Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Neeraj Kalyan.G, Shakthi Thangavel, Rajath D, Sai Sanwid Pradhan, Venketesh.S
Uploaded by
Neeraj Kalyan GandholiOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Neeraj Kalyan.G, Shakthi Thangavel, Rajath D, Sai Sanwid Pradhan, Venketesh.S
Uploaded by
Neeraj Kalyan GandholiCopyright:
Available Formats
SRI SATHYA SAI INSTITUTE OF HIGHER LEARNING
(Deemed to be University)
Prashanthi Nilayam
Glutamine and glutamate modulate mutant Huntingtin aggregation in
Yeast Model of Huntington’s Disease
Neeraj Kalyan.G, Shakthi thangavel, Rajath D, Sai Sanwid Pradhan, Venketesh.S*
INTRODUCTION: TARGETED PATHWAY:
• Huntington’s disease is an autosomal dominant disease belonging to Tri-Nucleotide repeat
expansion (TNRE) disease
• Expanded CAG repeats coding for polyQ stretch in the htt gene are the main cause of disease.
• Glutamine is a rich metabolite that plays an important role in inflammatory responses.
• Glutamate is a neurotransmitter and the glutamine glutamate shuttle is affected in case of the
Huntington’s disease.
• Glutamine also plays a key role in the activation of the mTOR pathway
MODELS ORGANISMS USED IN HUNTINGTON’S DISEASE RESULTS:
25Q 72Q
STUDY
CTRL (BY4742) CTRL: Yeast BY4742 strain
ΔGCV1
Yeast Cell lines C.elegans Zebra fish Mice Primates
WHY YEAST? ΔGDH1
o Single system
o Easy for genetic manipulations
o Very few variables for studies which makes the study easier. ΔSNZ1
o Helps in minimizing the use of the animal models
Very short life cycle so studying the progeny for disease takes less time
ΔSNO1
OBJECTIVES: ΔTOR1
• How does glutamine modulate the huntingtin protein aggregation?
GCV1: subunit of glycine cleavage complex
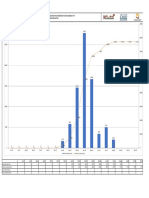
• Can glutamine and glutamate-mediated amyloid formation be reduced? CTRL+72Q ΔGLT1 (KO)+72Q
90000
80000
70000
60000
• Showing modulation in the pathway and its effect in the protein aggregation using the knockout 72Q
50000
40000
30000
20000
10000
yeast models and metabolites(inhibitors) 0
250000 1 2
200000
Glutamine(5mM) Florescence in GLT1
150000
100000
compared to CTRL
METHODOLOGY:
50000
0
400000 1 2
350000
300000
Glutamate(5mM)
250000
200000
150000
100000
50000
72Q
0
1 2
Glutamine(5mM)+ 300000
290000
280000
Nicotinic acid
270000
260000
250000
Glutamine
240000
(100uM) ctrl type
yeast
CTRL+72Q ΔGDH1 (KO)+72Q
300000
Glutamate
290000
72Q
280000
Culture
270000
260000
Revival
250000
240000
the Transfor Quantific Glutamine+NA
ctrl type
yeast
of the
400,000
plasmid mation of ation of Glutamate(5mM)
300,000
Midi- wild type 200,000
containin Quantific yeast the 100,000
prep for and Fluoresce 0
1 2
g bacteria ation cells fluoresce
plasmid knockout nce
(25Q and using using the nce
72Q
extractio
Nanodrop
yeast
electropor
imaging
observed CONCLUSION
n strains
obtained ation using • Glutamine is a potential metabolite for increasing the protein aggregation. The knockout yeast
from the
from add method ImageJ
stock models have shown increased mutant huntingtin aggregation in presence of glutamine.
gene
• Glutamate is a critical metabolite in clearing protein aggregation.
• α-ketoglutarate might be a reason for amyloidogenesis.
