Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Stack
Uploaded by
Badnaam Raja0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
8 views15 pagesCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
8 views15 pagesStack
Uploaded by
Badnaam RajaCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 15
Stack Data Structure
Prof. Jasmin T Jose
SCOPE
VIT Vellore
Stack
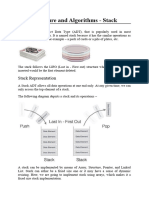
• A stack is a type of data structure that allows you access to a
single element at any given time
• LIFO structure (last-in first-out).
• The stack is an ordered list but the insertions and deletions are
restricted by certain rules.
• Objects can be inserted at any time, but only the last (the
most-recently inserted) object can be removed.
• Inserting an item is known as “pushing” onto the stack.
“Popping” off the stack is to removing an item.
• Stack is an Abstract Data Type (ADT)
Abstract Data Type (ADT)
• A logical view of the data objects together
with specifications of the operations required
to create and manipulate them.
• What is NOT an Abstract Data Type (in C)?
– Int -int is a built-in type in the C language
– Double-double is a built-in type in the C language
– These data types are already built into the
language.
Abstract Data Type (ADT)
• It is a data type that is NOT built into the language
• It is a data type that we will “build”.
• We will specify what it is, how it is used, etc.
• It is often defined in terms of its behavior rather
than its implemented representation
• An abstract data type is defined indirectly, only by
the operations that may be performed on it (i.e.
behavior)
Applications of Stack
• Reversing Data: We can use stacks to reverse
data. (example: files, strings). Very useful for
finding palindromes.
• Backtracking : Stacks can be used to backtrack
to achieve certain goals.
• Function calls: Perhaps the most important
application of stacks is to implement function
calls. Most compilers implement function calls
by using a stack.
Applications of Stack
• Arithmetic expression evaluation:
– An important application of stacks is in parsing.
– In high level languages, infix notation cannot be
used to evaluate expressions.
– A common technique is to convert an infix
notation into postfix notation, then evaluating it.
Stack
Operations on Stack
Implementation of stack
• In the array implementation, we would:
– Declare an array of fixed size (which determines the maximum size of
the stack).
– Keep a variable which always points to the “top” of the stack.
– Contains the array index of the “top” element.
• In the linked list implementation, we would:
– Maintain the stack as a linked list.
– A pointer variable top points to the start of the list.
– The first element of the linked list is considered as the stack top.
Declaration and creation
5
4
3
2
1
0
Push
void push (int element)
{
if (top == (MAXSIZE-1))
{
printf(“\n Stack overflow”);
exit(-1);
}
else
{
top ++;
st[top] = element;
}
}
POP
int pop ()
{
if (top == -1)
{
printf(“\n Stack underflow”);
exit(-1);
}
else
{
a = st[top]
Top--;
return a;
}
}
Is empty
int isempty()
{
if (top == -1)
return 1;
else
return (0);
}
Is full
int isfull()
{
if (top == (MAXSIZE–1))
return 1;
else
return (0);
}
• Applications:
– Reverse a string
– Recursive functions
– Undo operation(Ctrl z)
