0% found this document useful (0 votes)
1K views13 pagesStructure Vs Unstructured Approach
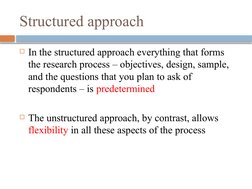
This document summarizes the key differences between structured and unstructured research approaches. A structured approach involves predetermined objectives, design, sample, and questions, while an unstructured approach allows more flexibility. Structured approaches are typically classified as quantitative research, while unstructured approaches are qualitative. The choice between the two should depend on the research aim and how the findings will be used. Quantitative research aims to quantify variations, uses predominantly quantitative variables, and analyzes data through statistics. Qualitative research aims to describe phenomena through nominal or ordinal scales without quantification. Both approaches have strengths and weaknesses.
Uploaded by
Saba HamzaCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
1K views13 pagesStructure Vs Unstructured Approach
This document summarizes the key differences between structured and unstructured research approaches. A structured approach involves predetermined objectives, design, sample, and questions, while an unstructured approach allows more flexibility. Structured approaches are typically classified as quantitative research, while unstructured approaches are qualitative. The choice between the two should depend on the research aim and how the findings will be used. Quantitative research aims to quantify variations, uses predominantly quantitative variables, and analyzes data through statistics. Qualitative research aims to describe phenomena through nominal or ordinal scales without quantification. Both approaches have strengths and weaknesses.
Uploaded by
Saba HamzaCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
- Introduction to Structured vs Unstructured Approach: Introduces the concept of structured versus unstructured approaches in research methodologies.
- Structured Approach: Discusses the characteristics of the structured approach, highlighting its focus on predetermined aspects and typical use in quantitative research.
- Choosing an Approach: Explores factors influencing the choice between quantitative and qualitative approaches based on research objectives and outcomes.
- Quantitative Research: Details the quantitative research approach, emphasizing quantification, variation measurement, and statistical analysis.
- Qualitative Research: Explains the nature of qualitative research, focusing on descriptive analysis without quantification, often used in exploratory studies.
- Conclusion: Concludes the presentation with a summary and closing remarks.