Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Module-III (4) Boilers in Food Industry
Uploaded by
Arpit Maknwal0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
108 views5 pagesSteam boilers are crucial equipment used in most food processing plants to generate steam for various operations like heating, sterilization, and drying. There are two main types of boilers used - fire-tube boilers that operate at lower pressures and produce cleaner steam, and water-tube boilers that operate at higher pressures and are suited for co-generation of electricity and process steam. Boilers need to be properly sized and have backup capacity to ensure a continuous supply of steam. Natural gas and LPG are preferred fuels due to producing combustion gases that don't contaminate foods. Steam offers precise temperature control and is the most efficient and versatile medium for heat transfer and sterilization in food manufacturing.
Original Description:
Original Title
Module-III (4) Boilers in Food Industry.pptx
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentSteam boilers are crucial equipment used in most food processing plants to generate steam for various operations like heating, sterilization, and drying. There are two main types of boilers used - fire-tube boilers that operate at lower pressures and produce cleaner steam, and water-tube boilers that operate at higher pressures and are suited for co-generation of electricity and process steam. Boilers need to be properly sized and have backup capacity to ensure a continuous supply of steam. Natural gas and LPG are preferred fuels due to producing combustion gases that don't contaminate foods. Steam offers precise temperature control and is the most efficient and versatile medium for heat transfer and sterilization in food manufacturing.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
108 views5 pagesModule-III (4) Boilers in Food Industry
Uploaded by
Arpit MaknwalSteam boilers are crucial equipment used in most food processing plants to generate steam for various operations like heating, sterilization, and drying. There are two main types of boilers used - fire-tube boilers that operate at lower pressures and produce cleaner steam, and water-tube boilers that operate at higher pressures and are suited for co-generation of electricity and process steam. Boilers need to be properly sized and have backup capacity to ensure a continuous supply of steam. Natural gas and LPG are preferred fuels due to producing combustion gases that don't contaminate foods. Steam offers precise temperature control and is the most efficient and versatile medium for heat transfer and sterilization in food manufacturing.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 5
Subject Code: FOOD315
Subject Name: Food Engineering-II
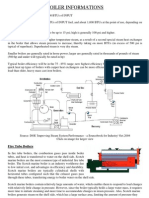
Module-III Boilers in Food Industry
Boilers for food processing industry
• Steam boilers are needed in most food processing plants to provide process steam, used
mainly in various operations, such as heating of process vessels, evaporators and
dryers, sterilization, blanching, and peeling. A medium size food plant (80 tons / day
raw material) may require a boiler producing about 10 tons/h of steam at 18 bar
pressure.
• Two principal types of steam boilers are used in the food processing industry, i.e. the
fire-tube and the water-tube boilers. The fire tube boilers operate at relatively lower
pressure (1–24 bar) and produce cleaner steam. The water- tube units operate at higher
pressures (100–140 bar) and they are suited for co- generation, i.e. electrical power and
exhaust steam of lower pressure for process heating. Co-generation is economical in
large food plants, requiring large amounts of low-pressure steam, e.g., beet sugar
plants.
A standby steam boiler of proper capacity may be necessary to provide process
steam during any boiler failure or breakdown.
Steam boilers are rated in Btu/h, kW or boiler HP (1 Btu/h = 0.293 W, 1 boiler HP
= 9.8 kW). The heat flux in the boiler heating surface is about 0.75 kW/ m2. The
boiler efficiency is about 85% with most of the thermal losses in the dry gases
and the moisture. Steam generation is about 1.4 t/h per MW.
In order to maintain the concentration of accumulated dissolved solids in steam
boilers below 3500 ppm, periodic discharge of hot water (blow down) is
practiced.
Fuel is used in food plants mostly for generating process steam and process
drying. Natural gas and liquefied propane (LPG) are preferred fuels in food
processing, because their combustion gases are not objectionable in direct contact
with food products. Fuel oil and coal can be used for indirect heating, i.e. through
heat exchangers.
Culinary steam of special quality is used when steam is injected in food products.
The steam must be free of objectionable chemicals used in boilers, which may be
carried into the food being heated. Culinary steam is usually produced from
potable water in a secondary system of a heat exchanger heated with high pressure
industrial steam.
We use steam in food manufacturing because it is the most efficient method of heat
transfer.
Partner this with its reliable, versatile and sterilizing qualities, it’s no wonder food
manufacturers across the globe use steam and its flexibility to cook their products
and clean equipment.
Steam is the only heat transfer medium available for direct food contact.
Steam offers precise temperature control through relatively simple, inexpensive
pressure control to deliver consistent heat across even the largest of vessels.
