Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Chapter Four Immune System
Uploaded by
Fayza Warmooge0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
9 views34 pagesCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
9 views34 pagesChapter Four Immune System
Uploaded by
Fayza WarmoogeCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 34
Chapter: four
immune system or immunology
Objectives: by the end of these chapter the learners should be
able to:
Define immune system
Explain the function of immune defenses
Describe the types of immune system
Name and explain the cells kills invading Antigen
Define the function of antibodies
Explain active and passive immunity
Continue
Immunity : is the ability of the body to defense against it
is self from foreign substances those causes diseases .
Immunology: is the study of physiology defense by which
the body destroy foreign matters both living and and living
Immune system: is a group of organs work to gather to
defense the body against diseases
Immune responses: are reactions of the body by foreign
substance inter the body ( E.g bacteria and virus)
Immune defenses performs
1) Protect against infection cause by microbes such
as( viruses ,bacteria, fungi and parasites)
2) Isolate or remove non- microbial foreign
3) Destroy cancer cells that arise in the body that
function known as(surveillance)
Immunity classified two categories
1.Innate immunity 2.Acquired immunity
Innate immunity :also called non –specific immunity
This immunity the body is born the ability of the body
recognize and rabidly destroy foreign substances, has no
specific and memory ,the response is the same each time
because there is no of previous encounter ,can acts against
bacteria in general
continue
Acquired immunity: also called specific immunity .
This immunity have ability of the body recognize and destroy certain
foreign substances improves each time , has specific and memory ,
Can distinguish between different kinds of bacteria
Four types of innate or non-specific immunity
1.Barries to entry microbes
Skin and mucous membranes lining the respiratory system, digestive
system and urinary tracts serves as mechanical barriers to entry the
(pathogens)
Oil glands by skin: secretion by chemicals that contain weaken or kill
bacteria in the skin
Upper respiratory tract is lined by ciliated cells that sweep mucus
and trapped up in to throat ,where they can swallowed
Stomach: has an acidic HCL which inhibit or kills the bacteria
continue
2.Inflammatory reaction: When ever tissues are damaged ,a series of
events occurs that is known as (inflammatory reaction)
3.Natural killer cells: (NK) are cells kill the virus- infected cells and
tumor cells they are granular lymphocytes.
4.Protective proteins
Complement proteins: are a group of(21 )proteins found in plasma
part of blood
Interferon proteins: are proteins that protect the body against viral
infections.
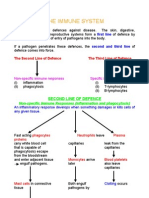
Skin and other external barriers : the
first line of Defense
Skin: is the largest organ of our body the outer layer of skin is
(epidermis) which as a barrier to the microbes.
Mucus membranes: found in the body cavity like the mucus
membrane of nose has mucus –coated hairs that traps and
filter dust and microbes from inhaled air
The fluids produce by various organs in the body and
membranes
Tear :the lacrimal glands of the eyes produce tear which
remove dust and microbes
Answer these questions
1.Define the following terms
A.Immunity
B.Immune system
C.Immunology
D.Immune response
2.Define inflammatory reaction?
3. Name the two mucus membranes in your body?
continue
4. Tell two types of immune system?
5. What is the function of HCL acid?
6.Define pathogens or microbes?
7.Tell two function of immune system?
8.Name the other name of innate immunity?
9. What is the function of ciliated cells in some
membranes your body?
continue
Saliva: salivary glands produce saliva. It washes the
microbes from the surface of the teeth and mucus
membrane of the mouth .