– Parenthesis balancing
– Infix to postfix or prefix conversion
– Evaluation of postfix expression
You might also like
- Dsa Unit 3Document120 pagesDsa Unit 3Hanu HanumanthNo ratings yet
- StackDocument36 pagesStackUditNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 - StackDocument77 pagesUnit 2 - StackAmutha RajiniNo ratings yet
- Data Structures Unit 1Document60 pagesData Structures Unit 1divyanshuvaishnav02No ratings yet
- Unit 3Document135 pagesUnit 3Tansu GangopadhyayNo ratings yet
- Exp 3 - Dsa Lab FileDocument10 pagesExp 3 - Dsa Lab Fileparamita.chowdhuryNo ratings yet
- Stack in Data StructuresDocument23 pagesStack in Data Structuresnofiya yousufNo ratings yet
- Abstract Data Types (Linked List and Stack)Document30 pagesAbstract Data Types (Linked List and Stack)MOSES ALLENNo ratings yet
- Unit VDocument10 pagesUnit VkflmorcillosNo ratings yet
- Data Structures: StackDocument19 pagesData Structures: StackShah GeeNo ratings yet
- 18CS32 - Module 2 NoDocument28 pages18CS32 - Module 2 NodwqvehmhtqofoizpsoNo ratings yet
- DSC Mod2Document27 pagesDSC Mod2Abrar AhmedNo ratings yet
- DSA2 Stacks (061808)Document35 pagesDSA2 Stacks (061808)redbutterfly100% (1)
- Data Structure - StackDocument39 pagesData Structure - StackShibani RanaNo ratings yet
- CH Datastructure StackDocument2 pagesCH Datastructure StackUma TNANo ratings yet
- StacksDocument17 pagesStackshibaNo ratings yet
- DS Mod2Document174 pagesDS Mod2Kumar Kaushal 040No ratings yet
- StacksDocument27 pagesStacksRitesh JanaNo ratings yet
- Data Structure Class Note - UNIT 2Document32 pagesData Structure Class Note - UNIT 2Revanth RavikantiNo ratings yet
- Year & Sem - II & III Section - A, B, C, D Subject - Data Structures & Algorithms Unit - IDocument77 pagesYear & Sem - II & III Section - A, B, C, D Subject - Data Structures & Algorithms Unit - IKunallNo ratings yet
- Stack and Queue-ClassDocument85 pagesStack and Queue-ClassRising ShineeNo ratings yet
- DSA UNIt 1Document77 pagesDSA UNIt 1hswarnkar23No ratings yet
- 05 StacksDocument31 pages05 StacksClarisse Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Stack QueueDocument62 pagesStack QueuedmumminaNo ratings yet
- Stack: LIFO (Last in First Out)Document13 pagesStack: LIFO (Last in First Out)GAUTAMI UPPADANo ratings yet
- Module 4 Stack Data StructureDocument22 pagesModule 4 Stack Data StructureJD DulatreNo ratings yet
- DataStructures Unit 2Document26 pagesDataStructures Unit 2bhaktiranjandas649No ratings yet
- Chapter 4 - StacksDocument38 pagesChapter 4 - StacksSolomon DawitNo ratings yet
- Stack, Queue and Recursion in Data StructureDocument26 pagesStack, Queue and Recursion in Data Structurechitvan KumarNo ratings yet
- C Programming and Data Structures (R20 Syllabus JNTUA, Anantapuramu)Document12 pagesC Programming and Data Structures (R20 Syllabus JNTUA, Anantapuramu)krupa522No ratings yet
- DS Notes FinalDocument146 pagesDS Notes FinaltopmotivezzNo ratings yet
- UNIT-4 Data Structures: Data Structures in C Are An Inevitable Part of ProgramsDocument18 pagesUNIT-4 Data Structures: Data Structures in C Are An Inevitable Part of ProgramsparmeshNo ratings yet
- UNIT2 Stacks QueuesDocument14 pagesUNIT2 Stacks QueuesSumit RajputNo ratings yet