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS REFERENCES
• Bhagawan Sri Sathya Sai Baba • The global prevalence of Huntington's disease (image courtesy: https://huntingtonstudygroup.org )
• Disease Biology Lab (Dr.S Venketesh and Reasearch scholars) • Ha, A. D., & Fung, V. S. C. (2012). Huntington’s disease. In Current Opinion in Neurology (Vol. 25, Issue 4, pp. 491–498).
• Department of Biosciences https://doi.org/10.1097/WCO.0b013e3283550c97
• Central Research Instruments Facility (CRIF), SSSIHL • Gois, A. M., Mendonça, D. M. F., Freire, M. A. M., & Santos, J. R. (2020). in Vitro and in Vivo Models of Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis: an
• Funding agencies Updated Overview. Brain Research Bulletin, 159(November 2019), 32–43. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.brainresbull.2020.03.012
• Sri Sai Sanwid Pradhan • Novak, M. J. U., & Tabrizi, S. J. (2010a). Clinical Review Huntington’s disease. British Medical Journal, 341(July), 34–40
• Sri Shakthi Thangavel SK
• Classmates
You might also like
- Apoptosis LectureDocument103 pagesApoptosis LectureGajanan SaykhedkarNo ratings yet
- Test Bank For Microbiology A Clinical Approach 2nd Edition Chapters 1 26 StrelkauskasDocument6 pagesTest Bank For Microbiology A Clinical Approach 2nd Edition Chapters 1 26 StrelkauskasDorothy Laclair100% (34)
- Eaton LVBreakers 70 C1446Document1 pageEaton LVBreakers 70 C1446Al JoNo ratings yet
- Medical Genetics at GlanceDocument116 pagesMedical Genetics at Glancedrabdulla977100% (4)
- 1 - Water and Gas Coning-AHEDocument78 pages1 - Water and Gas Coning-AHEAdel Ahmed AlkhaligyNo ratings yet
- LTE Strategic: Adaptive - TM8 - TrialDocument3 pagesLTE Strategic: Adaptive - TM8 - Trialbagoes sidharta100% (1)
- LTE Strategic: BreathingPilotDocument3 pagesLTE Strategic: BreathingPilotbagoes sidhartaNo ratings yet
- Trial - EUL-DCH Load BalancingDocument10 pagesTrial - EUL-DCH Load BalancingkafleNo ratings yet
- Situación Epidemiológica de Sarampión Rubeola y PFA Macro Oriente 14junio2021Document40 pagesSituación Epidemiológica de Sarampión Rubeola y PFA Macro Oriente 14junio2021cdc.inmunopreveniblesNo ratings yet
- Situación Epidemiológica de Sarampión Rubeola y PFA Macro Norte 17junio2021Document49 pagesSituación Epidemiológica de Sarampión Rubeola y PFA Macro Norte 17junio2021cdc.inmunopreveniblesNo ratings yet
- Situation Report On Dengue in Nepal-2023: Epidemiology and Disease Control DivisionDocument2 pagesSituation Report On Dengue in Nepal-2023: Epidemiology and Disease Control DivisionShubha KandelNo ratings yet
- Dekalb Covid-19 Epidemiology Report: Daily and Cumulative Covid-19 Case Counts, Dekalb CountyDocument13 pagesDekalb Covid-19 Epidemiology Report: Daily and Cumulative Covid-19 Case Counts, Dekalb CountyZachary HansenNo ratings yet
- Graphs-of-Cases-for - pptx25 July 2021Document8 pagesGraphs-of-Cases-for - pptx25 July 2021John Y FadrilanNo ratings yet
- Construction of Internal Roads and Infrastructure For 354 Residential Plots in Shakhbout City Kpi Unclassified ExcavationDocument15 pagesConstruction of Internal Roads and Infrastructure For 354 Residential Plots in Shakhbout City Kpi Unclassified ExcavationburereyNo ratings yet
