Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Signal Flow Graph
Uploaded by
Lee0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
16 views7 pagesOriginal Title
signal-flow-graph
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
16 views7 pagesSignal Flow Graph
Uploaded by
LeeCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 7
Signal Flow Graph
Engr. Marlon Peter G. Balingit
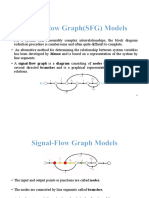
Signal Flow Graph is a Representation of
Block
• is a Representation of Block diagrams
• It is also used to determine the overall transfer function of a control
system
• It is an easier method to determine the transfer function as compared
to block diagram reduction as we do not have to reduce the SFG
• Example of constructional graph considers an algebraic equation.
Consider this equations:
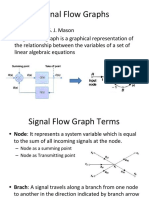
Elements of Signal flow graph
• Nodes - while creating an SFG, junction points are used to represent
variable also called as NODES.
• Branches – the nodes are connected together by lines are called
branches, the signal that travels from one node to another node along
these branches.
• Input node(source) – the signal which only has outgoing branches.
• Output node(sink) – node that has only incoming branches
• Path - It is a traversal of connected branches in the direction of branch
arrows such that no node is traversed more than once.
Elements of Signal flow graph
• Forward path – it is a path from input node to the output node.
• Forward path gain – it is the product of branches gain in traversing a
forward path
• Loop – it is a path which originates and terminates at the same node.
• Loop gain – it is a product of branch gains encountered in traversing a
loop.
• Self loop – loop with only one branch.
• Non-touching loops – loops are said to be non- touching if they do not
posses any common node.
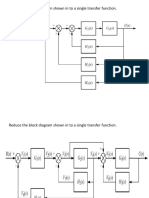
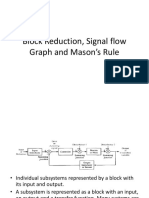
Equivalent representation of block diagram
into signal flow diagram
Equivalent representation of block diagram into
signal flow diagram
You might also like
- Signal Flow GraphDocument29 pagesSignal Flow GraphAhsan MoinNo ratings yet
- Lesson M3a Signal Flow Graphs Block DiagramsDocument30 pagesLesson M3a Signal Flow Graphs Block DiagramsAsif NoorNo ratings yet
- Reduce The Block Diagram Shown in To A Single Transfer FunctionDocument7 pagesReduce The Block Diagram Shown in To A Single Transfer FunctionMike PosktovaNo ratings yet
- On Signal Flow Graph Signal Flow GraphDocument20 pagesOn Signal Flow Graph Signal Flow Graphrub786No ratings yet
- 9 02 11 22Document19 pages9 02 11 22gamer manNo ratings yet
- Signal Flow GraphDocument13 pagesSignal Flow Graphee210002004No ratings yet
- Reduction of Multiple SubsystemsDocument29 pagesReduction of Multiple SubsystemsKez BeatingNo ratings yet
- Reduction of Multiple SubsystemsDocument27 pagesReduction of Multiple SubsystemsAdriano Mercedes Jr. CanoNo ratings yet
- Signal Flow GraphsDocument12 pagesSignal Flow GraphsDurveshNo ratings yet
- MEC522 Chapter 2 - StudentDocument60 pagesMEC522 Chapter 2 - Studentazim khanafiahNo ratings yet
- 1.3 Signal Flow GraphDocument33 pages1.3 Signal Flow Graphearnest normanNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2Document24 pagesLecture 2iptradersNo ratings yet
- W3 Lesson 2 - Dynamic, Finite State, and Complex Model - Module PDFDocument29 pagesW3 Lesson 2 - Dynamic, Finite State, and Complex Model - Module PDFyassin20dhmiNo ratings yet
- CE Unit 1Document84 pagesCE Unit 1P POORNA CHANDRA REDDYNo ratings yet
- Regulation & Control Ppt-1Document55 pagesRegulation & Control Ppt-1tadiwosNo ratings yet
- Unit I - Systems and Modelling: B.E., EEE, Semester 4, AY 2023-2024Document20 pagesUnit I - Systems and Modelling: B.E., EEE, Semester 4, AY 2023-2024Dr. C. V.No ratings yet
- Graph Data Structure PresentationDocument23 pagesGraph Data Structure PresentationGerald KapinguraNo ratings yet
- Block Diagram and Signal FlowDocument23 pagesBlock Diagram and Signal Floweltn s.No ratings yet
- FME 326 - Module 5 - Signal Flow and Block Diagram ModelsDocument47 pagesFME 326 - Module 5 - Signal Flow and Block Diagram ModelsJesse Jon FerolinoNo ratings yet
- Outline: - Introduction To Signal Flow Graphs - Signal-Flow Graph Models - BD To SFG - Mason's Gain FormulaDocument22 pagesOutline: - Introduction To Signal Flow Graphs - Signal-Flow Graph Models - BD To SFG - Mason's Gain FormulaShreya TripathiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 0Document7 pagesChapter 0Fatma ChouraNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4: Signal Flow GraphsDocument3 pagesChapter 4: Signal Flow GraphsMuhammed IfkazNo ratings yet
