Professional Documents
Culture Documents
PPT1
PPT1
Uploaded by
Lentera Peradaban0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
5 views7 pagesThe document compares the effects of the anticoagulants EDTA and heparin on hematocrit value examinations. A study was conducted using venous blood samples from random respondents anticoagulated with either 10% EDTA or 10% heparin. The hematocrit values were then measured using micro capillary tubes and a scale reader. The results found no significant difference in average hematocrit levels between the two anticoagulants, both giving an average of around 44%. The conclusion is that 10% EDTA and 10% heparin have no difference in their effect on hematocrit examination results using the micro method.
Original Description:
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document compares the effects of the anticoagulants EDTA and heparin on hematocrit value examinations. A study was conducted using venous blood samples from random respondents anticoagulated with either 10% EDTA or 10% heparin. The hematocrit values were then measured using micro capillary tubes and a scale reader. The results found no significant difference in average hematocrit levels between the two anticoagulants, both giving an average of around 44%. The conclusion is that 10% EDTA and 10% heparin have no difference in their effect on hematocrit examination results using the micro method.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
5 views7 pagesPPT1
PPT1
Uploaded by
Lentera PeradabanThe document compares the effects of the anticoagulants EDTA and heparin on hematocrit value examinations. A study was conducted using venous blood samples from random respondents anticoagulated with either 10% EDTA or 10% heparin. The hematocrit values were then measured using micro capillary tubes and a scale reader. The results found no significant difference in average hematocrit levels between the two anticoagulants, both giving an average of around 44%. The conclusion is that 10% EDTA and 10% heparin have no difference in their effect on hematocrit examination results using the micro method.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 7
THE DIFFERENCE
BETWEEN THE EDTA
AND HEPARIN
ANTICOAGULANT
EXAMINTAIONS ON
THE HEMATOCRIT
VALUE
01 INTRODUCTION 03 RESULTS/FINDINGS
TABLE OF
CONTENT 02 RESEARCH METHOD 04 CONCLUSION
INTRODUCTION
HEMATOLOGICAL EXAMINATION
Hematological examination involves various tests, including special blood
examination, routine blood examination, and complete blood count (CBC).
Special blood examination assesses peripheral blood, red blood cells,
reticulocytes, and platelets. Routine blood examination measures
hemoglobin, white blood cells, and erythrocyte sedimentation rate. CBC is
a fundamental test that provides an overall assessment of blood
components.
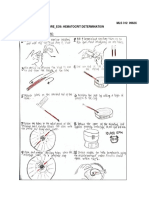
RESEARCH METHOD
The procedure for taking venous blood samples using EDTA and Heparin anticoagulants was carried out using a random
sampling technique
01 02 03 04
RESPONDENTS ANTICOAGULANT MICRO CAPILLARY TUBE HCT SCALE READER
The respondent sits with arms The vein is punctured with a Some of the blood is also put The micro capillary tube was
straight at heart level. The arm syringe, blood is drawn with a into the micro capillary tube then inserted into the micro
to be pierced is cleaned with syringe and poured into a vial hematocrit centrifuge, swirled
70% alcohol and dammed containing an anticoagulant for 5 minutes, the hematocrit
value was read using an HCT
scale reader.
RESULTS/FINDINGS
44% AVERAGE EDTA VS HEPARIN GENDER
no significant difference between the average hematocrit using 10% Gender differences also affect
the two anticoagulants, with an EDTA was 44.25%, whereas with hematocrit values, with women
average hematocrit value of 10% Heparin it was 43.15% having slightly lower values
around 44%.
CONCLUSION
the hematocrit values obtained (44%) were still within the normal range. Therefore, it can be
concluded that there is no difference in the results of the hematocrit examination using the
anticoagulants EDTA and Heparin with a concentration of 10% in venous blood samples
using the micro method.
