Professional Documents
Culture Documents
CCN Part 5
Uploaded by
116Tanzeel0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
8 views5 pagesOriginal Title
CCN_Part_5
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
8 views5 pagesCCN Part 5
Uploaded by
116TanzeelCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 5
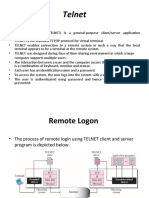
Remote Login: TELNET and SSH
• TErminaL NETwork is the standard TCP/IP
protocol for virtual terminal service as proposed
by ISO.
• It enables a connection to a remote system in
such a way that the local terminal appears to be a
terminal at the remote system.
• Concepts related to TELNET
– Time Sharing Environment
– Login: Local or Remote
– Network Virtual Terminal
Time-Sharing Environment
• It was designed at that time when most os, were operating in a
time-sharing environment (e.g., UNIX).
• A large computer supports multiple users.
• The interaction between a user and the computer occurs through a
terminal, which is usually a combination of keyboard, monitor, and
mouse.
• All of the processing must be done by the central computer.
• When a user types a character on the keyboard, the character is
usually sent to the computer and echoed to the monitor.
• Time-sharing creates an environment in which each user has the
illusion of a dedicated computer. The user can run a program,
access the system resources, switch from one program to another,
and so on.
Login
• In a time-sharing environment, users are part of the
system with some right to access resources.
• Each authorized user has an identification and
probably a password.
• Local Login: When a user logs into a local time-
sharing system, it is called local login.
• Remote Login: When a user wants to access an
application program or utility located on a remote
machine, he or she performs remote login.
Network Virtual Terminal (NVT)
• The mechanism to access a remote computer is
complex.
• This is because every computer and its operating
system accepts a special combination of characters
as tokens.
• E.g., The end-of-file token in a computer running the
DOS operating system is Ctrl+z, while the UNIX
operating system recognizes Ctrl+d.
You might also like
- Device DriversDocument46 pagesDevice DriversAsad ButtNo ratings yet
- NetworksDocument31 pagesNetworksKritikaNo ratings yet
- CommunicationDocument19 pagesCommunicationITs Me PrashNo ratings yet
- Adv Networking 3 1 1Document43 pagesAdv Networking 3 1 1vocarerambutanNo ratings yet
- Fundamental 2: Lec#03 Shugofa HassaniDocument21 pagesFundamental 2: Lec#03 Shugofa HassaniZainuddin ZainaakbaryNo ratings yet
- A1925317416 - 11002 - 30 - 2019 - Lec 35 TELNETDocument22 pagesA1925317416 - 11002 - 30 - 2019 - Lec 35 TELNETSarath ChandraNo ratings yet
- Computer Network: What Is Unicast?Document57 pagesComputer Network: What Is Unicast?Nazim Uddin MahmudNo ratings yet
- Telnet: Discuss Telnet in DetailDocument27 pagesTelnet: Discuss Telnet in DetailJayaprasannaNo ratings yet
- Os Unit-1 Part 1Document12 pagesOs Unit-1 Part 1Raza KashifNo ratings yet
- CSE 2320 - Systems Programming: Chapter 2: Operating Systems FunctionDocument17 pagesCSE 2320 - Systems Programming: Chapter 2: Operating Systems FunctionAlazar GetachewNo ratings yet
- Computer Network SlidesDocument24 pagesComputer Network SlidespsnvaratharajanNo ratings yet
- Suggestion It ExamDocument58 pagesSuggestion It ExamNazim Uddin MahmudNo ratings yet
