Professional Documents
Culture Documents
June 5
June 5
Uploaded by
Mhyr Pielago Camba0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
4 views5 pagesGregor Mendel developed the principles of inheritance through experiments with garden peas before the discovery of genes. He described the transmission of genetic traits from one generation to the next. Later, Punnett and Bateson discovered fundamental genetic processes like linkage and sex determination through experiments with poultry and sweet peas. Genetics is the study of heredity and the factors that affect the transmission of genes between generations. Key terms include phenotype, genotype, allele, gene, dominant, recessive, homozygous, heterozygous, and dihybrid cross.
Original Description:
Original Title
june 5 PPT
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentGregor Mendel developed the principles of inheritance through experiments with garden peas before the discovery of genes. He described the transmission of genetic traits from one generation to the next. Later, Punnett and Bateson discovered fundamental genetic processes like linkage and sex determination through experiments with poultry and sweet peas. Genetics is the study of heredity and the factors that affect the transmission of genes between generations. Key terms include phenotype, genotype, allele, gene, dominant, recessive, homozygous, heterozygous, and dihybrid cross.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
4 views5 pagesJune 5
June 5
Uploaded by
Mhyr Pielago CambaGregor Mendel developed the principles of inheritance through experiments with garden peas before the discovery of genes. He described the transmission of genetic traits from one generation to the next. Later, Punnett and Bateson discovered fundamental genetic processes like linkage and sex determination through experiments with poultry and sweet peas. Genetics is the study of heredity and the factors that affect the transmission of genes between generations. Key terms include phenotype, genotype, allele, gene, dominant, recessive, homozygous, heterozygous, and dihybrid cross.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 5
Gregor Mendel developed
three principles of inheritance
that described the
transmission of genetic traits,
before anyone knew genes
existed.
Garden peas (Pisum sativum)
Using poultry and sweet
peas, Punnett and
Bateson discovered some
of the fundamental
processes of Mendelian
genetics, including
linkage, sex
determination, sex
linkage, and the first
example of autosomal
(nonsexual chromosome)
linkage.
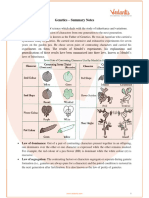
Genetics is the study of heredity and the factors
that affect the transmission of genes to
determine inherited characters from one
generation to the next.
Heredity is the transfer of traits genes from
parents to offspring.
Monohybrid Cross is the hybrid of two
individuals with homozygous genotypes which
result in the opposite phenotype for a certain
genetic trait.”
Phenotype is an individual's observable traits, such as
height, eye color and blood type.
Genotype is the genetic makeup of an organism.
Allele is one of two or more versions of DNA sequence
at a given genomic location.
Gene is the basic physical and functional unit of
heredity.
Dominant is the inheritance of traits that are typically
passed vertically from parent to child where both the
parent and the child are affected by the trait or disorder
that is related to that gene.
Recessive traits a trait that tends to be masked
by other inherited traits yet persists in a
population among heterozygous genotypes.
Homozygous/Homozygote is the presence of two
identical alleles at a particular gene locus.
Heterozygous/Heterozygote is the presence of
two different alleles at a particular gene locus.
Dihybrid Cros is a mating experiment between
two organisms that are identically hybrid for two
traits.
You might also like
- Chapter 2 International Trade and InvestmentDocument8 pagesChapter 2 International Trade and InvestmentMhyr Pielago Camba100% (1)
- Genetics in OrthodonticsDocument63 pagesGenetics in OrthodonticsPrachi Madan100% (20)
- Psychology - Genetics (Gregor Mendel)Document38 pagesPsychology - Genetics (Gregor Mendel)Kueni MariNo ratings yet
