Professional Documents
Culture Documents
GSM Architecture
Uploaded by
Technically Explained0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
18 views13 pagesComprehensive overview of GSM Archigtecture-
Also explains how signal travels from one cellular device to another
Include details about sim identification numbers and IMEI numbers
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentComprehensive overview of GSM Archigtecture-
Also explains how signal travels from one cellular device to another
Include details about sim identification numbers and IMEI numbers
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
18 views13 pagesGSM Architecture
Uploaded by
Technically ExplainedComprehensive overview of GSM Archigtecture-
Also explains how signal travels from one cellular device to another
Include details about sim identification numbers and IMEI numbers
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 13
Introduction
• Whole coverage area is divided into small cells
• Cell is a basic geographical unit of a cellular communication
• Mandatory that all cells must be symmetrical
• Cells are hexagonal to cover whole area
• Cluster is a group of cells
Important Abbreviations:
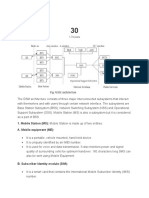
• Mobile Station (MS)
• Base Transceiver station ( BTS)
• Base Station controller ( BSC)
• Mobile switching center ( MSC)
• Home Location Register (HLR), Visitor Location Register (VLR), and the
Authentication Center (AuC)
• IMSI (International Mobile Subscriber Identifier)
• MSISDN (Mobile Station Integrated Services Digital Network)
• IMEI (International Mobile Equipment Identity)*#06#
GSM (Global System for Mobile Communications) is a standard for
cellular communication that was introduced in the 1980s and is still
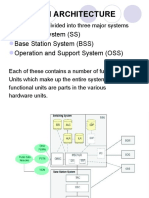
widely used today. The architecture of GSM is divided into three main
components:
1. Mobile Station (MS) Mobile phone with sim
2. Base Station Subsystem (BSS) ( Base Transceiver stations (BTS) &
Base station controller (BSC)
3. Network and Switching Subsystem (NSS) Mobile switching centre
( MSC) and registers
1-Mobile Station (MS): This is the user's mobile phone or other device
that communicates with the cellular network. The MS consists of the
Mobile Equipment (ME) and the Subscriber Identity Module (SIM).
• The ME is the physical device, such as a phone or tablet, that contains
the necessary hardware to communicate with the network. The SIM is
a smart card that contains information about the user's account,
including their phone number and other identifying information
• Each mobile equipment has a number known as the International
Mobile Equipment Identity.
• *#06# for IMEI number
• When one speaks on mobile phone, the sound waves are converted
to electrical signal by microphone in the mobile phone. The electrical
signal is converted to electromagnetic waves ( EM waves/ radio
waves) by antenna
• These EM waves/ radio waves are sent to Base transceiver station
( also called base station or tower)
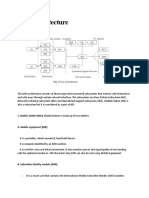
2-Base Station Subsystem (BSS): This component is responsible for
managing the communication between the MS and the network. The BSS is
made up of two main components: the Base Transceiver Station (BTS) and
the Base Station Controller (BSC)
• When a call is setup, signal is sent to base transceiver station( BTS) from
mobile station
• The BTS is a radio transmitter and receiver that communicates with the
MS. Each BTS covers a specific geographic area, known as a cell. The BSC
is responsible for managing multiple BTSs and coordinating the
communication between the BTSs and the network. The BSC is also
responsible for handovers
• Network and Switching Subsystem (NSS):
• The NSS is made up of four main components: the Mobile Switching Center
(MSC), the Home Location Register (HLR), the Visitor Location Register (VLR),
and the Authentication Center (AuC).
The MSC is the central switching hub for the network, responsible for routing
calls and messages between the MS and the rest of the network
IMSI (International Mobile Subscriber Identifier) is a number of 14-15 digits
which identifies a mobile subscriber by their SIM card. It is made up of several
parts, including a country code, a network code, and an individual string of digits
identifying each particular card within the mobile network
IMSI number is available on the packet of sim card, when It is initially bought
from a store.
The HLR ( Home Location register) is a database that contains
information about all the subscribers in the network, including their
account information and current location so it keeps database of all the
users who resides in the same geographical area
The home location register stores information ranging from phone
numbers to current location of the subscriber. Some data contained in
the home location register include the mobile Station International
Subscriber Directory Number (MSISDN) and the
International Mobile Subscriber Identity (IMSI) which is a unique
identifier of each subscriber identity module (SIM) and is the primary key
for each HLR record of each subscriber
The VLR ( Visitor Location register) is a database that contains
information about subscribers who are currently roaming in a specific
area so it keeps track of all the users who are visitors for that particular
geographical area
The AuC ( Authentication center) is responsible for authentication and
security, ensuring that only authorized users can access the network.
