Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Industrial Steam Process
Uploaded by
Pryce YurongCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Industrial Steam Process
Uploaded by
Pryce YurongCopyright:
Available Formats
Ethyl Feth V.
Sale
BSME-5
Industrial Steam Process Summary
Steam is used in a wide range of industries. Common applications for steam are, for
example, steam heated processes in plants and factories and steam driven turbines
in electric power plants, but the uses of steam in industry extend far beyond this.
Saturated and distributed at a positive pressure. In most cases, this means that it is
supplied to equipment at pressures above 0 MPaG (0 psig) and temperatures higher
than 100°C (212°F).
Heating applications for positive pressure steam can be found in food processing
factories, refineries, and chemical plants to name a few. Saturated steam is used as
the heating source for process fluid heat exchangers, reboilers, reactors, combustion
air preheaters, and other types of heat transfer equipment.
The use of steam for heating at temperatures below 100°C (212°F), traditionally the
temperature range in which hot water is used, has grown rapidly in recent years.
When vacuum saturated steam is used in the same manner as positive pressure
saturated steam, the temperature of the steam can be quickly changed by adjusting
the pressure, making it possible to achieve precise temperature control unlike
applications using hot water. However, a vacuum pump must be used in conjunction
with the equipment, because merely reducing the pressure will not drop it to below
atmospheric pressure.
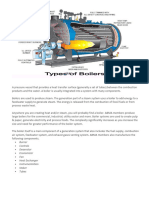
Boiler and Pressure Vessel Basics. Boilers are common devices for industrial heating
and humidification applications. Pressure vessels are typically defined as boilers or
tanks designed to operate at pressures much higher than ambient pressure, typically
delineated as greater than 15 psig.
All boilers are designed to include a heat source (furnace) and a heat ex-changer —
typically a system of tubes or piping — which allows water to be heated above its
boiling point. They may use three separate designs to accomplish water heating:
Fire-tube boilers feed hot gases through tubes connected to the furnace. The tubes
pass through a water-filled drum in order to transfer heat to the water.
Water-tube boilers feed water through a system of tubing. The tubing is surrounded
by a boiler drum filled with hot gases from the furnace; the heat in the drum is
transferred to the water tubing to generate steam.
Sectional boilers are constructed of several cast iron sections which are bolted
together. Simple sectional boilers consist of a firebox which directly heats a
corresponding water chamber.
When water is boiled into steam, it expands rapidly and can travel through tubes or
pipes at over 60 miles/hr (100 km/hr). While this results in an efficient means to
transfer energy, it can also easily cause corrosion or scaling due to improper boiler
operation or poor construction. This condition causes reduced steam quality, poor
efficiency and, under worst-case circumstances, catastrophic boiler failure. Failure is
also caused by over pressurization and insufficient water levels, the latter of which
causes overheating and vessel failure.
You might also like
- Boiler ReportDocument15 pagesBoiler Reportshridhar sutarNo ratings yet
- Steam Heat Energy Water Psi Kpa: Water-Tube Boiler Fossil Fuel-Fired Boilers Heat Recovery Boilers Heat Recovery BoilersDocument4 pagesSteam Heat Energy Water Psi Kpa: Water-Tube Boiler Fossil Fuel-Fired Boilers Heat Recovery Boilers Heat Recovery BoilersMarsNo ratings yet
