Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Reverse Logistics
Uploaded by
anushka0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
16 views10 pagesOriginal Title
Reverse Logistics (2).pptx
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
16 views10 pagesReverse Logistics
Uploaded by
anushkaCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 10
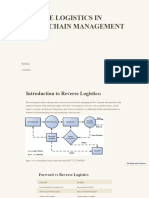
What is Reverse
Logistics?
• Reverse logistics refers to the supply
chain process of returning products
from end users back through the supply
chain to either the retailer or
manufacturer.
• Reverse logistics also includes executing
and managing return or exchange
related processes like exchange orders,
refurbishing and repair requests, and
return disposition, Reverse Logistics
offers condition-based returns
processing.
Types of reverse logistics
Returns management Return policy and procedure
• Most common type.
• Policy against which all customer returns are measured.
• Deals with regular customer returns and should represent a seamless,
hassle-free experience in order to boost customer loyalty and brand image. • It's good practice to keep these policies visible and easily accessible to customers
• Should be followed consistently by both customers and employees
Remanufacturing or refurbishment
• Helps organizations and retailers from forfeiting profit
Packaging management
• Helps eliminate unnecessary waste.
• Reuse packaging in order to reduce waste and save cost, instead of new
packaging for returned items.
Unsold products
• Returning items from end users or fulfillment centers back to manufacturers
• Commonly the result of delivery refusal, poor sales End of service life
• Returned at the end of the product’s useful life.
Delivery failure
• Manufacturers manage proper environmental disposal.
• Products cannot be delivered, they are returned to fulfillment centers
where they may be shipped back to the manufacturer
• Correcting the issue and resending. Rental equipment
• Rented or leased products
Repair and maintenance
• Sent back to the manufacturer for either disposal, recycling, or redeployment.
• Consumer electronics
The reverse logistics process
Depends on the:
• Type of reverse logistics
• Type of business the organization operates and in which industry
The five stages of reverse logistics
The five stages of reverse logistics
The goal of successful reverse logistics
• The goal of successful reverse logistics is to keep products moving in circularity
so that manufacturing, distribution, shipping and delivery, returns, repairs, and
disposal can all remain in sync as part of a constantly spinning model of
efficiency.
• This lower costs for organizations and subsequently their customers and end
users
• Adds value for the organization
Strategies to optimize reverse logistics
• Automate processes - Warehouse Management System (WMS) and Inventory
Management System (IMS).
• Use predictive analytics to anticipate returns
• Gather customer data
Gatekeeping
• It is the process of evaluating and
accepting return requests and
inspecting returned products to
meet the requirements for a
product exchange.
• Accept products that are damaged
only.
• Cost-effectivity for the company
Avoidance
• The goal is to screen products
before they enter the reverse
flow of logistics through the
supply chain.
• Minimizes the number of
returns
• Avoidance and gatekeeping
help from being overcrowded.
References
• https://www.ascm.org/lp/reverse-logistics/
• https://www.netsuite.com/portal/resource/articles/inventory-management/re
verse-logistics.shtml
• https://www.dhl.com/discover/en-global/logistics-advice/essential-guides/w
hat-is-reverse-logistics
• Admin. (2019, September 19). Reverse Logistics and Returns Management - Land, Sea, & Air Shipping Services -
InterlogUSA. Land, Sea, & Air Shipping Services - InterlogUSA.
https://www.interlogusa.com/answers/blog/reverse-logistics-returns-management/#:~:text=Effective%20gatekeeping%20and%
20avoidance%20strategies,decrease%20your%20damaged%20goods%20costs
.