- Cumulative CostDocument1 pageCumulative CostadlenaNo ratings yet
- DischargeDocument11 pagesDischargesaeedNo ratings yet
- Guaporé: Report Generated: 7 Feb 2022Document4 pagesGuaporé: Report Generated: 7 Feb 2022Everton Borges de SouzaNo ratings yet
- GSA Report Al Ahsa GovernorateDocument4 pagesGSA Report Al Ahsa GovernorateMohits952No ratings yet
- GSA - Report - Sintra (Santa Maria e São Miguel, São Martinho e São Pedro de Penaferrim)Document4 pagesGSA - Report - Sintra (Santa Maria e São Miguel, São Martinho e São Pedro de Penaferrim)ReparaçõesIlimitadasNo ratings yet
- GSA - Report - Kelurahan MerjosariDocument4 pagesGSA - Report - Kelurahan Merjosarim tommy hasan abadiNo ratings yet
- GSA Report Ninh BìnhDocument4 pagesGSA Report Ninh BìnhViet Cuong NguyenNo ratings yet
- QS Absolute Q and QiacuityDocument2 pagesQS Absolute Q and QiacuityRicardo LlNo ratings yet
- Vaccination Overview: Dekalb County Residents With at Least 1 DoseDocument4 pagesVaccination Overview: Dekalb County Residents With at Least 1 DoseZachary HansenNo ratings yet
- GSA Report MulyorejoDocument4 pagesGSA Report MulyorejoFajar SaelendraNo ratings yet
- GSA Report SidoarjoDocument4 pagesGSA Report SidoarjoAdzka. ANo ratings yet
- Interfaces For Renewable Energy SourcesDocument6 pagesInterfaces For Renewable Energy SourcesAmr MahdyNo ratings yet
- CYP1Q Ctg2Document8 pagesCYP1Q Ctg2Dastogir AlamNo ratings yet
- Who Covid-19-Update 41 20201207Document11 pagesWho Covid-19-Update 41 20201207RedNo ratings yet
- Perencanaan Sistem DistribusiDocument296 pagesPerencanaan Sistem Distribusideny misbahudinsyah100% (1)
- Rincian Pendapatan BLUD 2023 Perubahan Sept 2023Document42 pagesRincian Pendapatan BLUD 2023 Perubahan Sept 2023Dedi FaridNo ratings yet
- 111136.Bsc 05.Hw - Bltel.saaz - Aa EnoDocument27 pages111136.Bsc 05.Hw - Bltel.saaz - Aa EnoMikatechNo ratings yet
- Construction Industry AnalysisDocument132 pagesConstruction Industry AnalysisEleanorXuNo ratings yet
- External Situation Report 86 - 19 January 2022Document26 pagesExternal Situation Report 86 - 19 January 2022IndahNo ratings yet
- GSA - Report - Sana'a CityDocument4 pagesGSA - Report - Sana'a CityAbdulraheem SalmanNo ratings yet
- Quotation For ElectronicsDocument1 pageQuotation For ElectronicsAhmedNo ratings yet
- Project For Master's ProgramDocument25 pagesProject For Master's ProgramCelso MagnunNo ratings yet
- NTPC Quality Management 1 TQMDocument20 pagesNTPC Quality Management 1 TQM786tanmoyNo ratings yet
- Feature Trial Analysis - PA1Document3 pagesFeature Trial Analysis - PA1charan ThakurNo ratings yet
- Análisis Bioclimático - Aristote Mote HernándezDocument14 pagesAnálisis Bioclimático - Aristote Mote HernándezAristotte HernándezNo ratings yet
- 02 Update On Measles Rubella EliminationDocument32 pages02 Update On Measles Rubella Eliminationnavneet singhNo ratings yet
- N0078 - Nu Tech - PPM - January-2022Document3 pagesN0078 - Nu Tech - PPM - January-2022Praveen kumarNo ratings yet