- Boiler Thermo AssignmentDocument6 pagesBoiler Thermo AssignmentBassam0% (2)
- General Boiler InfoDocument14 pagesGeneral Boiler InfoHossam KhalilNo ratings yet
- Tugas Util (Boiler)Document4 pagesTugas Util (Boiler)AkhmadSumarnoNo ratings yet
- Assignment-Ali RazaDocument12 pagesAssignment-Ali RazaahsanNo ratings yet
- 1 Boiler Horse Power Is About 42Document9 pages1 Boiler Horse Power Is About 42Faaz Al WahabNo ratings yet
- Industrial Steam Boiler: ObjectiveDocument6 pagesIndustrial Steam Boiler: ObjectiveM. Hassan HaidderNo ratings yet
- #Lecture 3 - Steam GeneratorsDocument22 pages#Lecture 3 - Steam Generatorsmohamed EldesokyNo ratings yet
- Boiler TypesDocument9 pagesBoiler TypesSharif Muhammad HossainNo ratings yet
- PROCESS INDUSTRIAL CONTROL AUTOMATIC BOILERDocument17 pagesPROCESS INDUSTRIAL CONTROL AUTOMATIC BOILERPuven RanNo ratings yet
- Boiler 101: What Is A Boiler?Document2 pagesBoiler 101: What Is A Boiler?Samuel Acuña JimenezNo ratings yet
- Boiler IntroductionDocument17 pagesBoiler IntroductionDavid SilalahiNo ratings yet
- Types of BoilersDocument11 pagesTypes of Boilerscirius_cool100% (2)
- Boiler & AuxiliariesDocument13 pagesBoiler & Auxiliariesprats123456No ratings yet
- Food Process Engineering Lab 3. BOILER OPERATIONDocument22 pagesFood Process Engineering Lab 3. BOILER OPERATIONMuhyiddin Noor AfandiNo ratings yet
- Materials: Vessel Water FluidDocument8 pagesMaterials: Vessel Water FluidJinith MahajanNo ratings yet
- Introduction To BoilersDocument25 pagesIntroduction To BoilersDamith Buddhika Sri WimalarathnaNo ratings yet
- What Is A Boiler?Document40 pagesWhat Is A Boiler?prashant51No ratings yet
- BoilersDocument3 pagesBoilersatikulNo ratings yet
- Water Tube BoilerDocument8 pagesWater Tube Boilersandeep kumarNo ratings yet
- Lecture 7 - Steam Generators: Mechanics of Steam BoilersDocument7 pagesLecture 7 - Steam Generators: Mechanics of Steam BoilersIjazzzAliNo ratings yet
- Boiller Types Sabic PDFDocument40 pagesBoiller Types Sabic PDFMuhammad Hamza NaveedNo ratings yet
- Chapter Two Steam Power PlantDocument42 pagesChapter Two Steam Power PlantPercy Aduviri FloresNo ratings yet
- Steam BoilerDocument7 pagesSteam BoilerVishnu VardhanNo ratings yet
- 2.1. Marine Boilers PDFDocument48 pages2.1. Marine Boilers PDFBasong San67% (3)
- Materials: Pressure Vessel Steel Wrought Iron Stainless Steel Live Steam Copper Brass Fireboxes Steam LocomotivesDocument10 pagesMaterials: Pressure Vessel Steel Wrought Iron Stainless Steel Live Steam Copper Brass Fireboxes Steam LocomotivesVelampalli AshokNo ratings yet
- L&T ManualDocument60 pagesL&T ManualDineshNo ratings yet
- Thermal Power Plants: Assignment No 1 Boilers 17-MS-PT-PE (T) - 20 Muneeb Ur Rehman KhanDocument8 pagesThermal Power Plants: Assignment No 1 Boilers 17-MS-PT-PE (T) - 20 Muneeb Ur Rehman KhanSuper SiangohanNo ratings yet
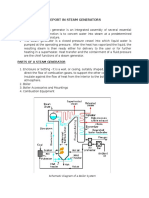
- Report in Steam Generators: Schematic Diagram of A Boiler SystemDocument18 pagesReport in Steam Generators: Schematic Diagram of A Boiler SystemZa YonNo ratings yet
- Steam Power PlantDocument39 pagesSteam Power PlantizharizumieNo ratings yet
- Waste Heat RecoveryDocument11 pagesWaste Heat RecoveryKashifKhan100% (1)
- Expo Calor InglesDocument3 pagesExpo Calor InglesJessica Andrea CalderonNo ratings yet
- Physical Study of A Steam Generating UnitDocument13 pagesPhysical Study of A Steam Generating Unitashier dave calulot80% (5)
- Assignment 1Document4 pagesAssignment 1Hamood AhmadNo ratings yet
- Boiler:: Working Principle of A BoilerDocument22 pagesBoiler:: Working Principle of A BoilerZeshan AbdullahNo ratings yet
- Boiler: MaterialsDocument10 pagesBoiler: MaterialssarojpapuNo ratings yet