• Equipment Identity Register (EIR):
• The EIR is the entity that decides whether a given mobile equipment
may be allowed onto the network. Each mobile equipment has a
number known as the International Mobile Equipment Identity.
On a cellular network, MSISDN (Mobile Station Integrated Services Digital Network) is the
phone number which identifies a device during calls or data session
• When you make a call on your mobile, there needs to be an effective way of connecting you to
the right recipient, and that recipient needs a way of identifying you. The same applies to one
device linking up with another on an IoT network.
• This is where an MSISDN is crucial. It is the unique number that identifies a subscriber on a
network.
• The exact length of an MSISDN varies from country to country, depending on the numbering
procedures set by local regulatory bodies. Typically however, it is 14 or 15 digits long (15 is the
maximum). It is made up of three elements:
• Country Code (CC)
• National Destination Code (NDC)
• Subscriber Number (SN): This is the part that is unique to each subscriber.
• The main difference between an MSISDN and an IMSI is:
• The MSISDN is the full “phone number” for a device.
• The IMSI is basically a technical identifier, used by the network operator.
• Both of these numbers are types of identifiers; each performing a distinct role.
• The international mobile subscriber identity (IMSI) is a 15-digit number that enables
the network operator to identify subscribers. It is stored on the SIM (subscriber identity
module). If a SIM is moved from a device, the IMSI moves with it. You cannot dial up an
IMSI. These numbers are used mostly by operators for network management purposes:
e.g. for checking the location of users
• MSISDNs are much more focused on facilitating connections between users and
devices. Unlike an IMSI, MSISDNs are not bound to a particular SIM. They can be
transferred from device to device and SIM to SIM
Operation subsystem (OSS)/operations and
maintenance center ( OMC)
• Administration and commercial operation (subscription, end
terminals, charging and billings and statistics)
• Security Management.
• Network configuration, Operation and Performance Management.
• Maintenance Tasks
You might also like
- Chapter 05 Intercompany Transactions Bonds and LeasesDocument49 pagesChapter 05 Intercompany Transactions Bonds and LeasesAndrea Mcnair-West100% (1)
- Manual C4 C5Document78 pagesManual C4 C5Leslie Morales75% (4)
- CS Core NetworkDocument19 pagesCS Core NetworkPedro YlliaNo ratings yet
- Ryan Higa's How To Write Good: PrologueDocument9 pagesRyan Higa's How To Write Good: PrologueIsabella Biedenharn89% (9)
- Introduction To GSMDocument3 pagesIntroduction To GSMYasir LiaqatNo ratings yet
- GSM ArchitectureDocument8 pagesGSM ArchitectureAbhishek PandeyNo ratings yet
- GSM - Global System For Mobile CommunicationDocument44 pagesGSM - Global System For Mobile Communicationvenkanna.rajNo ratings yet
- 2G Network: Elecom EtworkDocument13 pages2G Network: Elecom Etworkpg5555No ratings yet
- How To Find The Cell Id Location With MCC, MNC, Lac and Cellid (Cid)Document22 pagesHow To Find The Cell Id Location With MCC, MNC, Lac and Cellid (Cid)Tekilu YewubdarNo ratings yet
- Nepal Nepal TelecomDocument7 pagesNepal Nepal TelecomSigurko MatthewNo ratings yet
- Global System Mobility (GSM)Document28 pagesGlobal System Mobility (GSM)Zain ABNo ratings yet
- GSM Data CompleteDocument12 pagesGSM Data CompleteAdeel TajNo ratings yet
- Chapter Two: GSM Architecture OverviewDocument15 pagesChapter Two: GSM Architecture OverviewGoranNo ratings yet
- Unit IDocument19 pagesUnit IKiran janjalNo ratings yet
- GSM Network ComponentsDocument23 pagesGSM Network ComponentsShakeel AminNo ratings yet
- GSM KT Session - MTN Iran PRS: Created By: Majid NaseriDocument137 pagesGSM KT Session - MTN Iran PRS: Created By: Majid NaseriSaNo ratings yet
- GSM Network Structure: Lance WestDocument11 pagesGSM Network Structure: Lance Westmama doloresNo ratings yet