Steam offers the precision to ensure that the food produced is of the highest quality
for the manufacturers’ end-user consumers.
Thank you!
You might also like
- Thermal Rehabilitation (Azuma House)Document47 pagesThermal Rehabilitation (Azuma House)Haseeb Uz Zaman67% (6)
- The Hyperloop: The Future of TransportationDocument32 pagesThe Hyperloop: The Future of Transportationbcgg86% (14)
- MIP Thickener DesignDocument3 pagesMIP Thickener DesignHatem SalahNo ratings yet
- Technical Specification For 20 MVA Transformer PDFDocument21 pagesTechnical Specification For 20 MVA Transformer PDFamulya00428100% (10)
- Ups Aros Sentry Multistandard 40 80 Kva ManuelDocument48 pagesUps Aros Sentry Multistandard 40 80 Kva ManuelDieguiten286% (14)
- Manual de ServicioDocument196 pagesManual de ServicioJuan P. Ibanez CorreaNo ratings yet
- Dams: Parts, PakistanDocument22 pagesDams: Parts, PakistanEnigmatic Yousafzai100% (1)
- CHEN505 Note 1Document6 pagesCHEN505 Note 1OkePreciousEmmanuelNo ratings yet
- Industry ApplicationDocument4 pagesIndustry ApplicationAlexis Joshua LaceNo ratings yet
- Food Process Engineering Lab 3. BOILER OPERATIONDocument22 pagesFood Process Engineering Lab 3. BOILER OPERATIONMuhyiddin Noor AfandiNo ratings yet
- Assignment of Food Processing Plant Layout and DesignDocument9 pagesAssignment of Food Processing Plant Layout and DesignSadasis SinghNo ratings yet
- BOILERDocument8 pagesBOILERmobile legend practiceNo ratings yet
- Boiler ReportDocument15 pagesBoiler Reportshridhar sutarNo ratings yet
- Boiler 101: What Is A Boiler?Document2 pagesBoiler 101: What Is A Boiler?Samuel Acuña JimenezNo ratings yet
- Industrial Steam ProcessesDocument19 pagesIndustrial Steam ProcessesJohn Jhay Canlas100% (1)
- Boiler TypesDocument9 pagesBoiler TypesSharif Muhammad HossainNo ratings yet
- Boiler Structure and Principle (English)Document28 pagesBoiler Structure and Principle (English)Engr ImranNo ratings yet
- Industrial Steam ProcessDocument1 pageIndustrial Steam ProcessPryce YurongNo ratings yet
- Boiler Lab ReportDocument6 pagesBoiler Lab ReportYomal Wijesinghe0% (2)
- Tugas BoilerDocument33 pagesTugas BoilerAgus Dwi Nurcahyo JemberNo ratings yet
- Industrial Steam Boiler: ObjectiveDocument6 pagesIndustrial Steam Boiler: ObjectiveM. Hassan HaidderNo ratings yet
- Equipment Design - BOILERSDocument24 pagesEquipment Design - BOILERSEmyu ClaridadNo ratings yet
- Steam System Basics PDFDocument67 pagesSteam System Basics PDFEduardo Miranda100% (1)
- Assam Petrochemicals LimitedDocument14 pagesAssam Petrochemicals Limitedhimanshu gogoiNo ratings yet
- Boilers WebDocument16 pagesBoilers WebRobert MccoyNo ratings yet
- Final 26 - 53Document34 pagesFinal 26 - 53Bebe BucătaruNo ratings yet
- Increasing The Feed Water Tenperature: 6.4 Remedies 6.4.1 Remedies For Boiler To Increase EfficiencyDocument2 pagesIncreasing The Feed Water Tenperature: 6.4 Remedies 6.4.1 Remedies For Boiler To Increase EfficiencyAnonymous wJehCmNo ratings yet
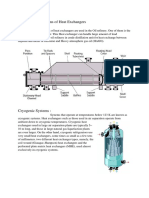
- Application of Heat ExchangersDocument2 pagesApplication of Heat ExchangersfintastellaNo ratings yet
- Boilers and Boiler Control Systems (Energy Engineering)Document22 pagesBoilers and Boiler Control Systems (Energy Engineering)Obayomi KennyNo ratings yet
- Process Steam System: Definition - What Does Mean?Document10 pagesProcess Steam System: Definition - What Does Mean?James VincentNo ratings yet
- INDUSTRIAL BOILERS-editedDocument9 pagesINDUSTRIAL BOILERS-editedComputer Graphics classNo ratings yet
- Waste Heat RecoveryDocument37 pagesWaste Heat Recoveryommech2020No ratings yet