THANK
YOU
You might also like
- MLS312 - Module04 - Explore - Experiment#6 - 0962 - Calpahi - Justine JadeDocument4 pagesMLS312 - Module04 - Explore - Experiment#6 - 0962 - Calpahi - Justine JadeJustine Jade Atew CalpahiNo ratings yet
- VPN Security Audit Assurance Program - Icq - Eng - 1012Document36 pagesVPN Security Audit Assurance Program - Icq - Eng - 1012S M Nafiul HossainNo ratings yet
- Hematocrit (HCT) : Publication DetailsDocument7 pagesHematocrit (HCT) : Publication DetailsPutri SyarifaniNo ratings yet
- Practical HB HV (Physiology)Document29 pagesPractical HB HV (Physiology)Madonna Hany naeemNo ratings yet
- Hematocrit (HCT) : June 2019Document7 pagesHematocrit (HCT) : June 2019لطيفة نورNo ratings yet
- Hematocrit - StatPearls - NCBI BookshelfDocument4 pagesHematocrit - StatPearls - NCBI BookshelfVincent ReyesNo ratings yet
- Development of Hematocrit Monitoring Sensor Using Screen Printed Carbon Electrode PDFDocument4 pagesDevelopment of Hematocrit Monitoring Sensor Using Screen Printed Carbon Electrode PDFKhaleda AliNo ratings yet
- Resume Pemeriksaan HematokritDocument25 pagesResume Pemeriksaan HematokritNurul Shabrina ChaerunnisaNo ratings yet
- Hematokrit: Dwipanggi AhyanaDocument7 pagesHematokrit: Dwipanggi AhyanaDwipanggiahyanaNo ratings yet
- Hema I Chapter 10 - PCVDocument24 pagesHema I Chapter 10 - PCVchris andrieNo ratings yet
- Hema Activity 3Document5 pagesHema Activity 3Nico LokoNo ratings yet
- University of Hargeisa: Introduction of Hematology IDocument19 pagesUniversity of Hargeisa: Introduction of Hematology IIsmo GurdeeyeNo ratings yet
- Tampil Jurnal Dr. Hafni FixDocument28 pagesTampil Jurnal Dr. Hafni FixCenyiqanita NurqanitaNo ratings yet
- 5PCVDocument19 pages5PCVRamadan PhysiologyNo ratings yet
- Lectura Complementaria. Método de Referencia para El Recuento de PlaquetasDocument5 pagesLectura Complementaria. Método de Referencia para El Recuento de PlaquetasFlor GianoNo ratings yet
- Haematology AnalyzerDocument78 pagesHaematology Analyzerswaraj sharmaNo ratings yet
- Hematocrit: Method of MeasurementDocument14 pagesHematocrit: Method of MeasurementRianaNurFatimahNo ratings yet
- FINAL Automated-HematologyDocument67 pagesFINAL Automated-HematologyDineshprakash GovindhrajNo ratings yet
- Fullpapers IJCPML 12-3-08Document4 pagesFullpapers IJCPML 12-3-08ryanNo ratings yet
- Traceability and Uncertainty of MINOCALDocument3 pagesTraceability and Uncertainty of MINOCALJakub CiepielskiNo ratings yet
- Technical College of Applied Sciences Medical Laboratory Science First Stage - Second Semester Lab Technic ReportDocument9 pagesTechnical College of Applied Sciences Medical Laboratory Science First Stage - Second Semester Lab Technic ReportELYANNo ratings yet
- Blood Grouping PDFDocument23 pagesBlood Grouping PDFMaxamed Cali AtomNo ratings yet
- Parameters of Automated Cell Counter Automation in Hematology Laboratory and CBC Via Automated Blood AnalyzerDocument40 pagesParameters of Automated Cell Counter Automation in Hematology Laboratory and CBC Via Automated Blood AnalyzerArslan Arshad100% (1)
- Hematology3 10Document23 pagesHematology3 10MohamedKecibaNo ratings yet
- Packed Cell Volume (PCV)Document24 pagesPacked Cell Volume (PCV)Eyasu demsewNo ratings yet
- Practical Clinical Hematology: Automated Hematology Cell CountersDocument54 pagesPractical Clinical Hematology: Automated Hematology Cell CountersFidaa JaafrahNo ratings yet
- Automated Hematology Cell CountersDocument53 pagesAutomated Hematology Cell CountersFidaa Jaafrah100% (2)
- Use of Fresh Blood For Quality Control: Erythrocyte Sedimentation RateDocument6 pagesUse of Fresh Blood For Quality Control: Erythrocyte Sedimentation RateTriana AmaliaNo ratings yet