- CSC204 - Chapter 1.1Document25 pagesCSC204 - Chapter 1.1AISYAH FARHANANo ratings yet
- Operating System Ch-1Document28 pagesOperating System Ch-1Sileshi Bogale HaileNo ratings yet
- TM - Module 1Document36 pagesTM - Module 1Thomas george. cNo ratings yet
- CSC204 - Chapter 1.1Document25 pagesCSC204 - Chapter 1.1Danish DanielNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 System StructuresDocument27 pagesChapter 2 System StructuresAmisha SharmaNo ratings yet
- Task CommunicationDocument22 pagesTask CommunicationsyedashmadNo ratings yet
- Unit 2Document64 pagesUnit 2sridharegspNo ratings yet
- Linux and Programming in C++Document25 pagesLinux and Programming in C++dhivya aNo ratings yet
- (M8-MAIN) - Operating Systems v1Document129 pages(M8-MAIN) - Operating Systems v1williemcgillie32No ratings yet
- Chapter2 CommunicationDocument7 pagesChapter2 CommunicationERENo ratings yet
- Operating System BasicsDocument35 pagesOperating System BasicsaliNo ratings yet
- Online Communication: Remote Login and File TransferDocument17 pagesOnline Communication: Remote Login and File Transferʚ VÎÑÕTH STÃR ɞNo ratings yet
- Applied Operating SystemDocument45 pagesApplied Operating SystemCheese BurgerNo ratings yet
- Structures OSDocument18 pagesStructures OSSahil NagarNo ratings yet
- WeekDocument58 pagesWeekMaaz ChowdhryNo ratings yet
- Computer Hands-On Exam RetajDocument15 pagesComputer Hands-On Exam RetajRetaj NaguibNo ratings yet
- Ite2002 (Unix Report)Document7 pagesIte2002 (Unix Report)AshishNo ratings yet
- Government College of Engineering, Nagpur: Operating System III Semester/ CSE (2021-2022)Document60 pagesGovernment College of Engineering, Nagpur: Operating System III Semester/ CSE (2021-2022)Vishal KesharwaniNo ratings yet
- Ite2002 (Unix Report) PDFDocument7 pagesIte2002 (Unix Report) PDFAshishNo ratings yet
- Lecture 5-Operating SystemsDocument47 pagesLecture 5-Operating SystemsMuhammad AliNo ratings yet
- Unit 3 Using The SystemDocument30 pagesUnit 3 Using The Systemfer_2880No ratings yet
- Topic 1.2 Os Functions and Components Oct22Document28 pagesTopic 1.2 Os Functions and Components Oct22AISYAH FARHANANo ratings yet
- Telnet and Remote LoginDocument5 pagesTelnet and Remote LoginBoobalan RNo ratings yet
- In The Today's Session We'll ReadDocument25 pagesIn The Today's Session We'll ReadRupesh GuptaNo ratings yet
- OS PPTDocument36 pagesOS PPTVatsal GhoghariNo ratings yet
- Computer Operation and Computing EnviromentsDocument35 pagesComputer Operation and Computing EnviromentssamNo ratings yet
- Os Unit-IDocument65 pagesOs Unit-ImudduswamyNo ratings yet
- Lect 1 OSDocument30 pagesLect 1 OSChogeNo ratings yet
- Os OverviewDocument26 pagesOs Overviewprajwalpatil224466100% (1)
- Operating System VariationsDocument27 pagesOperating System VariationsMuhammad MohsinNo ratings yet
- 1.2 DIfferent Types of Operating System and Its ServicesDocument7 pages1.2 DIfferent Types of Operating System and Its ServicesDarshit ChhatbarNo ratings yet
- Operating SystemDocument11 pagesOperating SystemSuhotra GuptaNo ratings yet
- Data ComDocument31 pagesData CompumaNo ratings yet
- IO Systems-1Document14 pagesIO Systems-1Syed HamzaNo ratings yet
- OS ServicesDocument56 pagesOS Servicespramod rockzNo ratings yet
- Evolution of OSDocument39 pagesEvolution of OS21PC12 - GOKUL DNo ratings yet
- Aos Sa1Document14 pagesAos Sa1Yan YanNo ratings yet