- World Wide Wireless StandardsDocument67 pagesWorld Wide Wireless Standardspalak goyalNo ratings yet
- GSM Network ArchitectureDocument13 pagesGSM Network ArchitectureZameer HussainNo ratings yet
- 20 CP 09Document7 pages20 CP 09INFOTAINMENT CHANNELNo ratings yet
- International Mobile Station Equipment Identity (IMEI)Document2 pagesInternational Mobile Station Equipment Identity (IMEI)Tashi DorjiNo ratings yet
- Global System For Mobile Communications (GSM) : Asad AliDocument66 pagesGlobal System For Mobile Communications (GSM) : Asad AliMuhammadwaqasnaseemNo ratings yet
- Network ArchitectureDocument17 pagesNetwork ArchitecturesumantabhuinNo ratings yet
- Mobile Computing1stDay19072018Document60 pagesMobile Computing1stDay19072018Kalyan DasNo ratings yet
- GSMDocument33 pagesGSMHemangi Priya Devi DasiNo ratings yet
- GSM Architecture: Switching System (SS) Base Station System (BSS) Operation and Support System (OSS)Document19 pagesGSM Architecture: Switching System (SS) Base Station System (BSS) Operation and Support System (OSS)aimslifeNo ratings yet
- GSM ArchitectureDocument18 pagesGSM Architecture34Shreya ChauhanNo ratings yet
- GSM SystemDocument13 pagesGSM Systemiamhridoy74No ratings yet
- GSM NW ArchitectureDocument3 pagesGSM NW ArchitectureSreepad BharanNo ratings yet
- GSM - Addresses and Identifiers (Imei, Imsi, Tmsi, Lmsi, Msisdn, MSRN)Document2 pagesGSM - Addresses and Identifiers (Imei, Imsi, Tmsi, Lmsi, Msisdn, MSRN)Avanti Mukhopadhaya100% (1)
- GSM Network ArchitectureDocument5 pagesGSM Network Architecturenarayanan07No ratings yet
- Mobile Networking Assignment: Harem Masroor Syed D/o. Syed Masroor AlamDocument34 pagesMobile Networking Assignment: Harem Masroor Syed D/o. Syed Masroor AlamHarem MasroorNo ratings yet
- The Network Switching SubsystemDocument5 pagesThe Network Switching SubsystemMehboob AliNo ratings yet
- Mobile Computing5thDay5.08.2019Document61 pagesMobile Computing5thDay5.08.2019Kalyan DasNo ratings yet
- GSM - Addresses and IdentifiersDocument3 pagesGSM - Addresses and IdentifiersFereidoun SadrNo ratings yet
- GSM ArchitectureDocument15 pagesGSM Architectureashok_rudraNo ratings yet
- Second Generation (2G) Cellular Radio SystemsDocument40 pagesSecond Generation (2G) Cellular Radio SystemsMd. Golam Sarwar JoyNo ratings yet
- A GSM Network Is Composed of Several Functional EntitiesDocument3 pagesA GSM Network Is Composed of Several Functional EntitiesNauman ChaudaryNo ratings yet
- Basic Knowledge For CDMA SystemDocument42 pagesBasic Knowledge For CDMA SystemSanjay GiriNo ratings yet
- MSC & BSCDocument16 pagesMSC & BSCfmsarwarNo ratings yet
- A Presentation On Call Flow in GSM Core: Presented byDocument31 pagesA Presentation On Call Flow in GSM Core: Presented byChowkidar Amit MishraNo ratings yet
- MC - Unit 2Document31 pagesMC - Unit 2Hrudhai SNo ratings yet
- Wireless Cellular CommunicationDocument96 pagesWireless Cellular CommunicationArjun P MNo ratings yet
- Mobile Communication SystemsDocument136 pagesMobile Communication SystemsJoseph JeremyNo ratings yet
- GSM ArchitectureDocument36 pagesGSM ArchitectureKashif AliNo ratings yet
- GSM OverviewDocument81 pagesGSM OverviewImran Khan100% (1)
- GSM Presentation-Asim IhsanDocument21 pagesGSM Presentation-Asim IhsanEngr Asim IhsanNo ratings yet
- GSM Architecture: 1. Mobile Station (MS) : Mobile Station Is Made Up of Two EntitiesDocument4 pagesGSM Architecture: 1. Mobile Station (MS) : Mobile Station Is Made Up of Two EntitiesNZOMO SAMUELNo ratings yet
- GSM SMS and Call FlowDocument21 pagesGSM SMS and Call FlowLendry NormanNo ratings yet
- GSM Network ArchitectureDocument5 pagesGSM Network ArchitecturePrashant KulkarniNo ratings yet
- Network ArchitectureDocument10 pagesNetwork ArchitectureTri NguyenNo ratings yet
- Pts Docomo - Mohit JainDocument28 pagesPts Docomo - Mohit JainMohit JainNo ratings yet
- GSM System Introduction 1Document0 pagesGSM System Introduction 1Shami TahirNo ratings yet
- GSM OverviewDocument6 pagesGSM OverviewSudeepta SahaNo ratings yet