- 5 Principles of Inheritance and VariationDocument7 pages5 Principles of Inheritance and VariationPreeti AgrawalNo ratings yet
- ACFrOgAfRr3sSsuCAkrajXlVJlNW9CEtIjaaAShbzz53F - BV5yV6DzQdxtAJFRZXXlCzNJ2z436IplXhlNZcLstm s3JGzE2BiehEN5Wj1zYDQg1luLD89ztag DeLdXlbq5Nbv38FIU g05ICjDocument32 pagesACFrOgAfRr3sSsuCAkrajXlVJlNW9CEtIjaaAShbzz53F - BV5yV6DzQdxtAJFRZXXlCzNJ2z436IplXhlNZcLstm s3JGzE2BiehEN5Wj1zYDQg1luLD89ztag DeLdXlbq5Nbv38FIU g05ICjCarl SeanNo ratings yet
- 9 InheritanceDocument6 pages9 InheritanceTalita KumalaNo ratings yet
- All Goods in The Hood 1Document17 pagesAll Goods in The Hood 1Rj EstabilloNo ratings yet
- Laws of Inheritance, Segregation, Assortment.Document14 pagesLaws of Inheritance, Segregation, Assortment.Hannah Charis L. BarabatNo ratings yet
- 9 InheritanceDocument6 pages9 InheritancePeter TingNo ratings yet
- ProjectDocument15 pagesProjectVaishakhi MuraliNo ratings yet
- Biology ProjectDocument11 pagesBiology ProjectAgnivo SahaNo ratings yet
- Genetic ReasoningDocument33 pagesGenetic ReasoningKeithdeLeonNo ratings yet
- 20 Biology of Heredity1700146491Document4 pages20 Biology of Heredity1700146491gbotemiajayi2009No ratings yet
- MODULE 1-GeneticsDocument13 pagesMODULE 1-GeneticsDivine Grace CincoNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Genetics Unit 3Document19 pagesIntroduction To Genetics Unit 3Vanee Gzz100% (1)
- Behavior GeneticsDocument3 pagesBehavior GeneticsNazreen S MNo ratings yet
- HeritageDocument11 pagesHeritagebrylledelayunNo ratings yet
- Heredity Line by LineDocument48 pagesHeredity Line by LineamaanmirzarollnoNo ratings yet
- GENETICSDocument5 pagesGENETICSYassine OUEDRAOGONo ratings yet
- 03 Laporan Genetika IMITASI RATIO FENOTIPEDocument8 pages03 Laporan Genetika IMITASI RATIO FENOTIPEhananNo ratings yet
- Principle of Inheritance and VeriationDocument21 pagesPrinciple of Inheritance and VeriationMohammed Anas ShaikhNo ratings yet
- Genetics Principle of HeredityDocument3 pagesGenetics Principle of HeredityBurning RoseNo ratings yet
- Genetics and HeredityDocument6 pagesGenetics and HeredityRenjyl Gay DeguinionNo ratings yet
- Genetic Counselling: The University of Sheffield 2010Document22 pagesGenetic Counselling: The University of Sheffield 2010amal 84No ratings yet
- Genetics and Heredity Margie de LeonDocument56 pagesGenetics and Heredity Margie de LeonCarmsNo ratings yet
- Heredity and Inherited TraitsDocument5 pagesHeredity and Inherited TraitsblehblehdadaNo ratings yet
- Introduction To GeneticsDocument29 pagesIntroduction To GeneticsNatalie Dela Cruz OngsiakoNo ratings yet
- Principles of Inheritance and GeniticsDocument19 pagesPrinciples of Inheritance and GeniticsVaishakhi MuraliNo ratings yet
- Class 10 Biology Chapter 3 Revision NotesDocument4 pagesClass 10 Biology Chapter 3 Revision NotesBHUPENDRA SINGHNo ratings yet
- Unit One Genetics: Mendelian InheritanceDocument41 pagesUnit One Genetics: Mendelian Inheritancedambar khatriNo ratings yet
- Genetics and TeratologyDocument21 pagesGenetics and Teratologypandem soniya0% (1)
- CBSE Class 10 Science Notes Chapter 9 Heredity and EvolutionDocument18 pagesCBSE Class 10 Science Notes Chapter 9 Heredity and EvolutionHarsh AgarwalNo ratings yet
- The Scientific Study of Genes and HeredityDocument1 pageThe Scientific Study of Genes and Hereditymay ann dimaanoNo ratings yet
- Heredity: Is The Passing of Traits From Parents To Offspring, Making Their Children Resemble ThemDocument10 pagesHeredity: Is The Passing of Traits From Parents To Offspring, Making Their Children Resemble ThemKha RenNo ratings yet
- Genetics Flash CardsDocument3 pagesGenetics Flash CardsAnte MihaljevićNo ratings yet
- HeredityDocument19 pagesHeredityichan0001No ratings yet
- Genetics: Centro Escolar Integrated School, IncDocument29 pagesGenetics: Centro Escolar Integrated School, InchaafizaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 - Genetic Control of Cell FunctionDocument7 pagesChapter 3 - Genetic Control of Cell FunctionSADAVEJO100% (1)
- Gene MappingDocument3 pagesGene MappingPaul NallaNo ratings yet
- Differences Within Genetic BehaviorDocument2 pagesDifferences Within Genetic BehaviorTALHA MEHMOODNo ratings yet
- General Biology 2 Second SemesterDocument49 pagesGeneral Biology 2 Second SemesterRuthie TabanguilNo ratings yet
- Abc BookDocument27 pagesAbc Bookapi-2397115460% (1)
