Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Projectile Motion
Uploaded by
dhany aarun0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
61 views4 pagesProjectile motion describes the path of an object thrown near Earth's surface under the influence of gravity alone. The object follows a curved trajectory. Gravity accelerates the object downward at a rate of 9.8 m/s^2, but does not affect its horizontal motion. The time of flight, horizontal range, and maximum height can be calculated using equations that consider the object's initial velocity, launch angle, and gravitational acceleration.
Original Description:
Notes
Original Title
projectile motion
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentProjectile motion describes the path of an object thrown near Earth's surface under the influence of gravity alone. The object follows a curved trajectory. Gravity accelerates the object downward at a rate of 9.8 m/s^2, but does not affect its horizontal motion. The time of flight, horizontal range, and maximum height can be calculated using equations that consider the object's initial velocity, launch angle, and gravitational acceleration.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
61 views4 pagesProjectile Motion
Uploaded by
dhany aarunProjectile motion describes the path of an object thrown near Earth's surface under the influence of gravity alone. The object follows a curved trajectory. Gravity accelerates the object downward at a rate of 9.8 m/s^2, but does not affect its horizontal motion. The time of flight, horizontal range, and maximum height can be calculated using equations that consider the object's initial velocity, launch angle, and gravitational acceleration.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 4
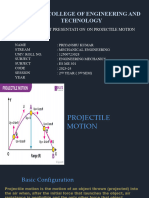
Projectile motion
Projectile motion is a form of motion experienced by an
object or particle that is projected near the Earth's surface
and moves along a curved path under the action of gravity
only. Air resistance to the motion of the body is to be
assumed absent in projectile motion.
Signs convention for velocities in
vertical direction
Upward positive
Downward negative
The point O is called the point of projection; θ is the angle of
projection and OB = Horizontal Range or Simply Range. The
total time taken by the particle from reaching O to B is called
the time of flight.
For finding different parameters related to projectile motion,
we can make use of differential equations of motions:
Accelerations in the horizontal projectile motion and vertical
projectile motion of a particle: When a particle is projected in
the air with some speed, the only force acting on it during its
time in the air is the acceleration due to gravity (g). This
acceleration acts vertically downward. There is no
acceleration in the horizontal direction, which means that the
velocity of the particle in the horizontal direction remains
constant.
Total Time of Flight:
Resultant displacement (s) = 0 in Vertical direction.
Therefore, by using the Equation of motion:
Horizontal Range: R
Horizontal Range (OA) = Horizontal component of velocity
(ux) × Total Flight Time (t)
Maximum Height:H
It is the highest point of the trajectory (point A). When the
ball is at point A, the vertical component of the velocity will
be zero.
You might also like
- 2 Motion in 2&3 DimensionsDocument26 pages2 Motion in 2&3 Dimensionsumer iqbalNo ratings yet
- Kinematics in Two DiamensionsDocument34 pagesKinematics in Two Diamensionsemanuel coatesNo ratings yet
- Projectile Motion1Document22 pagesProjectile Motion1MaRk Kenchi100% (2)
- Dynamics of Rigid BodiesDocument14 pagesDynamics of Rigid Bodiesrachelle rivadullaNo ratings yet
- Projectile MotionDocument32 pagesProjectile MotionJoyce EstrevencionNo ratings yet
- Projectile MotionDocument15 pagesProjectile MotionAnkit ChoudharyNo ratings yet
- Projectile Motion 2Document15 pagesProjectile Motion 2Ayman EidNo ratings yet
- Projectile MotionDocument15 pagesProjectile MotionFaith GuballaNo ratings yet
- Reviewer ScienceDocument2 pagesReviewer ScienceKeizer FiscoNo ratings yet
- Projectile MotionDocument14 pagesProjectile MotionMia Lorena JandocNo ratings yet
- PhysicsDocument5 pagesPhysicskrNo ratings yet
- ProjectDocument10 pagesProjectChonalyn LorenzoNo ratings yet
- Projectile MotionDocument10 pagesProjectile MotionAmmar IbrahimNo ratings yet
- Naveen Kumar PPT On Projectile MotionDocument17 pagesNaveen Kumar PPT On Projectile MotionBARUN SINGHNo ratings yet
- Q4-W1-Free-falling Object and Projectile MotionDocument17 pagesQ4-W1-Free-falling Object and Projectile Motionluispacifico.pagkalinawanNo ratings yet
- Motion in 2 DimensionsDocument33 pagesMotion in 2 DimensionsHoney Grace Dela CernaNo ratings yet
- Applied Physics Lab Complex Engineering Activity (Cea) SolutionDocument4 pagesApplied Physics Lab Complex Engineering Activity (Cea) SolutionAbdul SamadNo ratings yet
- Projectile MotionDocument4 pagesProjectile MotionaliNo ratings yet
