100% found this document useful (1 vote)
2K views5 pagesDiesel Rotary-Inline Injection
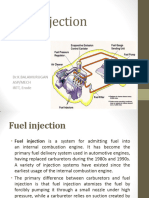
The document discusses two types of injection pumps used in diesel engines: distributor pumps and inline pumps. Distributor pumps have a single plunger and spinning rotor to distribute fuel, making the fuel shots consistent and the pump smaller. Inline pumps have multiple plungers but more moving parts. The document also discusses two common types of diesel injection systems - throttle body injection which is similar to carburetion, and multipoint injection which uses multiple injectors like gasoline engines. It concludes by describing the key components of a typical fuel injector - the nozzle and body which contain passages for high pressure fuel to enter and exit, controlled by a needle valve and spring.
Uploaded by
Kevin GegrimosCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
100% found this document useful (1 vote)
2K views5 pagesDiesel Rotary-Inline Injection
The document discusses two types of injection pumps used in diesel engines: distributor pumps and inline pumps. Distributor pumps have a single plunger and spinning rotor to distribute fuel, making the fuel shots consistent and the pump smaller. Inline pumps have multiple plungers but more moving parts. The document also discusses two common types of diesel injection systems - throttle body injection which is similar to carburetion, and multipoint injection which uses multiple injectors like gasoline engines. It concludes by describing the key components of a typical fuel injector - the nozzle and body which contain passages for high pressure fuel to enter and exit, controlled by a needle valve and spring.
Uploaded by
Kevin GegrimosCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
- Two Types of Injection Pump: Explains the basic function and types of injection pumps used in diesel engines, focusing on their operation and role in the fuel delivery process.
- Common Rail Diesel Injection: Introduces common rail diesel injection systems and explains two types used in modern diesel engines.
- Plunger and Barrel: Describes the reconditioning process and uses of plungers and barrels in fuel injection systems.
- Injector and Nozzle: Outlines the structure and function of fuel injectors and nozzles, explaining fuel path and pressure mechanisms.