- Heredity and GeneticsDocument3 pagesHeredity and GeneticsnaughtynageshNo ratings yet
- Genetics (From Ms. C)Document8 pagesGenetics (From Ms. C)FeiNo ratings yet
- Genetics-Some-Basic-Fundamentals-1Document6 pagesGenetics-Some-Basic-Fundamentals-1Kamaljeet DhaliwalNo ratings yet
- Chapter-5 Principles of Inheritance and VariationDocument9 pagesChapter-5 Principles of Inheritance and VariationbpmbhamoraNo ratings yet
- Mendelian GeneticsDocument26 pagesMendelian Geneticsdr.alkreissNo ratings yet
- 7 Woz 9 C BPXLSMPF 0 Co 507Document17 pages7 Woz 9 C BPXLSMPF 0 Co 507Venu GopalNo ratings yet
- Plant BreedingDocument39 pagesPlant BreedingCRISTY MAE JANDAYANNo ratings yet
- Basic Principles of GeneticsDocument3 pagesBasic Principles of GeneticsKuoRosalineNo ratings yet
- Class - X - Science - Heredity and Evolution - PPT PDFDocument11 pagesClass - X - Science - Heredity and Evolution - PPT PDFAvrian PradiptyaNo ratings yet
- Biol. 103 Lecture Note 3-2Document19 pagesBiol. 103 Lecture Note 3-2Alieu Solomon KeitaNo ratings yet
- Genetics and HeredityDocument25 pagesGenetics and HeredityMariam HishamNo ratings yet
- Heredity NotesDocument6 pagesHeredity NotesShri GaneshNo ratings yet
- Heredity: May C. Dorol 12 Stem 2Document5 pagesHeredity: May C. Dorol 12 Stem 2May DorolNo ratings yet
- HeredetyDocument32 pagesHeredetyAymen GuettoutNo ratings yet
- Non-Mendelian Patterns of Inheritance IntroductionDocument39 pagesNon-Mendelian Patterns of Inheritance IntroductionErica NatividadNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument1 pageUntitledSriNo ratings yet
- Worksheet Grade 10 VillaDocument1 pageWorksheet Grade 10 VillaMhyr Pielago CambaNo ratings yet
- Homogeneous and Nonhomogeneous Systems (Camba)Document15 pagesHomogeneous and Nonhomogeneous Systems (Camba)Mhyr Pielago CambaNo ratings yet
- Activity June 5Document1 pageActivity June 5Mhyr Pielago CambaNo ratings yet
- Activity CotDocument1 pageActivity CotMhyr Pielago CambaNo ratings yet
- 4th Quarter Activity 1Document1 page4th Quarter Activity 1Mhyr Pielago CambaNo ratings yet
- June 5 Activity 1Document1 pageJune 5 Activity 1Mhyr Pielago CambaNo ratings yet
- SaveDocument3 pagesSaveMhyr Pielago CambaNo ratings yet
- Demo Teaching Math 9 SimilaritiesDocument6 pagesDemo Teaching Math 9 SimilaritiesMhyr Pielago CambaNo ratings yet
- Punnet SquareDocument5 pagesPunnet SquareMhyr Pielago CambaNo ratings yet
- Tomorrow ScienceDocument13 pagesTomorrow ScienceMhyr Pielago CambaNo ratings yet
- Performance Evaluation SystemDocument8 pagesPerformance Evaluation SystemMhyr Pielago CambaNo ratings yet
- Environmental ImpactDocument5 pagesEnvironmental ImpactMhyr Pielago CambaNo ratings yet
- Country AttractivenessDocument8 pagesCountry AttractivenessMhyr Pielago CambaNo ratings yet
- Marketing Strategies and PlansDocument10 pagesMarketing Strategies and PlansMhyr Pielago CambaNo ratings yet
- Environmental AnalysisDocument10 pagesEnvironmental AnalysisMhyr Pielago CambaNo ratings yet
- Strategic Business Unit and Functional Level StrategiesDocument12 pagesStrategic Business Unit and Functional Level StrategiesMhyr Pielago CambaNo ratings yet
- Mission and ObjectivesDocument8 pagesMission and ObjectivesMhyr Pielago CambaNo ratings yet
- Internal AnalysisDocument10 pagesInternal AnalysisMhyr Pielago CambaNo ratings yet
- FS Questions CompilationsDocument28 pagesFS Questions CompilationsMhyr Pielago CambaNo ratings yet
- Nate 2Document6 pagesNate 2Mhyr Pielago CambaNo ratings yet
- Environmental Scanning TechniquesDocument9 pagesEnvironmental Scanning TechniquesMhyr Pielago CambaNo ratings yet
- SolidsDocument1 pageSolidsMhyr Pielago CambaNo ratings yet
- Strategic Management ProcessDocument11 pagesStrategic Management ProcessMhyr Pielago CambaNo ratings yet
- WorksheetWorks Print Handwriting Practice 1Document1 pageWorksheetWorks Print Handwriting Practice 1Mhyr Pielago CambaNo ratings yet
- Rebuttle CompleteDocument8 pagesRebuttle CompleteMhyr Pielago CambaNo ratings yet
- Business LetterDocument1 pageBusiness LetterMhyr Pielago CambaNo ratings yet
- Card GamesDocument1 pageCard GamesMhyr Pielago CambaNo ratings yet
- Dalton's Atomic TheoryDocument7 pagesDalton's Atomic TheoryMhyr Pielago CambaNo ratings yet
- Let Math Majorship 2022Document21 pagesLet Math Majorship 2022Mhyr Pielago CambaNo ratings yet