatory SystemDocument21 pagesCirculatory SystemYusuf AzeezNo ratings yet
- AcknowledgementDocument9 pagesAcknowledgementJovin AshickNo ratings yet
- Grade 6 The Heart and Circulatory System PDFDocument18 pagesGrade 6 The Heart and Circulatory System PDFniel justin lakerNo ratings yet
- IM AnSci 111 Module 4Document24 pagesIM AnSci 111 Module 4Riza Mae Duran RangasNo ratings yet
- Draw and Label The Different Organs Related To The Cardiovascular System. HeartDocument10 pagesDraw and Label The Different Organs Related To The Cardiovascular System. HeartShainaChescaEvansNo ratings yet
- 5.2 Transport in HumansDocument11 pages5.2 Transport in Humans박찬우No ratings yet
- BIO2 - 4.04 - ANIMAL GAS EXCHANGE AND CIRCULATION (v.2023 WITH VITAL SIGN MONITORING)Document80 pagesBIO2 - 4.04 - ANIMAL GAS EXCHANGE AND CIRCULATION (v.2023 WITH VITAL SIGN MONITORING)MARKIEL JUSTINE DOMOSMOGNo ratings yet
- HeartDocument20 pagesHeartKushala SaisriNo ratings yet
- Grade 6: The Heart and Circulatory SystemDocument18 pagesGrade 6: The Heart and Circulatory SystemEstanislao Villanueva ElemNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular SystemDocument10 pagesCardiovascular SystemDhea BugnaNo ratings yet
- Transport in AnimalsDocument19 pagesTransport in Animalsmohamed komiNo ratings yet
- Transport in Man NotesDocument9 pagesTransport in Man NotesYeo JhNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology of HeartDocument69 pagesAnatomy and Physiology of HeartRitu Arun Kaushik100% (1)
- Functions of The Circulatory SystemDocument12 pagesFunctions of The Circulatory SystemJulliane OrtizNo ratings yet
- Transport in AnimalsDocument10 pagesTransport in Animalswarona letangNo ratings yet
- Assignment # 3: Circulatory SystemDocument5 pagesAssignment # 3: Circulatory SystemJefferNo ratings yet
- In Partial Fulfillment of The Requirements in Biological ScienceDocument11 pagesIn Partial Fulfillment of The Requirements in Biological ScienceGodfrey Loth Sales Alcansare Jr.No ratings yet
- As Biology NotesDocument48 pagesAs Biology Notesella100% (1)
- B2U3 CirculationNotesDocument15 pagesB2U3 CirculationNotesVanusha Azzriel100% (1)
- Campbell Chapter 42 NotesDocument17 pagesCampbell Chapter 42 NotesRyan LiuNo ratings yet
- Review of Anatomy and Physiology of Blood Vessels and BloodDocument9 pagesReview of Anatomy and Physiology of Blood Vessels and BloodDan Ataniel EnsaladaNo ratings yet
- Circulatory SystemDocument21 pagesCirculatory SystemSaadNo ratings yet
- Natural Science ScopeDocument15 pagesNatural Science Scope18118No ratings yet
- 8 Transport in AnimalsDocument24 pages8 Transport in AnimalsMariam ShehabNo ratings yet
- Gen Bio (Circulatory System)Document18 pagesGen Bio (Circulatory System)Kit KathNo ratings yet
- Cnat AllDocument7 pagesCnat AllZaid Bin salmanNo ratings yet
- Biology - Circulatory System Notes 1Document13 pagesBiology - Circulatory System Notes 1archit.kulkarni7756No ratings yet
- 6th Lecture Human Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument8 pages6th Lecture Human Anatomy and PhysiologyDwnya S HasanNo ratings yet
- The Human Heart: Location, Size and ShapeDocument9 pagesThe Human Heart: Location, Size and ShapeL I G-Arijit HisabiaNo ratings yet
- University of Goce Delcev StipDocument11 pagesUniversity of Goce Delcev StipviktorijatalevskaNo ratings yet
- Transport in Animals BIOLOGY bySATRIADocument7 pagesTransport in Animals BIOLOGY bySATRIASatria HalimNo ratings yet
- A Simple Guide to the Heart beats, Related Diseases And Use in Disease DiagnosisFrom EverandA Simple Guide to the Heart beats, Related Diseases And Use in Disease DiagnosisRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Human Body Book | Introduction to the Circulatory System | Children's Anatomy & Physiology EditionFrom EverandHuman Body Book | Introduction to the Circulatory System | Children's Anatomy & Physiology EditionNo ratings yet