- Heat GeneratorDocument6 pagesHeat GeneratorZac Ryan CasteloNo ratings yet
- Boiler Flame Remote Adjustment System RepDocument41 pagesBoiler Flame Remote Adjustment System RepSiva KumarNo ratings yet
- Lecture 7 - Steam GeneratorsDocument6 pagesLecture 7 - Steam GeneratorsHussain Abbas100% (1)
- Coal-Based Electricity ProductionDocument11 pagesCoal-Based Electricity ProductionkirannainwalNo ratings yet
- Water-Tube Boilers - International Site For Spirax SarcoDocument7 pagesWater-Tube Boilers - International Site For Spirax SarcotahirNo ratings yet
- Report On Jenco Thermal Power PlantDocument18 pagesReport On Jenco Thermal Power PlantMuhammadAbbasJafriNo ratings yet
- Boiler: For The Limp Bizkit Song, SeeDocument12 pagesBoiler: For The Limp Bizkit Song, SeeMahesh G RajuNo ratings yet
- Boiler or Steam Generators 2020Document9 pagesBoiler or Steam Generators 2020Kaiser CarloNo ratings yet
- Chapter Three: Steam Generators 3.1 DefinitionDocument43 pagesChapter Three: Steam Generators 3.1 DefinitionHeber Farid Fabrica Quispe100% (1)
- Boilers: Espiritu, Christopher James Managuit, John Jeruel Querubin, Russel JohnDocument43 pagesBoilers: Espiritu, Christopher James Managuit, John Jeruel Querubin, Russel JohnRussel John Morillo Querubin100% (1)
- Macam Macam Ketel UapDocument8 pagesMacam Macam Ketel UapDwi CahyonoNo ratings yet
- Boiler Cont.Document9 pagesBoiler Cont.adnan mukhtarNo ratings yet
- Heat-Recovery Water Heating: OpportunitiesDocument6 pagesHeat-Recovery Water Heating: OpportunitiesDivyanshu AgrawalNo ratings yet
- Thermal power plant economiser guideDocument7 pagesThermal power plant economiser guideSteve M D'souzaNo ratings yet
- Fire Water Tube BoilerDocument12 pagesFire Water Tube BoilerFatma HelalNo ratings yet
- BoilerDocument90 pagesBoilerMargaret DaughertyNo ratings yet
- Boiler Tech.Document1 pageBoiler Tech.osbertanyamele25No ratings yet
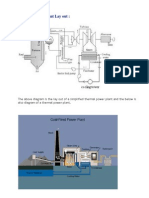
- Thermal Power Plant Lay OutDocument8 pagesThermal Power Plant Lay OutSaheli ChoudhuriNo ratings yet
- Boiler Design and Operation PDFDocument8 pagesBoiler Design and Operation PDFChungNguyenNo ratings yet
- Mechanics of the Household: A Course of Study Devoted to Domestic Machinery and Household Mechanical AppliancesFrom EverandMechanics of the Household: A Course of Study Devoted to Domestic Machinery and Household Mechanical AppliancesNo ratings yet
- How it Works: Dealing in simple language with steam, electricity, light, heat, sound, hydraulics, optics, etc., and with their applications to apparatus in common useFrom EverandHow it Works: Dealing in simple language with steam, electricity, light, heat, sound, hydraulics, optics, etc., and with their applications to apparatus in common useNo ratings yet
- The Complete HVAC BIBLE for Beginners: The Most Practical & Updated Guide to Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning Systems | Installation, Troubleshooting and Repair | Residential & CommercialFrom EverandThe Complete HVAC BIBLE for Beginners: The Most Practical & Updated Guide to Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning Systems | Installation, Troubleshooting and Repair | Residential & CommercialNo ratings yet
- Design and Fabrication of Vertical Axis Wind TurbineDocument20 pagesDesign and Fabrication of Vertical Axis Wind TurbinePryce YurongNo ratings yet
- Design and Fabrication of Vertical Axis Wind TurbineDocument20 pagesDesign and Fabrication of Vertical Axis Wind TurbinePryce YurongNo ratings yet
- NAME: Vincent Rey Olario: Bsme - 5Document11 pagesNAME: Vincent Rey Olario: Bsme - 5Pryce YurongNo ratings yet
- 2nd Assignment Sa Ipe 2Document9 pages2nd Assignment Sa Ipe 2Pryce YurongNo ratings yet
