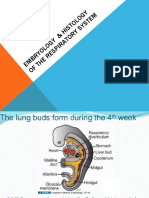
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
895 views27 pagesBlood Physiology Gutyon 14th Edition Chapter 35 Immunity
Innate immunity provides non-specific protection against pathogens. It involves barriers like skin and mucous membranes, inflammatory responses, phagocytosis, and proteins like lysozyme and complement. Acquired immunity develops from exposure to pathogens and provides long-lasting, pathogen-specific protection. It involves humoral immunity through antibodies and cell-mediated immunity through T cell responses. Both innate and acquired immunity work together to defend the host against infection.
Uploaded by
Dr Alamzeb JadoonCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
895 views27 pagesBlood Physiology Gutyon 14th Edition Chapter 35 Immunity
Innate immunity provides non-specific protection against pathogens. It involves barriers like skin and mucous membranes, inflammatory responses, phagocytosis, and proteins like lysozyme and complement. Acquired immunity develops from exposure to pathogens and provides long-lasting, pathogen-specific protection. It involves humoral immunity through antibodies and cell-mediated immunity through T cell responses. Both innate and acquired immunity work together to defend the host against infection.
Uploaded by
Dr Alamzeb JadoonCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
- Immunity Introduction
- Innate and Acquired Immunity
- Innate Immunity Details
- Acquired Immunity
- Lymphocytes and Lymphopoiesis
- Tolerance and Cytotoxicity
- Humoral Immunity
- Antibodies
- Memory Cells and Immunization
- Mechanisms of Antibodies and Complement System
- Lymphadenopathy and Antibiotics
- Allergy and Hypersensitivity Reactions