- Coronary Heart Disease: A Guide to Diagnosis and TreatmentFrom EverandCoronary Heart Disease: A Guide to Diagnosis and TreatmentRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (3)
- Human Body Book | Introduction to the Vascular System | Children's Anatomy & Physiology EditionFrom EverandHuman Body Book | Introduction to the Vascular System | Children's Anatomy & Physiology EditionNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care of Patient With Cardiac ArrestDocument78 pagesNursing Care of Patient With Cardiac ArrestNurhamizah Abd hamidNo ratings yet
- Guidelines For The Management of Congenital Heart Diseases in CH 2017Document105 pagesGuidelines For The Management of Congenital Heart Diseases in CH 2017Ludwig CaceresNo ratings yet
- OrthostaticDocument4 pagesOrthostaticRonel ResurricionNo ratings yet
- 28-31 Cardiovascular ProblemsDocument34 pages28-31 Cardiovascular ProblemsdelarakrishnafaithpNo ratings yet
- 4 - Congenital Heart DefectDocument42 pages4 - Congenital Heart DefectAlfiya HasnaNo ratings yet
- Ekg QuestionsDocument7 pagesEkg Questionsdayumthatsalonguser nameNo ratings yet
- Calcium Channel BlockersDocument15 pagesCalcium Channel Blockersfarmasi_hm100% (2)
- Sudden DeathDocument26 pagesSudden DeathAbang AzharNo ratings yet
- Coronary Artery Disease Cad2Document182 pagesCoronary Artery Disease Cad2Mamot MotNo ratings yet
- ABC of Clinical Electrocardiography Broad Complex Tachycardia-Part IDocument4 pagesABC of Clinical Electrocardiography Broad Complex Tachycardia-Part IIgnacio Aguilar ValdiviesoNo ratings yet
- MurmursDocument5 pagesMurmursAlexander G. Álvarez RojasNo ratings yet
- Pressure-Flow Relationships and Vascular Impedance in Man: J. I. T. H. D. T. EDocument13 pagesPressure-Flow Relationships and Vascular Impedance in Man: J. I. T. H. D. T. EMasterAlbus3dNo ratings yet
- Case Study: Congestive Heart Failure By: Daniel Angelo E. ArangoDocument7 pagesCase Study: Congestive Heart Failure By: Daniel Angelo E. ArangoDaniel Angelo ArangoNo ratings yet
- ECG Quiz Review and Practice Strip AnswersDocument7 pagesECG Quiz Review and Practice Strip AnswersAANo ratings yet
- Rhythm Disturbances in Patients With Heart Failure and Preserved Ejection FractionDocument1 pageRhythm Disturbances in Patients With Heart Failure and Preserved Ejection FractionVàli PiafNo ratings yet
- CARDIOVASCULAR ASSESSMENT NotesDocument6 pagesCARDIOVASCULAR ASSESSMENT NotesJunry PilapilNo ratings yet
- DEFIB PPT at PrakaraDocument52 pagesDEFIB PPT at Prakarakvl kandulaNo ratings yet
- READINGS PrintableDocument2 pagesREADINGS PrintableEniamrahs DnalonNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 ReviewDocument5 pagesUnit 2 Reviewduonghi3lpsNo ratings yet
- OMI 2018, MirandaDocument14 pagesOMI 2018, MirandaResidentes UrgenciasNo ratings yet
- Coronary Artery DiseaseDocument4 pagesCoronary Artery DiseaseViktoria Leeahna LehNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular SystemDocument74 pagesCardiovascular Systemاسامة محمد السيد رمضانNo ratings yet
- 856 t2sv87Document6 pages856 t2sv87AntonisNo ratings yet
- PG Sedici - BookDocument240 pagesPG Sedici - BookHoàng Anh NguyễnNo ratings yet
- The Mechanism Isorhythmic: of Synchronization A-VDocument11 pagesThe Mechanism Isorhythmic: of Synchronization A-VSheila AdiwinataNo ratings yet
- Criterios de Barcelona 2020Document22 pagesCriterios de Barcelona 2020Vallejo Romo Alberto CristianNo ratings yet
- Pulm Circ - 2013 - Forfia - Pulmonary Heart Disease The Heart Lung Interaction and Its Impact On Patient PhenotypesDocument15 pagesPulm Circ - 2013 - Forfia - Pulmonary Heart Disease The Heart Lung Interaction and Its Impact On Patient PhenotypesFanugrahNo ratings yet
- Multi-Phase CTA Head Protocol: Series 1) Non-Contrast CT: Series 2) Multi-Phase CT Angiography (mCTA)Document4 pagesMulti-Phase CTA Head Protocol: Series 1) Non-Contrast CT: Series 2) Multi-Phase CT Angiography (mCTA)AryaNo ratings yet
- Literature Review On Cardiovascular DiseaseDocument97 pagesLiterature Review On Cardiovascular DiseaseShaNaya ZarinNo ratings yet