Urine :cleaning of the urethra by the flow and slows down
urine microbial growth by the (urinary system)
Sebum : sebaceous ( oil) glands secrete and oily substance
called (sebum) that protective the covering the surface of
skin to dry
Blood clothing: helps the blood vessels to repair after
damage or wounds
Cellular counterattacks : the second line defense
Second line of defense : are group of cells ,tissues and organs
that work to gether to defense the body. The second line
defense include signals that produce inflammation ,fever
response white blood cells and proteins
Five kinds of leukocytes ( WBCS)
1) Neutrophils :are the most common type of WBCS,those kill bacteria
and fungi
2) Basophils: release histamine and other chemicals that promote the
inflammation
3) Eosinophils : release chemicals that reduce inflammation
4) Lymphocytes:are the smallest of WBCS
5) Monocytes: are the largest of WBCS
Five kinds of white blood cells
Inflammatory response
Inflammatory response: is localized ,nonspecific response to infected by
pathogen ,the tissues release chemical signals called Histamine . That
initiates a series of reactions that makes damaged area to become
red, painful and swollen. This cause increase permeability of capillaries
inflammation
Mechanism of
phagocytes( phagocytosis)
1. chemotaxis: is the process by which cells are attracted to the
bacteria .this is caused by the produce opsonin which is type
antibody
2. Attachment: phagocyte and bacteria attached together
3. Endocytosis: the formation of false feet ( pseudopodia) or simple
membrane that being to engulfed the bacteria
4. Vacuole formation: forms around the bacteria
Mechanism of
phagocytes( phagocytosis)
continue
5.killing/lysis: this can done Hydrogen peroxide or other lysins ,so
bacteria other foreign engulfed by using aerobic process
6.Digestion: lysosomes attached to the phagocytic vacuole and reales
their content in side them
Third line of defense: Acquired
immunity
The third line defense called adaptive immunity or acquired immunity .
It involved the production of type white blood cells which dived two
lymphocytes( B and T cells) which are specific .
B cells and T cells : responsible for cell- mediated immunity, develop
mature the bone marrow ,help the fight of cancer cells
Cells in the immune system
Antigen: is a substance that is foreign to the body to stimulates
immune response
Antibody: is a protein(immunoglobulin) made up plasma cells derived
from B lymphocytes ,secreted in response to fight antigen
Immune response: is the action of lymphocytes in response to enter
antigen to body
Antibodies( immunoglobulins Igs)
Antibodies: are globular proteins and from group of plasma protein
called immunoglobulins. The basic molecule common to all antibodies
consists of four polypeptide chain two long gain ( heavy chain ) two
short ( light chain)also Disulphide brideges hold the chains to gether
Each antibodies molecule has two identical antigen binding sites which
are formed by both light and heavy chains
The sequences of amino acids in these region make the specific three
dimensional shape, also have variable region which every antibodies
different the other one
continue
Antitoxin antibody: are group of antibodies which block the toxin
release bacteria such as those cause (diphtheria and tetanus)
Active and passive immunity
Active immunity : is the immunity gained when antigen enters the
body ,an immune response occurs then produced antibodies by
plasma cells
Passive immunity : is the gained with out an immune
response ,antibodies are injected ( artificial) or pass from mother to
child across the placenta or in breast milk (natural)
Natural immunity and Artificial immunity
Natural immunity: is the immunity gained by infected (active ) or by
receiving antibodies from the mother cross placenta or breast milk
(passive)
Artificial immunity: is the immunity gained either by vaccination