- GSM Architecture: Gopal ReddyDocument36 pagesGSM Architecture: Gopal ReddyRohan ChoudhuryNo ratings yet
- Communication SystemDocument9 pagesCommunication SystemNouman BajwaNo ratings yet
- GSM ArchitectureDocument11 pagesGSM ArchitectureHemangi Priya Devi DasiNo ratings yet
- GSM Fundamentals: Prepared by Asem Mohammed ShamsDocument38 pagesGSM Fundamentals: Prepared by Asem Mohammed ShamsMahmoud EL-BannaNo ratings yet
- Notes Optimization 2GDocument11 pagesNotes Optimization 2Gisaac brineNo ratings yet
- How We Make A CallDocument4 pagesHow We Make A CallAbuzarNo ratings yet
- GSM NetworkDocument23 pagesGSM NetworkLidiyaa WandeNo ratings yet
- Air Compressor Room Exhaust (30000CMH)Document1 pageAir Compressor Room Exhaust (30000CMH)Kumar sssssNo ratings yet
- Forms of Business Ownership - Unit 5Document20 pagesForms of Business Ownership - Unit 5Nishant Sharma100% (1)
- Encoder Incremental KoyoDocument3 pagesEncoder Incremental KoyovisypatyNo ratings yet
- Chandigarh Residential by LawsDocument19 pagesChandigarh Residential by LawsAnubhav AroraNo ratings yet
- Level Switch Vibration Liquiphant S FTL 70 71 TIDocument20 pagesLevel Switch Vibration Liquiphant S FTL 70 71 TIHerman SandyNo ratings yet
- BENGUET A TOUR ITINERARY PROPOSAL-1Document7 pagesBENGUET A TOUR ITINERARY PROPOSAL-1Jupiter MercaderoNo ratings yet
- Sumit Bhardwaj: Address: H.no. 215 A Nirman Nagar, Jaipur Rajasthan Tel: (M) : 9909744946Document6 pagesSumit Bhardwaj: Address: H.no. 215 A Nirman Nagar, Jaipur Rajasthan Tel: (M) : 9909744946Mohit chawlaNo ratings yet
- Simple Chemistry PBL 2.0 During PKPBDocument4 pagesSimple Chemistry PBL 2.0 During PKPBAryanaNo ratings yet
- 50 Globe Mackay Cable and Radio COrporation vs. Court of AppealsDocument4 pages50 Globe Mackay Cable and Radio COrporation vs. Court of AppealsGlomarie GonayonNo ratings yet
- Troubleshoot IP Configuration 3Document2 pagesTroubleshoot IP Configuration 3michaelNo ratings yet
- Annual Report 14 PDFDocument96 pagesAnnual Report 14 PDFgopalNo ratings yet
- HVAC Maintenance PDFDocument13 pagesHVAC Maintenance PDFКирилл СоколовNo ratings yet
- Pakistan's Investment Climate: The Way ForwardDocument9 pagesPakistan's Investment Climate: The Way ForwardInstitute of Policy StudiesNo ratings yet
- Ticketmaster Member Services - Print ReceiptDocument1 pageTicketmaster Member Services - Print Receipt8768263No ratings yet
- Brexit - Unravelling The Ties That Bind The Past, Present, and FutureDocument26 pagesBrexit - Unravelling The Ties That Bind The Past, Present, and FutureShoaib A. MalikNo ratings yet
- Name: Case Study On Organizational EfficiencyDocument2 pagesName: Case Study On Organizational EfficiencyLoriel50% (2)
- LXM23DU07M3X: Product Data SheetDocument10 pagesLXM23DU07M3X: Product Data SheetAshrafNo ratings yet
- AgaSlots SASDocument3 pagesAgaSlots SASManolo GonzalezNo ratings yet
- W3G500GN3303 EngDocument5 pagesW3G500GN3303 EngFabio VincenziNo ratings yet
- ACCESIONING, CorrectedDocument24 pagesACCESIONING, CorrectedEliza CalvadoresNo ratings yet
- Development Strategies of The Bahari Jawai Marine Tourism Coast Area Based On Community Empowerment in Sambas RegencyDocument10 pagesDevelopment Strategies of The Bahari Jawai Marine Tourism Coast Area Based On Community Empowerment in Sambas Regencyberagam09No ratings yet
- Banking Financial Institutions - SyllabusDocument8 pagesBanking Financial Institutions - SyllabusLove RosalunaNo ratings yet
- Rapport Annuel 2020 2021 EnglishDocument29 pagesRapport Annuel 2020 2021 EnglishOusseynou NdiayeNo ratings yet
- Multotec Trommel ScreensDocument6 pagesMultotec Trommel Screensalfredo_17110% (1)
- DVC-GBW May 2012 NewsletterDocument7 pagesDVC-GBW May 2012 NewsletterValeria KremserNo ratings yet
- Practice Test 1Document6 pagesPractice Test 1Glenn XyzzyllyzzyxNo ratings yet
- Electrical Noise and Sliding Electrical Contacts: November 2016Document5 pagesElectrical Noise and Sliding Electrical Contacts: November 2016ing jyaNo ratings yet