You might also like
- Reverse LogisticsDocument31 pagesReverse LogisticsPartha Pratim SenguptaNo ratings yet
- Types of Reverse Logistics BBLDocument11 pagesTypes of Reverse Logistics BBLPradeep RathodNo ratings yet
- Reverse LogisticsDocument37 pagesReverse Logisticsblogdogunleashed100% (7)
- Operation Management PPT (Group-3) - 1Document14 pagesOperation Management PPT (Group-3) - 1MD MERAJUDDINNo ratings yet
- Reverse Supply Chain ManagementDocument19 pagesReverse Supply Chain ManagementSana KhalilNo ratings yet
- Integrantes:: Aquima Mamani Alexs Arapa Puma Juan Carlos Barrantes Choque Lisbeth Condo Chuquitaype BernardinoDocument19 pagesIntegrantes:: Aquima Mamani Alexs Arapa Puma Juan Carlos Barrantes Choque Lisbeth Condo Chuquitaype BernardinoJimmy Manrique EnriquezNo ratings yet
- Reverse Supply Chain AND Green Supply Chain: NIFT Hyderabad By: Prerna Kaushal SinghDocument26 pagesReverse Supply Chain AND Green Supply Chain: NIFT Hyderabad By: Prerna Kaushal SinghRahulKumbhareNo ratings yet
- Reverse Supply Chain & Agro Supply ChainDocument21 pagesReverse Supply Chain & Agro Supply ChainBLANK PAPERNo ratings yet
- A Guide To Reverse Logistics - How It Works, Types and Strategies - NetSuiteDocument22 pagesA Guide To Reverse Logistics - How It Works, Types and Strategies - NetSuitepalomaviguzNo ratings yet
- Reverse LogisticsDocument5 pagesReverse Logisticsshashi singhNo ratings yet
- Reverse LogisticsDocument17 pagesReverse LogisticsMarvellous YeezorNo ratings yet
- Reverse Logistics and Reverse Flow in SCMDocument30 pagesReverse Logistics and Reverse Flow in SCMferin laila shajiNo ratings yet
- Reverse Logistics & Competitive StrategyDocument6 pagesReverse Logistics & Competitive Strategychops95luvNo ratings yet
- Reverse Supply Chain Management: Dr. Peeyush Mehta Vipul MathurDocument12 pagesReverse Supply Chain Management: Dr. Peeyush Mehta Vipul MathurpankajNo ratings yet
- Session 2 - Product DevelopmentDocument57 pagesSession 2 - Product Developmentsharma.divya0598No ratings yet
- Reverse Logistic: Daniela Mejia Conde Juanita Suarez CaypaDocument18 pagesReverse Logistic: Daniela Mejia Conde Juanita Suarez CaypaMrZero DzNo ratings yet
- Lecture 9 - Complete Slides On Reverse LogisticsDocument23 pagesLecture 9 - Complete Slides On Reverse LogisticsJoanna Tee Kai YinNo ratings yet
- Reverse Supply Chain Management: Dr. Peeyush Mehta Vipul MathurDocument12 pagesReverse Supply Chain Management: Dr. Peeyush Mehta Vipul Mathurabhishekgupta_limNo ratings yet
- Strategic Issues in SCDocument35 pagesStrategic Issues in SCSahil SharmaNo ratings yet
- Closed Loop Supply ChainDocument21 pagesClosed Loop Supply ChainNurrul JannathulNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8Document19 pagesChapter 8Wajeeha WasimNo ratings yet
- Chapter - 6 Quality Management and Control: Ataklty Adugna (Ass. Professor)Document49 pagesChapter - 6 Quality Management and Control: Ataklty Adugna (Ass. Professor)yared haftuNo ratings yet
- Module 4Document72 pagesModule 4Ananda KrishnanNo ratings yet
- What Is Reverse Logistics?: Supply Chain ManagementDocument9 pagesWhat Is Reverse Logistics?: Supply Chain ManagementAnush RaiNo ratings yet
- PPT2Document83 pagesPPT2Jane FransiscaNo ratings yet
- Returns ManagementDocument15 pagesReturns ManagementMajeed SedaburrNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Operations ManagementDocument71 pagesIntroduction To Operations ManagementPravin KumarNo ratings yet
- Reverse LogisticsDocument12 pagesReverse LogisticsSimran KhanNo ratings yet