- Chapter II RRLDocument5 pagesChapter II RRLPryce YurongNo ratings yet
- PROBLEM 4. A Generation Station of 1MW Supplied A Region Which Has The FollowingDocument2 pagesPROBLEM 4. A Generation Station of 1MW Supplied A Region Which Has The FollowingBensoyNo ratings yet
- Chapter II RRLDocument5 pagesChapter II RRLPryce YurongNo ratings yet
- Panel FV 275W KuhnDocument4 pagesPanel FV 275W KuhnNicolas SandovalNo ratings yet
- 10kw Hybrid System 57 6kwhDocument1 page10kw Hybrid System 57 6kwhardeasgrNo ratings yet
- On-Grid Solar System Saves Over Rs. 1 CroreDocument17 pagesOn-Grid Solar System Saves Over Rs. 1 CroreAHC IIAPNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 Geothermal Energy CTDocument33 pagesChapter 6 Geothermal Energy CTAdreana AmirahNo ratings yet
- Six Stroke Engine PresenationDocument33 pagesSix Stroke Engine PresenationshubhamNo ratings yet
- Steam TurbineDocument29 pagesSteam Turbine최승원100% (1)
- C5008098319 PDFDocument5 pagesC5008098319 PDFRamkishan SahuNo ratings yet
- Feed Water and Boiler Water of Steam GeneratorsDocument2 pagesFeed Water and Boiler Water of Steam GeneratorsIvicaT0% (2)
- Technical Guide Steam BoilersDocument343 pagesTechnical Guide Steam Boilersİbrahim Altan100% (11)
- Engine BlockDocument19 pagesEngine BlockBHAVESH JOSHINo ratings yet
- LMZ ReferenceDocument40 pagesLMZ ReferencesmitapadmapatNo ratings yet
- City and Guilds 9210 Level 6 Module - Unit 128 Applied ThermodynamicsDocument13 pagesCity and Guilds 9210 Level 6 Module - Unit 128 Applied ThermodynamicskhumisoNo ratings yet
- Book 9HA CCPP Operations Training at AEPLDocument174 pagesBook 9HA CCPP Operations Training at AEPLFazalur Rehman Babar100% (2)
- Ocean Energy GuideDocument7 pagesOcean Energy GuidehasanNo ratings yet
- Cost of Setting Up A 1MW Solar Plant in AndhraDocument3 pagesCost of Setting Up A 1MW Solar Plant in Andhrasreeramk13No ratings yet
- Gate Pass CancellationDocument2 pagesGate Pass CancellationArush SrivastavaNo ratings yet
- COG July August 2012Document110 pagesCOG July August 2012confyNo ratings yet
- WorkingsDocument13 pagesWorkingsuaminu422No ratings yet
- pp02 PDFDocument1 pagepp02 PDFc.a.g.p.No ratings yet
- Modelling and Simulation of Photovoltaic (PV) System During Partial Shading Based On A Two-Diode ModelDocument19 pagesModelling and Simulation of Photovoltaic (PV) System During Partial Shading Based On A Two-Diode ModelAnjali PriyadarsiniNo ratings yet
- Performance Test of Pelton TurbineDocument6 pagesPerformance Test of Pelton TurbineMd. Tariqul Islam MunnaNo ratings yet
- Water Jacket Curves - C7.1 Marine Propulsion EngineDocument3 pagesWater Jacket Curves - C7.1 Marine Propulsion EnginejudarangocaNo ratings yet
- INSPECTION OF STEAM BOILERS: KEY STEPS AND PROCEDURESDocument2 pagesINSPECTION OF STEAM BOILERS: KEY STEPS AND PROCEDURESavksk22No ratings yet
- TP CASABLANCA - Project - VC0-Report 1Document7 pagesTP CASABLANCA - Project - VC0-Report 1Manal ElkerzaziNo ratings yet
- Applications, Evaluations and Supportive Strategies of Distributed Energy Systems - A ReviewDocument19 pagesApplications, Evaluations and Supportive Strategies of Distributed Energy Systems - A ReviewKentner Chavez CorreaNo ratings yet
- TP01 5Document1 pageTP01 5oussamaNo ratings yet
- Excitation Failure: o o o oDocument2 pagesExcitation Failure: o o o oAbdulyunus AmirNo ratings yet
- Check Engine Compression with a Cranking Compression TestDocument1 pageCheck Engine Compression with a Cranking Compression TesttiaNo ratings yet
- Thermoelectric Peltier Cooler Module SelectionDocument5 pagesThermoelectric Peltier Cooler Module SelectionAditya DoyaleNo ratings yet
- 1-Ic EngineDocument66 pages1-Ic EngineTOBIN THOMAS ME100% (1)