- Applications Heat ExchangersDocument2 pagesApplications Heat ExchangersMesum IrfaniNo ratings yet
- Steam Heat Energy Water Psi Kpa: Water-Tube Boiler Fossil Fuel-Fired Boilers Heat Recovery Boilers Heat Recovery BoilersDocument4 pagesSteam Heat Energy Water Psi Kpa: Water-Tube Boiler Fossil Fuel-Fired Boilers Heat Recovery Boilers Heat Recovery BoilersMarsNo ratings yet
- Boiler IntroductionDocument17 pagesBoiler IntroductionDavid SilalahiNo ratings yet
- Important Questions & Answers: Process Auxiliaries and Utilities (GTU-3170516)Document24 pagesImportant Questions & Answers: Process Auxiliaries and Utilities (GTU-3170516)dhruv100% (4)
- Lesson 4Document11 pagesLesson 4Czyrra Lyn Dimapush FetalverNo ratings yet
- Boilers: Espiritu, Christopher James Managuit, John Jeruel Querubin, Russel JohnDocument43 pagesBoilers: Espiritu, Christopher James Managuit, John Jeruel Querubin, Russel JohnRussel John Morillo Querubin100% (1)
- Co Generation Unit 4Document52 pagesCo Generation Unit 4Johnson Johnson100% (2)
- Thermal Power Plants: Assignment No 1 Boilers 17-MS-PT-PE (T) - 20 Muneeb Ur Rehman KhanDocument8 pagesThermal Power Plants: Assignment No 1 Boilers 17-MS-PT-PE (T) - 20 Muneeb Ur Rehman KhanSuper SiangohanNo ratings yet
- Safety Operating Procedure of A Fire Tube BoilerDocument10 pagesSafety Operating Procedure of A Fire Tube BoilerJan Marvin Tamse0% (1)
- L&T ManualDocument60 pagesL&T ManualDineshNo ratings yet
- 06 - The Process of Wort Boiling 2 - 2Document3 pages06 - The Process of Wort Boiling 2 - 2StaccNo ratings yet
- 1 Boiler Horse Power Is About 42Document9 pages1 Boiler Horse Power Is About 42Faaz Al WahabNo ratings yet
- Thermal Engineering-BoilerDocument12 pagesThermal Engineering-BoilerJayNo ratings yet
- AA - Calderas de Baja TempDocument33 pagesAA - Calderas de Baja TempMarc AnmellaNo ratings yet
- Full ProjectDocument65 pagesFull ProjectPervin KumarNo ratings yet
- T PembakaranDocument34 pagesT Pembakarandimas setyawanNo ratings yet
- Study of Boiler Efficiency in Visakhapatnam Steel PlantDocument39 pagesStudy of Boiler Efficiency in Visakhapatnam Steel PlantPhanindra Guttula50% (2)
- On Suratgarh TPPDocument15 pagesOn Suratgarh TPPsubhampce085No ratings yet
- Waste Heat Recovery: V. Shanthan MT21HPE001Document9 pagesWaste Heat Recovery: V. Shanthan MT21HPE001Shanthan VardelliNo ratings yet
- Steam System Basics: Watertube BoilersDocument4 pagesSteam System Basics: Watertube BoilersNaNo ratings yet
- Boiler & AuxiliariesDocument13 pagesBoiler & Auxiliariesprats123456No ratings yet
- CHNO5Document20 pagesCHNO5Louie FhoegiNo ratings yet
- Oilon Chillheat: Optimized Cooling and Heating PerformanceDocument12 pagesOilon Chillheat: Optimized Cooling and Heating PerformanceMarceloNo ratings yet
- Classification of Heat Exchangers According To Their ApplicationsDocument9 pagesClassification of Heat Exchangers According To Their ApplicationsMohamed HassanNo ratings yet
- Attachment REPORTDocument39 pagesAttachment REPORTsemNo ratings yet
- Steam Power PlantDocument39 pagesSteam Power PlantizharizumieNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 PDFDocument26 pagesChapter 5 PDFHari650No ratings yet
- Introduction To BoilersDocument16 pagesIntroduction To BoilersZiauddin ChawdhryNo ratings yet
- Thermax Corporate Brochure Technology in ActionDocument28 pagesThermax Corporate Brochure Technology in ActionGoanengineerNo ratings yet
- Steam Firetube BoilersDocument2 pagesSteam Firetube BoilersmichtenbNo ratings yet
- HTM Section (Area Code 3008)Document7 pagesHTM Section (Area Code 3008)Hamza RiazNo ratings yet
- BoilersDocument3 pagesBoilersatikulNo ratings yet