- Module4 - PRODUCT AND SERVICE DESIGNDocument8 pagesModule4 - PRODUCT AND SERVICE DESIGNJadeNo ratings yet
- Product and Service DesignDocument48 pagesProduct and Service DesignsafisanayasuNo ratings yet
- Healthcare Waste MinimizationDocument50 pagesHealthcare Waste MinimizationPRAVIN BROWNNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2 - Lean and Agile ManufacturingDocument21 pagesLecture 2 - Lean and Agile ManufacturingDr. DINESH BABU. PNo ratings yet
- Retail Management 2Document12 pagesRetail Management 2mubeen.raza92620No ratings yet
- Supply Chain Management IntroductionDocument12 pagesSupply Chain Management IntroductionGeraldineNo ratings yet
- A Guide To Reverse LogisticsDocument4 pagesA Guide To Reverse LogisticssanzitNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Supply Chain ManagementDocument12 pagesIntroduction To Supply Chain ManagementDiana Rose BanoNo ratings yet
- Roopa Talwar Lecturer Dept. of Hospital Administration JNMCDocument44 pagesRoopa Talwar Lecturer Dept. of Hospital Administration JNMCSanjeev ChouguleNo ratings yet
- Reverse Logistics: Compiled byDocument20 pagesReverse Logistics: Compiled byjorgeNo ratings yet
- Supply Chain ManagementDocument63 pagesSupply Chain ManagementPrajna Shirsho ShomeNo ratings yet
- S5 - Inventory ManagementDocument27 pagesS5 - Inventory Managementhoussam machkourNo ratings yet
- Inventory ManagementDocument18 pagesInventory ManagementNeha Gupta100% (1)
- Module 5 6Document69 pagesModule 5 6The Killer SwitchNo ratings yet
- Global Sourcing and ProcurementDocument19 pagesGlobal Sourcing and ProcurementVinayak SaxenaNo ratings yet
- Returns Management: Supply Chain Management Group Presentation OnDocument16 pagesReturns Management: Supply Chain Management Group Presentation OnAbhishek ShankarNo ratings yet
- DistributionDocument19 pagesDistributiondeepash katalNo ratings yet
- Distribution Requirement PlanningDocument19 pagesDistribution Requirement Planningdeepash katalNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3Document26 pagesChapter 3rajmessi2001No ratings yet
- Accounting & Control: Cost ManagementDocument31 pagesAccounting & Control: Cost ManagementYunita WijayaNo ratings yet
- Presentation SlidesDocument35 pagesPresentation SlidesAkash SuryaNo ratings yet
- Coordinated Product and Supply Chain DesignDocument51 pagesCoordinated Product and Supply Chain DesignMohit Gupta100% (2)
- Sustainable Tendering GuidelinesDocument7 pagesSustainable Tendering GuidelinesAlanRichardsonNo ratings yet
- Reverse Logistics in Supply Chain ManagementDocument16 pagesReverse Logistics in Supply Chain Managementmohammad.hamza1701No ratings yet
- WK7 QualityDocument33 pagesWK7 QualityKohi BangNo ratings yet
- AC2105 Lesson 4Document28 pagesAC2105 Lesson 4Xu YunfanNo ratings yet
- Replenishment To Dispatch & BeyondDocument28 pagesReplenishment To Dispatch & BeyondPrasad Ganti100% (1)
- Lean AccountingDocument31 pagesLean Accountingjitendrasutar1975100% (2)
- Chapter 12Document62 pagesChapter 12Sanjay LohaniNo ratings yet
- Anushka Prakash Kamble AnushkaKamble - Career Development Plan 1650690 1921951281Document10 pagesAnushka Prakash Kamble AnushkaKamble - Career Development Plan 1650690 1921951281anushkaNo ratings yet
- Business Analytics Final PresentationDocument6 pagesBusiness Analytics Final PresentationanushkaNo ratings yet
- Week 5 EthicsDocument2 pagesWeek 5 EthicsanushkaNo ratings yet
- Descriptive ReportDocument4 pagesDescriptive ReportanushkaNo ratings yet
- Anushka Prakash Kamble OBHR Analysis 1650692 801803561Document11 pagesAnushka Prakash Kamble OBHR Analysis 1650692 801803561anushkaNo ratings yet