- Block Reduction and Masons Rule - 1Document52 pagesBlock Reduction and Masons Rule - 1dedekNo ratings yet
- BD SFG Mason S RuleDocument37 pagesBD SFG Mason S Rulesabbir hossainNo ratings yet
- Graphs: Kok Boon Shiong JTPDocument45 pagesGraphs: Kok Boon Shiong JTPPuteri Qani'ahNo ratings yet
- Rohini 27072873676Document7 pagesRohini 27072873676VIKASH YADAVNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 - DSDocument67 pagesChapter 6 - DSpruthvirajdesai204No ratings yet
- Session 6Document50 pagesSession 6Shayan ChatterjeeNo ratings yet
- Lecture 10Document60 pagesLecture 10Dilshad CiziriNo ratings yet
- Biomedical Control Systems (BCS) : Module Leader: DR Muhammad ArifDocument31 pagesBiomedical Control Systems (BCS) : Module Leader: DR Muhammad ArifBhavik PrajapatiNo ratings yet
- Lecture06 Signal Flow GraphDocument13 pagesLecture06 Signal Flow GraphSai AdarshNo ratings yet
- Control System Models or RepresentationsDocument9 pagesControl System Models or RepresentationsTrisha SARMIENTONo ratings yet
- Control System Models or RepresentationsDocument9 pagesControl System Models or RepresentationsTrisha SARMIENTONo ratings yet
- Campus Networking Workshop: Layer-2 Network DesignDocument101 pagesCampus Networking Workshop: Layer-2 Network DesignTsega TeklewoldNo ratings yet
- Signal Flow Graph and Block DiagramDocument23 pagesSignal Flow Graph and Block DiagramSolayao, Jan Marvin J.No ratings yet
- Chapter 9 - Activity DiagramDocument28 pagesChapter 9 - Activity DiagramBabyAyang ArNo ratings yet
- Seminar Topic:-Programming of PLC (Ladder Programming) : Presented By: - Guided ByDocument14 pagesSeminar Topic:-Programming of PLC (Ladder Programming) : Presented By: - Guided ByShubam SharmaNo ratings yet
- Gates, Circuits, and Boolean AlgebraDocument27 pagesGates, Circuits, and Boolean AlgebraUsman SiddiquiNo ratings yet
- Types of Graphs in Data StructuresDocument18 pagesTypes of Graphs in Data StructuresJahangir AliNo ratings yet
- Routing AlgorithmsDocument17 pagesRouting AlgorithmsRani MuraliNo ratings yet
- 1509846749lecture 11. 2k14eee Signal Flow GraphDocument62 pages1509846749lecture 11. 2k14eee Signal Flow GraphAmin KhanNo ratings yet
- Feedback and Control System: Signal Flow GraphsDocument59 pagesFeedback and Control System: Signal Flow GraphsBenj MendozaNo ratings yet
- GraphsDocument3 pagesGraphsRajesh KumarNo ratings yet
- Multistage and Combining NetworksDocument16 pagesMultistage and Combining NetworksNausheen SaharNo ratings yet
- RoutingDocument41 pagesRoutingJallapally sai chandanaNo ratings yet
- 2.block Diagrams and SFG L14Document13 pages2.block Diagrams and SFG L14VijayKumarNo ratings yet
- 33333CON1 (Signal Flow Graph)Document60 pages33333CON1 (Signal Flow Graph)Ahmed JamalNo ratings yet
- Layer2 Network DesignDocument102 pagesLayer2 Network DesignAlex VillaNo ratings yet
- Layer 2 Network Design: Carlos Vicente University of Oregon Cvicente@uoregon - EduDocument103 pagesLayer 2 Network Design: Carlos Vicente University of Oregon Cvicente@uoregon - Eduobee1234No ratings yet
- Mason's Gain FormulaDocument4 pagesMason's Gain Formulailg1No ratings yet
- Lecture 5-2 Signal Flow Graphs PDFDocument60 pagesLecture 5-2 Signal Flow Graphs PDFالبياتي محمدNo ratings yet
- DMS-12 GraphsDocument45 pagesDMS-12 GraphsShykh IQraNo ratings yet
- lecture - 5-2 - signal - flow - graphs المنهج PDFDocument60 pageslecture - 5-2 - signal - flow - graphs المنهج PDFTariq ZeyadNo ratings yet
- Enabling TechnologiesDocument25 pagesEnabling TechnologiesReg NdhlovuNo ratings yet
- GRAPHSDocument38 pagesGRAPHSasdNo ratings yet
- Graph Theory in Electrical EngineeringDocument25 pagesGraph Theory in Electrical EngineeringPappuNo ratings yet
- Campus Networking Workshop Garnet/Nsrc: Layer-2 Network DesignDocument103 pagesCampus Networking Workshop Garnet/Nsrc: Layer-2 Network Designjcy1978No ratings yet
- 2.routing Shortest Path RoutingDocument26 pages2.routing Shortest Path RoutingDivya K.SNo ratings yet
- Sensors and TransducersDocument17 pagesSensors and TransducersLeeNo ratings yet
- Unit 1Document14 pagesUnit 1LeeNo ratings yet
- Fcs ActivityDocument3 pagesFcs ActivityLeeNo ratings yet
- Matrices 1Document27 pagesMatrices 1LeeNo ratings yet
- Solving and Plotting Matrices Using MatlabDocument5 pagesSolving and Plotting Matrices Using MatlabLeeNo ratings yet
- Lesson.1. Types of WavesDocument14 pagesLesson.1. Types of WavesLeeNo ratings yet