- (Aos) M1Document6 pages(Aos) M1Faith SangilNo ratings yet
- Net Tech 2Document15 pagesNet Tech 2AnukulNo ratings yet
- Welcome To Our Presentation: Today Our Topic Is Operating SystemDocument21 pagesWelcome To Our Presentation: Today Our Topic Is Operating SystemKRZ. Arpon Root HackerNo ratings yet
- File System Calls PPTDocument63 pagesFile System Calls PPTpower starNo ratings yet
- OS - Unit-1 (Amiraj) - VisionPapers - inDocument14 pagesOS - Unit-1 (Amiraj) - VisionPapers - inpanchaldev.1454No ratings yet
- TelnetDocument11 pagesTelnetjamalabbasi281998No ratings yet
- Internet-CombinedDocument252 pagesInternet-CombinedArch SharNo ratings yet
- CH01 - OSY Overview of Operating SystemDocument78 pagesCH01 - OSY Overview of Operating SystemPrathmesh GuravNo ratings yet
- IVDocument35 pagesIVpcs prasannaNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Internet (1) ShubroDocument19 pagesIntroduction To Internet (1) ShubroShubrojyoti ChowdhuryNo ratings yet
- Cyber CrimepptDocument17 pagesCyber Crimeppt116TanzeelNo ratings yet
- Technical Report Writing FormatDocument9 pagesTechnical Report Writing Format116TanzeelNo ratings yet
- Ai 4Document7 pagesAi 4116TanzeelNo ratings yet
- Full Final Case Study AiDocument5 pagesFull Final Case Study Ai116TanzeelNo ratings yet
- Assignment Number 03Document1 pageAssignment Number 03116TanzeelNo ratings yet
- Experiment No 3 CssDocument2 pagesExperiment No 3 Css116TanzeelNo ratings yet
- Technical Paper Writing Cover and Front PagesDocument7 pagesTechnical Paper Writing Cover and Front Pages116TanzeelNo ratings yet
- Css Module 3Document12 pagesCss Module 3116TanzeelNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 CSSDocument18 pagesUnit 1 CSS116TanzeelNo ratings yet
- Check Out The Sample SOPsDocument5 pagesCheck Out The Sample SOPs116TanzeelNo ratings yet
- System Programming and Operating SystemDocument234 pagesSystem Programming and Operating System116TanzeelNo ratings yet
- Module-5 Imp QuesDocument1 pageModule-5 Imp Ques116TanzeelNo ratings yet
- SPCC Practical 1Document4 pagesSPCC Practical 1116TanzeelNo ratings yet
- SPCC Lab (2023)Document1 pageSPCC Lab (2023)116TanzeelNo ratings yet
- SE Module4Document27 pagesSE Module4116TanzeelNo ratings yet
- Business Meetings & DocumentationDocument24 pagesBusiness Meetings & Documentation116TanzeelNo ratings yet
- Advanced Technical Writing (Proposal)Document16 pagesAdvanced Technical Writing (Proposal)116TanzeelNo ratings yet
- SE Module2Document35 pagesSE Module2116TanzeelNo ratings yet
- SE - Module 3Document20 pagesSE - Module 3116TanzeelNo ratings yet
- Module-2 Imp QuesDocument1 pageModule-2 Imp Ques116TanzeelNo ratings yet
- Module-3 Imp QuesDocument1 pageModule-3 Imp Ques116TanzeelNo ratings yet
- SE Module1Document25 pagesSE Module1116TanzeelNo ratings yet
- Unit5 QB CN AIML MUDocument1 pageUnit5 QB CN AIML MU116TanzeelNo ratings yet
- Module-1 Imp QuesDocument2 pagesModule-1 Imp Ques116TanzeelNo ratings yet
- Unit3 QB CN AIML MUDocument1 pageUnit3 QB CN AIML MU116TanzeelNo ratings yet
- Unit4 QB CN AIML MUDocument1 pageUnit4 QB CN AIML MU116TanzeelNo ratings yet
- CCN Part 3Document13 pagesCCN Part 3116TanzeelNo ratings yet
- Unit1 QB CN AIML MUDocument1 pageUnit1 QB CN AIML MU116TanzeelNo ratings yet
- CCN Part 4Document15 pagesCCN Part 4116TanzeelNo ratings yet
- Unit2 QB CN AIML MUDocument1 pageUnit2 QB CN AIML MU116TanzeelNo ratings yet