- Projectile Motion NewDocument27 pagesProjectile Motion NewAnandraj GovindarajNo ratings yet
- Cntent 1234Document23 pagesCntent 1234anujNo ratings yet
- Math Investigatory ProjectDocument9 pagesMath Investigatory ProjectKavinn100% (1)
- Motion in Two Dimensions - CeLOEDocument24 pagesMotion in Two Dimensions - CeLOEMuhammad GustianNo ratings yet
- Kinematics of TranslationDocument5 pagesKinematics of TranslationMarjorie Anne Pazcoguin MarcaydaNo ratings yet
- Science 9 19.1 Horizontal ProjectilesDocument30 pagesScience 9 19.1 Horizontal ProjectilesCutszNo ratings yet
- Projectile Motion Launched at An AngleDocument20 pagesProjectile Motion Launched at An AngleArgel EvangelistaNo ratings yet
- Genphysics1 Lesson 2Document19 pagesGenphysics1 Lesson 2Ariane AngelesNo ratings yet
- Projectile MotionDocument8 pagesProjectile MotionBaltazar MarcosNo ratings yet
- Projectile MotionDocument218 pagesProjectile MotionMarielleNo ratings yet
- Physics: Note 3: RecallDocument5 pagesPhysics: Note 3: RecallLuis GonzalesNo ratings yet
- Science ActivityDocument3 pagesScience Activitymark caleb gulpricNo ratings yet
- Chapter TwoDocument80 pagesChapter TwoMekashaw AndargeNo ratings yet
- KINEMATICSDocument27 pagesKINEMATICSHhitika KapoorNo ratings yet
- Types of Motion: Five Kinematic EquationsDocument2 pagesTypes of Motion: Five Kinematic EquationsAngelaNo ratings yet
- Projectile and Circulatory Motion NotesDocument6 pagesProjectile and Circulatory Motion NotesAditya MauriyaNo ratings yet
- Projectile MotionDocument91 pagesProjectile MotionPrecious BalgunaNo ratings yet
- Projectile Motion II (Science Presentation)Document17 pagesProjectile Motion II (Science Presentation)dempearl2315No ratings yet
- Science ReviewerDocument4 pagesScience Reviewermelody multifanNo ratings yet
- Laboratory Report: Experiment # 5Document9 pagesLaboratory Report: Experiment # 5Juliana Mickaela MercadoNo ratings yet
- 02 Projectiles and Variable Acceleration HANDOUTDocument16 pages02 Projectiles and Variable Acceleration HANDOUTaioplayz951No ratings yet
- Phys 10 Unit1Document58 pagesPhys 10 Unit1HanaNo ratings yet
- g9 ReviewerDocument1 pageg9 ReviewerrubeneciavNo ratings yet
- Relative MotionDocument5 pagesRelative MotionMaria Lourdes MagtaasNo ratings yet
- ProjectileDocument18 pagesProjectileMehs AishiteruNo ratings yet
- Non-Uniform Linear MotionDocument31 pagesNon-Uniform Linear MotionDini Eka Lanjar SaputriNo ratings yet
- Bernoulli Vs Newton: Lift Vs DragDocument4 pagesBernoulli Vs Newton: Lift Vs DragABHIJEETNo ratings yet
- Year 11 Autumn NotesDocument14 pagesYear 11 Autumn NotesPatrick Chukwunonso A.No ratings yet
- Additional Theory Inclined PlaneDocument2 pagesAdditional Theory Inclined PlaneMuhd RusyaidiNo ratings yet
- Lec 4 - Motion in 2 DDocument40 pagesLec 4 - Motion in 2 DJugesh KumarNo ratings yet
- Year 11 Autumn Notes UpdatedDocument21 pagesYear 11 Autumn Notes UpdatedPatrick Chukwunonso A.No ratings yet
- Projectile MotionDocument50 pagesProjectile MotionHazel Cosep RicoNo ratings yet
- Projectile Motion 2Document53 pagesProjectile Motion 2akhNo ratings yet
- Plugin ProjectileCircularMotionNotDocument2 pagesPlugin ProjectileCircularMotionNotMoon XyleNo ratings yet
- Dynamic Meteorology 5Document32 pagesDynamic Meteorology 5ADNo ratings yet
- REVIEWERDocument1 pageREVIEWERJanna PiqueroNo ratings yet
- Experiment 5 - Projectile Motion Mathematical Description of Projectile MotionDocument5 pagesExperiment 5 - Projectile Motion Mathematical Description of Projectile MotionmusabNo ratings yet
- Att a7S5je88MkmQqc1hXrTbWuWrBwq1lUPl5RL8ltVMsIwDocument3 pagesAtt a7S5je88MkmQqc1hXrTbWuWrBwq1lUPl5RL8ltVMsIwprincesssophia020709No ratings yet
- Motion Under GravityDocument1 pageMotion Under Gravityanonymousisabelle2009No ratings yet
- Mod 7Document7 pagesMod 7S M AkashNo ratings yet
- PDF Projectile MotionDocument23 pagesPDF Projectile Motionlorenzomaster530No ratings yet
- Class Test 1Document2 pagesClass Test 1dhany aarunNo ratings yet
- Biology QnsDocument7 pagesBiology Qnsdhany aarunNo ratings yet
- Energy FormsDocument6 pagesEnergy Formsdhany aarunNo ratings yet
- Radioactivity - Nuclear Physics NOTEsDocument9 pagesRadioactivity - Nuclear Physics NOTEsdhany aarunNo ratings yet
- Second Sem DefinitionsDocument4 pagesSecond Sem Definitionsdhany aarunNo ratings yet
- Force On A Current Carrying Wire QnsDocument1 pageForce On A Current Carrying Wire Qnsdhany aarunNo ratings yet
- The Energy Finally Stored by The Capacitor?Document12 pagesThe Energy Finally Stored by The Capacitor?dhany aarunNo ratings yet
- Capacitance - MCQ: Dhanya ArunDocument8 pagesCapacitance - MCQ: Dhanya Arundhany aarunNo ratings yet
- Electrical Quantities 6 QPDocument13 pagesElectrical Quantities 6 QPdhany aarunNo ratings yet
- Converting Between Metric UnitsDocument2 pagesConverting Between Metric Unitsdhany aarunNo ratings yet
- Hooke's Law (Multiple Choice) QPDocument8 pagesHooke's Law (Multiple Choice) QPdhany aarunNo ratings yet