Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Project
Uploaded by
Chonalyn Lorenzo0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
14 views10 pagesThis document discusses factors that affect the speed and distance of objects in free fall. It states that free fall is the downward movement of an object under the influence of Earth's gravitational force. The main factors mentioned are air resistance, velocity, the object's shape and surface area, and the angle at which it is thrown. Key terms defined include projectile, projectile motion, trajectory, horizontal motion, and vertical motion.
Original Description:
Original Title
project
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document discusses factors that affect the speed and distance of objects in free fall. It states that free fall is the downward movement of an object under the influence of Earth's gravitational force. The main factors mentioned are air resistance, velocity, the object's shape and surface area, and the angle at which it is thrown. Key terms defined include projectile, projectile motion, trajectory, horizontal motion, and vertical motion.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
14 views10 pagesProject
Uploaded by
Chonalyn LorenzoThis document discusses factors that affect the speed and distance of objects in free fall. It states that free fall is the downward movement of an object under the influence of Earth's gravitational force. The main factors mentioned are air resistance, velocity, the object's shape and surface area, and the angle at which it is thrown. Key terms defined include projectile, projectile motion, trajectory, horizontal motion, and vertical motion.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 10
UAM in Vertical Motion
What factors do you think
affect the speed and distance
of an object in free fall?
FREE FALL
The downward movement of an object, under the influence
of the gravitational force of the earth, is called free fall.
Acceleration due to gravity: The acceleration produced in a
body that is falling freely, under the influence of the
gravitational force of the earth is called the acceleration
due to gravity 'g'.
Free fall occurs where the only force acting
on an object is gravity. Because
gravitational acceleration on earth is
constant, the distance an object falls is
proportional to the time spent falling.
The elements involved in falling can affect it in
different ways. The first of these elements is air
resistance. Other elements include velocity, the
shape and surface area of the object, and the
angle at which the object is thrown.
Air resistance is also known as drag, is a kind of friction (a
force that opposes motion) which occurs between air and
another object. It is the force that the object experiences as
it passes through the air.
TERMS:
Projetile – any object that once projected or dropped continues in motion by its own
inertia and is influenced only by the downward force of gravity.
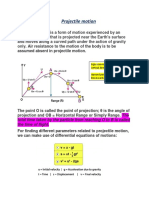
Projectile motion – is a form of motion in which an object or projectile is thrown near
the Earth’s surface and it moves along curved path under the action of gravity ONLY.
Trajectory – curved path
Horizontal Motion – motion of a ball rolling freely along a level surface
Vertical Motion - motion of a freely falling object; force due to gravity
You might also like
- The Legends of The SarimanokDocument6 pagesThe Legends of The SarimanokChonalyn LorenzoNo ratings yet
- Q4-W1-Free-falling Object and Projectile MotionDocument17 pagesQ4-W1-Free-falling Object and Projectile Motionluispacifico.pagkalinawanNo ratings yet
- Projectile MotionDocument15 pagesProjectile MotionFaith GuballaNo ratings yet
- Spectrum Reading - Grade 6 EbookDocument22 pagesSpectrum Reading - Grade 6 Ebookmony.mohamed.89No ratings yet
- Free Fall - Common Term For Any Motion That, in Theory, IsDocument1 pageFree Fall - Common Term For Any Motion That, in Theory, IsJhune Dominique GalangNo ratings yet
- Force Causes Change in Motion By: Avigael MarayaDocument18 pagesForce Causes Change in Motion By: Avigael MarayaHazel LiporadaNo ratings yet
- Initial VelocityDocument1 pageInitial VelocityWakee Bautista MangawerzNo ratings yet
- Friction and Gravity LessonDocument21 pagesFriction and Gravity LessonPaul100% (1)
- Free Fall: Mass WeightDocument5 pagesFree Fall: Mass WeightChuchuLoloNo ratings yet
- Reviewer ScienceDocument2 pagesReviewer ScienceKeizer FiscoNo ratings yet
- Get 229 - Class SevenDocument24 pagesGet 229 - Class SevenAbdulfattah AbdulsalamNo ratings yet
- Friction and GravityDocument15 pagesFriction and Gravityapi-325945020No ratings yet
- Caida LibreDocument3 pagesCaida LibreLuis Angel BárcenasNo ratings yet
- Projectile MotionDocument4 pagesProjectile Motiondhany aarunNo ratings yet
- Force EditedDocument20 pagesForce EditedCirille AgpaoaNo ratings yet
- Free Fall and Circular MotionDocument1 pageFree Fall and Circular MotionZenly AlleraNo ratings yet
- g9 ReviewerDocument1 pageg9 ReviewerrubeneciavNo ratings yet