- Platelet Estimation by Manual and AutomationDocument4 pagesPlatelet Estimation by Manual and AutomationKamran DawoodNo ratings yet
- CARDIODocument50 pagesCARDIOssuraynieNo ratings yet
- Variations in The Full Blood Count Parameters - q1Document14 pagesVariations in The Full Blood Count Parameters - q1rince noveliaNo ratings yet
- Pandey 2020Document5 pagesPandey 2020my accountNo ratings yet
- Determination of Hematocrit (HCT) (Packed Cell Volume PCV) : Physiology Lab-4Document16 pagesDetermination of Hematocrit (HCT) (Packed Cell Volume PCV) : Physiology Lab-4Ali KhanNo ratings yet
- Venous Blood CollectionDocument4 pagesVenous Blood CollectionSheila Mae BuenavistaNo ratings yet
- (Lesson 10-1) - Quality Assurance, Hemocytometry, Thoma PipetsDocument22 pages(Lesson 10-1) - Quality Assurance, Hemocytometry, Thoma PipetselleNo ratings yet
- Hemoglobin Determination: Cyanmethemoglobin MethodDocument32 pagesHemoglobin Determination: Cyanmethemoglobin MethodNasser DabiNo ratings yet
- RBC Indices & ESRDocument23 pagesRBC Indices & ESRPamela BesanaNo ratings yet
- Physiology Practical For 1st Year Institute Pharmacy StudentsDocument14 pagesPhysiology Practical For 1st Year Institute Pharmacy StudentsSnipper HunterNo ratings yet
- Blood System Tests and Procedures 6-20Document1 pageBlood System Tests and Procedures 6-20Egamberdiyev IslombekNo ratings yet
- Declaration of Traceability and Uncertainty For Myt-3D, Myt-5D and Myt-CALDocument1 pageDeclaration of Traceability and Uncertainty For Myt-3D, Myt-5D and Myt-CALAna-Maria CroitoruNo ratings yet
- Comparison of ABX PENTRA 120 Retic, Sysmex R-2000, Flow Cytometry, and Manual CountsDocument10 pagesComparison of ABX PENTRA 120 Retic, Sysmex R-2000, Flow Cytometry, and Manual CountsdayanaNo ratings yet
- Delaney - Ject 2010,42Document6 pagesDelaney - Ject 2010,42Muzammil AhmedNo ratings yet
- Hematocrit (HCT) (Packed Cell Volume PCV) : Objectives: ToDocument19 pagesHematocrit (HCT) (Packed Cell Volume PCV) : Objectives: ToRamadan PhysiologyNo ratings yet
- Zhang 2000Document6 pagesZhang 2000hoangkiett0904No ratings yet
- New Criteria For The Differentiation Between Transudates and ExudatesDocument3 pagesNew Criteria For The Differentiation Between Transudates and ExudatesIndahNo ratings yet
- Determination of Hematocrit (HCT) (Packed Cell Volume PCV) : Physiology Lab-1Document17 pagesDetermination of Hematocrit (HCT) (Packed Cell Volume PCV) : Physiology Lab-1ELYANNo ratings yet
- Hematological: TestsDocument40 pagesHematological: Testspupun8965No ratings yet
- Platelet CountDocument18 pagesPlatelet CountThabshiraNo ratings yet
- Ijpo 3 (2) 351-353Document3 pagesIjpo 3 (2) 351-353anggaririnNo ratings yet
- MICROHEMATOCRITDocument19 pagesMICROHEMATOCRITNico LokoNo ratings yet
- Hematology Presentation 2Document57 pagesHematology Presentation 2lemmabekeleNo ratings yet
- 273 615 1 PBDocument6 pages273 615 1 PBIkki MarphyNo ratings yet
- Automated Hematology Analyzer: Presenter: DR - KeerthyDocument95 pagesAutomated Hematology Analyzer: Presenter: DR - KeerthyadiNo ratings yet
- Hematology Analyzer (Coulter Method)Document22 pagesHematology Analyzer (Coulter Method)Sanchia Janita Khodijah100% (1)
- Comparative Analysis of Erythrocyte Sedimentation Rate Measured by Automated and Manual Methods in Anaemic PatientsDocument5 pagesComparative Analysis of Erythrocyte Sedimentation Rate Measured by Automated and Manual Methods in Anaemic PatientsRaffaharianggaraNo ratings yet
- Automated CBC AnalyzerDocument3 pagesAutomated CBC AnalyzeralbascoNo ratings yet
- Hematology Finals SallybusDocument18 pagesHematology Finals Sallybusmomin.laangNo ratings yet
- 2012 Sysmex Red Blood Cell IndicesDocument7 pages2012 Sysmex Red Blood Cell IndicesGregorio De Las CasasNo ratings yet