( active) or by injecting antibodies ( passive)
School bursede secondery
Grade :form four
Subject biology
Chapter :four immune system or immunology
Teacher : zainab cabdilaahi muxumed
You might also like
- Innate - Adaptive Immunity POGILDocument14 pagesInnate - Adaptive Immunity POGILJulie Tyler0% (1)
- VCE Biology Unit 3 Summaries - Immune SystemDocument7 pagesVCE Biology Unit 3 Summaries - Immune SystemDJTofiNo ratings yet
- Anatomy & Physiology of DengueDocument8 pagesAnatomy & Physiology of DengueYim Yim25% (4)
- Nonspecific Body Defenses and Immunity: Ms. Ma. Ethel B. Bergantinos, RNDocument51 pagesNonspecific Body Defenses and Immunity: Ms. Ma. Ethel B. Bergantinos, RNjonna casumpangNo ratings yet
- Organization of Immune SystemDocument44 pagesOrganization of Immune SystemSaubie AslamiahNo ratings yet
- Immunity System Form 4 Ombioligy4uDocument9 pagesImmunity System Form 4 Ombioligy4uMostaphe mohamoudNo ratings yet
- Respiratory System Respiration BreathingDocument46 pagesRespiratory System Respiration BreathingZayyani Mohd NoorNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Immunology Lecture IDocument48 pagesIntroduction To Immunology Lecture IEsra Nur ELMASNo ratings yet
- Innate and Adaptive Immunity: Cells, Organs and FunctionsDocument17 pagesInnate and Adaptive Immunity: Cells, Organs and FunctionsBasma RagabNo ratings yet
- Non-Specific Host Defenses Against Microbial PathogensDocument5 pagesNon-Specific Host Defenses Against Microbial PathogensSakil MunnaNo ratings yet
- Human Health & DiseasesDocument55 pagesHuman Health & DiseasesSAGAR PADALKARNo ratings yet
- IMMUNITYDocument23 pagesIMMUNITYFlorence Lynn BaisacNo ratings yet
- Non Specific HostDocument46 pagesNon Specific HostAdrian BautistaNo ratings yet
- Passive Voice Immunity ExplainedDocument4 pagesPassive Voice Immunity ExplainedTwin KileNo ratings yet
- Elements of the Immune System and Their Roles in DefenseDocument73 pagesElements of the Immune System and Their Roles in Defensechicubs3794No ratings yet
- Biology 2 3rd Quarter MLG 1 PDFDocument21 pagesBiology 2 3rd Quarter MLG 1 PDFMichael John LozanoNo ratings yet
- Lecture 4Document9 pagesLecture 4Smasher AustineNo ratings yet
- Chapter 25 BioDocument11 pagesChapter 25 Biosgangwar2005sgNo ratings yet
- Immune System and Disease WorksheetsDocument17 pagesImmune System and Disease Worksheets박찬우100% (1)
- Comilla University: Assignment On Course Title Course Code Submitted ToDocument25 pagesComilla University: Assignment On Course Title Course Code Submitted Tojabed sarkarNo ratings yet
- Makalah Bahasa Inggris Isi (English) 2003Document26 pagesMakalah Bahasa Inggris Isi (English) 2003Reza ShinodaNo ratings yet
- Immunity Combined Lectures-1Document46 pagesImmunity Combined Lectures-1Irfan UllahNo ratings yet
- Introduction To ImmunityDocument54 pagesIntroduction To ImmunityHadi Adam100% (1)
- Iv. Review of Anatomy and Physiology Figure 1. The Immune SystemDocument7 pagesIv. Review of Anatomy and Physiology Figure 1. The Immune SystemNejie Zarrah Diaz100% (1)
- Lec # 4 Body Defence SystemsDocument31 pagesLec # 4 Body Defence SystemssamotherlianNo ratings yet
- Nonspecific Defenses Against InfectionDocument7 pagesNonspecific Defenses Against Infection101744No ratings yet
- Form 5 Biology Chapter 1 Transport (C)Document34 pagesForm 5 Biology Chapter 1 Transport (C)Marcus LeeNo ratings yet
- Innate Immune System: Fast and Broadly Effective: BacteriaDocument3 pagesInnate Immune System: Fast and Broadly Effective: BacteriaRIDANo ratings yet
- 4'th Crew 1. Evya A (130210103043) 2. Ridlo Firmansyah (130210103078) 3. Zainatuh Arifa (130210103066) 4. Heni Lusiana (130210103044)Document47 pages4'th Crew 1. Evya A (130210103043) 2. Ridlo Firmansyah (130210103078) 3. Zainatuh Arifa (130210103066) 4. Heni Lusiana (130210103044)Heni LusianaNo ratings yet