- Ej104 - Multiple Elements in Drinking Water - 9820Document2 pagesEj104 - Multiple Elements in Drinking Water - 9820pravin kondeNo ratings yet
- A Wideband Scalar Network Analyzer For Biomedical Dehydration MeasurementsDocument4 pagesA Wideband Scalar Network Analyzer For Biomedical Dehydration MeasurementsAsha LathaNo ratings yet
- A25 Brochure PDFDocument2 pagesA25 Brochure PDFron cadungogNo ratings yet
- GSA Report AlexandriaDocument4 pagesGSA Report AlexandriayehiaelsagawyNo ratings yet
- HLD 65KDocument1 pageHLD 65KgilbertomjcNo ratings yet
- GSA Report LimaDocument4 pagesGSA Report LimaRubénNo ratings yet
- (TUGAS BU AGNES) (NIM2120424777) Tatiana Ssika WardaniDocument4 pages(TUGAS BU AGNES) (NIM2120424777) Tatiana Ssika WardaniTatiana Siska WardaniNo ratings yet
- GSA Report - BengkalisDocument4 pagesGSA Report - BengkalisIskandar Ismail.07No ratings yet
- CellTiterGlo 3D Cell Viability Assay TM412Document18 pagesCellTiterGlo 3D Cell Viability Assay TM412Victor Matias BarriosNo ratings yet
- Synthetic Control SlidesDocument47 pagesSynthetic Control Slidesbautista vidalNo ratings yet
- GSA Report BogotáDocument4 pagesGSA Report BogotáLAURA SANCHEZ TANGARIFENo ratings yet
- Presentation by Dewan Mushtaq GroupDocument21 pagesPresentation by Dewan Mushtaq Groupmms_mzNo ratings yet
- Bogotá: Report Generated: 9 Feb 2022Document3 pagesBogotá: Report Generated: 9 Feb 2022David Alexander CeronNo ratings yet
- GSA Report La LibddertadDocument4 pagesGSA Report La LibddertadOscar CamposNo ratings yet
- Microwave Book Processing of MaterialsDocument5 pagesMicrowave Book Processing of MaterialsRavindra BadigerNo ratings yet
- Dekalb Covid-19 Epidemiology Report: Daily and Cumulative Covid-19 Case Counts, Dekalb CountyDocument13 pagesDekalb Covid-19 Epidemiology Report: Daily and Cumulative Covid-19 Case Counts, Dekalb CountyZachary HansenNo ratings yet
- LiposomasDocument11 pagesLiposomasiris elianaNo ratings yet
- Introduction Solar EnergyDocument31 pagesIntroduction Solar EnergyVincentius ValdiNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Higher Level Paper 3: Instructions To CandidatesDocument36 pagesChemistry Higher Level Paper 3: Instructions To CandidatesHUI GABRIEL YAN LUNG G10L-13No ratings yet
- Media Charge - Dynamics - SAG Mills - ModifiedDocument85 pagesMedia Charge - Dynamics - SAG Mills - Modifiededwin javier valdivia guillenNo ratings yet
- Photovoltaic Simulation Tools ComparisonDocument11 pagesPhotovoltaic Simulation Tools ComparisonIvan BevandaNo ratings yet
- StrengthsDocument1 pageStrengthsNeeraj Kalyan GandholiNo ratings yet
- ProtocolsDocument11 pagesProtocolsNeeraj Kalyan GandholiNo ratings yet
- Jenna - Jewell@Utsouthwestern - Edu: Glutamine and Asparagine Sensing by Mtorc1Document18 pagesJenna - Jewell@Utsouthwestern - Edu: Glutamine and Asparagine Sensing by Mtorc1Neeraj Kalyan GandholiNo ratings yet
- Protocol For Cell Cycle Analysis Using Flow CytometryDocument6 pagesProtocol For Cell Cycle Analysis Using Flow CytometryNeeraj Kalyan GandholiNo ratings yet
- Work To Be DoneDocument4 pagesWork To Be DoneNeeraj Kalyan GandholiNo ratings yet
- Biology Form 5 Notes Chapter 1Document39 pagesBiology Form 5 Notes Chapter 1Mayghen SelvanayagamNo ratings yet