- Projectile MotionDocument22 pagesProjectile MotionHarshVasoya100% (1)
- Chapter 3 Section 1 Newton's Second LawDocument16 pagesChapter 3 Section 1 Newton's Second LawMelissa MilfordNo ratings yet
- Att a7S5je88MkmQqc1hXrTbWuWrBwq1lUPl5RL8ltVMsIwDocument3 pagesAtt a7S5je88MkmQqc1hXrTbWuWrBwq1lUPl5RL8ltVMsIwprincesssophia020709No ratings yet
- Grade 9 - Science (PROJECTILE MOTION)Document21 pagesGrade 9 - Science (PROJECTILE MOTION)Mae CalaraNo ratings yet
- Aristotelian and Galilean Concepts On MotionDocument25 pagesAristotelian and Galilean Concepts On MotionPacalso Mark Roldan VizcarraNo ratings yet
- Forceandmotion 181112055529Document36 pagesForceandmotion 181112055529FernandoNo ratings yet
- Motion Under GravityDocument1 pageMotion Under Gravityanonymousisabelle2009No ratings yet
- Kinematics in Two DiamensionsDocument34 pagesKinematics in Two Diamensionsemanuel coatesNo ratings yet
- Force Flash CardsDocument2 pagesForce Flash CardsMaki ShurikenNo ratings yet
- What Is A Projectile?: Unit 1 Unit 2Document4 pagesWhat Is A Projectile?: Unit 1 Unit 2Josh Achaso LabragueNo ratings yet
- Study Guide For Yr 7 PhyDocument1 pageStudy Guide For Yr 7 PhyJOY BOYNo ratings yet
- Understanding Gravity - PHYSICS FORM 4Document23 pagesUnderstanding Gravity - PHYSICS FORM 4Noor100% (3)
- Projectile MotionDocument22 pagesProjectile MotionChris PuelasNo ratings yet
- Projectile MotionDocument15 pagesProjectile MotionAnkit ChoudharyNo ratings yet
- Projectile Motion 2Document15 pagesProjectile Motion 2Ayman EidNo ratings yet
- Genphysics1 Lesson 2Document19 pagesGenphysics1 Lesson 2Ariane AngelesNo ratings yet
- Practical 2: Contact Forces Action-at-a-Distance ForcesDocument18 pagesPractical 2: Contact Forces Action-at-a-Distance ForcespersonwithheartNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 Lesson 2 Gravity and Friction 2020Document4 pagesUnit 1 Lesson 2 Gravity and Friction 2020Hasheema Al SulamiNo ratings yet
- Phys 10 Unit1Document58 pagesPhys 10 Unit1HanaNo ratings yet
- What Is A Projectile?: Defining ProjectilesDocument3 pagesWhat Is A Projectile?: Defining ProjectilesJeje NutNo ratings yet
- Esc 17 1Document21 pagesEsc 17 1elaco56No ratings yet
- Aristotelian vs. Galilean Views of MotionDocument1 pageAristotelian vs. Galilean Views of MotionCharisse Mendoza100% (1)
- Physical Science ReportDocument27 pagesPhysical Science ReportKryzhna Jalyn EribalNo ratings yet
- Sub Lesson 2Document13 pagesSub Lesson 2Ashutosh Kumar SinghNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3 - Free-Body DiagramDocument8 pagesLecture 3 - Free-Body DiagramMarjorie Jean AnogNo ratings yet
- Forces & Motion - NotesDocument5 pagesForces & Motion - NotesMr : NADe?RNo ratings yet
- Terminal VelocityDocument7 pagesTerminal VelocitymvtbalanNo ratings yet
- ProjectileDocument18 pagesProjectileMehs AishiteruNo ratings yet
- T2 S 211 Types of Forces Display Posters - Ver - 2Document6 pagesT2 S 211 Types of Forces Display Posters - Ver - 2Minerva MamdouhNo ratings yet
- Projectile Motion: Motion in Two DimensionsDocument17 pagesProjectile Motion: Motion in Two DimensionsCarenn San JuanNo ratings yet
- Friction and GravityDocument15 pagesFriction and GravityAshton MartinNo ratings yet
- Force and PressureDocument36 pagesForce and PressureBhuvaneswari BalaNo ratings yet
- Force and MotionDocument115 pagesForce and MotionMyra Ramirez Ramos90% (10)
- Meaning of Force: Definition of Force and The Type of ForcesDocument15 pagesMeaning of Force: Definition of Force and The Type of ForcesDASH100% (1)
- Type of Force Description of ForceDocument2 pagesType of Force Description of Forcezaiayra71No ratings yet
- Template Recovered File 2Document18 pagesTemplate Recovered File 2Nathaniel Shawn L. DukaNo ratings yet
- 7th Lesson Newtons Laws of MotionDocument27 pages7th Lesson Newtons Laws of MotionMRmister123No ratings yet
- Second Quarter - Lesson 3Document31 pagesSecond Quarter - Lesson 3Emanuel MacasoNo ratings yet
- Science Grade 6 CDCDocument3 pagesScience Grade 6 CDCVlad VizcondeNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1.4 - Projectile MotionDocument2 pagesLesson 1.4 - Projectile MotionLourraine GaldonesNo ratings yet
- Dynamics 2Document49 pagesDynamics 2Zubair FarooqNo ratings yet
- Terminal Velocity and ProjectilesDocument2 pagesTerminal Velocity and ProjectilesKariye Knowmore KalungaNo ratings yet
- Types of ForcesDocument3 pagesTypes of Forcesaleakim13XDNo ratings yet
- EcologicalDocument27 pagesEcologicalChonalyn LorenzoNo ratings yet
- Ecological RelationshipDocument35 pagesEcological RelationshipChonalyn LorenzoNo ratings yet
- Respiratory SystemDocument31 pagesRespiratory SystemChonalyn LorenzoNo ratings yet
- Final-DNA-vs-RNA EditedDocument20 pagesFinal-DNA-vs-RNA EditedChonalyn LorenzoNo ratings yet
- ClimateDocument22 pagesClimateChonalyn LorenzoNo ratings yet
- Constellations Rev5Document32 pagesConstellations Rev5Chonalyn LorenzoNo ratings yet
- What Is The Scientific MethodDocument4 pagesWhat Is The Scientific MethodChonalyn LorenzoNo ratings yet