- Immunology: Ectoparasites (I.e. Bed Bugs, Louse, Mites, Ticks and Fleas) Attach Themselves ToDocument18 pagesImmunology: Ectoparasites (I.e. Bed Bugs, Louse, Mites, Ticks and Fleas) Attach Themselves ToPrince RichardsNo ratings yet
- ANATOMYDocument3 pagesANATOMYKara Faith DeocadesNo ratings yet
- Immune SystemDocument56 pagesImmune SystemGerome CausapinNo ratings yet
- Reaction of BodDocument4 pagesReaction of BodLalit KumarNo ratings yet
- Immunity and AllergyDocument72 pagesImmunity and Allergyonlyforu_3No ratings yet
- Chapter 2 ImmunityDocument7 pagesChapter 2 ImmunityQaran PrintingNo ratings yet
- What Is Immunity?Document37 pagesWhat Is Immunity?heer100% (1)
- Body Defences Against Diseases. Lec. 8Document36 pagesBody Defences Against Diseases. Lec. 8AYO NELSONNo ratings yet
- Drugs Acting on the Immune System and InflammationDocument16 pagesDrugs Acting on the Immune System and InflammationRellie Castro0% (2)
- 11.the Human Immune SystemDocument32 pages11.the Human Immune Systemمحمد عدلي عدلانNo ratings yet
- ImmunesystemDocument69 pagesImmunesystemayamgosonggosongNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Immunology, Lecture# 4 (Dr. Adeela Naureen)Document6 pagesIntroduction To Immunology, Lecture# 4 (Dr. Adeela Naureen)arissa noorNo ratings yet
- InflammationDocument40 pagesInflammationSangameswaran B.BNo ratings yet
- Basic Immunology: An Overview of the Immune System and Its FunctionsDocument101 pagesBasic Immunology: An Overview of the Immune System and Its FunctionsZas VutraNo ratings yet
- Bloods: Red Blood CellsDocument7 pagesBloods: Red Blood CellsScribd UserNo ratings yet
- The First Line of Defense For The Body. These Defenses Are Normally Part ofDocument3 pagesThe First Line of Defense For The Body. These Defenses Are Normally Part offlex gyNo ratings yet
- The Immune System DefencesDocument6 pagesThe Immune System DefencesKa-Shun Leung100% (1)
- Defence Mechanism of The BodyDocument44 pagesDefence Mechanism of The BodysayafyousafzaiNo ratings yet
- Immunity: by Ashok K TiwariDocument42 pagesImmunity: by Ashok K TiwariXEDGER09No ratings yet
- A.Ince - Lab 3 (Immunology Review Quiz)Document8 pagesA.Ince - Lab 3 (Immunology Review Quiz)ameeraNo ratings yet
- Nonspecific and Specific DefensesDocument3 pagesNonspecific and Specific DefensesLorenz Jude CańeteNo ratings yet
- Immunology: Ectoparasites (I.e. Bed Bugs, Louse, Mites, Ticks and Fleas) Attach Themselves ToDocument18 pagesImmunology: Ectoparasites (I.e. Bed Bugs, Louse, Mites, Ticks and Fleas) Attach Themselves ToTamicka BonnickNo ratings yet
- W8 Immunology and ImmunizationDocument9 pagesW8 Immunology and ImmunizationJamie De LunaNo ratings yet
- Non-Specific and Specific Body Defense MechanismsDocument14 pagesNon-Specific and Specific Body Defense MechanismsJr D BayzNo ratings yet
- Lesson 6 Immune SystemDocument13 pagesLesson 6 Immune SystemBrent PatarasNo ratings yet
- Immune System And Function, A Simple Guide And Related ConditionsFrom EverandImmune System And Function, A Simple Guide And Related ConditionsRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (2)
- The Slim Book of Health Pearls: Man the Barricades - The Story of the Immune SystemFrom EverandThe Slim Book of Health Pearls: Man the Barricades - The Story of the Immune SystemNo ratings yet
- Boosting the Immune System: Natural Strategies to Supercharge Our Body’s ImmunityFrom EverandBoosting the Immune System: Natural Strategies to Supercharge Our Body’s ImmunityNo ratings yet
- Super Immunity For Beginners: Boost Your Body's Defence, Prevent Diseases and Disorders, Live Healhier and Longer LifeFrom EverandSuper Immunity For Beginners: Boost Your Body's Defence, Prevent Diseases and Disorders, Live Healhier and Longer LifeNo ratings yet
- Women and Autoimmune Disease: The Mysterious Ways Your Body Betrays ItselfFrom EverandWomen and Autoimmune Disease: The Mysterious Ways Your Body Betrays ItselfRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (3)