- Gene Expression, RNA, Transcription and Translation: Higher Human BiologyDocument58 pagesGene Expression, RNA, Transcription and Translation: Higher Human BiologyShruthiNo ratings yet
- Medical Lab Technician - Job DescriptionDocument2 pagesMedical Lab Technician - Job DescriptionBolarinwa Abdul-JalhaliNo ratings yet
- Lecture 6 - VectorsDocument10 pagesLecture 6 - Vectorsmyselfuniquesoumyadeep100% (1)
- H1 Revision Notes DNA and GenomicsDocument6 pagesH1 Revision Notes DNA and GenomicsJiaLi XieNo ratings yet
- Mutations: What Is A Mutation?Document4 pagesMutations: What Is A Mutation?Miriam Du BaltazarNo ratings yet
- NEA - Interim List of Household Products and Active Ingredients For Disinfection of The COVID-19 VirusDocument8 pagesNEA - Interim List of Household Products and Active Ingredients For Disinfection of The COVID-19 VirusatllNo ratings yet
- Epidemiology of COVID 19Document31 pagesEpidemiology of COVID 19Kranthi Kumar ReddyNo ratings yet
- Ap Bio Unit 6 Quick Study CardDocument1 pageAp Bio Unit 6 Quick Study CardAbhi ShahNo ratings yet
- 10 3 2 Ijmr PDFDocument4 pages10 3 2 Ijmr PDFSindhu ShreeNo ratings yet
- Ebook Principles of Tissue Engineering PDF Full Chapter PDFDocument67 pagesEbook Principles of Tissue Engineering PDF Full Chapter PDFbernard.moore610100% (20)
- Histo (MCQ) PDFDocument6 pagesHisto (MCQ) PDFstuffNo ratings yet
- Interworld College of Science and TechnologyDocument2 pagesInterworld College of Science and TechnologyGerald Cabungason PresiadosNo ratings yet
- SOS ChromoTestDocument2 pagesSOS ChromoTestAldinaNo ratings yet
- MIMS Abbreviation IndexDocument1 pageMIMS Abbreviation IndexDwi cahyaniNo ratings yet
- Valuable CattleDocument2 pagesValuable CattleGurmeet BrarNo ratings yet
- Biotech Module2Document12 pagesBiotech Module2Aldrin M. ObiasNo ratings yet
- Tacke2016 - Treatment For Hepatitis B in Patients With Drug ResistanceDocument7 pagesTacke2016 - Treatment For Hepatitis B in Patients With Drug ResistanceClarisa AnindyaNo ratings yet
- Study QuestionsssssssDocument6 pagesStudy QuestionsssssssHarley FavorNo ratings yet
- Rice GenomeDocument26 pagesRice GenomePavani Gaja100% (1)
- Oxoid and Remel Microbiology Products For Pharmaceutical ApplicationsDocument2 pagesOxoid and Remel Microbiology Products For Pharmaceutical ApplicationsFrengki Hadi Eko Santoso0% (1)
- Microbe Mission: UMN Gopher InvitationalDocument10 pagesMicrobe Mission: UMN Gopher InvitationalsriniNo ratings yet
- EVMS Critical Care COVID-19 ProtocolDocument30 pagesEVMS Critical Care COVID-19 ProtocolRichard HermanNo ratings yet
- CAPE Biology Unit 1 - 13-Cell Cycle and Mitosis - 2024-FinalDocument161 pagesCAPE Biology Unit 1 - 13-Cell Cycle and Mitosis - 2024-FinalKEMEISHA MILLERNo ratings yet
- Product Datasheet: MCM7 Antibody NBP1-85721Document5 pagesProduct Datasheet: MCM7 Antibody NBP1-85721JoaoNo ratings yet
- Conversion MG - DL To Mmol - LDocument6 pagesConversion MG - DL To Mmol - LshrinivastNo ratings yet
- MDR-TB and XDR-TB: Ndoh 4 October 2006Document40 pagesMDR-TB and XDR-TB: Ndoh 4 October 2006Eta Calvin ObenNo ratings yet