- Multi - Fuel Boiler TechnologyDocument9 pagesMulti - Fuel Boiler TechnologyVijay KumarNo ratings yet
- Prepared By: Zerihun Kassa: UM at EABSC, Dec 2018Document32 pagesPrepared By: Zerihun Kassa: UM at EABSC, Dec 2018zerihun kassaNo ratings yet
- Mechanics of the Household: A Course of Study Devoted to Domestic Machinery and Household Mechanical AppliancesFrom EverandMechanics of the Household: A Course of Study Devoted to Domestic Machinery and Household Mechanical AppliancesNo ratings yet
- Desho TauDocument1 pageDesho TauArpit MaknwalNo ratings yet
- Module-II (3) Thermal Time CalculationDocument5 pagesModule-II (3) Thermal Time CalculationArpit MaknwalNo ratings yet
- Module-III (2) Dry Bulb Wet Bulb TemperatureDocument4 pagesModule-III (2) Dry Bulb Wet Bulb TemperatureArpit MaknwalNo ratings yet
- Module-IV (2) Evaporator and Its TypesDocument9 pagesModule-IV (2) Evaporator and Its TypesArpit MaknwalNo ratings yet
- Arpit. Maknwal. Resume PDFDocument2 pagesArpit. Maknwal. Resume PDFArpit MaknwalNo ratings yet
- Technip Introduces New Diving Support Vessel Deep ExplorerDocument2 pagesTechnip Introduces New Diving Support Vessel Deep Explorermuhammad ilyasNo ratings yet
- Reporte HOMER WIND 5kW-PV 6.36kWDocument10 pagesReporte HOMER WIND 5kW-PV 6.36kWlandoa junNo ratings yet
- Ernest Rutherford 1Document8 pagesErnest Rutherford 1api-400268497No ratings yet
- Siemons - Cello Bowing TechniqueDocument15 pagesSiemons - Cello Bowing TechniqueMassa Awaj100% (2)
- Manual 45001-2018Document34 pagesManual 45001-2018Mohamed HabibNo ratings yet
- Infrared SpectrosDocument3 pagesInfrared SpectrosAmanda CarvalhoNo ratings yet
- FM Course OutlineDocument4 pagesFM Course Outlinev rajuNo ratings yet
- NEM Power-Systems BrochureDocument16 pagesNEM Power-Systems Brochurehung100% (1)
- Manual PDFDocument202 pagesManual PDFEdwin GallardoNo ratings yet
- Manual Minicas 2Document12 pagesManual Minicas 2ecotexano100% (1)
- PVC BendingDocument6 pagesPVC BendingFrancis Al Maghanoy GabisonNo ratings yet
- 65043-Ga Rig Air Compressor.Document82 pages65043-Ga Rig Air Compressor.J&CNo ratings yet
- The Effect of Using An Ethanol Blended Fuel On Emissions in An SI EngineDocument6 pagesThe Effect of Using An Ethanol Blended Fuel On Emissions in An SI EngineVinay GowdaNo ratings yet
- EPF FW Demand Calculation NoteDocument14 pagesEPF FW Demand Calculation NoteEmamokeNo ratings yet
- 1.1. Iso 11507-2007 (E)Document15 pages1.1. Iso 11507-2007 (E)Khin Khin ThawNo ratings yet
- Furnace Oil ProjectDocument16 pagesFurnace Oil ProjectRohit PNo ratings yet
- Cylinder Cover Assembly KG170-02000: Fuel Oil System KG170-09000Document1 pageCylinder Cover Assembly KG170-02000: Fuel Oil System KG170-09000Александр ЩеблыкинNo ratings yet
- Extra High Voltage Ac Transmission Engineering by R D Begamudre PDFDocument2 pagesExtra High Voltage Ac Transmission Engineering by R D Begamudre PDFAllison67% (3)
- Diagramas Electricos Waukesaha - MergedDocument76 pagesDiagramas Electricos Waukesaha - MergedivanNo ratings yet
- Daily Activities Report Maintenance Baru Gas Plant & Teluk Lembu Delivery StationDocument30 pagesDaily Activities Report Maintenance Baru Gas Plant & Teluk Lembu Delivery StationMaintenance BentuNo ratings yet
- Theoretical Study of Hydrogen Bond Formation in Trimethylene Glycol-Water ComplexDocument13 pagesTheoretical Study of Hydrogen Bond Formation in Trimethylene Glycol-Water ComplexChern YuanNo ratings yet
- Pe Lab Manual 2016Document44 pagesPe Lab Manual 2016MukundKulkarniNo ratings yet
- SM00092A - NX Fault CodesDocument43 pagesSM00092A - NX Fault Codesdario_es60% (5)