- Data Structure and Algorithms - StackDocument3 pagesData Structure and Algorithms - StackBharti PatelNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 StackDocument73 pagesUnit 2 StackNone OtherNo ratings yet
- WINSEM2018-19 - CSE2003 - ETH - SJT311 - VL2018195002472 - Reference Material I - Introduction - Stack - QueueDocument51 pagesWINSEM2018-19 - CSE2003 - ETH - SJT311 - VL2018195002472 - Reference Material I - Introduction - Stack - QueuekumarklNo ratings yet
- Module 2Document23 pagesModule 2saikiran110077No ratings yet
- Unit - 2 Linear Data Structures (Stacks)Document15 pagesUnit - 2 Linear Data Structures (Stacks)Lavanya JNo ratings yet
- Stack ADTDocument48 pagesStack ADTArun SNo ratings yet
- Lecture 6 Stack DataStructure in C++Document40 pagesLecture 6 Stack DataStructure in C++Simple lyrics100% (1)
- 2b Stacks QueuesDocument49 pages2b Stacks QueuesAnNo ratings yet
- Unit IDocument101 pagesUnit IMugizhan NagendiranNo ratings yet
- Module-2 DS NotesDocument25 pagesModule-2 DS Notesanikaitsarkar.20ecNo ratings yet
- StacksDocument31 pagesStacksJohn Patrick RaagasNo ratings yet
- Data Structures: What Is Information?Document63 pagesData Structures: What Is Information?Suma PrakashNo ratings yet
- Open Elective2: Subject: Data Structures Using Python: Unit 4:stack and QueueDocument54 pagesOpen Elective2: Subject: Data Structures Using Python: Unit 4:stack and QueueSahil RathodNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 StacksDocument23 pagesUnit 2 Stackstestingupon1No ratings yet
- C++ - Unit IVDocument50 pagesC++ - Unit IVElamathi LNo ratings yet
- Lecture 4Document32 pagesLecture 4NodirNo ratings yet
- STACKS wk7Document29 pagesSTACKS wk7brightnanor19No ratings yet
- E-School Education Hub Data Structures: Stacks and Queues Using Lists Raw DataDocument6 pagesE-School Education Hub Data Structures: Stacks and Queues Using Lists Raw DataPavni TripathiNo ratings yet
- DSA 10 QuestionDocument23 pagesDSA 10 Questionlandgesantosh240No ratings yet
- StacksDocument121 pagesStacksYirga Deres TikuyeNo ratings yet
- Abstract Data Types (Adts) : Applications of Data StructuresDocument16 pagesAbstract Data Types (Adts) : Applications of Data StructuresSuryaNo ratings yet
- DownloadDATA STRUCTURES AND ALGORITHMS - Unit 2Document24 pagesDownloadDATA STRUCTURES AND ALGORITHMS - Unit 2radonNo ratings yet
- Module - IIDocument54 pagesModule - IIangel0724No ratings yet
- 005 - DS StackDocument65 pages005 - DS StackSSUET Course ModeratorNo ratings yet
- DS IntroductionDocument43 pagesDS IntroductionKarthikeyini SNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 STACKDocument55 pagesChapter 4 STACKfitsum tekaNo ratings yet
- Counting SortDocument7 pagesCounting SortBadnaam RajaNo ratings yet
- Tower of HanoiDocument5 pagesTower of HanoiBadnaam RajaNo ratings yet
- Iterative Algm ComplexityDocument14 pagesIterative Algm ComplexityBadnaam RajaNo ratings yet
- Stack ApplnDocument15 pagesStack ApplnBadnaam RajaNo ratings yet
- Asymtotic NotationsDocument15 pagesAsymtotic NotationsBadnaam RajaNo ratings yet
- Bubble SortDocument98 pagesBubble SortBadnaam RajaNo ratings yet
- Circular Queue PDFDocument15 pagesCircular Queue PDFBadnaam RajaNo ratings yet
- Binary SearchDocument22 pagesBinary SearchBadnaam RajaNo ratings yet
- Algorithm AnalysisDocument37 pagesAlgorithm AnalysisBadnaam RajaNo ratings yet