- A Noninvasive Strategy For Screening Prospective Blood Donors For Anemia 2005Document8 pagesA Noninvasive Strategy For Screening Prospective Blood Donors For Anemia 2005azizk83No ratings yet
- SopDocument22 pagesSopSnowhyte KwakuNo ratings yet
- Quick guide to Laboratory Medicine: a student's overviewFrom EverandQuick guide to Laboratory Medicine: a student's overviewNo ratings yet
- 361 Chapter 9 MC SolutionsDocument24 pages361 Chapter 9 MC SolutionsLouie De La TorreNo ratings yet
- Automotive Exam 2nd GradingDocument2 pagesAutomotive Exam 2nd GradingHomer SotoNo ratings yet
- NullDocument13 pagesNullapi-25886385100% (1)
- E37, E38 & E67. Operating System Compatibility Reference ListDocument6 pagesE37, E38 & E67. Operating System Compatibility Reference Listjavier hurtadoNo ratings yet
- Moisture Density TestDocument30 pagesMoisture Density TestPaul Eric SalesNo ratings yet
- DOT Line Shape Form Space MediaDocument13 pagesDOT Line Shape Form Space MediaIgor KanderaNo ratings yet
- Teza 11 FiloDocument2 pagesTeza 11 FiloSebaNo ratings yet
- Vineet Sharma - Procurement - RDIDocument4 pagesVineet Sharma - Procurement - RDIDheeraj ChauhanNo ratings yet
- Overview of Artificial IntelligenceDocument57 pagesOverview of Artificial IntelligenceAfri YantoNo ratings yet
- Concrete WorksDocument82 pagesConcrete WorksarnoldalejadoNo ratings yet
- The Honors Program at Ferris State University - Annual Report 2018Document24 pagesThe Honors Program at Ferris State University - Annual Report 2018ferrishonorsNo ratings yet
- Англійська мова зробивDocument3 pagesАнглійська мова зробивrobert12309123.zNo ratings yet
- Elcometer 224 S Operating ManualDocument3 pagesElcometer 224 S Operating ManualDale WadeNo ratings yet
- Dental Wax UpDocument4 pagesDental Wax UpJoselyn RodriguezNo ratings yet
- KDP57WS655Document4 pagesKDP57WS655scribdlogosNo ratings yet
- TB 1Document20 pagesTB 1Dr.Hira EmanNo ratings yet
- 290161-2019-Reiterating DILG MC No. 2016-146 On The20220628-11-1civh47Document2 pages290161-2019-Reiterating DILG MC No. 2016-146 On The20220628-11-1civh47WayneNoveraNo ratings yet
- Harvesting and Marketing Powerpoint Lesson5Document21 pagesHarvesting and Marketing Powerpoint Lesson5OfeliaNo ratings yet
- Visualizing Concepts With A Domain ModelDocument16 pagesVisualizing Concepts With A Domain ModelEmil SayseNo ratings yet
- Fortis Wind Energy Alize 10kW Wind TurbineDocument2 pagesFortis Wind Energy Alize 10kW Wind TurbineROSMADI BIN ABDULLAHNo ratings yet
- INCROPERA Solucion Aletas 234Document15 pagesINCROPERA Solucion Aletas 234Juan GuerreroNo ratings yet
- Standard Print Italic Alphabet Handwriting Practice Activity Book, Donnette E Davis, ST Aiden's HomeschoolDocument29 pagesStandard Print Italic Alphabet Handwriting Practice Activity Book, Donnette E Davis, ST Aiden's HomeschoolDonnette Davis100% (2)
- Four-Year Clinical Evaluation of A Self-Adhesive Luting Agent For Ceramic InlaysDocument12 pagesFour-Year Clinical Evaluation of A Self-Adhesive Luting Agent For Ceramic InlaysheycoolalexNo ratings yet
- USG ParuDocument28 pagesUSG ParuViany RehansyahNo ratings yet
- BillSTMT 4588260000514267Document3 pagesBillSTMT 4588260000514267Fahad AhmedNo ratings yet
- Innowood - Composite Wood External Cladding System: Certificate Number: CM70093 Rev1Document4 pagesInnowood - Composite Wood External Cladding System: Certificate Number: CM70093 Rev1Johao HernandezNo ratings yet
- OMNI Modules - Installation OptionsDocument9 pagesOMNI Modules - Installation OptionsfarhanNo ratings yet
- Exercise 3. Indicate, by A, B, C, Etc., To Which of The Following ClauseDocument11 pagesExercise 3. Indicate, by A, B, C, Etc., To Which of The Following ClauseNguyễn Anh HuyNo ratings yet
- MRCHDocument27 pagesMRCHFijimol FranklineNo ratings yet