Professional Documents
Culture Documents
CP4 Summary
Uploaded by
Ahmad Patel0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
13 views2 pagesOriginal Title
CP4-summary
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
13 views2 pagesCP4 Summary
Uploaded by
Ahmad PatelCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
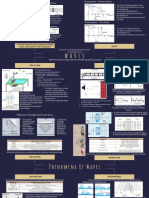
Describing Waves Amplitude
Definitions Low High
Time period: Time it takes for one full
Transverse Waves: wave to pass a point (seconds).
Frequency: The number of waves passing a
Particles vibrate at right angles to the
point per second (Hertz).
direction the wave is travelling. Eg light.
Longitudinal Waves: Wavelength: The distance between 2 High Short
frequency
crests or 2 troughs (metres). wavelength
Particles vibrate parallel to the direction
Amplitude: The maximum distance away Low Long
the wave is travelling. Eg sound. from the rest position (metres)
frequency wavelength
Refraction When a wave
enters a more
CP4 Wave speeds
Incident ray Normal dense material, Wave speed (v, in m/s)
Angle of
it bends towards d is distance (d, in
Refraction: is the change in incidence
i the normal.
metres) divided by
speed and direction when a Angle of
time (t, in seconds).
refraction v x t
wave enters a new material. r
i Waves can be shown
Normal: is the line at 90o to the as wavefronts (like Wave speed (v, in
boundary of the new material, looking down on the m/s) is frequency (f,
in hertz) multiplied v
that meets the ray at the r When a wave sea). Waves can be
boundary.
enters a less refracted towards the by wavelength (λ, in
Normal dense material, normal in shallow
it bends away
metres). f x λ
water
from the normal. Produced by S Meunier
Describing Waves Wave speeds
Refraction
CP4
You might also like
- Waves MMDocument2 pagesWaves MManis farzanaNo ratings yet
- Mind MapsDocument3 pagesMind MapsGiannaNo ratings yet
- Physics 1: Wave Motion and Sound WavesDocument5 pagesPhysics 1: Wave Motion and Sound WavesArafat Lomangcolob BauntoNo ratings yet
- AQA Physics Topic 6 Waves Knowledge OrganiserDocument7 pagesAQA Physics Topic 6 Waves Knowledge OrganiserthaingocnhinNo ratings yet
- Wave Properties PosterDocument1 pageWave Properties Posterjaxsonsalminen1302No ratings yet
- Physics 17 - General Wave PropertiesDocument43 pagesPhysics 17 - General Wave PropertiesHakim Abbas100% (1)
- CH 10 - General WaveDocument52 pagesCH 10 - General WaveThaw ThawNo ratings yet
- Waves (Complete) Oct SessionDocument28 pagesWaves (Complete) Oct Sessionaliayanraza5No ratings yet
- Waves (Physics) ? 2Document3 pagesWaves (Physics) ? 2Hiral KatyalNo ratings yet
- General Wave PropertiesDocument17 pagesGeneral Wave PropertieshexrazorsharpNo ratings yet
- 5.1 WaveDocument13 pages5.1 WaveMazni HanisahNo ratings yet
- Physics 17 - General Wave PropertiesDocument43 pagesPhysics 17 - General Wave PropertiesBlack IrisNo ratings yet
- WavesDocument50 pagesWavesanas.asif2008No ratings yet
- Physics CH 05 Sound Notes Hany Elgezawy Pre Igcse Y8Document13 pagesPhysics CH 05 Sound Notes Hany Elgezawy Pre Igcse Y8maxprime558No ratings yet
- Physics Fast Revision NotesDocument8 pagesPhysics Fast Revision NotesdivyanshagrawalbsNo ratings yet
- Untitled DocumentDocument1 pageUntitled Documentapi-385992165No ratings yet
- IGCSE 2 Phy General Properties of WavesDocument102 pagesIGCSE 2 Phy General Properties of WavesKanwal KhanNo ratings yet
- Clem Waves Lesson02 PresentationDocument29 pagesClem Waves Lesson02 PresentationAldiona DaulleNo ratings yet
- Physics 17 - General Wave PropertiesDocument43 pagesPhysics 17 - General Wave Propertiesccbpxprwd2No ratings yet
- College of Arts and Sciences Department of Mathematics and PhysicsDocument4 pagesCollege of Arts and Sciences Department of Mathematics and PhysicsBethel Divine JuanNo ratings yet
- Wave SummaryDocument2 pagesWave SummarylwazilegendsNo ratings yet
- Physics 17 - General Wave Properties-OrigDocument43 pagesPhysics 17 - General Wave Properties-OrigRodel VerzosaNo ratings yet
- WAVESDocument1 pageWAVESsophiadionora9No ratings yet