- Compendium of Trick Plays - Nihon KiinDocument220 pagesCompendium of Trick Plays - Nihon KiinFrédéric Vieira100% (2)
- N 5 C 6527 C 1 B 5 CebDocument16 pagesN 5 C 6527 C 1 B 5 CebMusonda MwenyaNo ratings yet
- Program TemplateDocument2 pagesProgram TemplateErwin MigalangNo ratings yet
- Memory Organisation in Embedded SystemsDocument12 pagesMemory Organisation in Embedded SystemsUthra SowrirajanNo ratings yet
- Immu Lite 1000Document6 pagesImmu Lite 1000ciolo1981No ratings yet
- RIp Van Winkle A2 Teachers NotesDocument3 pagesRIp Van Winkle A2 Teachers NotesLuisa RodríguezNo ratings yet
- Akkordsymbole EDocument15 pagesAkkordsymbole Ehope72No ratings yet
- Parts of SpeechDocument6 pagesParts of SpeechShalsa Maita rundiNo ratings yet
- Design of Sensor Nodes in Underwater Sensor Networks: Yu Yang, Zhang Xiaomin, Peng BO, Fu YujingDocument5 pagesDesign of Sensor Nodes in Underwater Sensor Networks: Yu Yang, Zhang Xiaomin, Peng BO, Fu Yujinghari9923No ratings yet
- Gmid Methodology Using Evolutionary Algorithms andDocument5 pagesGmid Methodology Using Evolutionary Algorithms andwallace20071No ratings yet
- Lesson Plan LightDocument3 pagesLesson Plan LightadiNo ratings yet
- Engineering Mathematics For Gate Chapter1Document52 pagesEngineering Mathematics For Gate Chapter1Charan Reddy100% (1)
- IP Microwave Solution - 20090617-V4Document51 pagesIP Microwave Solution - 20090617-V4Gossan Anicet100% (2)
- Vedic MythologyDocument4 pagesVedic MythologyDaniel MonteiroNo ratings yet
- Vocabulary in Context PowerpointDocument47 pagesVocabulary in Context Powerpointhaneenlatif50% (2)
- Islanded Microgrid BenchmarkDocument7 pagesIslanded Microgrid BenchmarkDinithi LaknaNo ratings yet
- Exercice Thermodynamics PART IDocument8 pagesExercice Thermodynamics PART Ichitl.23bi14075No ratings yet
- Irish PlacenamesDocument24 pagesIrish PlacenamesKate A. RoseNo ratings yet
- Seminar 2Document8 pagesSeminar 2Ульяна ХовановаNo ratings yet
- INGLES There Are Two Ways of Telling Somebody What Another Person SaidDocument5 pagesINGLES There Are Two Ways of Telling Somebody What Another Person Saidcatherin gonzalezNo ratings yet
- Transient Conduction: Spatial Effects, Semi-Infinite Solids, and Finite-Difference MethodsDocument58 pagesTransient Conduction: Spatial Effects, Semi-Infinite Solids, and Finite-Difference MethodsJkun gamingNo ratings yet
- R&W Lesson PlanDocument4 pagesR&W Lesson Planمحمد فاريزNo ratings yet
- To Err Is Human To Forgive Is Divine EssayDocument4 pagesTo Err Is Human To Forgive Is Divine Essayibnorvbaf100% (2)
- 6475c919ebcbc 208Document3 pages6475c919ebcbc 208Saleem AbbasNo ratings yet
- ST10F280 JT3Document186 pagesST10F280 JT3Carlos Geeket' El HalabiNo ratings yet
- International Journal For Clergy July 1990: J. Robert Spangler, Longest Serving Ministry Editor, RetiresDocument32 pagesInternational Journal For Clergy July 1990: J. Robert Spangler, Longest Serving Ministry Editor, RetiresDaniel HalápiNo ratings yet
- ElevenDocument10 pagesElevenapi-252903312No ratings yet
- Akbar Birbal List of FoolsDocument3 pagesAkbar Birbal List of Foolsp v charviNo ratings yet
- Hwy Beg Exit Test ADocument3 pagesHwy Beg Exit Test AAdriana ChaconNo ratings yet
- Explicit Instruction - SyllablesDocument20 pagesExplicit Instruction - Syllablesapi-217065852No ratings yet