- WIKADocument246 pagesWIKACuan 3No ratings yet
- Transkrip Akademik Academic Transcript Sementara: Mimosa PudicaDocument2 pagesTranskrip Akademik Academic Transcript Sementara: Mimosa Pudicaanon_639661161No ratings yet
- Edited by Foxit Reader Copyright (C) by Foxit Software Company, 2005-2007 ForDocument1 pageEdited by Foxit Reader Copyright (C) by Foxit Software Company, 2005-2007 ForChristopher RoyNo ratings yet
- Export MarketingDocument74 pagesExport MarketingkaurpreetgillNo ratings yet
- Deal Making and NegotiationDocument18 pagesDeal Making and NegotiationMarites TagaytayanNo ratings yet
- SUV Program BrochureDocument4 pagesSUV Program BrochurerahuNo ratings yet
- Wipro Case StudyDocument10 pagesWipro Case StudyNisha Bhagat0% (1)
- SUBJECT: International Business ASSINGMENT: Wal-Mart Case StudyDocument3 pagesSUBJECT: International Business ASSINGMENT: Wal-Mart Case StudyUsman TariqNo ratings yet
- Research Proposal MaK IRfDocument14 pagesResearch Proposal MaK IRfMayank GuptNo ratings yet
- Issue Management/Public Relations PlanDocument29 pagesIssue Management/Public Relations Planaliciamgriffith100% (5)
- Ketan MehtaDocument5 pagesKetan Mehtasourabh100ravNo ratings yet
- Cash Flow Management of Banijya BankDocument19 pagesCash Flow Management of Banijya BankPrashant McFc Adhikary0% (1)
- Case Studies EdM404 - TecsonNoesonB.Document15 pagesCase Studies EdM404 - TecsonNoesonB.Noeson TecsonNo ratings yet
- Inventories, Biological Assets, Etc.Document3 pagesInventories, Biological Assets, Etc.Jobelle Candace Flores AbreraNo ratings yet
- Nestle Sales PromotionDocument14 pagesNestle Sales PromotionMarco Devison80% (5)
- Al Meezan Investment Management LTD: Statement of AccountDocument5 pagesAl Meezan Investment Management LTD: Statement of AccountZishan Ali MeesamNo ratings yet
- Sealed Air CorporationDocument7 pagesSealed Air Corporationhadil_1No ratings yet
- Final Project On Employee Retention in Private Sector.. MurtiDocument66 pagesFinal Project On Employee Retention in Private Sector.. MurtiRishabh GuptaNo ratings yet
- The Birth of The Gods and The Origins of Agriculture, ReviewDocument20 pagesThe Birth of The Gods and The Origins of Agriculture, ReviewSamuel100% (1)
- Partnership AccountingDocument8 pagesPartnership Accountingferdinand kan pennNo ratings yet
- Famii KarooraDocument9 pagesFamii KarooraIbsa MohammedNo ratings yet
- Types of Bank AccountsDocument20 pagesTypes of Bank AccountsNisarg Khamar73% (11)
- Test Bank For International Economics 14th Edition Robert CarbaughDocument24 pagesTest Bank For International Economics 14th Edition Robert Carbaughcourtneyharrisbpfyrkateq100% (43)
- Strategic Cost ManagementDocument25 pagesStrategic Cost ManagementPriAnca GuptaNo ratings yet
- Shell Digital Marketing StrategiesDocument69 pagesShell Digital Marketing StrategiesFiorella AvalosNo ratings yet
- Asisgn. 1 Mod 2 - NCA HELD FOR SALE & DISCONTINUED OPNS.Document5 pagesAsisgn. 1 Mod 2 - NCA HELD FOR SALE & DISCONTINUED OPNS.Kristine Vertucio0% (1)
- Part 2 Basic Accounting Journalizing LectureDocument11 pagesPart 2 Basic Accounting Journalizing LectureKong Aodian100% (2)
- Study Notes On Cost AccountingDocument69 pagesStudy Notes On Cost AccountingPriyankaJainNo ratings yet
- University of Petroleum & Energy Studies: School of Business, DehradunDocument51 pagesUniversity of Petroleum & Energy Studies: School of Business, DehradunmayankNo ratings yet
- Main Project of SHGDocument27 pagesMain Project of SHGMinal DalviNo ratings yet