- Pre Task - Fraiber ZambranoDocument5 pagesPre Task - Fraiber ZambranoLugar De La Mancha MuñozNo ratings yet
- 10 - WaveDocument13 pages10 - WavejethvadevashyaNo ratings yet
- WavesDocument1 pageWavesJordan ChizickNo ratings yet
- WINSEM2023-24 BPHY101L TH VL2023240501910 2024-01-04 Reference-Material-IIDocument1 pageWINSEM2023-24 BPHY101L TH VL2023240501910 2024-01-04 Reference-Material-IIakshat.2075No ratings yet
- Transverse WavesDocument4 pagesTransverse WavesRatnasari Mohamad AshaariNo ratings yet
- Lp3 Physics For EngineersDocument72 pagesLp3 Physics For EngineersEly CabangunayNo ratings yet
- 01A. Waves (01-41)Document41 pages01A. Waves (01-41)Mupli RajeshNo ratings yet
- Waves MaterialDocument80 pagesWaves MaterialPonharish kumar.JNo ratings yet
- Mechanical Waves2Document29 pagesMechanical Waves2Dennis ANo ratings yet
- Physics WavesDocument9 pagesPhysics WavesKRZ. Arpon Root HackerNo ratings yet
- Lecture - 4 - Wave MotionDocument46 pagesLecture - 4 - Wave MotionAlkgema Stores100% (1)
- Handout 8 WavesDocument6 pagesHandout 8 WavesMary Grace AcostaNo ratings yet
- Wave MechanicsDocument77 pagesWave MechanicsAlbasher SahibuddinNo ratings yet
- WAVE MOTION PPT Lecture Part 1 RevisedDocument25 pagesWAVE MOTION PPT Lecture Part 1 RevisedRitzNo ratings yet
- Narayana Physics Module With Exercise-908-987Document40 pagesNarayana Physics Module With Exercise-908-987vihasithsanamNo ratings yet
- WAVESDocument5 pagesWAVESNicolas KhanNo ratings yet
- Waves and SuperpositionsDocument19 pagesWaves and SuperpositionsTazrin BibortonNo ratings yet
- WavesDocument13 pagesWavesRoqaya BadawyNo ratings yet
- CfE Waves and Sound NOTES NAT 4 With Answers.Document26 pagesCfE Waves and Sound NOTES NAT 4 With Answers.Ross O'BrienNo ratings yet
- Wave Motion NotesDocument4 pagesWave Motion NotesRehan KhanNo ratings yet
- Pravindra Singh PWSFAC75824 20225611125646512974Document249 pagesPravindra Singh PWSFAC75824 20225611125646512974jkNo ratings yet
- Elastic Waves and Sound FisicaDocument13 pagesElastic Waves and Sound FisicaGiorgia Maria VittiNo ratings yet
- 1a.waves (1-41)Document41 pages1a.waves (1-41)bsreekanthphysicsNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 IGCSEDocument8 pagesChapter 3 IGCSENajia UmarNo ratings yet
- Lecture2 7 Waves & SoundDocument21 pagesLecture2 7 Waves & SoundDragana SekulicNo ratings yet
- Handout On Waves and SoundDocument4 pagesHandout On Waves and SoundLorna BacligNo ratings yet
- Waves: Concept MapDocument52 pagesWaves: Concept MapZULHISYAM BIN NORDIN MoeNo ratings yet
- WavesDocument26 pagesWavesceline.the988No ratings yet
- General Wave Properties - Free Exam AcademyDocument10 pagesGeneral Wave Properties - Free Exam AcademysinojiayogNo ratings yet
- WavesDocument11 pagesWavesdilsharakaviNo ratings yet
- Physics: Chapter 7 - Waves and SuperpositionDocument17 pagesPhysics: Chapter 7 - Waves and Superpositionkelly angNo ratings yet
- Dianadavis Physics 20 WavesDocument4 pagesDianadavis Physics 20 WavesVonNo ratings yet
- Architectural Acoustics: Classification of WavesDocument7 pagesArchitectural Acoustics: Classification of WavesHaidy AshrafNo ratings yet
- Chapter 15 - WavesDocument15 pagesChapter 15 - WavesMayank ShahabadeeNo ratings yet
- HSC Physics Module 3: Waves & ThermodynamicsDocument30 pagesHSC Physics Module 3: Waves & ThermodynamicswillNo ratings yet
- Waves Notes Physics o LevelDocument20 pagesWaves Notes Physics o Levelkwikiriza safiruNo ratings yet
- How Do Waves Behave? How Are They Measured? Physics Lessons for Kids | Children's Physics BooksFrom EverandHow Do Waves Behave? How Are They Measured? Physics Lessons for Kids | Children's Physics BooksNo ratings yet
- GCSEChem So Wseparate 2 yDocument85 pagesGCSEChem So Wseparate 2 yAhmad PatelNo ratings yet
- GCSEBiol So Wcombined 2 yDocument57 pagesGCSEBiol So Wcombined 2 yAhmad PatelNo ratings yet
- Surds Revision 3Document2 pagesSurds Revision 3Ahmad PatelNo ratings yet
- CB1 Revision Mat PDFDocument2 pagesCB1 Revision Mat PDFAhmad PatelNo ratings yet