0% found this document useful (0 votes)
172 views25 pagesComprehensive Guide to Bearing Types
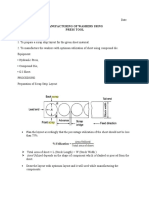
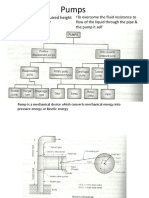
The document discusses different types of bearings including their components, characteristics, loads they can handle, applications, and common failure modes. It covers ball bearings, roller bearings, and their uses in applications like machine tools, automotive axles, and electric motors.
Uploaded by
Mitul patelCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
172 views25 pagesComprehensive Guide to Bearing Types
The document discusses different types of bearings including their components, characteristics, loads they can handle, applications, and common failure modes. It covers ball bearings, roller bearings, and their uses in applications like machine tools, automotive axles, and electric motors.
Uploaded by
Mitul patelCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd